Abstract
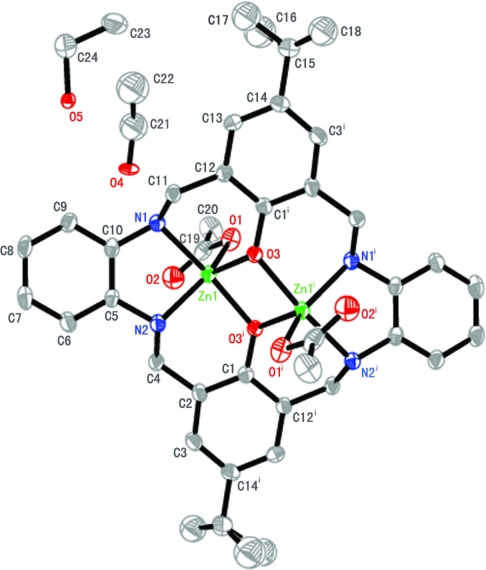
In the title compound, [Zn2(C36H42N4O2)(CH3COO)2]·2CH3CH2OH, a centrosymmetric dinuclear zinc macrocyclic complex is accompanied by two half-occupied ethanol solvent molecues resulting in a 1:2 macrocycle–solvent composition. The ZnII atom has a square-pyramidal geometry arising from an N2O3 donor set, being coordinated by two N atoms and two O atoms from the macrocyclic ligand in the equatorial sites and one O atom from an acetate anion in the apical site. The two ZnII atoms are linked by two phenolate O atoms, generating a four-membered Zn2O2 ring at the centre of the macrocycle. The tert-butyl group shows rotational disorder over two sets of sites in a 0.552 (12):0.448 (12) ratio. In the crystal, N—H⋯O and O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds are seen and a short intramolecular C—H⋯O contact occurs.
Related literature
For background to the biochemistry of zinc compounds, see: Lipscomb & Straeter (1996 ▶); Burley et al. (1990 ▶); Roderick & Mathews (1993 ▶); Bazzicalupi et al. (1997 ▶). For related structures, see: Dutta et al. (2005 ▶); Liu et al. (2007 ▶). For further synthetic details, see: Tian et al. (1999 ▶).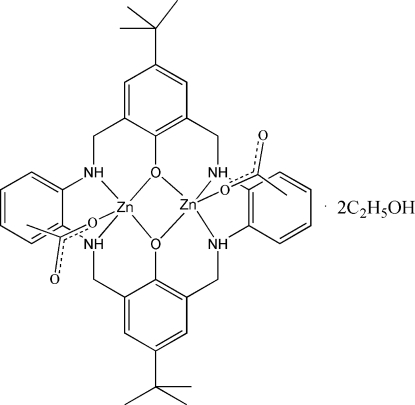
Experimental
Crystal data
[Zn2(C36H42N4O2)(C2H3O2)2]·2C2H6O
M r = 903.70
Triclinic,
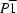
a = 9.0566 (3) Å
b = 10.8410 (5) Å
c = 14.2828 (5) Å
α = 71.246 (4)°
β = 86.514 (3)°
γ = 78.362 (3)°
V = 1300.56 (9) Å3
Z = 1
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.97 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.45 × 0.25 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Oxford Diffraction Gemini R Ultra diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction, 2006 ▶) T min = 0.748, T max = 0.824
11846 measured reflections
6368 independent reflections
4133 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.035
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.077
wR(F 2) = 0.253
S = 1.05
6368 reflections
285 parameters
655 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 1.15 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.77 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis CCD (Oxford Diffraction, 2006 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis RED (Oxford Diffraction, 2006 ▶); data reduction: CrysAlis RED; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809021990/hb2961sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809021990/hb2961Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Selected bond lengths (Å).
| Zn1—O1 | 2.025 (5) |
| Zn1—O3 | 2.033 (4) |
| Zn1—O3i | 2.043 (4) |
| Zn1—N2 | 2.100 (5) |
| Zn1—N1 | 2.104 (5) |
Symmetry code: (i) 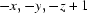 .
.
