Abstract
In the title compound, C11H14N2O4, all non-H atoms lie in a mirror plane except for one of the methyl groups which deviates from the mirror plane by 0.919 (3) Å and is twisted by a torsion angle of 62.9 (2)°. An intramolecular N—H⋯O hydrogen bond generates an S(6) ring motif. In the crystal packing, the molecules are linked together by O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming dimers with graph-set motif R 2 2(8) which propagate along the a-axis direction. C—H⋯O contacts link adjacent dimers with a graph-set motif C 2 2(7), forming chains along b, and further consolidate the structure into a three-dimensional network. The crystal packing is further strengthened by short intermolecular O⋯O=C [2.655 (4) Å] contacts.
Related literature
Nitro benzoic acid derivatives are important intermediates for the synthesis of various heterocyclic compounds of pharmacological interest, see: Brouillette et al. (1999 ▶); Williams et al. (1995 ▶). For the structure of 4-(tert-butylamino)-3-nitrobenzoate, see: Mohd Maidin et al. (2008 ▶). For hydrogen-bond motifs, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶). For stability of the temperature controller used in the data collection, see: Cosier & Glazer (1986 ▶).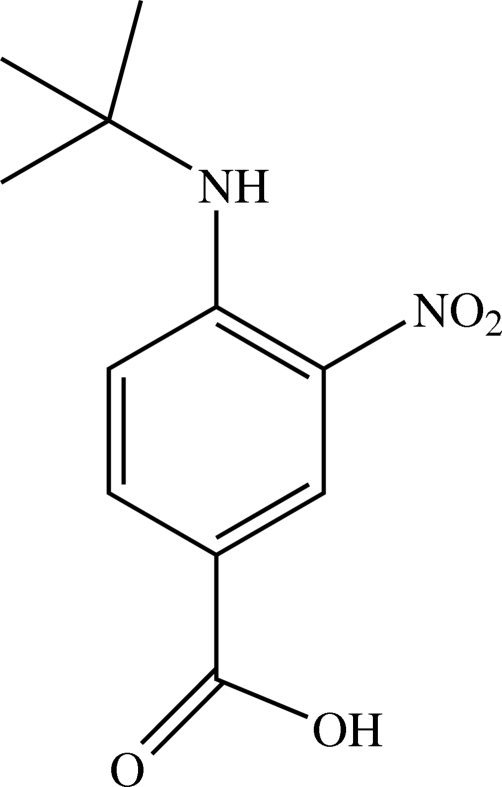
Experimental
Crystal data
C11H14N2O4
M r = 238.24
Monoclinic,
a = 20.8125 (15) Å
b = 6.7412 (5) Å
c = 8.0793 (5) Å
β = 90.863 (6)°
V = 1133.41 (14) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.11 mm−1
T = 100 K
0.39 × 0.10 × 0.03 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005 ▶) T min = 0.959, T max = 0.997
6267 measured reflections
1418 independent reflections
985 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.057
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.065
wR(F 2) = 0.153
S = 1.11
1418 reflections
107 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.37 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.31 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2005 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: SHELXTL; software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809015487/tk2439sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809015487/tk2439Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1O1⋯O2i | 0.82 (4) | 1.83 (4) | 2.655 (4) | 178 (4) |
| C1—H1A⋯O3ii | 0.93 | 2.52 | 3.407 (4) | 161 |
| N2—H1N2⋯O4 | 0.81 (4) | 1.97 (4) | 2.641 (4) | 139 (4) |
| C9—H9C⋯O2iii | 0.96 | 2.53 | 3.437 (3) | 158 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 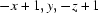 ; (ii)
; (ii) 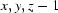 ; (iii)
; (iii) 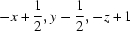 .
.
Acknowledgments
SNNB, ASAR and SAH are grateful to Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM) for funding the synthetic chemistry work under the University Research Grant (1001/PFARMASI/815026). SNNB thanks USM for a post–doctoral research fellowship. HKF and SRJ thank the Malaysian Government and Universiti Sains Malaysia for the Science Fund grant No. 305/PFIZIK/613312. SRJ thanks Universiti Sains Malaysia for a post–doctoral research fellowship. HKF also thanks Universiti Sains Malaysia for the Research University Golden Goose grant No. 1001/PFIZIK/811012.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Nitro benzoic acid derivatives are important intermediates for the synthesis of various heterocyclic compounds of pharmacological interest (Brouillette et al., 1999; Williams et al., 1995). As a part of our ongoing study on such compounds, in this paper, we present the crystal structure of the title compound (I) which was synthesized as an intermediate.
