Abstract
The title compound, C8H9N5O, was synthesized by the reaction of ethyl 2-(benzotriazol-1-yl)acetate with hydrazine hydrate in ethanol. In the amide group, the C—N bond is relatively short [1.3283 (16) Å], suggesting some degree of electronic delocalization in the molecule. In the crystal structure, molecules are linked into infinite chains along the a axis by intermolecular O—H⋯N hydrogen bonding.
Related literature
For general background to multiple-hydrogen-bonding N-heterocyclic systems as potential supramolecular reagents, see: Portalone (2007 ▶); Portalone & Colapietro (2007 ▶, 2008 ▶); For related structures, see: Shi et al. (2007a
▶,b
▶); Ji et al. (2008 ▶); For bond-length data, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶). 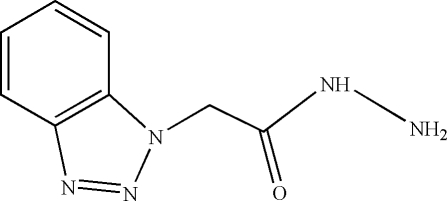
Experimental
Crystal data
C8H9N5O
M r = 191.20
Monoclinic,

a = 5.1434 (9) Å
b = 6.5885 (12) Å
c = 25.754 (5) Å
β = 94.227 (3)°
V = 870.4 (3) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.11 mm−1
T = 295 K
0.12 × 0.10 × 0.06 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.988, T max = 0.994
4367 measured reflections
1528 independent reflections
1364 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.015
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.030
wR(F 2) = 0.079
S = 1.04
1528 reflections
135 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.13 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.15 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2005 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: SHELXTL; software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809021199/bg2267sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809021199/bg2267Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N4—H1⋯O1i | 0.86 | 2.18 | 2.9977 (14) | 159 |
Symmetry code: (i) 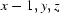 .
.
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by the Postgraduate Foundation of Taishan University (grant No. Y04–2–08).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
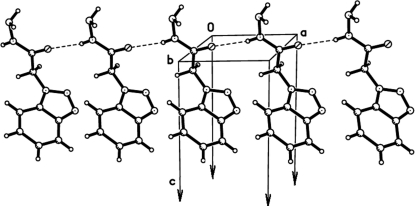
In our previous papers(Shi et al., 2007a; Shi et al., 2007b; Ji et al., 2008;), we have reported a number of Schiff-bases by the reaction of benzotriazol-1-yl-acetic acid hydrazide with relevant aldehyde or ketone. As a part of a more general study of multiple-hydrogen-bonding N-heterocyclic systems as potential supramolecular reagents (Portalone, 2007; Portalone & Colapietro, 2007, 2008), the title compound, (I), was synthesized and its crystal structure determined. The asymmetric unit of the (I) comprises one independent molecule. In (I) (Fig. 1), the bond lengths and angles are in good agreement with the expected values (Allen et al., 1987). In the crystal structure (Fig. 2), the molecules are linked into infinite chains by O—H···N hydrogen bond.
Experimental
The title compound was synthesized by the reaction of benzotriazol-1-yl-acetic acid ethyl ester(1 mmol) with hydrazine hydrate 85% (1.1 mmol)in ethanol (20 ml) under reflux conditions (348 K) for 24 h. The solvent was removed and the solid product recrystallized from tetrahydrofuran. After four days colorless crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction study were obtained.
Refinement
All H atoms were placed in idealized positions (C—H = 0.93— 0.97 Å, N—H = 0.86 Å) and refined as riding atoms. For those bound to C, Uiso(H) = 1.2 or 1.5Ueq(C). while for those bound to N, Uiso(H) = 1.2 Ueq(N).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I), with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.
The structure of the infinite chains formed via hydrogen bonds, H atoms have been omitted for clarity. The dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds.