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C4—H4A⋯O2 | 0.97 | 2.45 | 3.246 (10) | 139 |
| N1—H1N⋯O4 | 0.86 (7) | 2.23 (7) | 2.952 (9) | 141 (6) |
| N2—H2N⋯O5ii | 0.87 (4) | 2.13 (4) | 2.999 (9) | 175 (4) |
| O4—H4⋯O2iii | 0.82 | 2.06 | 2.768 (10) | 145 |
| O5—H5⋯O1iv | 0.82 | 1.92 | 2.700 (9) | 159 |
Symmetry codes: (ii) 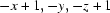 ; (iii)
; (iii) 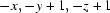 ; (iv)
; (iv) 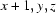 .
.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 20471014), the Program for New Century Excellent Talents in Chinese Universities (NCET-05–0320), the Fok Ying Tung Education Foundation and the Analysis and Testing Foundation of Northeast Normal University for support.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Zinc is an essential element for all forms of life and plays a critical role in various functions, both structural and catalytic, in proteins and enzymes (Lipscomb et al.,1996; Burley et al.,1990; Roderick & Mathews, 1993). In addition, some synthetic dinuclear zinc(II) compounds appears to have functions in dephosphorylation (Bazzicalupi et al.,1997). As part of out studies in this area, the title compound, (I), a new dinuclear zinc(II) compound has been synthesized, and its structure is reported here (Fig. 1).
The complete macrocycle is generated by a crystallographic inversion centre The coordination environment around zinc is a square-pyramid with two N atoms and two O atoms from the macrocyclic (C36H44N4O2) ligand occupying the basal positions and one O atom from a acetate anion occupying the apical position. The two zinc atoms are bridged by two phenolate O atoms to generate a four-membered Zn2O2 ring. The Zn—O and Zn—N distances are normal (Dutta et al., 2005).
Experimental
To a stirred methanol (30 ml) suspension of the schiff base C36H40N4O2 (0.5 mmol), which was synthesized by the methods reported previously (Tian et al., 1999), was added solid NaBH4 (0.5 g, 13 mmol) in small portions. Over a period of 0.5 h when the red solid material gradually went into solution, and eventually an amorphous yellow mass precipitated. After 1 h, the formed yellow powder products (H2L) were filtrated off and washed thoroughly with water and ethanol, and dried in avacuum (yield 54%).
The title compound was prepared by reaction between the ligand (H2L) and zinc acetate. A mixture of H2L (0.108 g, 0.2 mmol) and Zn(OAc)2.6H2O (0.117 g, 0.4 mmol) in ethanol (20 ml) was heated with stirring to yield a clear pale yellow solution. Filtration and cooling to room temperature resulted in formation of a crystalline precipitate. Recrystallization by slow evaporation of an ethanol solution of the compound resulted in well-formed yellow blocks of (I) (yield 46%).
Refinement