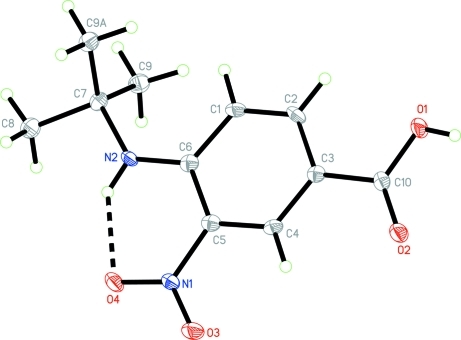
In the asymmetric unit of (I), all non-hydrogen atoms lie in a mirror plane except the methyl-C9A moiety, which is deviated from the mean plane by 0.919 (3) Å and twisted by a torsion angle C6–N2–C7–C9 of 62.9 (2) Å.
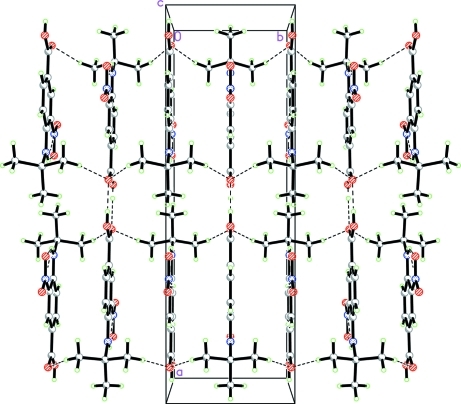
An intramolecular N—H···O hydrogen bond generates a ring of motif S(6) (Bernstein et al., 1995) (Fig. 1). In the crystal packing, the molecules are linked together by O—H···O hydrogen bonds to form dimers with the graph set motif R22(8) which propagate along the a-direction (Table 1). C—H···O contacts link adjacent dimers with a graph set motif C22(7) (Fig. 2) to form chains along the b-direction and further consolidate the structure into a 3D network. The crystal packing is further strengthened by short intermolecular O···Oi-ii = 2.655 (4)Å contacts; symmetry code: (i) 1-x, y, 1-z; (ii) 1-x, 1-y, 1-z.
Experimental
Compound (I) was prepared by refluxing ethyl 4-(tert-butylamino)-3-nitrobenzoate (0.7 g, 0.0026 mol) (Mohd Maidin et al., 2008) and KOH (0.14 g, 0.0026 mol) in aqueous ethanol (10 ml) for 3 h. Ethanol was then removed in vacuo and the reaction mixture was diluted with water (15 ml). The aqueous layer was washed with dichloromethane (10 ml × 2) and acidified with concentrated hydrochloric acid to bring about the precipitation of the desired benzoic acid. Recrystallization of the precipitate with hot ethyl acetate afforded yellow crystals of the title compound (I).
Refinement
H atoms were positioned geometrically [C–H = 0.93–0.96 Å] and refined using a riding model with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) and 1.5Ueq(methyl C). A rotating–group model was used for the methyl groups. The O- and N-bound hydrogen atoms were located from the Fourier map and allowed to refine freely.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I), showing 50% probability displacement ellipsoids and the atom numbering scheme. Intramolecular hydrogen bonding is shown as a dashed line. [Symmetry code used to generate methyl moiety C9A: x, -y + 1, z]
Fig. 2.
The crystal packing of (I), viewed along the c axis. Dashed lines indicate the hydrogen bonding and C—H···O contacts.
Crystal data
| C11H14N2O4 | F(000) = 504 |
| Mr = 238.24 | Dx = 1.396 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/m | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -C 2y | Cell parameters from 1829 reflections |
| a = 20.8125 (15) Å | θ = 3.2–30.6° |
| b = 6.7412 (5) Å | µ = 0.11 mm−1 |
| c = 8.0793 (5) Å | T = 100 K |
| β = 90.863 (6)° | Plate, yellow |
| V = 1133.41 (14) Å3 | 0.39 × 0.10 × 0.03 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEXII CCD area-detector diffractometer | 1418 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 985 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.057 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 2.0° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2005) | h = −26→26 |
| Tmin = 0.959, Tmax = 0.997 | k = −8→8 |
| 6267 measured reflections | l = −10→10 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.065 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.153 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.11 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.058P)2 + 2.3728P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 1418 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 107 parameters | Δρmax = 0.37 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.31 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. The crystal was placed in the cold stream of an Oxford Cyrosystems Cobra open-flow nitrogen cryostat (Cosier & Glazer, 1986) operating at 100.0 (1) K. |
