Abstract
The title compound, C18H18FN3O2, adopts a trans conformation with respect to the C=N double bond. The dihedral angle between the two benzene rings is: 59.73 (6)°. Two independent N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link the molecules into layers parallel to (101).
Related literature
For biologically active phthalic diamides, see: Coronado et al. (1994 ▶); Tohnishi et al. (2000 ▶). For the preparation of the title compound, see: Zaky (2002 ▶); Shigeru et al. (2003 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C18H18FN3O2
M r = 327.35
Monoclinic,
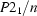
a = 13.316 (3) Å
b = 8.8904 (18) Å
c = 14.102 (3) Å
β = 91.10 (3)°
V = 1669.2 (6) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 123 K
0.30 × 0.30 × 0.30 mm
Data collection
Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID IP diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (ABSCOR; Higashi,1995 ▶) T min = 0.944, T max = 0.972
15335 measured reflections
3833 independent reflections
2302 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.046
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.039
wR(F 2) = 0.069
S = 1.02
3833 reflections
228 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.24 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3
Data collection: RAPID-AUTO (Rigaku, 2000 ▶); cell refinement: RAPID-AUTO; data reduction: CrystalStructure (Molecular Structure Corporation and Rigaku, 2000 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809022181/ya2090sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809022181/ya2090Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N3—H1⋯O2i | 0.875 (15) | 2.127 (15) | 2.9887 (16) | 168.4 (14) |
| N1—H2⋯O1ii | 0.850 (15) | 1.976 (15) | 2.8256 (16) | 177.8 (15) |
Symmetry codes: (i) 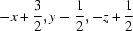 ; (ii)
; (ii) 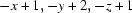 .
.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NNSFC) (grant No. 20572129), National Basic Research Program of China (2003CB114405) and National Key Project of Scientific and Technical Supporting Programs Funded by Ministry of Science & Technology of China (No. 2006BAE01AE01–11).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Phthalic diamides possess insecticidal properties due to their ability to activate ryanodine receptor (Coronado et al., 1994; Tohnishi et al., 2000). The title compound (I), a new phthalic diamide derivative, was synthesized by the condensation of N-aminophthalimide with 4-fluorobenzaldehyde followed by a ring-opening reaction using isopropyl amine (Zaky, 2002; Shigeru et al., 2003).
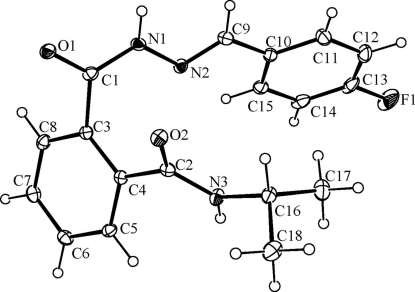
The molecular structure of the title compound is shown in Fig. 1. Molecule was proved to be a trans -isomer with respect to the C9=N2 double bond.
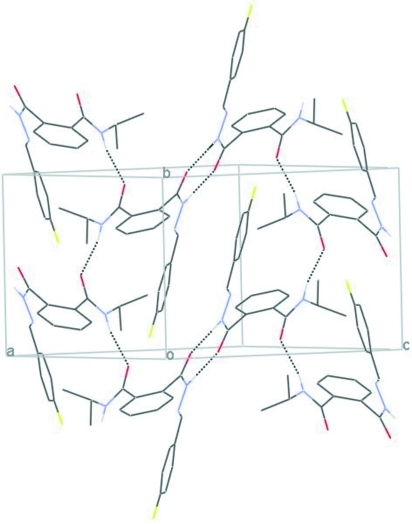
There are two independent N—H···O bonds (Table 1), which link molecules into the layers parallel to (101) plane (Fig. 2).
Experimental
To a solution of N-aminophthalimide (1.62 g, 10 mmol) and 4-fluorobenzaldehyde (1.24 g, 10 mmol) in 1,4-dioxane (100 ml), 12 N HCl (0.1 ml) was added at room temperature. After stirring for 5–10 min, a solution of isopropyl amine (1.16 g, 20 mmol) in 1,4-dioxane (10 ml) was added; the reaction mixture was stirred overnight at room temperature. After the solvent was evaporated under reduced pressure, the resulting mixture was dissolved in ethyl acetate (80 ml), washed with H2O (3×30 ml) and dried with anhydrous sodium sulfate to give the title compound (2.01 g, 61.5%). Single crystals suitable for X-ray diffraction analysis were obtained by slow evaporation of ethanol solution at room temperature over one week.
Refinement
The H atoms bound to N atoms were located in a difference Fourier map and refined isotropically [N—H 0.850 (15), 0.875 (15) Å]. The remaining H atoms were positioned geometrically and included in the refinement in riding model approximation with C—H 0.95 (aromatic), 0.98 (methyl), 1.00 (methyne), and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C)[1.5Ueq(C) for methyl H atoms].
