Abstract
In the title compound, C8H12O4S, the two five-membered rings both adopt envelope conformations. In the crystal, weak C—H⋯O interactions link neighbouring molecules.
Related literature
The title compound is a precursor for the preparation of an important nucleoside drug. For applications of nucleosides in the fields of biology, drugs and chemistry, see: Goodyear et al. (2005 ▶); Simons (2001 ▶); Vittori et al. (2006 ▶).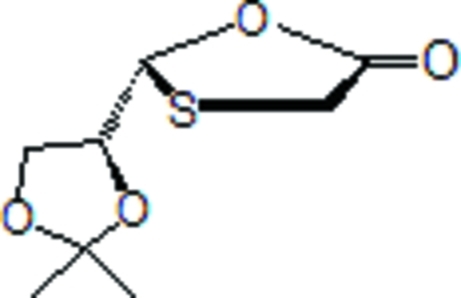
Experimental
Crystal data
C8H12O4S
M r = 204.24
Monoclinic,
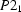
a = 6.5528 (13) Å
b = 9.4029 (19) Å
c = 7.9240 (16) Å
β = 106.60 (3)°
V = 467.89 (16) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.33 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.50 × 0.20 × 0.15 mm
Data collection
Rigaku Saturn CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku/MSC, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.859, T max = 0.952
1941 measured reflections
1705 independent reflections
1275 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.056
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.042
wR(F 2) = 0.129
S = 1.01
1705 reflections
119 parameters
1 restraint
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.24 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.20 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 593 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: −0.01 (13)
Data collection: RAPID-AUTO (Rigaku/MSC, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: RAPID-AUTO; data reduction: CrystalStructure (Rigaku/MSC, 2005 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680902039X/wn2324sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680902039X/wn2324Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1—H1A⋯O3i | 0.97 | 2.58 | 3.428 (4) | 146 |
| C1—H1B⋯O2ii | 0.97 | 2.41 | 3.306 (6) | 153 |
| C3—H3⋯O2iii | 0.98 | 2.55 | 3.265 (4) | 129 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 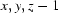 ; (ii)
; (ii) 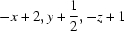 ; (iii)
; (iii) 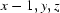 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the National Science Foundation of China (30340070) and the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2006AA100216) for financial support.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Nucleosides are a very important series of compounds in the fields of biology, drugs and chemistry (Simons, 2001); as an example, lamivudine is used as a drug for HIV and HBV diseases (Goodyear et al., 2005; Vittori et al., 2006). Studies of the synthesis of nucleoside mimetics are essential.
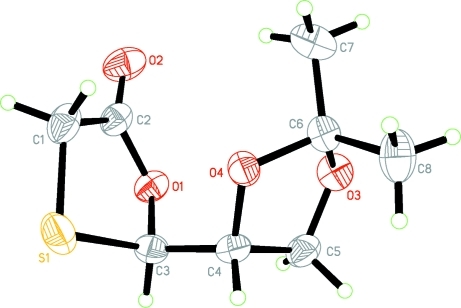
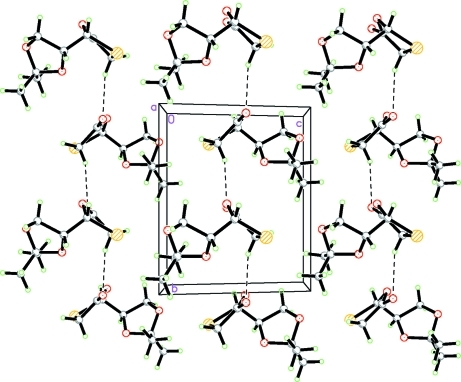
The purpose of this structure determination was to establish the molecular conformation of the title compound obtained by coupling (R)-(+)-2,2-dimethyl-1,3-dioxolane-4-carboxaldehyde with 2-mercaptoacetic acid. The chirality at the 2-position (C3) is R; this satisfies our requirements for the preparation of corresponding L-nucleosides. All bond lengths and bond angles have expected values. The two 5-membered rings both adopt envelope conformations with atoms C3 and C6 at the flap. Three intermolecular C—H···O interactions link neighbouring molecules.