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.44372 (12) | 0.5000 | 0.3166 (3) | 0.0189 (6) | |
| O2 | 0.43314 (11) | 0.5000 | 0.5919 (3) | 0.0185 (6) | |
| O3 | 0.22447 (11) | 0.5000 | 0.8193 (3) | 0.0198 (6) | |
| O4 | 0.13560 (11) | 0.5000 | 0.6766 (3) | 0.0187 (6) | |
| N1 | 0.19540 (13) | 0.5000 | 0.6848 (3) | 0.0130 (6) | |
| N2 | 0.13842 (13) | 0.5000 | 0.3497 (4) | 0.0131 (6) | |
| C1 | 0.24626 (16) | 0.5000 | 0.2381 (4) | 0.0142 (7) | |
| H1A | 0.2298 | 0.5000 | 0.1304 | 0.017* | |
| C2 | 0.31116 (16) | 0.5000 | 0.2615 (4) | 0.0145 (7) | |
| H2A | 0.3377 | 0.5000 | 0.1700 | 0.017* | |
| C3 | 0.33894 (15) | 0.5000 | 0.4217 (4) | 0.0122 (7) | |
| C4 | 0.29869 (16) | 0.5000 | 0.5563 (4) | 0.0126 (7) | |
| H4A | 0.3163 | 0.5000 | 0.6628 | 0.015* | |
| C5 | 0.23216 (16) | 0.5000 | 0.5349 (4) | 0.0130 (7) | |
| C6 | 0.20244 (16) | 0.5000 | 0.3726 (4) | 0.0129 (7) | |
| C7 | 0.09935 (16) | 0.5000 | 0.1929 (4) | 0.0145 (7) | |
| C8 | 0.02967 (16) | 0.5000 | 0.2518 (4) | 0.0184 (8) | |
| H8B | 0.0008 | 0.5000 | 0.1581 | 0.028* | |
| H8C | 0.0228 | 0.3861 | 0.3206 | 0.028* | |
| C9 | 0.11138 (11) | 0.3105 (4) | 0.0926 (3) | 0.0169 (6) | |
| H9A | 0.1558 | 0.3044 | 0.0627 | 0.025* | |
| H9B | 0.0850 | 0.3120 | −0.0060 | 0.025* | |
| H9C | 0.1008 | 0.1966 | 0.1581 | 0.025* | |
| C10 | 0.40933 (15) | 0.5000 | 0.4522 (4) | 0.0132 (7) | |
| H1N2 | 0.1189 (18) | 0.5000 | 0.435 (5) | 0.015 (10)* | |
| H1O1 | 0.4804 (19) | 0.5000 | 0.341 (5) | 0.010 (10)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0086 (13) | 0.0327 (15) | 0.0154 (14) | 0.000 | 0.0005 (10) | 0.000 |
| O2 | 0.0121 (12) | 0.0293 (14) | 0.0142 (13) | 0.000 | 0.0012 (10) | 0.000 |
| O3 | 0.0207 (13) | 0.0282 (14) | 0.0104 (12) | 0.000 | 0.0002 (10) | 0.000 |
| O4 | 0.0130 (13) | 0.0279 (14) | 0.0153 (13) | 0.000 | 0.0045 (10) | 0.000 |
| N1 | 0.0154 (15) | 0.0119 (14) | 0.0117 (15) | 0.000 | 0.0033 (11) | 0.000 |
| N2 | 0.0113 (15) | 0.0189 (15) | 0.0092 (15) | 0.000 | 0.0029 (12) | 0.000 |
| C1 | 0.0197 (18) | 0.0147 (17) | 0.0082 (17) | 0.000 | −0.0002 (14) | 0.000 |
| C2 | 0.0176 (18) | 0.0131 (16) | 0.0129 (18) | 0.000 | 0.0074 (14) | 0.000 |
| C3 | 0.0155 (17) | 0.0082 (15) | 0.0128 (17) | 0.000 | 0.0004 (13) | 0.000 |
| C4 | 0.0172 (17) | 0.0109 (16) | 0.0096 (17) | 0.000 | −0.0014 (13) | 0.000 |
| C5 | 0.0178 (18) | 0.0085 (15) | 0.0126 (17) | 0.000 | 0.0016 (13) | 0.000 |
| C6 | 0.0166 (17) | 0.0088 (15) | 0.0134 (17) | 0.000 | 0.0003 (14) | 0.000 |
| C7 | 0.0132 (17) | 0.0158 (17) | 0.0142 (17) | 0.000 | −0.0026 (13) | 0.000 |
| C8 | 0.0173 (18) | 0.0215 (18) | 0.0164 (18) | 0.000 | −0.0021 (14) | 0.000 |
| C9 | 0.0184 (12) | 0.0163 (12) | 0.0160 (12) | −0.0014 (10) | −0.0014 (10) | 0.0003 (10) |
| C10 | 0.0134 (17) | 0.0093 (16) | 0.0170 (18) | 0.000 | 0.0027 (14) | 0.000 |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C10 | 1.318 (4) | C3—C4 | 1.383 (5) |
| O1—H1O1 | 0.79 (4) | C3—C10 | 1.482 (5) |
| O2—C10 | 1.226 (4) | C4—C5 | 1.393 (5) |
| O3—N1 | 1.236 (4) | C4—H4A | 0.9300 |
| O4—N1 | 1.245 (4) | C5—C6 | 1.441 (5) |
| N1—C5 | 1.442 (4) | C7—C8 | 1.533 (5) |
| N2—C6 | 1.343 (4) | C7—C9 | 1.536 (3) |
| N2—C7 | 1.495 (4) | C7—C9i | 1.536 (3) |
| N2—H1N2 | 0.80 (4) | C8—H8B | 0.9595 |
| C1—C2 | 1.361 (5) | C8—H8C | 0.9600 |
| C1—C6 | 1.429 (5) | C9—H9A | 0.9600 |
| C1—H1A | 0.9300 | C9—H9B | 0.9600 |
| C2—C3 | 1.409 (5) | C9—H9C | 0.9600 |
