Abstract
In the molecule of the title compound, C25H16N4, the pyridine rings are oriented at a dihedral angle of 0.92 (3)°, while the dihedral angle between the benzene ring and the adjacent pyridine ring is 56.51 (3)°. In the crystal structure, intermolecular N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds link the molecules into centrosymmetric dimers, forming R 2 2(16) ring motifs. π–π contacts between the pyridine ring and the indole ring system and between the pyridine rings [centroid–centroid distances = 3.923 (2) and 3.724 (2) Å] may further stabilize the structure. Two weak C—H⋯π interactions are also present.
Related literature
For general background, see: da Silva et al. (2001 ▶); Joshi & Chand (1982 ▶); Namba et al. (2005 ▶). For a related structure, see: Zhu et al., (2008 ▶). For bond-length data, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶). For ring-motifs, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶).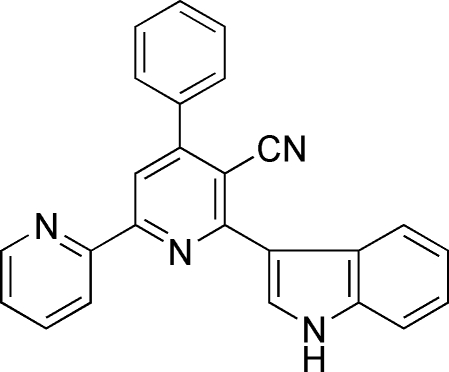
Experimental
Crystal data
C25H16N4
M r = 372.42
Triclinic,
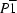
a = 9.7744 (16) Å
b = 9.7927 (11) Å
c = 11.233 (2) Å
α = 73.121 (13)°
β = 86.008 (16)°
γ = 63.853 (10)°
V = 921.5 (3) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.08 mm−1
T = 291 K
0.55 × 0.35 × 0.30 mm
Data collection
Rigaku Mercury diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (ABSCOR; Jacobson, 1998 ▶) T min = 0.966, T max = 0.976
8987 measured reflections
3349 independent reflections
2614 reflections with I > 2/s(I)
R int = 0.027
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.054
wR(F 2) = 0.126
S = 1.12
3349 reflections
263 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.16 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.21 e Å−3
Data collection: CrystalClear (Rigaku/MSC, 2001 ▶); cell refinement: CrystalClear; data reduction: CrystalStructure (Rigaku/MSC, 2004 ▶); program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEPII (Johnson, 1976 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97 and PLATON.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809016195/hk2679sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809016195/hk2679Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N4—H4⋯N3i | 0.86 | 2.23 | 3.066 (2) | 164 |
| C12—H12⋯Cg5ii | 0.93 | 2.84 | 3.649 (3) | 146 |
| C23—H23⋯Cg4iii | 0.93 | 2.91 | 3.711 (3) | 145 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 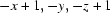 ; (ii)
; (ii) 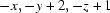 ; (iii)
; (iii) 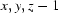 . Cg4 and Cg5 are the centroids of the C11–C16 and C20–C25 rings, respectively.
. Cg4 and Cg5 are the centroids of the C11–C16 and C20–C25 rings, respectively.
Acknowledgments
This work was sponsored by the ‘Qing Lan’ Project of Jiangsu Province for Excellent Young Teachers of XuZhou College of Industrial Technology, and the Special Foundation of the President of Xuzhou Medical College.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Indole nucleus is a well known heterocycle (da Silva et al., 2001). Compounds carrying the indole moiety exhibit antibacterial and fungicidal activities (Joshi & Chand, 1982). Moreover, the bipyridines and the related complexes have also found numerous applications in asymmetric catalysis, photoinduced electron transfer, and polymer and dendrimer science (Namba et al., 2005). As a part of our programme devoted to the preparation of functionalized indole derivatives, we synthesized a series of indole substituted heterocycles (Zhu et al., 2008). We report herein the crystal structure of the title compound.