The N-bonded H atoms were located in a difference map and their positions were freely refined. The other H atoms were placed in calculated positions (O—H = 0.82Å, C—H = 0.93–0.96Å) and refined as riding with Uiso(H) =1.2Ueq(C,N) or 1.5Ueq(methyl C). The methyl entities of the tert-butyl group are disordered over two sets of sites in a 0.552 (12):0.448 (12) ratio. The highest difference peak is 1.55 Å from O5 and the deepest difference hole is 0.77 Å from C17'. The anisotropic displacement factors of the disordered atoms were restrained to be nearly isotropic. Additionally, the solvent of ethanol molecule is disordered in two positions (the occupancies were fixed as 0.5:0.5).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I). Displaceement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level and H atoms have been omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| [Zn2(C36H42N4O2)(C2H3O2)2]·2C2H6O | Z = 1 |
| Mr = 903.70 | F(000) = 476 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.154 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 9.0566 (3) Å | Cell parameters from 2131 reflections |
| b = 10.8410 (5) Å | θ = 3.1–26.5° |
| c = 14.2828 (5) Å | µ = 0.97 mm−1 |
| α = 71.246 (4)° | T = 293 K |
| β = 86.514 (3)° | Block, yellow |
| γ = 78.362 (3)° | 0.45 × 0.25 × 0.20 mm |
| V = 1300.56 (9) Å3 |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Gemini R Ultra diffractometer | 6368 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 4133 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.035 |
| Detector resolution: 10.0 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 29.8°, θmin = 4.4° |
| ω scans | h = −11→12 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction, 2006) | k = −14→14 |
| Tmin = 0.748, Tmax = 0.824 | l = −18→19 |
| 11846 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.077 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.253 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.05 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.1644P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 6368 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 285 parameters | Δρmax = 1.15 e Å−3 |
| 655 restraints | Δρmin = −0.77 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| Zn1 | 0.05562 (7) | 0.12433 (7) | 0.50054 (5) | 0.0340 (3) | |
| C1 | −0.1270 (7) | −0.0328 (6) | 0.6667 (4) | 0.0348 (12) | |
| C2 | −0.0490 (7) | −0.0070 (7) | 0.7384 (5) | 0.0393 (13) | |
| C3 | −0.0831 (8) | −0.0639 (8) | 0.8383 (5) | 0.0466 (15) | |
| H3 | −0.0290 | −0.0493 | 0.8858 | 0.056* | |
| C4 | 0.0649 (7) | 0.0818 (7) | 0.7131 (5) | 0.0414 (13) | |
| H4A | 0.0126 | 0.1736 | 0.6901 | 0.050* | |
| H4B | 0.1207 | 0.0693 | 0.7724 | 0.050* | |
| C5 | 0.3043 (7) | 0.1208 (6) | 0.6217 (5) | 0.0378 (12) | |
| C6 | 0.3920 (8) | 0.1117 (7) | 0.7007 (6) | 0.0465 (14) | |
| H6 | 0.3657 | 0.0661 | 0.7646 | 0.056* | |
| C7 | 0.5162 (8) | 0.1685 (8) | 0.6863 (6) | 0.0509 (15) | |
| H7 | 0.5743 | 0.1609 | 0.7401 | 0.061* | |
| C8 | 0.5554 (8) | 0.2371 (8) | 0.5923 (6) | 0.0489 (15) | |
| H8 | 0.6404 | 0.2755 | 0.5821 | 0.059* | |
| C9 | 0.4671 (7) | 0.2484 (7) | 0.5129 (6) | 0.0454 (14) | |
