Abstract
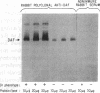
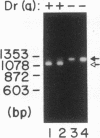
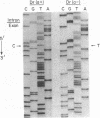
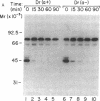
The Dra antigen belongs to the Cromer-related blood group system, a series of antigens on decay accelerating factor (DAF), a glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-anchored membrane protein that protects host cells from complement-mediated damage. We studied the rare inherited Dr(a-) phenotype to ascertain the associated biochemical and functional changes in DAF and to characterize the basis for this polymorphism. Radioimmunoassay assay and flow cytometric analysis of Dr(a-) erythrocytes demonstrated 40% of normal surface expression of DAF but normal levels of several other glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins, distinguishing this phenotype from that of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. Western blots confirmed this reduced DAF expression and indicated a slightly faster mobility of the molecule on SDS-PAGE. Despite the reduced DAF expression, Dr(a-) erythrocytes functioned normally in the complement lysis sensitivity assay. Utilization of the polymerase chain reaction to amplify mononuclear cell genomic DNA from three unrelated Dr(a-) individuals demonstrated that a point mutation underlies the Dr(a-) phenotype: a C to T change in nucleotide 649 resulting in a serine165 to leucine change. This defines the Drb allele of DAF, which can be distinguished from Dra by a Taq I restriction fragment length polymorphism. We created transfected Chinese hamster ovary cell lines expressing either the Dra or the Drb allelic form of DAF. These allele-specific transfectants were tested by inhibition of hemagglutination or flow cytometry and confirmed the specificity of anti-Dra alloantisera. The allele-specific transfectants could form the basis of a new serological approach to immunohematology.
Full text
PDF

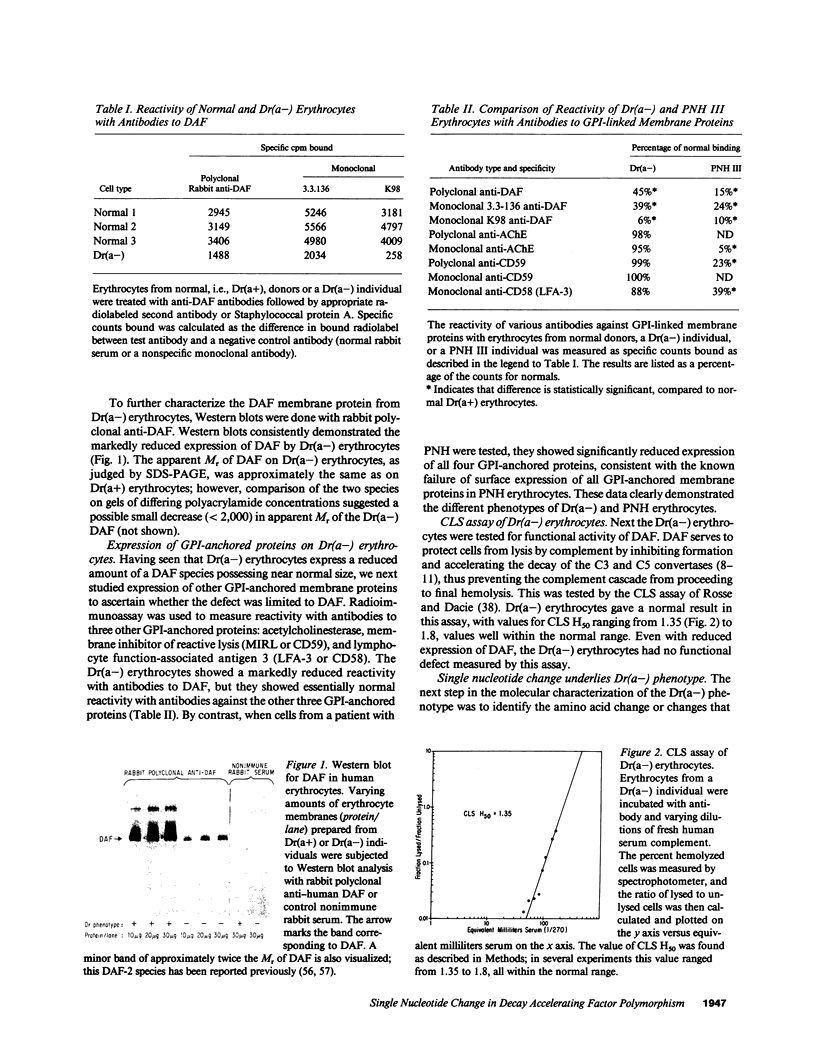
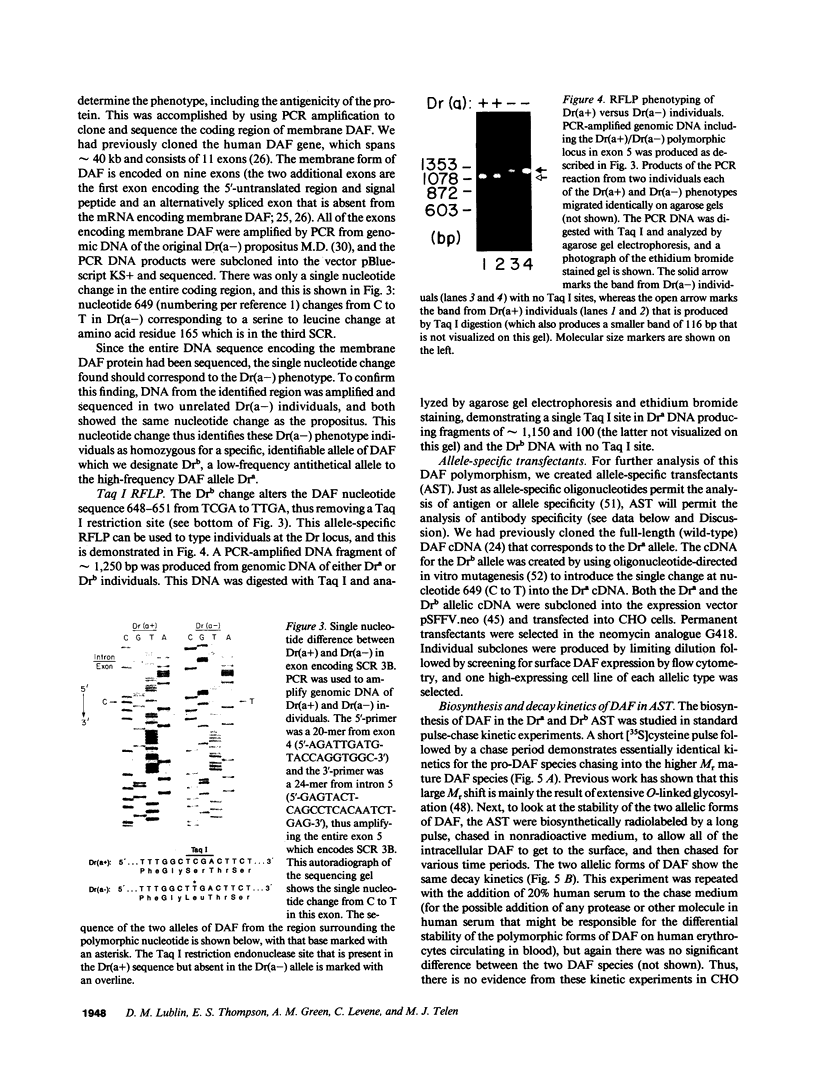
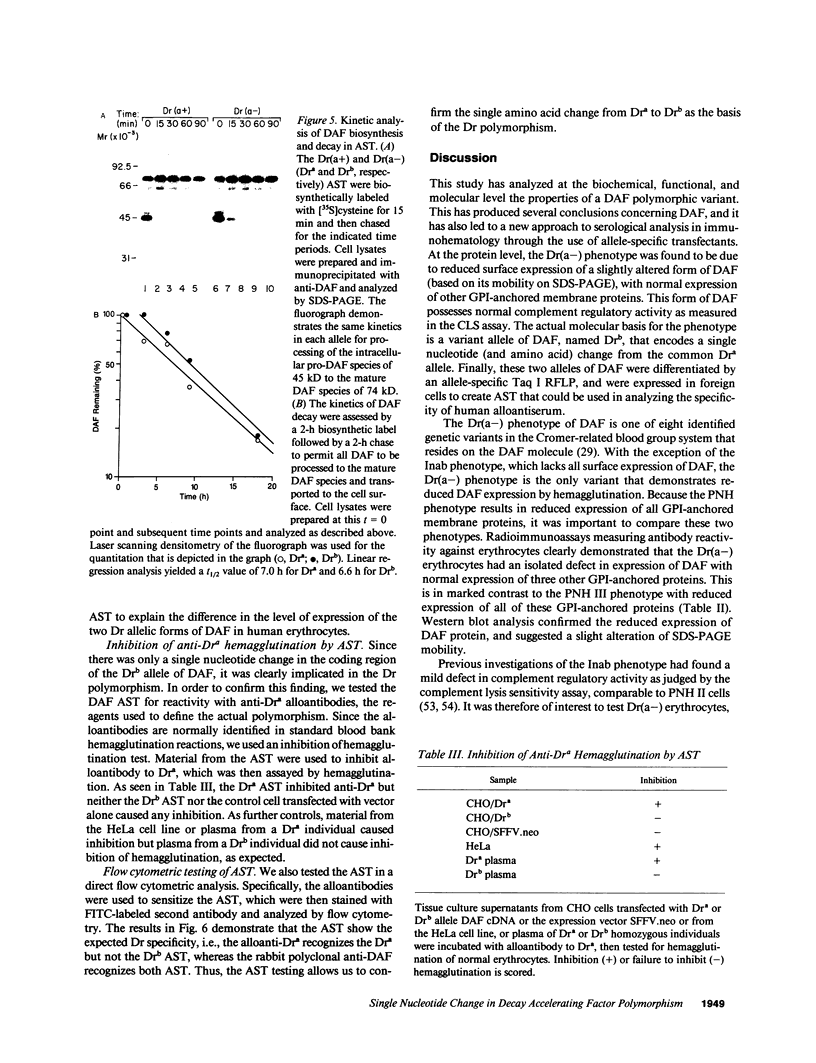
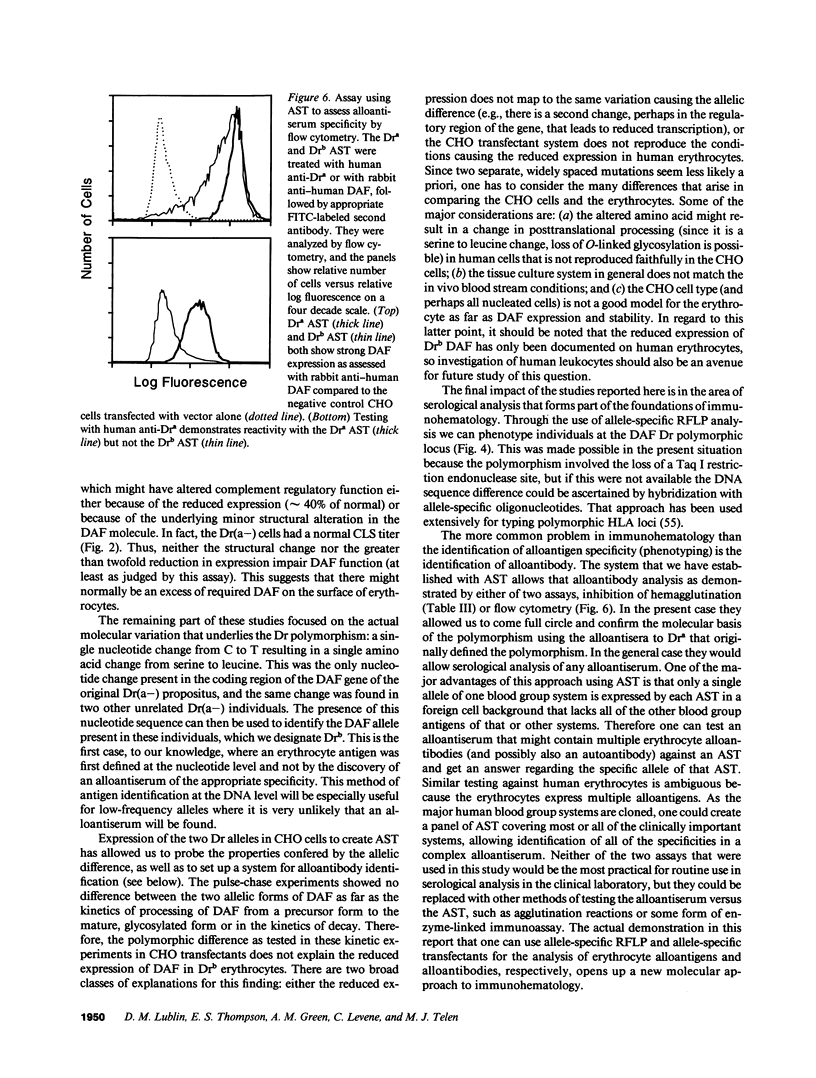


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asch A. S., Kinoshita T., Jaffe E. A., Nussenzweig V. Decay-accelerating factor is present on cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells. J Exp Med. 1986 Jan 1;163(1):221–226. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.1.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caras I. W., Davitz M. A., Rhee L., Weddell G., Martin D. W., Jr, Nussenzweig V. Cloning of decay-accelerating factor suggests novel use of splicing to generate two proteins. Nature. 1987 Feb 5;325(6104):545–549. doi: 10.1038/325545a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow F. L., Telen M. J., Rosse W. F. The acetylcholinesterase defect in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria: evidence that the enzyme is absent from the cell membrane. Blood. 