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of (I); displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level. H atoms are shown as small circles of arbitrary radius.
Fig. 2.
The crystal packing of (I) viewed along the [101] direction; hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C18H18FN3O2 | F(000) = 688 |
| Mr = 327.35 | Dx = 1.303 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 15335 reflections |
| a = 13.316 (3) Å | θ = 2.1–27.5° |
| b = 8.8904 (18) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 14.102 (3) Å | T = 123 K |
| β = 91.10 (3)° | Block, colourless |
| V = 1669.2 (6) Å3 | 0.30 × 0.30 × 0.30 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Rigaku R-AXIS RAPID IP diffractometer | 3833 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2302 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.046 |
| Detector resolution: 10.00 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 2.1° |
| Ω scans | h = −17→17 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (ABSCOR; Higashi,1995) | k = −11→11 |
| Tmin = 0.944, Tmax = 0.972 | l = −18→18 |
| 15335 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.039 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.069 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.015P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.02 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 3833 reflections | Δρmax = 0.24 e Å−3 |
| 228 parameters | Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.0285 (8) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.62786 (10) | 0.87434 (17) | 0.48465 (10) | 0.0197 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.70864 (10) | 0.80962 (16) | 0.29308 (10) | 0.0179 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.72241 (10) | 0.78555 (15) | 0.47071 (10) | 0.0168 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.76143 (10) | 0.75512 (15) | 0.38154 (10) | 0.0162 (3) | |
| C5 | 0.85500 (10) | 0.68578 (15) | 0.37629 (10) | 0.0197 (3) | |
| H5 | 0.8819 | 0.6634 | 0.3160 | 0.024* | |
| C6 | 0.90921 (11) | 0.64909 (16) | 0.45774 (11) | 0.0228 (4) | |
| H6 | 0.9739 | 0.6050 | 0.4531 | 0.027* | |
| C7 | 0.86928 (10) | 0.67651 (16) | 0.54567 (11) | 0.0236 (4) | |
| H7 | 0.9057 | 0.6494 | 0.6017 | 0.028* | |
| C8 | 0.77595 (10) | 0.74366 (16) | 0.55190 (10) | 0.0216 (4) | |
| H8 | 0.7482 | 0.7613 | 0.6124 | 0.026* | |
| C9 | 0.44987 (11) | 0.65483 (17) | 0.36494 (10) | 0.0222 (4) | |
| H9 | 0.3990 | 0.7297 | 0.3628 | 0.027* | |
| C10 | 0.43139 (10) | 0.50842 (17) | 0.32041 (10) | 0.0215 (4) | |
| C11 | 0.35688 (11) | 0.49509 (19) | 0.24980 (11) | 0.0299 (4) | |
| H11 | 0.3173 | 0.5803 | 0.2331 | 0.036* | |
| C12 | 0.33975 (12) | 0.3594 (2) | 0.20378 (12) | 0.0384 (5) | |
| H12 | 0.2904 | 0.3510 | 0.1545 | 0.046* | |
| C13 | 0.39601 (13) | 0.2385 (2) | 0.23155 (12) | 0.0366 (5) | |
| C14 | 0.46863 (12) | 0.24391 (18) | 0.30209 (11) | 0.0307 (4) | |
| H14 | 0.5053 | 0.1565 | 0.3202 | 0.037* | |
| C15 | 0.48647 (11) | 0.38099 (17) | 0.34587 (11) | 0.0237 (4) | |
| H15 | 0.5371 | 0.3882 | 0.3940 | 0.028* | |
| C16 | 0.66213 (10) | 0.75633 (16) | 0.12683 (10) | 0.0221 (4) | |
| H16 | 0.6111 | 0.8369 | 0.1373 | 0.027* | |
| C17 | 0.60856 (12) | 0.61917 (18) | 0.08583 (11) | 0.0326 (4) | |
| H17A | 0.6574 | 0.5385 | 0.0758 | 0.049* | |
| H17B | 0.5762 | 0.6458 | 0.0251 | 0.049* | |
| H17C | 0.5576 | 0.5848 | 0.1301 | 0.049* | |
| C18 | 0.74105 (11) | 0.81707 (18) | 0.05991 (11) | 0.0311 (4) | |
| H18A | 0.7736 | 0.9053 | 0.0886 | 0.047* | |
| H18B | 0.7087 | 0.8457 | −0.0004 | 0.047* | |
| H18C | 0.7915 | 0.7392 | 0.0486 | 0.047* | |
| F1 | 0.37958 (8) | 0.10376 (12) | 0.18747 (7) | 0.0603 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.53997 (9) | 0.82179 (14) | 0.44990 (9) | 0.0204 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.53387 (8) | 0.68275 (13) | 0.40673 (8) | 0.0196 (3) | |