Experimental
A solution of (R)-(+)-2,2-dimethyl -1,3-dioxolane-4-carboxaldehyde (6.51 g, 50.0 mmol) and 2-mercaptoacetic acid (4.20 ml, 60.0 mmol) in toluene (200 ml) was heated under reflux for 1.5 h. After the reaction mixture was cooled to room temperature, a saturated aqueous solution of NaHCO3 (30 ml) was added and these two layers were separated. The organic layer was washed with brine, dried (MgSO4) and concentrated under reduced pressure. The residue was isolated through short column chromatography on silica gel, which was eluted with EtOAc-petroleum to give the target compound (4.96 g, 48%). m.p. 75–77°C.
50 mg of the final product was dissolved in petroleum ether (5 ml) and the solution was kept at room temperature for 2 days to give colorless single crystals.
Refinement
H atoms were included in the riding model approximation, with C—H distances 0.96–0.98 Å, and with Uiso(H) = kUeq(C), where k = 1.5 for methyl H and 1.2 for all other H atoms.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of the title compound with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 30% probability level. Hydrogen atoms are drawn as spheres of arbitrary radius.
Fig. 2.
The crystal packing of the title compound, viewed along the a axis. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C8H12O4S | F(000) = 216 |
| Mr = 204.24 | Dx = 1.450 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 6.5528 (13) Å | Cell parameters from 1941 reflections |
| b = 9.4029 (19) Å | θ = 2.7–27.5° |
| c = 7.9240 (16) Å | µ = 0.33 mm−1 |
| β = 106.60 (3)° | T = 293 K |
| V = 467.89 (16) Å3 | Block, colourless |
| Z = 2 | 0.50 × 0.20 × 0.15 mm |
Data collection
| Rigaku Saturn CCD area-detector diffractometer | 1705 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1275 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.056 |
| Detector resolution: 10.00 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 2.7° |
| Ω scans | h = −8→8 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku/MSC, 2005) | k = −12→11 |
| Tmin = 0.859, Tmax = 0.952 | l = −10→10 |
| 1941 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.042 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.088P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.129 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| S = 1.01 | Δρmax = 0.24 e Å−3 |
| 1705 reflections | Δρmin = −0.20 e Å−3 |
| 119 parameters | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| 1 restraint | Extinction coefficient: 0.102 (15) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 593 Friedel pairs |
| Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map | Flack parameter: −0.01 (13) |
Special details
| Experimental. 1H NMR(CDCl3,P.P.M.): 1.41 (d, 6 H), 3.58(d, 4 H), 3.77 (d, 1 H), 3.92 (dd, 1 H), 4.12 (dd, 1 H), 4.35 (m, 1 H), 5.45(d, 1 H). |
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| S1 | 0.57296 (17) | 0.19608 (12) | 0.31212 (10) | 0.0733 (4) | |
| O1 | 0.7766 (4) | 0.0255 (3) | 0.5605 (3) | 0.0514 (6) | |
| O2 | 1.1103 (4) | 0.0457 (3) | 0.5630 (4) | 0.0734 (8) | |