1985 Oct;66(4):940–945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Glycolipid anchoring of plasma membrane proteins. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1990;6:1–39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.06.110190.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels G. Cromer-related antigens--blood group determinants on decay-accelerating factor. Vox Sang. 1989;56(4):205–211. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1989.tb02030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A., Simmons D. L., Hale G., Harrison R. A., Tighe H., Lachmann P. J., Waldmann H. CD59, an LY-6-like protein expressed in human lymphoid cells, regulates the action of the complement membrane attack complex on homologous cells. J Exp Med. 1989 Sep 1;170(3):637–654. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davitz M. A., Low M. G., Nussenzweig V. Release of decay-accelerating factor (DAF) from the cell membrane by phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PIPLC). Selective modification of a complement regulatory protein. J Exp Med. 1986 May 1;163(5):1150–1161. doi: 10.1084/jem.163.5.1150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fambrough D. M., Engel A. G., Rosenberry T. L. Acetylcholinesterase of human erythrocytes and neuromuscular junctions: homologies revealed by monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1078–1082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Felgner P. L., Gadek T. R., Holm M., Roman R., Chan H. W., Wenz M., Northrop J. P., Ringold G. M., Danielsen M. Lipofection: a highly efficient, lipid-mediated DNA-transfection procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7413–7417. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhlbrigge R. C., Fine S. M., Unanue E. R., Chaplin D. D. Expression of membrane interleukin 1 by fibroblasts transfected with murine pro-interleukin 1 alpha cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5649–5653. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Inoue T., Ogawa K., Iida K., Tamura N. The mechanism of action of decay-accelerating factor (DAF). DAF inhibits the assembly of C3 convertases by dissociating C2a and Bb. J Exp Med. 1987 Nov 1;166(5):1221–1228. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.5.1221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzberg K. M., Pindyck J., Mosesson M. W., Grieninger G. Thyroid hormone stimulation of plasma protein synthesis in cultured hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jan 25;256(2):563–566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holguin M. H., Wilcox L. A., Bernshaw N. J., Rosse W. F., Parker C. J. Erythrocyte membrane inhibitor of reactive lysis: effects of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C on the isolated and cell-associated protein. Blood. 