Abstract
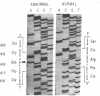
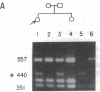
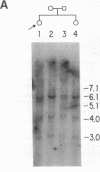
A substitution for a highly conserved non-glycine residue in the triple-helical domain of the pro alpha 2(I) collagen molecule was found in an individual with a variant of the Marfan syndrome. A single base change resulted in substitution of arginine618 by glutamine at the Y position of a Gly-X-Y repeat, and is responsible for the decreased migration in SDS-polyacrylamide gels of some pro alpha 2(I) chains of type I collagen synthesized by dermal fibroblasts from this individual. Family studies suggest that this substitution was inherited from the individual's father who also produces abnormally migrating pro alpha 2(I) collagen chains and shares some of the abnormal skeletal features. This single base change creates a new Bsu36 I (Sau I, Mst II) restriction site detectable in genomic DNA by Southern blot analysis when probed with a COL1A2 fragment. The analysis of 52 control individuals (103 chromosomes) was negative for the new Bsu36 I site, suggesting that the substitution is not a common polymorphism.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard M. P., Chu M. L., Myers J. C., Ramirez F., Eikenberry E. F., Prockop D. J. Nucleotide sequences of complementary deoxyribonucleic acids for the pro alpha 1 chain of human type I procollagen. Statistical evaluation of structures that are conserved during evolution. Biochemistry. 1983 Oct 25;22(22):5213–5223. doi: 10.1021/bi00291a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C. A rapid alkaline extraction method for the isolation of plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:243–255. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00059-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonadio J., Holbrook K. A., Gelinas R. E., Jacob J., Byers P. H. Altered triple helical structure of type I procollagen in lethal perinatal osteogenesis imperfecta. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1734–1742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucek R. J., Noble N. L., Gunja-Smith Z., Butler W. T. The Marfan syndrome: a deficiency in chemically stable collagen cross-links. N Engl J Med. 1981 Oct 22;305(17):988–991. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198110223051705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers P. H., Siegel R. C., Peterson K. E., Rowe D. W., Holbrook K. A., Smith L. T., Chang Y. H., Fu J. C. Marfan syndrome: abnormal alpha 2 chain in type I collagen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7745–7749. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole W. G., Chan D., Chambers G. W., Walker I. D., Bateman J. F. Deletion of 24 amino acids from the pro-alpha 1(I) chain of type I procollagen in a patient with the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VII. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 25;261(12):5496–5503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgleish R., Hawkins J. R., Keston M. Exclusion of the alpha 2(I) and alpha 1(III) collagen genes as the mutant loci in a Marfan syndrome family. J Med Genet. 1987 Mar;24(3):148–151. doi: 10.1136/jmg.24.3.148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre D. R., Paz M. A., Gallop P. M. Cross-linking in collagen and elastin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:717–748. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.003441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyre D. R., Shapiro F. D., Aldridge J. F. A heterozygous collagen defect in a variant of the Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VII. Evidence for a deleted amino-telopeptide domain in the pro-alpha 2(I) chain. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11322–11329. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields G. B., Van Wart H. E., Birkedal-Hansen H. Sequence specificity of human skin fibroblast collagenase. Evidence for the role of collagen structure in determining the collagenase cleavage site. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6221–6226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francomano C. A., Streeten E. A., Meyers D. A., Pyeritz R. E. Marfan syndrome: exclusion of genetic linkage to three major collagen genes. Am J Med Genet. 1988 Feb;29(2):457–462. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320290233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glesby M. J., Pyeritz R. E. Association of mitral valve prolapse and systemic abnormalities of connective tissue. A phenotypic continuum. JAMA. 1989 Jul 28;262(4):523–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godfrey M., Menashe V., Weleber R. G., Koler R. D., Bigley R. H., Lovrien E., Zonana J., Hollister D. W. Cosegregation of elastin-associated microfibrillar abnormalities with the Marfan phenotype in families. Am J Hum Genet. 1990 Apr;46(4):652–660. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janeczko R. A., Ramirez F. Nucleotide and amino acid sequences of the entire human alpha 1 (III) collagen. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 25;17(16):6742–6742. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.16.6742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg T., Müller P. K. The marfan's syndrome. In vitro study of collagen metabolism in tissue specimens of the aorta. Exp Cell Biol. 1977;45(3-4):207–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuivaniemi H., Tromp G., Chu M. L., Prockop D. J. Structure of a full-length cDNA clone for the prepro alpha 2(I) chain of human type I procollagen. Comparison with the chicken gene confirms unusual patterns of gene conservation. Biochem J. 1988 Jun 15;252(3):633–640. doi: 10.1042/bj2520633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers J. C., Dickson L. A., de Wet W. J., Bernard M. P., Chu M. L., Di Liberto M., Pepe G., Sangiorgi F. O., Ramirez F. Analysis of the 3' end of the human pro-alpha 2(I) collagen gene. Utilization of multiple polyadenylation sites in cultured fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):10128–10135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noel D., Nikaido K., Ames G. F. A single amino acid substitution in a histidine-transport protein drastically alters its mobility in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Biochemistry. 1979 Sep 18;18(19):4159–4165. doi: 10.1021/bi00586a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogilvie D. J., Wordsworth B. P., Priestley L. M., Dalgleish R., Schmidtke J., Zoll B., Sykes B. C. Segregation of all four major fibrillar collagen genes in the Marfan syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 1987 Dec;41(6):1071–1082. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinnell S. R., Krane S. M., Kenzora J. E., Glimcher M. J. A heritable disorder of connective tissue. Hydroxylysine-deficient collagen disease. N Engl J Med. 1972 May 11;286(19):1013–1020. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197205112861901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priest R. E., Moinuddin J. F., Priest J. H. Letter: Collagen of Marfan syndrome is abnormally soluble. Nature. 1973 Oct 5;245(5423):264–266. doi: 10.1038/245264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro J. R., Burn V. E., Chipman S. D., Velis K. P., Bansal M. Osteoporosis and familial idiopathic scoliosis: association with an abnormal alpha 2(I) collagen. Connect Tissue Res. 1989;21(1-4):117–124. doi: 10.3109/03008208909050002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Su M. W., Lee B., Ramirez F., Machado M., Horton W. Nucleotide sequence of the full length cDNA encoding for human type II procollagen. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9473–9473. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsipouras P., Børresen A. L., Bamforth S., Harper P. S., Berg K. Marfan syndrome: exclusion of genetic linkage to the COL1A2 gene. Clin Genet. 1986 Nov;30(5):428–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil D., Bernard M., Combates N., Wirtz M. K., Hollister D. W., Steinmann B., Ramirez F. Identification of a mutation that causes exon skipping during collagen pre-mRNA splicing in an Ehlers-Danlos syndrome variant. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 25;263(18):8561–8564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil D., Bernard M., Gargano S., Ramirez F. The pro alpha 2(V) collagen gene is evolutionarily related to the major fibrillar-forming collagens. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 12;15(1):181–198. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.1.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenstrup R. J., Cohn D. H., Cohen T., Byers P. H. Arginine for glycine substitution in the triple-helical domain of the products of one alpha 2(I) collagen allele (COL1A2) produces the osteogenesis imperfecta type IV phenotype. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 5;263(16):7734–7740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenstrup R. J., Murad S., Pinnell S. R. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VI: clinical manifestations of collagen lysyl hydroxylase deficiency. J Pediatr. 1989 Sep;115(3):405–409. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(89)80839-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willing M. C., Cohn D. H., Starman B., Holbrook K. A., Greenberg C. R., Byers P. H. Heterozygosity for a large deletion in the alpha 2(I) collagen gene has a dramatic effect on type I collagen secretion and produces perinatal lethal osteogenesis imperfecta. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8398–8404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirtz M. K., Glanville R. W., Steinmann B., Rao V. H., Hollister D. W. Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type VIIB. Deletion of 18 amino acids comprising the N-telopeptide region of a pro-alpha 2(I) chain. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16376–16385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong W. W., Zweers A., Cohen L. H. Influence of single amino acid substitutions on electrophoretic mobility of sodium dodecyl sulfate-protein complexes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 May 30;82(2):532–539. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)90907-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet W., Bernard M., Benson-Chanda V., Chu M. L., Dickson L., Weil D., Ramirez F. Organization of the human pro-alpha 2(I) collagen gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):16032–16036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]