Abstract
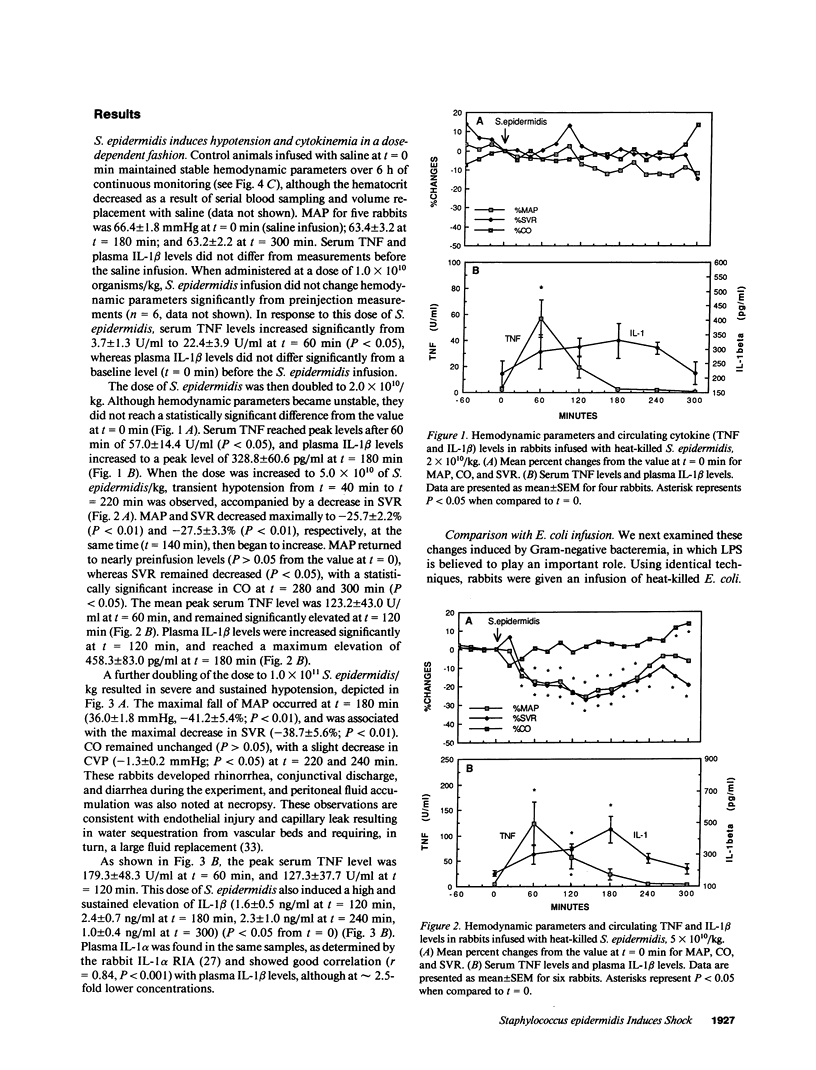
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and IL-1 are thought to mediate many of the pathophysiologic changes of endotoxemia and Gram-negative bacteremia. In these studies, heat-killed Staphylococcus epidermidis were infused into rabbits to determine whether an endotoxin (LPS)-free microorganism also elicits cytokinemia and the physiologic abnormalities seen in Gram-negative bacteremia. S. epidermidis induced complement activation, circulating TNF and IL-1, and hypotension to the same degree as did one-twentieth the number of heat-killed Escherichia coli. Circulating IL-1 beta levels had a greater correlation coefficient (r = 0.81, P less than 0.001) with the degree of hypotension than TNF levels (r = 0.48, P less than 0.02). Leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, diffuse pulmonary capillary aggregation of neutrophils, and hepatic necrosis with neutrophil infiltration were observed to the same extent after either S. epidermidis or E. coli infusion. However, S. epidermidis infusion did not induce significant (less than 60 pg/ml) endotoxemia, whereas E. coli infusion resulted in high (11,000 pg/ml) serum endotoxin levels. S. epidermidis, E. coli, LPS, or S. epidermidis-derived lipoteichoic acid (LTA) induced TNF and IL-1 from blood mononuclear cells in vitro. E. coli organisms and LPS were at least 100-fold more potent than S. epidermidis or LTA. Thus, a shock-like state with similar levels of complement activation as well as circulating levels of IL-1 and TNF were observed following either S. epidermidis or E. coli. These data provide further evidence that host factors such as IL-1 and TNF are common mediators of the septic shock syndrome regardless of the organism.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bessin P., Bonnet J., Apffel D., Soulard C., Desgroux L., Pelas I., Benveniste J. Acute circulatory collapse caused by platelet-activating factor (PAF-acether) in dogs. Eur J Pharmacol. 1983 Jan 21;86(3-4):403–413. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(83)90190-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beutler B., Milsark I. W., Cerami A. C. Passive immunization against cachectin/tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effect of endotoxin. Science. 1985 Aug 30;229(4716):869–871. doi: 10.1126/science.3895437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevilacqua M. P., Pober J. S., Majeau G. R., Fiers W., Cotran R. S., Gimbrone M. A., Jr Recombinant tumor necrosis factor induces procoagulant activity in cultured human vascular endothelium: characterization and comparison with the actions of interleukin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4533–4537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bone R. C., Fisher C. J., Jr, Clemmer T. P., Slotman G. J., Metz C. A., Balk R. A. Sepsis syndrome: a valid clinical entity. Methylprednisolone Severe Sepsis Study Group. Crit Care Med. 1989 May;17(5):389–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burchard K. W., Minor L. B., Slotman G. J., Gann D. S. Staphylococcus epidermidis sepsis in surgical patients. Arch Surg. 1984 Jan;119(1):96–100. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1984.01390130078014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. G., Clark B. D., Wingfield P., Schmeissner U., Losberger C., Dinarello C. A., Shaw A. R. Rabbit IL-1. Cloning, expression, biologic properties, and transcription during endotoxemia. J Immunol. 1989 Apr 1;142(7):2299–2306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. G., Tompkins R. G., Gelfand J. A., Michie H. R., Stanford G. G., van der Meer J. W., Endres S., Lonnemann G., Corsetti J., Chernow B. Circulating interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor in septic shock and experimental endotoxin fever. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jan;161(1):79–84. doi: 10.1093/infdis/161.