Abstract
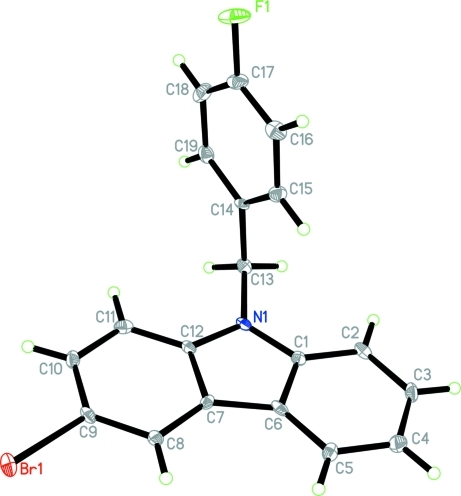
The title compound, C19H13BrFN, was synthesized by N-alkylation of 1-chloromethyl-4-fluorobenzene with 3-bromo-9H-carbazole. The carbazole ring system is essentially planar (r.m.s. deviation of 0.024 Å for the non-H atoms) and forms a dihedral angle of 88.2 (3)° with the benzene ring.
Related literature
For a similar structure, see: Huang et al. (2007 ▶). For the synthetic procedure, see: Duan et al. (2005a
▶,b
▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
C19H13BrFN
M r = 354.21
Orthorhombic,
a = 17.407 (4) Å
b = 15.068 (3) Å
c = 5.5865 (11) Å
V = 1465.3 (5) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 2.81 mm−1
T = 113 K
0.18 × 0.12 × 0.08 mm
Data collection
Rigaku Saturn diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku/MSC, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.632, T max = 0.806
9581 measured reflections
2577 independent reflections
2294 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.050
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.032
wR(F 2) = 0.070
S = 0.99
2577 reflections
199 parameters
1 restraint
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.43 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.69 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 1139 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: 0.004 (12)
Data collection: CrystalClear (Rigaku/MSC, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: CrystalClear; data reduction: CrystalClear; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680901976X/gk2211sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680901976X/gk2211Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
N-Alkyl carbazoles possess valuable pharmaceutical properties. In this paper, synthesis and the crystal structure of 3-bromo-9-(4-fluorobenzyl)-9H-carbazole is reported
The carbazole ring is essentially planar, with a r.m.s. deviation from the mean plane of 0.024 Å for the non-hydrogen atoms. The dihedral angle formed between the carbazole unit and the benzene ring is 88.2 (3) Å.
Experimental
The title compound was prepared according to the procedure of Duan et al. (2005a,b). A solution of potassium hydroxide (0.67 g) in dimethylformamide (8 ml) was stirred at room temperature for 20 min. 3-Bromo-9H-carbazole (1.0 g, 4 mmol) was added and the mixture stirred for a further 40 min. A solution of 1-(chloromethyl)-4-fluorobenzene (0.87 g, 6 mmol) in dimethylformamide (5 ml) was added dropwise with stirring. The resulting mixture was then stirred at room temperature for 12 h and poured into water (100 ml), yielding a white precipitate. The solid product was filtered off, washed with cold water and recrystallized from EtOH, giving crystals of the title compound. Yield: 1.27 g (89.5%); m.p. 420–422 K. The title compound (40 mg) was dissolved in a mixture of chloroform (5 ml) and ethanol (5 ml) and the solution was kept at room temperature for 13 days. Evaporation of the solution gave colourless crystals suitable for X-ray analysis.
Refinement
All H atoms were included in the idealized positions and refined in a riding model approximation with C—H distances of 0.93 (benzene) and 0.97 (methylene) Å, and with Uiso(H) = 1.2xUeq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of the title compound with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 30% probability level. H atoms are presented as spheres of arbitrary radius.