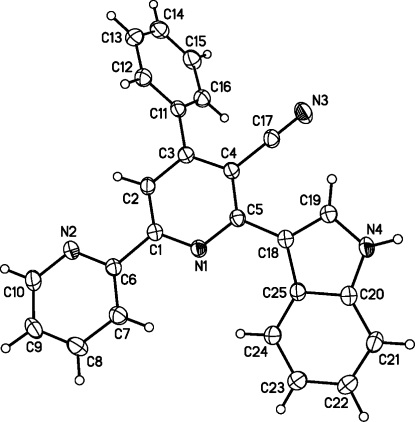
In the molecule of the title compound (Fig 1), the bond lengths (Allen et al., 1987) and angles are within normal ranges. The indole ring system A (N4/C18-C25) is planar with a maximum deviation of -0.021 (3) Å for atom C25. Rings B (N1/C1-C5), C (N2/C6-C10) and D (C11-C16) are, of course, planar, and they are oriented at dihedral angles of A/B = 23.01 (3), A/C = 23.61 (3), A/D = 74.90 (3), B/C = 0.92 (3), B/D = 56.51 (3) and C/D = 56.51 (3) °. So, rings B and C are nearly coplanar.
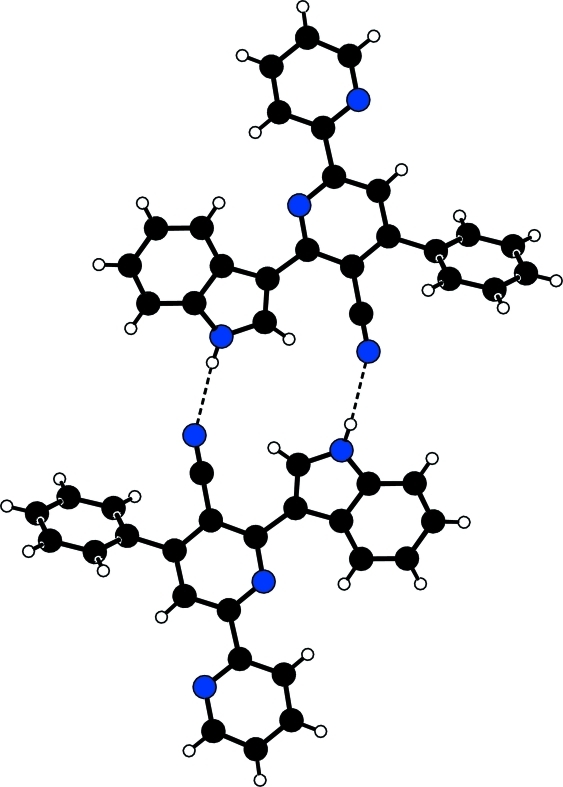
In the crystal structure, intermolecular N-H···N hydrogen bonds (Table 1) link the molecules into centrosymmetric dimers forming R22(16) ring motifs (Fig. 2) (Bernstein et al., 1995), in which they may be effective in the stabilization of the structure. The π–π contacts between the pyridine ring and the indole ring system and the pyridine rings, Cg1—Cg2i and Cg2—Cg3ii [symmetry codes: (i) -x, 2 - y, 1 - z, (ii) -x, 1 - y, 1 - z, where Cg1, Cg2 and Cg3 are centroids of the rings (N4/C18-C20/C25), B (N1/C1-C5) and C (N2/C6-C10), respectively] may further stabilize the structure, with centroid-centroid distances of 3.923 (2) and 3.724 (2) Å. There also exist two weak C—H···π interactions (Table 1).
Experimental
The title compound was prepared by one-pot reaction of 3-cyanoacetyl indole (2 mmol), benzaldehyde (2 mmol) and 2-acetyl pyridine (2 mmol) in present of ammonium acetate in ethanol. After refluxing for 5 h, the reaction mixture was cooled and washed with small amount of cool ethanol. The crude product was filtered and single crystals of the title compound were obtained from ethanol solution by slow evaporation at room temperature (yield; 80%, m.p. 567-568 K). Spectroscopic analysis: IR (KBr, n, cm-1): 3337, 3050, 2218, 1573, 1535, 1438, 1214, 1145, 850, 745, 703. 1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO-d6): 11.89 (br s, 1H, NH), 8.78 (d, J = 4.4 Hz, 1H, ArH), 8.58 (d, J = 8.0 Hz, 1H, ArH), 8.41 (d, J = 5.2 Hz, 2H, ArH), 8.31 (s, 1H, ArH), 8.11 (m, 1H, ArH), 7.79-7.81 (m, 2H, ArH), 7.56-7.66 (m, 5H, ArH), 7.24-7.29 (m, 2H, ArH)
Refinement
H atoms were positioned geometrically, with N-H = 0.86 Å (for NH) and C-H = 0.93 Å for aromatic H and constrained to ride on their parent atoms with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C,N).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title molecule, with the atom-numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.