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. G., van der Meer J. W., Kwiatkowski D., Endres S., Lonnemann G., Burke J. F., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 beta in human plasma: optimization of blood collection, plasma extraction, and radioimmunoassay methods. Lymphokine Res. 1988 Winter;7(4):457–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen G. D., Bisno A. L., Parisi J. T., McLaughlin B., Hester M. G., Luther R. W. Nosocomial septicemia due to multiply antibiotic-resistant Staphylococcus epidermidis. Ann Intern Med. 1982 Jan;96(1):1–10. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-96-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J., McConnell J. S. Observations on the measurement and evaluation of endotoxemia by a quantitative limulus lysate microassay. J Infect Dis. 1984 Dec;150(6):916–924. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.6.916. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Cannon J. G., Wolff S. M., Bernheim H. A., Beutler B., Cerami A., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, O'Connor J. V. Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is an endogenous pyrogen and induces production of interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1986 Jun 1;163(6):1433–1450. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.6.1433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doebber T. W., Wu M. S., Robbins J. C., Choy B. M., Chang M. N., Shen T. Y. Platelet activating factor (PAF) involvement in endotoxin-induced hypotension in rats. Studies with PAF-receptor antagonist kadsurenone. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Mar 29;127(3):799–808. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(85)80014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon D. T., Ruddy S., Schur P. H., McCabe W. R. Activation of the properdin pathway of complement in patients with gram-negative of bacteremia. N Engl J Med. 1975 May 1;292(18):937–940. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197505012921802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong Y., Tracey K. J., Moldawer L. L., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. B., Kenney J. S., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Allison A. C., Lowry S. F. Antibodies to cachectin/tumor necrosis factor reduce interleukin 1 beta and interleukin 6 appearance during lethal bacteremia. J Exp Med. 1989 Nov 1;170(5):1627–1633. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.5.1627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girardin E., Grau G. E., Dayer J. M., Roux-Lombard P., Lambert P. H. Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 in the serum of children with severe infectious purpura. N Engl J Med. 1988 Aug 18;319(7):397–400. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198808183190703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hesse D. G., Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Manogue K. R., Palladino M. A., Jr, Cerami A., Shires G. T., Lowry S. F. Cytokine appearance in human endotoxemia and primate bacteremia. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1988 Feb;166(2):147–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikejima T., Okusawa S., Ghezzi P., van der Meer J. W., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin-1 induces tumor necrosis factor (TNF) in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells in vitro and a circulating TNF-like activity in rabbits. J Infect Dis. 1990 Jul;162(1):215–223. doi: 10.1093/infdis/162.1.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikejima T., Okusawa S., van der Meer J. W., Dinarello C. A. Induction by toxic-shock-syndrome toxin-1 of a circulating tumor necrosis factor-like substance in rabbits and of immunoreactive tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 from human mononuclear cells. J Infect Dis. 1988 Nov;158(5):1017–1025. doi: 10.1093/infdis/158.5.1017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg C., Marceau F., Hugli T. E. C5a-induced hemodynamic and hematologic changes in the rabbit. Role of cyclooxygenase products and polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Am J Pathol. 1987 Sep;128(3):471–483. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. A., Pfaller M. A., Wenzel R. P. Coagulase-negative staphylococcal bacteremia. Mortality and hospital stay. Ann Intern Med. 1989 Jan 1;110(1):9–16. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-110-1-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathison J. C., Wolfson E., Ulevitch R. J. Participation of tumor necrosis factor in the mediation of gram negative bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced injury in rabbits. J Clin Invest. 1988 Jun;81(6):1925–1937. doi: 10.1172/JCI113540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michie H. R., Manogue K. R., Spriggs D. R., Revhaug A., O'Dwyer S., Dinarello C. A., Cerami A., Wolff S. M., Wilmore D. W. Detection of circulating tumor necrosis factor after endotoxin administration. N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 9;318(23):1481–1486. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806093182301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Movat H. Z., Burrowes C. E., Cybulsky M. I., Dinarello C. A. Acute inflammation and a Shwartzman-like reaction induced by interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor. Synergistic action of the cytokines in the induction of inflammation and microvascular injury. Am J Pathol. 1987 Dec;129(3):463–476. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nafziger D. A., Wenzel R. P. Coagulase-negative staphylococci. Epidemiology, evaluation, and therapy. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1989 Dec;3(4):915–929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natanson C., Danner R. L., Elin R. J., Hosseini J. M., Peart K. W., Banks S. M., MacVittie T. J., Walker R. I., Parrillo J. E. Role of endotoxemia in cardiovascular dysfunction and mortality. Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus challenges in a canine model of human septic shock. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jan;83(1):243–251. doi: 10.1172/JCI113866. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson K., Björk P., Bergenfeldt M., Hageman R., Thompson R. C. Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist reduces mortality from endotoxin shock. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):550–552. doi: 10.1038/348550a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oken M. M., Peterson P. K., Wilkinson B. J. Endogenous pyrogen production by human blood monocytes stimulated by staphylococcal cell wall components. Infect Immun. 1981 Jan;31(1):208–213. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.1.208-213.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okusawa S., Dinarello C. A., Yancey K. B., Endres S., Lawley T. J., Frank M. M., Burke J. F., Gelfand J. A. C5a induction of human interleukin 1. Synergistic effect with endotoxin or interferon-gamma. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 15;139(8):2635–2640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okusawa S., Gelfand J. A., Ikejima T., Connolly R. J., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin 1 induces a shock-like state in rabbits. Synergism with tumor necrosis factor and the effect of cyclooxygenase inhibition. J Clin Invest. 1988 Apr;81(4):1162–1172. doi: 10.1172/JCI113431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okusawa S., Yancey K. B., van der Meer J. W., Endres S., Lonnemann G., Hefter K., Frank M. M., Burke J. F., Dinarello C. A., Gelfand J. A. C5a stimulates secretion of tumor necrosis factor from human mononuclear cells in vitro. Comparison with secretion of interleukin 1 beta and interleukin 1 alpha. J Exp Med. 1988 Jul 1;168(1):443–448. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.1.443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker M. M., Parrillo J. E. Septic shock. Hemodynamics and pathogenesis. JAMA. 1983 Dec 23;250(24):3324–3327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavek K., Piper P. J., Smedegård G. Anaphylatoxin-induced shock and two patterns of anaphylactic shock: hemodynamics and mediators. Acta Physiol Scand. 1979 Apr;105(4):393–403. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1979.tb00103.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohlman T. H., Stanness K. A., Beatty P. G., Ochs H. D., Harlan J. M. An endothelial cell surface factor(s) induced in vitro by lipopolysaccharide, interleukin 1, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha increases neutrophil adherence by a CDw18-dependent mechanism. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4548–4553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ponce de Leon S., Wenzel R. P. Hospital-acquired bloodstream infections with Staphylococcus epidermidis. Review of 100 cases. Am J Med. 1984 Oct;77(4):639–644. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(84)90354-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon G. L., Gelfand J. A., Connolly R. A., O'Donnell T. F., Jr, Gorbach S. L. Experimental Bacteroides fragilis bacteremia in a primate model: evidence that Bacteroides fragilis does not promote the septic shock syndrome. J Trauma. 1985 Dec;25(12):1156–1162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smedegård G., Cui L. X., Hugli T. E. Endotoxin-induced shock in the rat. A role for C5a. Am J Pathol. 1989 Sep;135(3):489–497. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. H., O'Hanley P., Shapiro J. M., Mihm F. G., Satoh P. S., Collins J. A., Raffin T. A. Effects of anti-C5a antibodies on the adult respiratory distress syndrome in septic primates. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jun;77(6):1812–1816. doi: 10.1172/JCI112506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terashita Z., Imura Y., Nishikawa K., Sumida S. Is platelet activating factor (PAF) a mediator of endotoxin shock? Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb 26;109(2):257–261. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90427-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tewari A., Buhles W. C., Jr, Starnes H. F., Jr Preliminary report: effects of interleukin-1 on platelet counts. Lancet. 1990 Sep 22;336(8717):712–714. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)92206-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tojo M., Yamashita N., Goldmann D. A., Pier G. B. Isolation and characterization of a capsular polysaccharide adhesin from Staphylococcus epidermidis. J Infect Dis. 1988 Apr;157(4):713–722. doi: 10.1093/infdis/157.4.713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Beutler B., Lowry S. F., Merryweather J., Wolpe S., Milsark I. W., Hariri R. J., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Zentella A., Albert J. D. Shock and tissue injury induced by recombinant human cachectin. Science. 1986 Oct 24;234(4775):470–474. doi: 10.1126/science.3764421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Fong Y., Hesse D. G., Manogue K. R., Lee A. T., Kuo G. C., Lowry S. F., Cerami A. Anti-cachectin/TNF monoclonal antibodies prevent septic shock during lethal bacteraemia. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):662–664. doi: 10.1038/330662a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tracey K. J., Lowry S. F., Fahey T. J., 3rd, Albert J. D., Fong Y., Hesse D., Beutler B., Manogue K. R., Calvano S., Wei H. Cachectin/tumor necrosis factor induces lethal shock and stress hormone responses in the dog. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1987 May;164(5):415–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tredget E. E., Yu Y. M., Zhong S., Burini R., Okusawa S., Gelfand J. A., Dinarello C. A., Young V. R., Burke J. F. Role of interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor on energy metabolism in rabbits. Am J Physiol. 1988 Dec;255(6 Pt 1):E760–E768. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.255.6.E760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakabayashi G., Gelfand J. A., Burke J. F., Thompson R. C., Dinarello C. A. A specific receptor antagonist for interleukin 1 prevents Escherichia coli-induced shock in rabbits. FASEB J. 1991 Mar 1;5(3):338–343. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.3.1825816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg J. R., Wright D. J., Guz A. Interleukin-1 and tumour necrosis factor cause hypotension in the conscious rabbit. Clin Sci (Lond) 1988 Sep;75(3):251–255. doi: 10.1042/cs0750251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wicken A. J., Knox K. W. Lipoteichoic acids: a new class of bacterial antigen. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1161–1167. doi: 10.1126/science.46620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