1990 Jan 1;75(1):284–289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänsch G. M., Schönermark S., Roelcke D. Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria type III. Lack of an erythrocyte membrane protein restricting the lysis by C5b-9. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jul;80(1):7–12. doi: 10.1172/JCI113065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita T., Medof M. E., Silber R., Nussenzweig V. Distribution of decay-accelerating factor in the peripheral blood of normal individuals and patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):75–92. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.75. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinoshita T., Rosenfeld S. I., Nussenzweig V. A high m.w. form of decay-accelerating factor (DAF-2) exhibits size abnormalities in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria erythrocytes. J Immunol. 1987 May 1;138(9):2994–2998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene C., Harel N., Kende G., Papo S., Bradford M. F., Daniels G. L. A second Dr(a-) proposita with anti-Dra and a family with the Dr(a-) phenotype in two generations. Transfusion. 1987 Jan-Feb;27(1):64–65. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1987.27187121478.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levene C., Harel N., Lavie G., Greenberg S., Laird-Fryer B., Daniels G. L. A "new" phenotype confirming a relationship between Cra and Tca. Transfusion. 1984 Jan-Feb;24(1):13–15. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1984.24184122551.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin R. C., Herman J., Henry L., Daniels G. L. A family showing inheritance of the Inab phenotype. Transfusion. 1988 Sep-Oct;28(5):427–429. doi: 10.1046/j.1537-2995.1988.28588337329.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low M. G., Saltiel A. R. Structural and functional roles of glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol in membranes. Science. 1988 Jan 15;239(4837):268–275. doi: 10.1126/science.3276003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lublin D. M., Atkinson J. P. Decay-accelerating factor: biochemistry, molecular biology, and function. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:35–58. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.000343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lublin D. M., Krsek-Staples J., Pangburn M. K., Atkinson J. P. Biosynthesis and glycosylation of the human complement regulatory protein decay-accelerating factor. J Immunol. 