| H9 | 0.4931 | 0.2953 | 0.4493 | 0.055* | |
| C10 | 0.3420 (7) | 0.1915 (6) | 0.5269 (5) | 0.0375 (12) | |
| C11 | 0.3368 (7) | 0.1223 (7) | 0.3804 (5) | 0.0397 (13) | |
| H11A | 0.3798 | 0.0336 | 0.4223 | 0.048* | |
| H11B | 0.4192 | 0.1649 | 0.3484 | 0.048* | |
| C12 | 0.2376 (7) | 0.1125 (7) | 0.3023 (5) | 0.0397 (13) | |
| C13 | 0.2679 (8) | 0.1641 (8) | 0.2016 (5) | 0.0513 (15) | |
| H13 | 0.3412 | 0.2163 | 0.1820 | 0.062* | |
| C14 | 0.1915 (9) | 0.1397 (8) | 0.1302 (5) | 0.0530 (16) | |
| C15 | 0.2210 (10) | 0.2038 (10) | 0.0195 (6) | 0.070 (2) | |
| C16 | 0.0903 (18) | 0.274 (2) | −0.0392 (19) | 0.106 (6)* | 0.448 (12) |
| H16A | 0.0088 | 0.2276 | −0.0169 | 0.159* | 0.448 (12) |
| H16B | 0.1117 | 0.2812 | −0.1072 | 0.159* | 0.448 (12) |
| H16C | 0.0625 | 0.3617 | −0.0331 | 0.159* | 0.448 (12) |
| C17 | 0.3466 (18) | 0.269 (2) | −0.0069 (17) | 0.078 (5)* | 0.448 (12) |
| H17A | 0.4286 | 0.2207 | 0.0380 | 0.117* | 0.448 (12) |
| H17B | 0.3183 | 0.3576 | −0.0035 | 0.117* | 0.448 (12) |
| H17C | 0.3774 | 0.2721 | −0.0730 | 0.117* | 0.448 (12) |
| C18 | 0.276 (3) | 0.084 (2) | −0.022 (2) | 0.101 (6)* | 0.448 (12) |
| H18A | 0.3649 | 0.0287 | 0.0136 | 0.151* | 0.448 (12) |
| H18B | 0.2996 | 0.1178 | −0.0908 | 0.151* | 0.448 (12) |
| H18C | 0.1983 | 0.0336 | −0.0136 | 0.151* | 0.448 (12) |
| C16' | 0.146 (3) | 0.3448 (14) | −0.0045 (17) | 0.106 (5)* | 0.552 (12) |
| H16D | 0.0426 | 0.3503 | 0.0157 | 0.158* | 0.552 (12) |
| H16E | 0.1510 | 0.3878 | −0.0745 | 0.158* | 0.552 (12) |
| H16F | 0.1963 | 0.3879 | 0.0297 | 0.158* | 0.552 (12) |
| C17' | 0.373 (3) | 0.163 (3) | 0.0001 (18) | 0.106 (5)* | 0.552 (12) |
| H17D | 0.3988 | 0.0676 | 0.0228 | 0.160* | 0.552 (12) |
| H17E | 0.4347 | 0.1978 | 0.0340 | 0.160* | 0.552 (12) |
| H17F | 0.3908 | 0.1950 | −0.0697 | 0.160* | 0.552 (12) |
| C18' | 0.154 (2) | 0.1537 (17) | −0.0493 (15) | 0.083 (4)* | 0.552 (12) |
| H18D | 0.0463 | 0.1770 | −0.0471 | 0.124* | 0.552 (12) |
| H18E | 0.1845 | 0.0589 | −0.0303 | 0.124* | 0.552 (12) |
| H18F | 0.1882 | 0.1926 | −0.1152 | 0.124* | 0.552 (12) |
| C19 | −0.1180 (8) | 0.3676 (7) | 0.4525 (7) | 0.0524 (18) | |
| C20 | −0.2183 (11) | 0.4959 (9) | 0.3983 (7) | 0.074 (3) | |
| H20A | −0.2489 | 0.4915 | 0.3365 | 0.110* | |
| H20B | −0.1644 | 0.5672 | 0.3861 | 0.110* | |
| H20C | −0.3057 | 0.5112 | 0.4376 | 0.110* | |
| C21 | 0.192 (3) | 0.573 (3) | 0.260 (2) | 0.107 (7)* | 0.50 |
| H21A | 0.2097 | 0.6567 | 0.2627 | 0.129* | 0.50 |
| H21B | 0.0950 | 0.5895 | 0.2286 | 0.129* | 0.50 |
| C22 | 0.308 (3) | 0.525 (3) | 0.197 (2) | 0.117 (7)* | 0.50 |
| H22A | 0.3097 | 0.5925 | 0.1341 | 0.176* | 0.50 |
| H22B | 0.2863 | 0.4467 | 0.1867 | 0.176* | 0.50 |
| H22C | 0.4052 | 0.5031 | 0.2281 | 0.176* | 0.50 |
| C23 | 0.690 (2) | 0.287 (2) | 0.1224 (14) | 0.081 (5) | 0.50 |
| H23A | 0.7180 | 0.3421 | 0.0591 | 0.121* | 0.50 |
| H23B | 0.5824 | 0.3020 | 0.1279 | 0.121* | 0.50 |
| H23C | 0.7284 | 0.1956 | 0.1289 | 0.121* | 0.50 |
| C24 | 0.7513 (19) | 0.3194 (16) | 0.1974 (12) | 0.058 (4) | 0.50 |