Crystal data
| C8H9N5O | F(000) = 400 |
| Mr = 191.20 | Dx = 1.459 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 2593 reflections |
| a = 5.1434 (9) Å | θ = 2.4–28.0° |
| b = 6.5885 (12) Å | µ = 0.11 mm−1 |
| c = 25.754 (5) Å | T = 295 K |
| β = 94.227 (3)° | Block, colorless |
| V = 870.4 (3) Å3 | 0.12 × 0.10 × 0.06 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer | 1528 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1364 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.015 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 25.1°, θmin = 3.2° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005) | h = −4→6 |
| Tmin = 0.988, Tmax = 0.994 | k = −7→7 |
| 4367 measured reflections | l = −28→30 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.030 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.079 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.04 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0333P)2 + 0.233P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 1528 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 135 parameters | Δρmax = 0.13 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.15 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 1.08675 (16) | 0.24854 (14) | 0.01128 (4) | 0.0432 (3) | |
| N1 | 1.3431 (2) | 0.14371 (19) | 0.16751 (5) | 0.0505 (3) | |
| N2 | 1.2038 (2) | 0.05513 (19) | 0.12958 (5) | 0.0496 (3) | |
| N3 | 0.9953 (2) | 0.17411 (18) | 0.11547 (4) | 0.0422 (3) | |
| N4 | 0.65313 (19) | 0.25384 (17) | −0.00905 (4) | 0.0419 (3) | |
| H1 | 0.5024 | 0.2240 | 0.0012 | 0.050* | |
| N5 | 0.6667 (2) | 0.3428 (2) | −0.05866 (5) | 0.0503 (3) | |
| C1 | 1.2246 (2) | 0.3253 (2) | 0.17817 (5) | 0.0406 (3) | |
| C2 | 1.2914 (3) | 0.4759 (2) | 0.21540 (5) | 0.0496 (4) | |
| H2 | 1.4385 | 0.4637 | 0.2384 | 0.060* | |
| C3 | 1.1312 (3) | 0.6408 (2) | 0.21632 (6) | 0.0537 (4) | |
| H3 | 1.1698 | 0.7424 | 0.2407 | 0.064* | |
| C4 | 0.9094 (3) | 0.6612 (2) | 0.18138 (6) | 0.0534 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.8067 | 0.7768 | 0.1832 | 0.064* | |
| C5 | 0.8397 (3) | 0.5166 (2) | 0.14492 (5) | 0.0466 (3) | |
| H5 | 0.6933 | 0.5306 | 0.1218 | 0.056* | |
| C6 | 1.0018 (2) | 0.3468 (2) | 0.14460 (5) | 0.0377 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.8079 (3) | 0.1139 (2) | 0.07360 (5) | 0.0460 (3) | |
| H7A | 0.6341 | 0.1507 | 0.0825 | 0.055* | |
| H7B | 0.8133 | −0.0323 | 0.0695 | 0.055* | |
| C8 | 0.8630 (2) | 0.21429 (19) | 0.02251 (5) | 0.0356 (3) | |
| H9 | 0.723 (3) | 0.250 (2) | −0.0799 (6) | 0.073 (6)* | |
| H8 | 0.785 (3) | 0.441 (2) | −0.0551 (8) | 0.078 (6)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0277 (5) | 0.0555 (6) | 0.0466 (5) | −0.0038 (4) | 0.0045 (4) | −0.0023 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0450 (7) | 0.0599 (8) | 0.0460 (7) | 0.0030 (6) | −0.0010 (5) | 0.0029 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0472 (7) | 0.0518 (7) | 0.0500 (7) | 0.0030 (6) | 0.0051 (5) | 0.0005 (6) |
| N3 | 0.0399 (6) | 0.0508 (7) | 0.0358 (6) | −0.0038 (5) | 0.0024 (5) | −0.0031 (5) |
| N4 | 0.0272 (5) | 0.0526 (7) | 0.0457 (6) | −0.0030 (5) | 0.0021 (4) | −0.0043 (5) |
| N5 | 0.0434 (7) | 0.0582 (8) | 0.0483 (7) | 0.0013 (6) | −0.0040 (6) | 0.0003 (6) |
| C1 | 0.0351 (7) | 0.0530 (8) | 0.0342 (7) | −0.0047 (6) | 0.0054 (5) | 0.0039 (6) |
| C2 | 0.0394 (7) | 0.0720 (10) | 0.0372 (7) | −0.0136 (7) | 0.0009 (6) | −0.0029 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0515 (9) | 0.0611 (10) | 0.0497 (9) | −0.0159 (7) | 0.0114 (7) | −0.0143 (7) |
| C4 | 0.0499 (9) | 0.0521 (9) | 0.0598 (9) | −0.0013 (7) | 0.0145 (7) | −0.0043 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0382 (7) | 0.0574 (9) | 0.0441 (8) | −0.0003 (6) | 0.0025 (6) | 0.0020 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0346 (7) | 0.0484 (8) | 0.0303 (6) | −0.0061 (6) | 0.0053 (5) | 0.0010 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0387 (7) | 0.0582 (9) | 0.0412 (7) | −0.0125 (6) | 0.0044 (6) | −0.0072 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0292 (6) | 0.0384 (7) | 0.0392 (7) | −0.0035 (5) | 0.0027 (5) | −0.0110 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C8 | 1.2280 (14) | C1—C2 | 1.405 (2) |