| O3 | 0.8026 (4) | 0.1607 (2) | 0.9331 (3) | 0.0560 (6) | |
| O4 | 0.7352 (4) | 0.2936 (2) | 0.6920 (3) | 0.0482 (5) | |
| C1 | 0.8546 (6) | 0.1980 (5) | 0.3737 (4) | 0.0612 (9) | |
| H1A | 0.9049 | 0.1803 | 0.2718 | 0.073* | |
| H1B | 0.9075 | 0.2899 | 0.4225 | 0.073* | |
| C2 | 0.9307 (6) | 0.0859 (4) | 0.5061 (4) | 0.0502 (8) | |
| C3 | 0.5800 (5) | 0.1011 (4) | 0.5101 (4) | 0.0509 (8) | |
| H3 | 0.4622 | 0.0328 | 0.4851 | 0.061* | |
| C4 | 0.5669 (5) | 0.1947 (4) | 0.6584 (4) | 0.0486 (7) | |
| H4 | 0.4302 | 0.2451 | 0.6269 | 0.058* | |
| C5 | 0.5987 (5) | 0.1192 (5) | 0.8312 (4) | 0.0567 (9) | |
| H5A | 0.4914 | 0.1477 | 0.8871 | 0.068* | |
| H5B | 0.5915 | 0.0169 | 0.8144 | 0.068* | |
| C6 | 0.8418 (5) | 0.2954 (4) | 0.8756 (4) | 0.0486 (8) | |
| C7 | 1.0731 (6) | 0.3117 (5) | 0.9004 (6) | 0.0742 (11) | |
| H7A | 1.1010 | 0.4044 | 0.8614 | 0.111* | |
| H7B | 1.1201 | 0.2405 | 0.8330 | 0.111* | |
| H7C | 1.1483 | 0.3006 | 1.0228 | 0.111* | |
| C8 | 0.7487 (7) | 0.4089 (5) | 0.9608 (5) | 0.0743 (12) | |
| H8A | 0.7778 | 0.5000 | 0.9182 | 0.111* | |
| H8B | 0.8106 | 0.4046 | 1.0861 | 0.111* | |
| H8C | 0.5975 | 0.3954 | 0.9332 | 0.111* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| S1 | 0.0745 (6) | 0.0908 (9) | 0.0459 (4) | −0.0108 (6) | 0.0034 (4) | 0.0026 (5) |
| O1 | 0.0541 (13) | 0.0404 (12) | 0.0659 (14) | −0.0020 (10) | 0.0269 (11) | −0.0011 (11) |
| O2 | 0.0606 (17) | 0.0628 (18) | 0.107 (2) | 0.0052 (14) | 0.0402 (16) | −0.0045 (16) |
| O3 | 0.0649 (15) | 0.0446 (14) | 0.0563 (12) | 0.0047 (11) | 0.0139 (10) | 0.0108 (11) |
| O4 | 0.0566 (12) | 0.0465 (12) | 0.0411 (10) | −0.0113 (11) | 0.0132 (9) | 0.0000 (9) |
| C1 | 0.082 (2) | 0.053 (2) | 0.0589 (18) | −0.012 (2) | 0.0367 (17) | −0.0009 (17) |
| C2 | 0.059 (2) | 0.0397 (17) | 0.0597 (18) | −0.0016 (15) | 0.0293 (16) | −0.0084 (14) |
| C3 | 0.0457 (16) | 0.0508 (19) | 0.0557 (17) | −0.0117 (15) | 0.0134 (14) | −0.0050 (16) |
| C4 | 0.0389 (14) | 0.0522 (19) | 0.0563 (15) | −0.0025 (15) | 0.0163 (12) | 0.0032 (17) |
| C5 | 0.0558 (19) | 0.060 (2) | 0.062 (2) | −0.0076 (17) | 0.0287 (17) | 0.0027 (16) |
| C6 | 0.0548 (19) | 0.0429 (18) | 0.0453 (16) | 0.0041 (15) | 0.0100 (14) | 0.0022 (13) |
| C7 | 0.058 (2) | 0.065 (3) | 0.088 (3) | −0.0082 (19) | 0.004 (2) | −0.004 (2) |
| C8 | 0.106 (3) | 0.057 (2) | 0.063 (2) | 0.015 (2) | 0.027 (2) | −0.0093 (18) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| S1—C1 | 1.769 (4) | C3—H3 | 0.9800 |
| S1—C3 | 1.795 (4) | C4—C5 | 1.504 (5) |
| O1—C2 | 1.333 (4) | C4—H4 | 0.9800 |
| O1—C3 | 1.425 (4) | C5—H5A | 0.9700 |
| O2—C2 | 1.195 (4) | C5—H5B | 0.9700 |
| O3—C6 | 1.395 (4) | C6—C8 | 1.483 (5) |
| O3—C5 | 1.405 (4) | C6—C7 | 1.480 (5) |
| O4—C4 | 1.408 (4) | C7—H7A | 0.9600 |
| O4—C6 | 1.423 (4) | C7—H7B | 0.9600 |
| C1—C2 | 1.470 (5) | C7—H7C | 0.9600 |
| C1—H1A | 0.9700 | C8—H8A | 0.9600 |
| C1—H1B | 0.9700 | C8—H8B | 0.9600 |
| C3—C4 | 1.490 (5) | C8—H8C | 0.9600 |
| C1—S1—C3 | 89.97 (16) | O3—C5—C4 | 104.7 (3) |
| C2—O1—C3 | 113.9 (3) | O3—C5—H5A | 110.8 |
| C6—O3—C5 | 107.4 (3) | C4—C5—H5A | 110.8 |