| N3 | 0.70850 (9) | 0.71718 (14) | 0.21866 (9) | 0.0214 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.63114 (7) | 0.99350 (11) | 0.53105 (7) | 0.0257 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.66866 (7) | 0.93655 (11) | 0.29200 (7) | 0.0217 (3) | |
| H1 | 0.7381 (11) | 0.6294 (17) | 0.2210 (11) | 0.038 (5)* | |
| H2 | 0.4879 (11) | 0.8765 (18) | 0.4542 (10) | 0.039 (5)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0210 (8) | 0.0190 (8) | 0.0193 (9) | −0.0014 (7) | 0.0050 (6) | 0.0005 (7) |
| C2 | 0.0172 (8) | 0.0152 (8) | 0.0215 (9) | −0.0017 (7) | 0.0023 (6) | 0.0018 (7) |
| C3 | 0.0184 (7) | 0.0108 (7) | 0.0214 (8) | −0.0035 (6) | 0.0021 (6) | −0.0015 (6) |
| C4 | 0.0178 (8) | 0.0110 (7) | 0.0197 (8) | −0.0028 (6) | 0.0009 (6) | 0.0006 (7) |
| C5 | 0.0210 (8) | 0.0172 (8) | 0.0210 (9) | −0.0002 (7) | 0.0043 (6) | −0.0024 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0191 (8) | 0.0187 (8) | 0.0305 (10) | 0.0035 (7) | −0.0017 (7) | 0.0004 (7) |
| C7 | 0.0258 (8) | 0.0215 (8) | 0.0233 (9) | −0.0006 (7) | −0.0052 (7) | 0.0030 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0260 (8) | 0.0222 (8) | 0.0168 (8) | −0.0028 (7) | 0.0026 (6) | −0.0006 (7) |
| C9 | 0.0184 (8) | 0.0221 (9) | 0.0262 (9) | 0.0009 (7) | 0.0017 (7) | 0.0001 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0181 (8) | 0.0267 (9) | 0.0197 (9) | −0.0052 (7) | 0.0038 (6) | −0.0024 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0228 (9) | 0.0406 (10) | 0.0264 (10) | −0.0045 (8) | −0.0005 (7) | −0.0008 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0292 (10) | 0.0578 (13) | 0.0284 (11) | −0.0181 (10) | 0.0031 (8) | −0.0149 (10) |
| C13 | 0.0406 (11) | 0.0358 (11) | 0.0339 (11) | −0.0211 (9) | 0.0180 (8) | −0.0213 (9) |
| C14 | 0.0332 (10) | 0.0252 (9) | 0.0343 (10) | −0.0042 (8) | 0.0161 (8) | −0.0049 (8) |
| C15 | 0.0219 (8) | 0.0259 (9) | 0.0235 (9) | −0.0045 (7) | 0.0056 (7) | −0.0009 (8) |
| C16 | 0.0262 (9) | 0.0204 (8) | 0.0197 (9) | 0.0081 (7) | −0.0045 (7) | −0.0010 (7) |
| C17 | 0.0368 (10) | 0.0280 (9) | 0.0326 (10) | 0.0038 (8) | −0.0088 (8) | −0.0045 (8) |
| C18 | 0.0387 (10) | 0.0294 (9) | 0.0253 (10) | 0.0072 (8) | 0.0010 (7) | 0.0025 (8) |
| F1 | 0.0638 (7) | 0.0548 (7) | 0.0630 (8) | −0.0279 (6) | 0.0211 (6) | −0.0401 (6) |
| N1 | 0.0160 (7) | 0.0170 (7) | 0.0283 (8) | 0.0009 (6) | 0.0017 (6) | −0.0049 (6) |
| N2 | 0.0213 (7) | 0.0164 (6) | 0.0211 (7) | −0.0029 (6) | 0.0028 (5) | −0.0033 (6) |
| N3 | 0.0283 (8) | 0.0166 (7) | 0.0192 (7) | 0.0067 (6) | −0.0036 (6) | −0.0018 (6) |
| O1 | 0.0229 (6) | 0.0202 (6) | 0.0340 (7) | −0.0007 (5) | 0.0037 (5) | −0.0103 (5) |
| O2 | 0.0267 (6) | 0.0135 (5) | 0.0247 (6) | 0.0028 (5) | 0.0004 (5) | 0.0015 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—O1 | 1.2455 (16) | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| C1—N1 | 1.3438 (18) | C12—C13 | 1.363 (2) |
| C1—C3 | 1.5022 (19) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C2—O2 | 1.2476 (16) | C13—F1 | 1.3656 (18) |
| C2—N3 | 1.3330 (18) | C13—C14 | 1.375 (2) |
| C2—C4 | 1.500 (2) | C14—C15 | 1.385 (2) |
| C3—C8 | 1.3879 (19) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C4 | 1.3964 (19) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C4—C5 | 1.3934 (18) | C16—N3 | 1.4658 (18) |
| C5—C6 | 1.3836 (19) | C16—C17 | 1.521 (2) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C16—C18 | 1.5247 (19) |
| C6—C7 | 1.380 (2) | C16—H16 | 1.0000 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | C17—H17A | 0.9800 |
| C7—C8 | 1.3831 (18) | C17—H17B | 0.9800 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9500 | C17—H17C | 0.9800 |
| C8—H8 | 0.9500 | C18—H18A | 0.9800 |