| N1—N2 | 1.3057 (16) | C2—C3 | 1.365 (2) |
| N1—C1 | 1.3795 (19) | C2—H2 | 0.9300 |
| N2—N3 | 1.3559 (16) | C3—C4 | 1.407 (2) |
| N3—C6 | 1.3620 (17) | C3—H3 | 0.9300 |
| N3—C7 | 1.4478 (16) | C4—C5 | 1.367 (2) |
| N4—C8 | 1.3283 (16) | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| N4—N5 | 1.4120 (17) | C5—C6 | 1.3957 (19) |
| N4—H1 | 0.8600 | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| N5—H9 | 0.884 (9) | C7—C8 | 1.5179 (18) |
| N5—H8 | 0.888 (9) | C7—H7A | 0.9700 |
| C1—C6 | 1.3909 (18) | C7—H7B | 0.9700 |
| N2—N1—C1 | 108.09 (11) | C4—C3—H3 | 119.1 |
| N1—N2—N3 | 108.75 (11) | C5—C4—C3 | 122.15 (14) |
| N2—N3—C6 | 110.41 (10) | C5—C4—H4 | 118.9 |
| N2—N3—C7 | 120.74 (12) | C3—C4—H4 | 118.9 |
| C6—N3—C7 | 128.83 (12) | C4—C5—C6 | 115.87 (13) |
| C8—N4—N5 | 122.88 (10) | C4—C5—H5 | 122.1 |
| C8—N4—H1 | 118.6 | C6—C5—H5 | 122.1 |
| N5—N4—H1 | 118.6 | N3—C6—C1 | 104.05 (11) |
| N4—N5—H9 | 108.2 (12) | N3—C6—C5 | 133.05 (12) |
| N4—N5—H8 | 106.8 (13) | C1—C6—C5 | 122.90 (12) |
| H9—N5—H8 | 108.4 (17) | N3—C7—C8 | 111.69 (10) |
| N1—C1—C6 | 108.69 (12) | N3—C7—H7A | 109.3 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 131.22 (13) | C8—C7—H7A | 109.3 |
| C6—C1—C2 | 120.08 (13) | N3—C7—H7B | 109.3 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 117.16 (13) | C8—C7—H7B | 109.3 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 121.4 | H7A—C7—H7B | 107.9 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 121.4 | O1—C8—N4 | 123.60 (12) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 121.83 (14) | O1—C8—C7 | 121.49 (11) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.1 | N4—C8—C7 | 114.87 (10) |
| C1—N1—N2—N3 | −0.50 (14) | C7—N3—C6—C5 | 0.5 (2) |
| N1—N2—N3—C6 | 0.98 (15) | N1—C1—C6—N3 | 0.71 (13) |
| N1—N2—N3—C7 | 179.30 (11) | C2—C1—C6—N3 | −178.58 (12) |
| N2—N1—C1—C6 | −0.15 (14) | N1—C1—C6—C5 | −179.03 (12) |
| N2—N1—C1—C2 | 179.04 (14) | C2—C1—C6—C5 | 1.68 (19) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | −179.77 (14) | C4—C5—C6—N3 | 178.92 (13) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −0.66 (19) | C4—C5—C6—C1 | −1.43 (19) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.5 (2) | N2—N3—C7—C8 | −97.25 (14) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.7 (2) | C6—N3—C7—C8 | 80.72 (16) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.2 (2) | N5—N4—C8—O1 | −1.0 (2) |
| N2—N3—C6—C1 | −1.02 (13) | N5—N4—C8—C7 | −178.60 (12) |
| C7—N3—C6—C1 | −179.17 (12) | N3—C7—C8—O1 | 34.61 (18) |
| N2—N3—C6—C5 | 178.67 (14) | N3—C7—C8—N4 | −147.76 (12) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N4—H1···O1i | 0.86 | 2.18 | 2.9977 (14) | 159 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1, y, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: BG2267).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Bruker (2005). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Ji, N.-N. & Shi, Z.-Q. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Portalone, G. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o3232.
- Portalone, G. & Colapietro, M. (2007). Acta Cryst. C63, o655–o658. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Portalone, G. & Colapietro, M. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.-Q., Ji, N.-N., Zheng, Z.-B. & Li, J.-K. (2007a). Acta Cryst. E63, o4561.
- Shi, Z.-Q., Ji, N.-N., Zheng, Z.-B. & Li, J.-K. (2007b). Acta Cryst. E63, o4642.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809021199/bg2267sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809021199/bg2267Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report