Crystal data
| C19H13BrFN | Dx = 1.606 Mg m−3 |
| Mr = 354.21 | Melting point = 420–422 K |
| Orthorhombic, Pna21 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2c -2n | Cell parameters from 4959 reflections |
| a = 17.407 (4) Å | θ = 1.8–27.9° |
| b = 15.068 (3) Å | µ = 2.81 mm−1 |
| c = 5.5865 (11) Å | T = 113 K |
| V = 1465.3 (5) Å3 | Prism, colorless |
| Z = 4 | 0.18 × 0.12 × 0.08 mm |
| F(000) = 712 |
Data collection
| Rigaku Saturn diffractometer | 2577 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: rotating anode | 2294 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| confocal multilayer X-ray optic | Rint = 0.050 |
| Detector resolution: 7.31 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 1.8° |
| ω and φ scans | h = −20→20 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrystalClear; Rigaku/MSC, 2005) | k = −11→17 |
| Tmin = 0.632, Tmax = 0.806 | l = −6→6 |
| 9581 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.032 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.070 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0325P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 0.99 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.002 |
| 2577 reflections | Δρmax = 0.43 e Å−3 |
| 199 parameters | Δρmin = −0.69 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 1139 Friedel pairs |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Flack parameter: 0.004 (12) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br1 | 0.257719 (15) | 0.68839 (2) | 1.21455 (15) | 0.02390 (12) | |
| F1 | 0.64152 (11) | 1.09557 (12) | 0.7028 (5) | 0.0424 (5) | |
| N1 | 0.53809 (16) | 0.69284 (17) | 0.5849 (5) | 0.0157 (7) | |
| C1 | 0.58579 (15) | 0.63539 (19) | 0.7103 (7) | 0.0154 (6) | |
| C2 | 0.66123 (18) | 0.6094 (2) | 0.6612 (6) | 0.0195 (8) | |
| H2 | 0.6871 | 0.6304 | 0.5270 | 0.023* | |
| C3 | 0.69613 (18) | 0.5514 (2) | 0.8188 (6) | 0.0224 (9) | |
| H3 | 0.7461 | 0.5328 | 0.7882 | 0.027* | |
| C4 | 0.6585 (2) | 0.5198 (2) | 1.0230 (7) | 0.0240 (9) | |
| H4 | 0.6837 | 0.4815 | 1.1273 | 0.029* | |
| C5 | 0.58356 (18) | 0.5459 (2) | 1.0697 (6) | 0.0187 (8) | |
| H5 | 0.5582 | 0.5247 | 1.2046 | 0.022* | |
| C6 | 0.54659 (18) | 0.6037 (2) | 0.9140 (6) | 0.0156 (8) | |
| C7 | 0.47175 (18) | 0.6440 (2) | 0.9118 (6) | 0.0137 (7) | |
| C8 | 0.40789 (17) | 0.6400 (2) | 1.0641 (5) | 0.0163 (8) | |
| H8 | 0.4078 | 0.6034 | 1.1982 | 0.020* | |
| C9 | 0.34574 (19) | 0.6916 (2) | 1.0091 (6) | 0.0165 (8) | |
| C10 | 0.34296 (18) | 0.7470 (2) | 0.8090 (6) | 0.0183 (8) | |
| H10 | 0.2991 | 0.7804 | 0.7778 | 0.022* | |
| C11 | 0.40517 (18) | 0.7520 (2) | 0.6580 (6) | 0.0199 (8) | |
| H11 | 0.4044 | 0.7896 | 0.5260 | 0.024* | |
| C12 | 0.46916 (15) | 0.70008 (18) | 0.7062 (8) | 0.0144 (6) | |
| C13 | 0.56110 (19) | 0.7523 (2) | 0.3949 (6) | 0.0188 (8) | |
| H13A | 0.5193 | 0.7572 | 0.2808 | 0.023* | |
| H13B | 0.6047 | 0.7268 | 0.3119 | 0.023* | |
| C14 | 0.58251 (18) | 0.8443 (2) | 0.4797 (6) | 0.0136 (7) | |
| C15 | 0.62396 (17) | 0.8572 (2) | 0.6911 (8) | 0.0210 (7) | |
| H15 | 0.6382 | 0.8084 | 0.7833 | 0.025* | |
| C16 | 0.64408 (18) | 0.9420 (2) | 0.7646 (6) | 0.0253 (10) | |
| H16 | 0.6720 | 0.9504 | 0.9047 | 0.030* | |
| C17 | 0.6225 (2) | 1.0122 (2) | 0.6294 (6) | 0.0258 (9) | |
| C18 | 0.5814 (2) | 1.0036 (2) | 0.4166 (7) | 0.0280 (9) | |
| H18 | 0.5677 | 1.0528 | 0.3257 | 0.034* | |
| C19 | 0.56160 (18) | 0.9178 (2) | 0.3464 (6) | 0.0211 (8) | |
| H19 | 0.5336 | 0.9097 | 0.2062 | 0.025* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br1 | 0.01522 (18) | 0.0313 (2) | 0.02516 (18) | 0.00202 (13) | 0.0037 (3) | −0.0041 (2) |
| F1 | 0.0644 (14) | 0.0163 (10) | 0.0464 (12) | −0.0111 (9) | 0.0121 (17) | −0.0079 (14) |
| N1 | 0.0132 (16) | 0.0153 (16) | 0.0187 (16) | −0.0052 (12) | 0.0024 (12) | −0.0004 (13) |