| H24A | 0.7141 | 0.4124 | 0.1901 | 0.070* | 0.50 |
| H24B | 0.8602 | 0.3056 | 0.1912 | 0.070* | 0.50 |
| O1 | −0.0909 (5) | 0.2773 (5) | 0.4110 (4) | 0.0537 (13) | |
| O2 | −0.0635 (7) | 0.3485 (6) | 0.5334 (5) | 0.0669 (15) | |
| O3 | −0.1018 (5) | 0.0163 (4) | 0.5695 (3) | 0.0338 (9) | |
| O4 | 0.1846 (10) | 0.4916 (7) | 0.3531 (5) | 0.0344 (18) | 0.50 |
| H4 | 0.1170 | 0.5264 | 0.3826 | 0.052* | 0.50 |
| O5 | 0.7114 (8) | 0.2386 (7) | 0.2940 (5) | 0.0252 (15) | 0.50 |
| H5 | 0.7511 | 0.2567 | 0.3367 | 0.038* | 0.50 |
| H2N | 0.205 (8) | −0.030 (3) | 0.652 (5) | 0.050 (6)* | |
| H1N | 0.225 (12) | 0.271 (6) | 0.394 (5) | 0.095 (4)* | |
| N2 | 0.1736 (6) | 0.0556 (5) | 0.6353 (4) | 0.0366 (11) | |
| N1 | 0.2504 (6) | 0.2002 (5) | 0.4438 (4) | 0.0342 (11) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Zn1 | 0.0304 (4) | 0.0382 (4) | 0.0374 (5) | −0.0082 (3) | 0.0014 (3) | −0.0165 (3) |
| C1 | 0.031 (3) | 0.042 (3) | 0.036 (3) | −0.006 (2) | 0.003 (2) | −0.019 (2) |
| C2 | 0.035 (3) | 0.049 (3) | 0.041 (3) | −0.009 (2) | 0.001 (2) | −0.024 (3) |
| C3 | 0.043 (3) | 0.065 (4) | 0.038 (3) | −0.013 (3) | 0.000 (3) | −0.022 (3) |
| C4 | 0.040 (3) | 0.052 (3) | 0.040 (3) | −0.015 (2) | 0.003 (2) | −0.022 (2) |
| C5 | 0.029 (2) | 0.044 (3) | 0.047 (3) | −0.009 (2) | −0.001 (2) | −0.023 (2) |
| C6 | 0.040 (3) | 0.058 (3) | 0.049 (3) | −0.012 (3) | −0.002 (3) | −0.026 (3) |
| C7 | 0.038 (3) | 0.063 (4) | 0.061 (4) | −0.011 (3) | −0.009 (3) | −0.030 (3) |
| C8 | 0.032 (3) | 0.061 (4) | 0.060 (4) | −0.016 (3) | −0.005 (3) | −0.024 (3) |
| C9 | 0.036 (3) | 0.054 (3) | 0.053 (3) | −0.015 (3) | 0.003 (3) | −0.023 (3) |
| C10 | 0.030 (2) | 0.041 (3) | 0.048 (3) | −0.008 (2) | 0.000 (2) | −0.023 (2) |
| C11 | 0.032 (3) | 0.052 (3) | 0.044 (3) | −0.014 (2) | 0.006 (2) | −0.024 (2) |
| C12 | 0.035 (3) | 0.051 (3) | 0.040 (3) | −0.015 (2) | 0.007 (2) | −0.022 (3) |
| C13 | 0.048 (3) | 0.067 (4) | 0.046 (3) | −0.025 (3) | 0.010 (3) | −0.021 (3) |
| C14 | 0.055 (3) | 0.069 (4) | 0.042 (3) | −0.021 (3) | 0.009 (3) | −0.024 (3) |
| C15 | 0.071 (4) | 0.095 (5) | 0.050 (4) | −0.035 (4) | 0.011 (3) | −0.021 (4) |
| C19 | 0.035 (4) | 0.041 (4) | 0.077 (5) | −0.008 (3) | 0.003 (4) | −0.014 (4) |
| C20 | 0.077 (6) | 0.055 (5) | 0.083 (6) | 0.014 (4) | −0.017 (5) | −0.027 (5) |
| C23 | 0.067 (10) | 0.097 (12) | 0.058 (9) | −0.011 (9) | 0.004 (8) | 0.000 (9) |
| C24 | 0.060 (9) | 0.051 (8) | 0.062 (9) | −0.008 (7) | −0.013 (7) | −0.016 (7) |
| O1 | 0.042 (3) | 0.040 (3) | 0.078 (4) | −0.001 (2) | −0.005 (2) | −0.021 (2) |
| O2 | 0.067 (4) | 0.057 (3) | 0.069 (4) | −0.002 (3) | −0.012 (3) | −0.014 (3) |
| O3 | 0.033 (2) | 0.039 (2) | 0.033 (2) | −0.0101 (17) | 0.0037 (17) | −0.0157 (18) |
| O4 | 0.056 (5) | 0.015 (3) | 0.024 (4) | −0.001 (3) | 0.009 (4) | 0.000 (3) |
| O5 | 0.026 (4) | 0.024 (4) | 0.027 (4) | −0.008 (3) | −0.004 (3) | −0.008 (3) |
| N2 | 0.034 (3) | 0.042 (3) | 0.040 (3) | −0.010 (2) | 0.000 (2) | −0.019 (2) |