| C9—N2 | 1.2786 (17) | C18—H18B | 0.9800 |
| C9—C10 | 1.464 (2) | C18—H18C | 0.9800 |
| C9—H9 | 0.9500 | N1—N2 | 1.3796 (16) |
| C10—C15 | 1.393 (2) | N1—H2 | 0.850 (15) |
| C10—C11 | 1.3972 (19) | N3—H1 | 0.875 (15) |
| C11—C12 | 1.386 (2) | ||
| O1—C1—N1 | 120.58 (13) | C11—C12—H12 | 121.1 |
| O1—C1—C3 | 119.65 (13) | C12—C13—F1 | 118.60 (17) |
| N1—C1—C3 | 119.72 (13) | C12—C13—C14 | 123.75 (16) |
| O2—C2—N3 | 123.63 (14) | F1—C13—C14 | 117.65 (18) |
| O2—C2—C4 | 119.68 (13) | C13—C14—C15 | 117.74 (17) |
| N3—C2—C4 | 116.68 (13) | C13—C14—H14 | 121.1 |
| C8—C3—C4 | 119.79 (13) | C15—C14—H14 | 121.1 |
| C8—C3—C1 | 116.84 (13) | C14—C15—C10 | 121.07 (15) |
| C4—C3—C1 | 123.16 (13) | C14—C15—H15 | 119.5 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 118.82 (13) | C10—C15—H15 | 119.5 |
| C5—C4—C2 | 120.26 (13) | N3—C16—C17 | 109.39 (12) |
| C3—C4—C2 | 120.64 (12) | N3—C16—C18 | 110.32 (12) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 120.86 (14) | C17—C16—C18 | 111.86 (13) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.6 | N3—C16—H16 | 108.4 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.6 | C17—C16—H16 | 108.4 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 120.02 (14) | C18—C16—H16 | 108.4 |
| C7—C6—H6 | 120.0 | C16—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 120.0 | C16—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 119.69 (14) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—H7 | 120.2 | C16—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 120.2 | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—C3 | 120.76 (13) | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 119.6 | C16—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| C3—C8—H8 | 119.6 | C16—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| N2—C9—C10 | 120.58 (14) | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| N2—C9—H9 | 119.7 | C16—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—H9 | 119.7 | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C15—C10—C11 | 118.54 (15) | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| C15—C10—C9 | 121.96 (14) | C1—N1—N2 | 121.06 (13) |
| C11—C10—C9 | 119.49 (14) | C1—N1—H2 | 118.7 (11) |
| C12—C11—C10 | 121.04 (16) | N2—N1—H2 | 120.2 (11) |
| C12—C11—H11 | 119.5 | C9—N2—N1 | 114.89 (12) |
| C10—C11—H11 | 119.5 | C2—N3—C16 | 122.92 (13) |
| C13—C12—C11 | 117.83 (16) | C2—N3—H1 | 121.8 (10) |
| C13—C12—H12 | 121.1 | C16—N3—H1 | 115.3 (10) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N3—H1···O2i | 0.875 (15) | 2.127 (15) | 2.9887 (16) | 168.4 (14) |
| N1—H2···O1ii | 0.850 (15) | 1.976 (15) | 2.8256 (16) | 177.8 (15) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+3/2, y−1/2, −z+1/2; (ii) −x+1, −y+2, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: YA2090).
References
- Coronado, R., Morrissette, J., Sukhareva, M. & Vaughan, D. M. (1994). Am. J. Physiol.266, 1485–1504. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Higashi, T. (1995). ABSCOR Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Molecular Structure Corporation and Rigaku (2000). CrystalStructure MSC, The Woodlands, Texas, USA, and Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Rigaku (2000). RAPID-AUTO Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Shigeru, N., Takeshi, S., Etsuko, M. & Yasuo, K. (2003). Synth. Commun.33, 87–98.
- Tohnishi, M., Nakao, H., Kohno, E., Nishida, T., Furuya, T., Shimizu, T., Seo, A., Sakata, K., Fujioka, S. & Kanno, H. (2000). Eur. Patent No. EP1006107.
- Zaky, H. T. (2002). Heterocycl. Commun 8, 355–360.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809022181/ya2090sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809022181/ya2090Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report