1986 Sep 1;137(5):1629–1635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lublin D. M., Lemons R. S., Le Beau M. M., Holers V. M., Tykocinski M. L., Medof M. E., Atkinson J. P. The gene encoding decay-accelerating factor (DAF) is located in the complement-regulatory locus on the long arm of chromosome 1. J Exp Med. 1987 Jun 1;165(6):1731–1736. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.6.1731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medof M. E., Kinoshita T., Nussenzweig V. Inhibition of complement activation on the surface of cells after incorporation of decay-accelerating factor (DAF) into their membranes. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1558–1578. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medof M. E., Kinoshita T., Silber R., Nussenzweig V. Amelioration of lytic abnormalities of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria with decay-accelerating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2980–2984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medof M. E., Lublin D. M., Holers V. M., Ayers D. J., Getty R. R., Leykam J. F., Atkinson J. P., Tykocinski M. L. Cloning and characterization of cDNAs encoding the complete sequence of decay-accelerating factor of human complement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):2007–2011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.2007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medof M. E., Walter E. I., Roberts W. L., Haas R., Rosenberry T. L. Decay accelerating factor of complement is anchored to cells by a C-terminal glycolipid. Biochemistry. 1986 Nov 4;25(22):6740–6747. doi: 10.1021/bi00370a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medof M. E., Walter E. I., Rutgers J. L., Knowles D. M., Nussenzweig V. Identification of the complement decay-accelerating factor (DAF) on epithelium and glandular cells and in body fluids. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):848–864. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merry A. H., Rawlinson V. I., Uchikawa M., Daha M. R., Sim R. B. Studies on the sensitivity to complement-mediated lysis of erythrocytes (Inab phenotype) with a deficiency of DAF (decay accelerating factor). Br J Haematol. 1989 Oct;73(2):248–253. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb00260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson-Weller A., Burge J., Fearon D. T., Weller P. F., Austen K. F. Isolation of a human erythrocyte membrane glycoprotein with decay-accelerating activity for C3 convertases of the complement system. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):184–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson-Weller A., March J. P., Rosen C. E., Spicer D. B., Austen K. F. Surface membrane expression by human blood leukocytes and platelets of decay-accelerating factor, a regulatory protein of the complement system. Blood. 