| C4—O4—C6 | 109.3 (2) | O3—C5—H5B | 110.8 |
| C2—C1—S1 | 107.7 (3) | C4—C5—H5B | 110.8 |
| C2—C1—H1A | 110.2 | H5A—C5—H5B | 108.9 |
| S1—C1—H1A | 110.2 | O3—C6—O4 | 103.9 (3) |
| C2—C1—H1B | 110.2 | O3—C6—C8 | 111.5 (3) |
| S1—C1—H1B | 110.2 | O4—C6—C8 | 109.2 (3) |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 108.5 | O3—C6—C7 | 109.1 (3) |
| O2—C2—O1 | 119.9 (3) | O4—C6—C7 | 108.8 (3) |
| O2—C2—C1 | 126.4 (3) | C8—C6—C7 | 113.8 (4) |
| O1—C2—C1 | 113.7 (3) | C6—C7—H7A | 109.5 |
| O1—C3—C4 | 109.0 (3) | C6—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| O1—C3—S1 | 106.8 (2) | H7A—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—S1 | 113.7 (3) | C6—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| O1—C3—H3 | 109.1 | H7A—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 109.1 | H7B—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| S1—C3—H3 | 109.1 | C6—C8—H8A | 109.5 |
| O4—C4—C3 | 108.7 (2) | C6—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| O4—C4—C5 | 104.0 (3) | H8A—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 114.5 (3) | C6—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| O4—C4—H4 | 109.8 | H8A—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 109.8 | H8B—C8—H8C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 109.8 | ||
| C3—S1—C1—C2 | 19.2 (3) | S1—C3—C4—O4 | −57.3 (3) |
| C3—O1—C2—O2 | 168.2 (3) | O1—C3—C4—C5 | −54.1 (3) |
| C3—O1—C2—C1 | −13.0 (4) | S1—C3—C4—C5 | −173.1 (2) |
| S1—C1—C2—O2 | 171.1 (3) | C6—O3—C5—C4 | 28.4 (3) |
| S1—C1—C2—O1 | −7.6 (4) | O4—C4—C5—O3 | −11.8 (4) |
| C2—O1—C3—C4 | −96.1 (3) | C3—C4—C5—O3 | 106.7 (3) |
| C2—O1—C3—S1 | 27.2 (3) | C5—O3—C6—O4 | −33.7 (3) |
| C1—S1—C3—O1 | −26.0 (3) | C5—O3—C6—C8 | 83.8 (3) |
| C1—S1—C3—C4 | 94.2 (3) | C5—O3—C6—C7 | −149.6 (3) |
| C6—O4—C4—C3 | −130.9 (3) | C4—O4—C6—O3 | 25.9 (3) |
| C6—O4—C4—C5 | −8.5 (3) | C4—O4—C6—C8 | −93.2 (4) |
| O1—C3—C4—O4 | 61.7 (3) | C4—O4—C6—C7 | 142.0 (3) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C1—H1A···O3i | 0.97 | 2.58 | 3.428 (4) | 146 |
| C1—H1B···O2ii | 0.97 | 2.41 | 3.306 (6) | 153 |
| C3—H3···O2iii | 0.98 | 2.55 | 3.265 (4) | 129 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, y, z−1; (ii) −x+2, y+1/2, −z+1; (iii) x−1, y, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: WN2324).
References
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Goodyear, M. D., Hill, M. L., West, J. P. & Whitehead, A. J. (2005). Tetrahedron Lett.46, 8535–8538.
- Rigaku/MSC (2005). CrystalClear, CrystalStructure and RAPID-AUTO Rigaku/MSC Inc., The Woodlands, Texas, USA.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Simons, C. (2001). Nucleoside Mimetics, Their Chemistry and Biological Properties Amsterdam: Gordon and Breach Science Publisher.
- Vittori, S., Dal Ben, D., Lambertucci, C., Marucci, G., Volpini, R. & Cristalli, G. (2006). Curr. Med. Chem.13, 3529–3552. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680902039X/wn2324sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680902039X/wn2324Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report