| C1 | 0.0149 (15) | 0.0133 (15) | 0.0180 (15) | −0.0033 (12) | −0.003 (2) | −0.004 (2) |
| C2 | 0.0160 (17) | 0.0242 (19) | 0.018 (2) | −0.0069 (15) | 0.0010 (14) | −0.0034 (16) |
| C3 | 0.0119 (19) | 0.020 (2) | 0.035 (2) | 0.0037 (15) | −0.0007 (16) | −0.0073 (17) |
| C4 | 0.023 (2) | 0.017 (2) | 0.032 (2) | 0.0003 (17) | −0.0037 (17) | −0.0009 (18) |
| C5 | 0.018 (2) | 0.0174 (19) | 0.0203 (18) | 0.0009 (16) | −0.0073 (16) | −0.0043 (16) |
| C6 | 0.0133 (18) | 0.0165 (19) | 0.0170 (18) | −0.0070 (15) | 0.0033 (15) | −0.0080 (16) |
| C7 | 0.0151 (18) | 0.0103 (18) | 0.0158 (17) | 0.0010 (15) | −0.0042 (14) | −0.0019 (16) |
| C8 | 0.0145 (19) | 0.0160 (18) | 0.0185 (18) | −0.0024 (16) | −0.0019 (14) | 0.0004 (16) |
| C9 | 0.0114 (19) | 0.018 (2) | 0.0197 (19) | −0.0047 (15) | 0.0032 (15) | −0.0067 (16) |
| C10 | 0.0132 (19) | 0.0189 (19) | 0.0228 (18) | 0.0016 (15) | −0.0032 (14) | −0.0026 (15) |
| C11 | 0.0247 (19) | 0.0155 (18) | 0.020 (2) | −0.0040 (16) | −0.0033 (14) | 0.0011 (15) |
| C12 | 0.0134 (14) | 0.0137 (16) | 0.0161 (15) | −0.0035 (12) | 0.003 (2) | −0.0022 (19) |
| C13 | 0.0177 (19) | 0.021 (2) | 0.0177 (17) | −0.0020 (16) | 0.0011 (15) | 0.0000 (17) |
| C14 | 0.0124 (18) | 0.0126 (18) | 0.0158 (17) | −0.0036 (15) | 0.0083 (14) | −0.0013 (16) |
| C15 | 0.0239 (17) | 0.0190 (17) | 0.0201 (18) | −0.0012 (14) | 0.000 (2) | 0.004 (2) |
| C16 | 0.0259 (19) | 0.027 (2) | 0.023 (3) | −0.0048 (16) | 0.0036 (15) | −0.0061 (17) |
| C17 | 0.031 (2) | 0.015 (2) | 0.031 (2) | −0.0017 (17) | 0.0144 (16) | −0.0045 (17) |
| C18 | 0.032 (2) | 0.021 (2) | 0.031 (2) | 0.0086 (19) | 0.0079 (19) | 0.0025 (19) |
| C19 | 0.0169 (19) | 0.028 (2) | 0.0184 (19) | −0.0005 (17) | 0.0032 (15) | 0.0038 (17) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Br1—C9 | 1.915 (3) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| F1—C17 | 1.363 (4) | C9—C10 | 1.396 (5) |
| N1—C12 | 1.382 (4) | C10—C11 | 1.375 (4) |
| N1—C1 | 1.389 (4) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C13 | 1.446 (4) | C11—C12 | 1.387 (4) |
| C1—C2 | 1.398 (4) | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C6 | 1.410 (5) | C13—C14 | 1.512 (4) |
| C2—C3 | 1.381 (5) | C13—H13A | 0.9700 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C13—H13B | 0.9700 |
| C3—C4 | 1.399 (5) | C14—C19 | 1.383 (4) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C14—C15 | 1.397 (5) |
| C4—C5 | 1.387 (5) | C15—C16 | 1.387 (4) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.389 (5) | C16—C17 | 1.353 (5) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C6—C7 | 1.437 (4) | C17—C18 | 1.394 (6) |
| C7—C8 | 1.401 (4) | C18—C19 | 1.394 (5) |
| C7—C12 | 1.427 (5) | C18—H18 | 0.9300 |
| C8—C9 | 1.368 (5) | C19—H19 | 0.9300 |
| C12—N1—C1 | 108.7 (3) | C9—C10—H10 | 120.1 |
| C12—N1—C13 | 123.5 (3) | C10—C11—C12 | 118.9 (3) |
| C1—N1—C13 | 126.2 (3) | C10—C11—H11 | 120.6 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 129.6 (3) | C12—C11—H11 | 120.6 |
| N1—C1—C6 | 109.2 (3) | N1—C12—C11 | 130.3 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 121.2 (3) | N1—C12—C7 | 108.7 (2) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 117.8 (3) | C11—C12—C7 | 121.0 (3) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 121.1 | N1—C13—C14 | 114.0 (3) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 121.1 | N1—C13—H13A | 108.8 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 121.9 (3) | C14—C13—H13A | 108.8 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.0 | N1—C13—H13B | 108.8 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.0 | C14—C13—H13B | 108.8 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 119.8 (3) | H13A—C13—H13B | 107.6 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.1 | C19—C14—C15 | 118.7 (3) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.1 | C19—C14—C13 | 120.0 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.7 (3) | C15—C14—C13 | 121.3 (3) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.2 | C16—C15—C14 | 120.5 (3) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.2 | C16—C15—H15 | 119.7 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 119.6 (3) | C14—C15—H15 | 119.7 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 133.6 (3) | C17—C16—C15 | 119.0 (3) |