| N1 | 0.032 (3) | 0.037 (3) | 0.037 (3) | −0.005 (2) | 0.000 (2) | −0.017 (2) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Zn1—O1 | 2.025 (5) | C16—H16A | 0.9600 |
| Zn1—O3 | 2.033 (4) | C16—H16B | 0.9600 |
| Zn1—O3i | 2.043 (4) | C16—H16C | 0.9600 |
| Zn1—N2 | 2.100 (5) | C17—H17A | 0.9600 |
| Zn1—N1 | 2.104 (5) | C17—H17B | 0.9600 |
| Zn1—Zn1i | 3.0670 (13) | C17—H17C | 0.9600 |
| C1—O3 | 1.341 (7) | C18—H18A | 0.9600 |
| C1—C2 | 1.407 (8) | C18—H18B | 0.9600 |
| C1—C12i | 1.412 (9) | C18—H18C | 0.9600 |
| C2—C3 | 1.403 (9) | C16'—H16D | 0.9600 |
| C2—C4 | 1.501 (9) | C16'—H16E | 0.9600 |
| C3—C14i | 1.370 (10) | C16'—H16F | 0.9600 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C17'—H17D | 0.9600 |
| C4—N2 | 1.496 (8) | C17'—H17E | 0.9600 |
| C4—H4A | 0.9700 | C17'—H17F | 0.9600 |
| C4—H4B | 0.9700 | C18'—H18D | 0.9600 |
| C5—C6 | 1.385 (9) | C18'—H18E | 0.9600 |
| C5—C10 | 1.386 (9) | C18'—H18F | 0.9600 |
| C5—N2 | 1.470 (8) | C19—O2 | 1.223 (10) |
| C6—C7 | 1.363 (10) | C19—O1 | 1.276 (9) |
| C6—H6 | 0.9300 | C19—C20 | 1.497 (11) |
| C7—C8 | 1.374 (11) | C20—H20A | 0.9600 |
| C7—H7 | 0.9300 | C20—H20B | 0.9600 |
| C8—C9 | 1.386 (10) | C20—H20C | 0.9600 |
| C8—H8 | 0.9300 | C21—O4 | 1.34 (3) |
| C9—C10 | 1.371 (9) | C21—C22 | 1.47 (3) |
| C9—H9 | 0.9300 | C21—H21A | 0.9700 |
| C10—N1 | 1.456 (8) | C21—H21B | 0.9700 |
| C11—N1 | 1.511 (7) | C22—H22A | 0.9600 |
| C11—C12 | 1.517 (9) | C22—H22B | 0.9600 |
| C11—H11A | 0.9700 | C22—H22C | 0.9600 |
| C11—H11B | 0.9700 | C23—C24 | 1.40 (2) |
| C12—C13 | 1.398 (10) | C23—H23A | 0.9600 |
| C12—C1i | 1.412 (9) | C23—H23B | 0.9600 |
| C13—C14 | 1.387 (10) | C23—H23C | 0.9600 |
| C13—H13 | 0.9300 | C24—O5 | 1.446 (18) |
| C14—C3i | 1.370 (10) | C24—H24A | 0.9700 |
| C14—C15 | 1.540 (11) | C24—H24B | 0.9700 |
| C15—C17' | 1.40 (2) | O3—Zn1i | 2.043 (4) |
| C15—C16 | 1.426 (11) | O4—H4 | 0.8200 |
| C15—C17 | 1.426 (11) | O5—H5 | 0.8200 |
| C15—C18' | 1.475 (17) | N2—H2N | 0.87 (3) |
| C15—C16' | 1.479 (11) | N1—H1N | 0.86 (3) |
| C15—C18 | 1.57 (2) | ||
| O1—Zn1—O3 | 96.05 (19) | H16A—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
| O1—Zn1—O3i | 105.62 (19) | C15—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| O3—Zn1—O3i | 82.40 (17) | H16A—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| O1—Zn1—N2 | 144.5 (2) | H16B—C16—H16C | 109.5 |
| O3—Zn1—N2 | 88.07 (18) | C15—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| O3i—Zn1—N2 | 109.82 (19) | C15—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| O1—Zn1—N1 | 95.6 (2) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| O3—Zn1—N1 | 168.18 (18) | C15—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| O3i—Zn1—N1 | 92.33 (17) | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| N2—Zn1—N1 | 83.8 (2) | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| O1—Zn1—Zn1i | 104.44 (14) | C15—C18—H18A | 109.5 |
| O3—Zn1—Zn1i | 41.32 (11) | C15—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| O3i—Zn1—Zn1i | 41.08 (11) | H18A—C18—H18B | 109.5 |