| C2—H2A | 0.9300 | ||
| C10—O1—H1O1 | 109 (3) | N2—C6—C1 | 122.6 (3) |
| O3—N1—O4 | 121.5 (3) | N2—C6—C5 | 122.5 (3) |
| O3—N1—C5 | 118.6 (3) | C1—C6—C5 | 114.9 (3) |
| O4—N1—C5 | 119.9 (3) | N2—C7—C8 | 104.0 (3) |
| C6—N2—C7 | 130.0 (3) | N2—C7—C9 | 110.88 (17) |
| C6—N2—H1N2 | 113 (3) | C8—C7—C9 | 109.04 (18) |
| C7—N2—H1N2 | 117 (3) | N2—C7—C9i | 110.88 (17) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 122.5 (3) | C8—C7—C9i | 109.04 (18) |
| C2—C1—H1A | 118.7 | C9—C7—C9i | 112.6 (3) |
| C6—C1—H1A | 118.7 | C7—C8—H8B | 109.9 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 121.4 (3) | C7—C8—H8C | 109.3 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 119.3 | H8B—C8—H8C | 111.1 |
| C3—C2—H2A | 119.3 | C7—C9—H9A | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 118.5 (3) | C7—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C10 | 118.5 (3) | H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C10 | 122.9 (3) | C7—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 121.0 (3) | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 119.5 | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 119.5 | O2—C10—O1 | 123.3 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.7 (3) | O2—C10—C3 | 122.6 (3) |
| C4—C5—N1 | 115.8 (3) | O1—C10—C3 | 114.2 (3) |
| C6—C5—N1 | 122.5 (3) | ||
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.0 | C2—C1—C6—N2 | 180.0 |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.0 | C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.0 |
| C1—C2—C3—C10 | 180.0 | C4—C5—C6—N2 | 180.0 |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.0 | N1—C5—C6—N2 | 0.0 |
| C10—C3—C4—C5 | 180.0 | C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.0 |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.0 | N1—C5—C6—C1 | 180.0 |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | 180.0 | C6—N2—C7—C8 | 180.0 |
| O3—N1—C5—C4 | 0.0 | C6—N2—C7—C9 | 62.9 (2) |
| O4—N1—C5—C4 | 180.0 | C6—N2—C7—C9i | −62.9 (2) |
| O3—N1—C5—C6 | 180.0 | C4—C3—C10—O2 | 0.0 |
| O4—N1—C5—C6 | 0.0 | C2—C3—C10—O2 | 180.0 |
| C7—N2—C6—C1 | 0.0 | C4—C3—C10—O1 | 180.0 |
| C7—N2—C6—C5 | 180.0 | C2—C3—C10—O1 | 0.0 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x, −y+1, z.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1O1···O2ii | 0.82 (4) | 1.83 (4) | 2.655 (4) | 178 (4) |
| C1—H1A···O3iii | 0.93 | 2.52 | 3.407 (4) | 161 |
| N2—H1N2···O4 | 0.81 (4) | 1.97 (4) | 2.641 (4) | 139 (4) |
| C9—H9C···O2iv | 0.96 | 2.53 | 3.437 (3) | 158 |
Symmetry codes: (ii) −x+1, y, −z+1; (iii) x, y, z−1; (iv) −x+1/2, y−1/2, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: TK2439).
References
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl.34, 1555–1573.
- Brouillette, J. W., Atigadda, V. R., Luo, M., Air, G. M., Babu, Y. S. & Bantia, S. (1999). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett.9, 1901–1906. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2005). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cosier, J. & Glazer, A. M. (1986). J. Appl. Cryst.19, 105–107.
- Mohd Maidin, S. M., Abdul Rahim, A. S., Osman, H., Kia, R. & Fun, H.-K. (2008). Acta Cryst. E64, o1550–o1551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Williams, M., Bischofberger, N., Swaminathan, S. & Kim, C. U. (1995). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett.5, 2251–2254.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809015487/tk2439sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809015487/tk2439Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report