| C1—C6—C7 | 106.8 (3) | C17—C16—H16 | 120.5 |
| C8—C7—C12 | 119.3 (3) | C15—C16—H16 | 120.5 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 134.1 (3) | C16—C17—F1 | 119.0 (4) |
| C12—C7—C6 | 106.6 (3) | C16—C17—C18 | 123.1 (3) |
| C9—C8—C7 | 117.8 (3) | F1—C17—C18 | 117.8 (4) |
| C9—C8—H8 | 121.1 | C17—C18—C19 | 116.9 (3) |
| C7—C8—H8 | 121.1 | C17—C18—H18 | 121.5 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 123.2 (3) | C19—C18—H18 | 121.5 |
| C8—C9—Br1 | 118.9 (3) | C14—C19—C18 | 121.7 (3) |
| C10—C9—Br1 | 117.9 (3) | C14—C19—H19 | 119.1 |
| C11—C10—C9 | 119.8 (3) | C18—C19—H19 | 119.1 |
| C11—C10—H10 | 120.1 | ||
| C12—N1—C1—C2 | −178.2 (3) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 1.3 (5) |
| C13—N1—C1—C2 | −12.3 (5) | C1—N1—C12—C11 | 176.9 (3) |
| C12—N1—C1—C6 | 1.0 (3) | C13—N1—C12—C11 | 10.5 (5) |
| C13—N1—C1—C6 | 166.9 (3) | C1—N1—C12—C7 | −1.6 (3) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 179.3 (3) | C13—N1—C12—C7 | −167.9 (3) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.1 (5) | C10—C11—C12—N1 | −179.9 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.7 (5) | C10—C11—C12—C7 | −1.7 (5) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.9 (5) | C8—C7—C12—N1 | −180.0 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.5 (5) | C6—C7—C12—N1 | 1.5 (4) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.1 (5) | C8—C7—C12—C11 | 1.4 (5) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −178.7 (3) | C6—C7—C12—C11 | −177.1 (3) |
| N1—C1—C6—C5 | −179.0 (3) | C12—N1—C13—C14 | 72.0 (4) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.3 (5) | C1—N1—C13—C14 | −92.0 (4) |
| N1—C1—C6—C7 | −0.1 (4) | N1—C13—C14—C19 | −141.1 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | 179.2 (3) | N1—C13—C14—C15 | 39.5 (4) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | −0.4 (7) | C19—C14—C15—C16 | −0.4 (5) |
| C1—C6—C7—C8 | −179.1 (4) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 179.1 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—C12 | 177.9 (4) | C14—C15—C16—C17 | 0.5 (5) |
| C1—C6—C7—C12 | −0.8 (4) | C15—C16—C17—F1 | 179.3 (3) |
| C12—C7—C8—C9 | −0.8 (5) | C15—C16—C17—C18 | −0.7 (5) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | 177.3 (3) | C16—C17—C18—C19 | 0.8 (5) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | 0.5 (5) | F1—C17—C18—C19 | −179.2 (3) |
| C7—C8—C9—Br1 | −179.6 (2) | C15—C14—C19—C18 | 0.5 (5) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | −0.8 (5) | C13—C14—C19—C18 | −178.9 (3) |
| Br1—C9—C10—C11 | 179.4 (2) | C17—C18—C19—C14 | −0.7 (5) |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: GK2211).
References
- Duan, X. M., Han, J., Chen, L. G., Xu, Y. J. & Li, Y. (2005a). Fine Chem.22, 39–40.
- Duan, X. M., Han, J., Chen, L. G., Xu, Y. J. & Li, Y. (2005b). Fine Chem.22, 52.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Huang, P.-M., Duan, X.-M. & Yang, D.-W. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o1264–o1265.
- Rigaku/MSC (2005). CrystalClear Rigaku/MSC, The Woodlands, Texas, USA.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680901976X/gk2211sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680901976X/gk2211Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report