| N2—Zn1—Zn1i | 101.75 (15) | C15—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| N1—Zn1—Zn1i | 132.53 (13) | H18A—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| O3—C1—C2 | 122.6 (6) | H18B—C18—H18C | 109.5 |
| O3—C1—C12i | 118.4 (5) | C15—C16'—H16D | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—C12i | 119.0 (6) | C15—C16'—H16E | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 118.2 (6) | H16D—C16'—H16E | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C4 | 118.5 (6) | C15—C16'—H16F | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—C4 | 123.2 (6) | H16D—C16'—H16F | 109.5 |
| C14i—C3—C2 | 123.6 (6) | H16E—C16'—H16F | 109.5 |
| C14i—C3—H3 | 118.2 | C15—C17'—H17D | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 118.2 | C15—C17'—H17E | 109.5 |
| N2—C4—C2 | 112.9 (5) | H17D—C17'—H17E | 109.5 |
| N2—C4—H4A | 109.0 | C15—C17'—H17F | 109.5 |
| C2—C4—H4A | 109.0 | H17D—C17'—H17F | 109.5 |
| N2—C4—H4B | 109.0 | H17E—C17'—H17F | 109.5 |
| C2—C4—H4B | 109.0 | C15—C18'—H18D | 109.5 |
| H4A—C4—H4B | 107.8 | C15—C18'—H18E | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C10 | 119.2 (6) | H18D—C18'—H18E | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—N2 | 121.9 (6) | C15—C18'—H18F | 109.5 |
| C10—C5—N2 | 118.9 (5) | H18D—C18'—H18F | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 121.1 (7) | H18E—C18'—H18F | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—H6 | 119.5 | O2—C19—O1 | 120.5 (7) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.5 | O2—C19—C20 | 122.1 (7) |
| C6—C7—C8 | 119.9 (7) | O1—C19—C20 | 117.4 (8) |
| C6—C7—H7 | 120.0 | C19—C20—H20A | 109.5 |
| C8—C7—H7 | 120.0 | C19—C20—H20B | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 119.4 (6) | H20A—C20—H20B | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 120.3 | C19—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 120.3 | H20A—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—C8 | 121.0 (7) | H20B—C20—H20C | 109.5 |
| C10—C9—H9 | 119.5 | O4—C21—C22 | 116 (2) |
| C8—C9—H9 | 119.5 | O4—C21—H21A | 108.2 |
| C9—C10—C5 | 119.4 (6) | C22—C21—H21A | 108.2 |
| C9—C10—N1 | 121.4 (6) | O4—C21—H21B | 108.2 |
| C5—C10—N1 | 119.2 (5) | C22—C21—H21B | 108.2 |
| N1—C11—C12 | 112.1 (5) | H21A—C21—H21B | 107.4 |
| N1—C11—H11A | 109.2 | C21—C22—H22A | 109.5 |
| C12—C11—H11A | 109.2 | C21—C22—H22B | 109.5 |
| N1—C11—H11B | 109.2 | H22A—C22—H22B | 109.5 |
| C12—C11—H11B | 109.2 | C21—C22—H22C | 109.5 |
| H11A—C11—H11B | 107.9 | H22A—C22—H22C | 109.5 |
| C13—C12—C1i | 119.9 (6) | H22B—C22—H22C | 109.5 |
| C13—C12—C11 | 121.2 (6) | C24—C23—H23A | 109.5 |
| C1i—C12—C11 | 118.3 (6) | C24—C23—H23B | 109.5 |
| C14—C13—C12 | 121.6 (7) | H23A—C23—H23B | 109.5 |
| C14—C13—H13 | 119.2 | C24—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| C12—C13—H13 | 119.2 | H23A—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| C3i—C14—C13 | 117.6 (7) | H23B—C23—H23C | 109.5 |
| C3i—C14—C15 | 121.7 (7) | C23—C24—O5 | 111.0 (14) |