1985 May;65(5):1237–1244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson-Weller A., March J. P., Rosenfeld S. I., Austen K. F. Affected erythrocytes of patients with paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria are deficient in the complement regulatory protein, decay accelerating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):5066–5070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.5066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post T. W., Arce M. A., Liszewski M. K., Thompson E. S., Atkinson J. P., Lublin D. M. Structure of the gene for human complement protein decay accelerating factor. J Immunol. 1990 Jan 15;144(2):740–744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rey-Campos J., Rubinstein P., Rodriguez de Cordoba S. Decay-accelerating factor. Genetic polymorphism and linkage to the RCA (regulator of complement activation) gene cluster in humans. J Exp Med. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):246–252. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.1.246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosse W. F., Dacie J. V. Immune lysis of normal human and paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria (PNH) red blood cells. I. The sensitivity of PNH red cells to lysis by complement and specific antibody. J Clin Invest. 1966 May;45(5):736–748. doi: 10.1172/JCI105388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosse W. F., Parker C. J. Paroxysmal nocturnal haemoglobinuria. Clin Haematol. 1985 Feb;14(1):105–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Bugawan T. L., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Analysis of enzymatically amplified beta-globin and HLA-DQ alpha DNA with allele-specific oligonucleotide probes. Nature. 1986 Nov 13;324(6093):163–166. doi: 10.1038/324163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Madrid F., Krensky A. M., Ware C. F., Robbins E., Strominger J. L., Burakoff S. J., Springer T. A. Three distinct antigens associated with human T-lymphocyte-mediated cytolysis: LFA-1, LFA-2, and LFA-3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7489–7493. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7489. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scharf S. J., Friedmann A., Brautbar C., Szafer F., Steinman L., Horn G., Gyllensten U., Erlich H. A. HLA class II allelic variation and susceptibility to pemphigus vulgaris. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3504–3508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seya T., Farries T., Nickells M., Atkinson J. P. Additional forms of human decay-accelerating factor (DAF). J Immunol. 1987 Aug 15;139(4):1260–1267. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spring F. A., Judson P. A., Daniels G. L., Parsons S. F., Mallinson G., Anstee D. J. A human cell-surface glycoprotein that carries Cromer-related blood group antigens on erythrocytes and is also expressed on leucocytes and platelets. Immunology. 