| C13—C14—C15 | 120.6 (7) | C23—C24—H24A | 109.4 |
| C17'—C15—C16 | 135.3 (16) | O5—C24—H24A | 109.4 |
| C17'—C15—C17 | 45.7 (11) | C23—C24—H24B | 109.4 |
| C16—C15—C17 | 113.1 (11) | O5—C24—H24B | 109.4 |
| C17'—C15—C18' | 98.4 (13) | H24A—C24—H24B | 108.0 |
| C16—C15—C18' | 56.2 (11) | C19—O1—Zn1 | 106.4 (5) |
| C17—C15—C18' | 122.3 (14) | C1—O3—Zn1 | 128.5 (4) |
| C17'—C15—C16' | 123.3 (15) | C1—O3—Zn1i | 113.8 (4) |
| C16—C15—C16' | 50.1 (11) | Zn1—O3—Zn1i | 97.60 (17) |
| C17—C15—C16' | 78.5 (13) | C21—O4—H4 | 109.5 |
| C18'—C15—C16' | 105.0 (10) | C24—O5—H5 | 109.5 |
| C17'—C15—C14 | 108.8 (12) | C5—N2—C4 | 114.9 (5) |
| C16—C15—C14 | 115.4 (13) | C5—N2—Zn1 | 107.9 (4) |
| C17—C15—C14 | 118.0 (11) | C4—N2—Zn1 | 107.6 (4) |
| C18'—C15—C14 | 116.1 (10) | C5—N2—H2N | 109 (5) |
| C16'—C15—C14 | 105.7 (12) | C4—N2—H2N | 107 (5) |
| C17'—C15—C18 | 58.0 (8) | Zn1—N2—H2N | 110 (5) |
| C16—C15—C18 | 102.3 (11) | C10—N1—C11 | 110.9 (5) |
| C17—C15—C18 | 99.6 (14) | C10—N1—Zn1 | 108.1 (4) |
| C18'—C15—C18 | 46.8 (10) | C11—N1—Zn1 | 110.1 (3) |
| C16'—C15—C18 | 145.6 (14) | C10—N1—H1N | 124 (7) |
| C14—C15—C18 | 105.2 (12) | C11—N1—H1N | 93 (7) |
| C15—C16—H16A | 109.5 | Zn1—N1—H1N | 109 (7) |
| C15—C16—H16B | 109.5 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y, −z+1.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C4—H4A···O2 | 0.97 | 2.45 | 3.246 (10) | 139 |
| N1—H1N···O4 | 0.86 (7) | 2.23 (7) | 2.952 (9) | 141 (6) |
| N2—H2N···O5ii | 0.87 (4) | 2.13 (4) | 2.999 (9) | 175 (4) |
| O4—H4···O2iii | 0.82 | 2.06 | 2.768 (10) | 145 |
| O5—H5···O1iv | 0.82 | 1.92 | 2.700 (9) | 159 |
Symmetry codes: (ii) −x+1, −y, −z+1; (iii) −x, −y+1, −z+1; (iv) x+1, y, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HB2961).
References
- Bazzicalupi, C., Bencini, A., Bianchi, A., Fusi, V., Giorgi, C., Paoletti, P., Valtancoli, B. & Zanchi, D. (1997). Inorg. Chem.36, 2784–2790. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Burley, S. K., David, P. R., Taylor, A. & Lipscomb, W. N. (1990). Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 87, 6878–6882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Dutta, B., Bag, P., Flörke, U. & Nag, K. (2005). Inorg. Chem 44, 147–157. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Lipscomb, W. N. & Straeter, N. (1996). Chem. Rev.96, 2375–2434. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Liu, J., Ma, J.-F., Li, S.-L. & Ping, G.-J. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, m1954.
- Oxford Diffraction (2006). CrysAlis CCD and CrysAlis RED Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Abingdon, England.
- Roderick, S. & Mathews, B. W. (1993). Biochemistry, 32, 3907–3912. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y. Q., Tong, J., Frenzen, G. & Sun, J. Y. (1999). J. Org. Chem.64, 1442–1446. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809021990/hb2961sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809021990/hb2961Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report