1987 Oct;62(2):307–313. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stafford H. A., Tykocinski M. L., Lublin D. M., Holers V. M., Rosse W. F., Atkinson J. P., Medof M. E. Normal polymorphic variations and transcription of the decay accelerating factor gene in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):880–884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita Y., Negoro T., Matsuda T., Sakamoto T., Tomita M. Improved method for the isolation and preliminary characterization of human DAF (decay-accelerating factor). J Biochem. 1986 Jul;100(1):143–150. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita Y., Tobe T., Oda E., Tomita M., Yasukawa K., Yamaji N., Takemoto T., Furuichi K., Takayama M., Yano S. Molecular cloning and characterization of MACIF, an inhibitor of membrane channel formation of complement. J Biochem. 1989 Oct;106(4):555–557. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. DNA sequence analysis with a modified bacteriophage T7 DNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jul;84(14):4767–4771. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.14.4767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telen M. J., Eisenbarth G. S., Haynes B. F. Human erythrocyte antigens. Regulation of expression of a novel erythrocyte surface antigen by the inhibitor Lutheran In(Lu) gene. J Clin Invest. 1983 Jun;71(6):1878–1886. doi: 10.1172/JCI110943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telen M. J., Green A. M. The Inab phenotype: characterization of the membrane protein and complement regulatory defect. Blood. 1989 Jul;74(1):437–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telen M. J., Hall S. E., Green A. M., Moulds J. J., Rosse W. F. Identification of human erythrocyte blood group antigens on decay-accelerating factor (DAF) and an erythrocyte phenotype negative for DAF. J Exp Med. 1988 Jun 1;167(6):1993–1998. doi: 10.1084/jem.167.6.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Telen M. J., Scearce R. M., Haynes B. F. Human erythrocyte antigens. III. Characterization of a panel of murine monoclonal antibodies that react with human erythrocyte and erythroid precursor membranes. Vox Sang. 1987;52(3):236–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1423-0410.1987.tb03035.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalman L. S., Wood L. M., Frank M. M., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Deficiency of the homologous restriction factor in paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. J Exp Med. 1987 Feb 1;165(2):572–577. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.2.572. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]