A partial packing diagram of the title compound. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C25H16N4 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 372.42 | F(000) = 388 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.342 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Melting point = 567–568 K |
| a = 9.7744 (16) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71070 Å |
| b = 9.7927 (11) Å | Cell parameters from 3008 reflections |
| c = 11.233 (2) Å | θ = 3.1–25.3° |
| α = 73.121 (13)° | µ = 0.08 mm−1 |
| β = 86.008 (16)° | T = 291 K |
| γ = 63.853 (10)° | Block, yellow |
| V = 921.5 (3) Å3 | 0.55 × 0.35 × 0.30 mm |
Data collection
| Rigaku Mercury diffractometer | 3349 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2614 reflections with I > 2/s(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.027 |
| Detector resolution: 7.31 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 25.3°, θmin = 3.1° |
| ω scans | h = −11→11 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (ABSCOR; Jacobson, 1998) | k = −10→11 |
| Tmin = 0.966, Tmax = 0.976 | l = −13→13 |
| 8987 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.054 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.126 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.12 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0538P)2 + 0.1499P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3349 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 263 parameters | Δρmax = 0.16 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.20 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2sigma(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| N1 | 0.94201 (16) | 0.20772 (17) | 0.54741 (13) | 0.0355 (4) | |
| N2 | 1.20413 (18) | 0.3774 (2) | 0.44026 (14) | 0.0455 (4) | |
| N3 | 0.5855 (2) | 0.1895 (2) | 0.28547 (16) | 0.0606 (5) | |
| N4 | 0.64100 (17) | −0.04598 (18) | 0.69177 (14) | 0.0422 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.5936 | −0.1043 | 0.7025 | 0.051* | |
| C1 | 1.01436 (19) | 0.2799 (2) | 0.46717 (16) | 0.0347 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.98275 (19) | 0.3310 (2) | 0.33960 (16) | 0.0371 (4) | |
| H2 | 1.0382 | 0.3776 | 0.2873 | 0.045* | |
| C3 | 0.86846 (19) | 0.3126 (2) | 0.28960 (16) | 0.0353 (4) | |
| C4 | 0.79281 (19) | 0.2362 (2) | 0.37308 (16) | 0.0348 (4) | |
| C5 | 0.83308 (19) | 0.1829 (2) | 0.50305 (16) | 0.0334 (4) | |
| C6 | 1.13427 (19) | 0.3032 (2) | 0.52184 (16) | 0.0354 (4) | |
| C7 | 1.1727 (2) | 0.2494 (2) | 0.64913 (18) | 0.0449 (5) | |
| H7 | 1.1226 | 0.1981 | 0.7039 | 0.054* | |
| C8 | 1.2862 (2) | 0.2731 (3) | 0.6929 (2) | 0.0519 (5) | |
| H8 | 1.3135 | 0.2383 | 0.7779 | 0.062* | |
| C9 | 1.3586 (2) | 0.3482 (2) | 0.6104 (2) | 0.0494 (5) | |
| H9 | 1.4361 | 0.3648 | 0.6378 | 0.059* | |
| C10 | 1.3136 (2) | 0.3981 (3) | 0.4861 (2) | 0.0521 (5) | |
| H10 | 1.3625 | 0.4497 | 0.4302 | 0.063* | |
| C11 | 0.8284 (2) | 0.3777 (2) | 0.15322 (16) | 0.0379 (4) | |
| C12 | 0.9407 (2) | 0.3356 (2) | 0.07066 (17) | 0.0445 (5) | |
| H12 | 1.0400 | 0.2617 | 0.1010 | 0.053* | |
| C13 | 0.9065 (3) | 0.4026 (3) | −0.05660 (18) | 0.0529 (6) | |
| H13 | 0.9823 | 0.3725 | −0.1114 | 0.063* | |
| C14 | 0.7602 (3) | 0.5140 (3) | −0.10229 (19) | 0.0555 (6) | |
| H14 | 0.7376 | 0.5599 | −0.1878 | 0.067* | |
| C15 | 0.6484 (3) | 0.5570 (3) | −0.02151 (19) | 0.0532 (6) | |
| H15 | 0.5498 | 0.6323 | −0.0525 | 0.064* | |
| C16 | 0.6809 (2) | 0.4891 (2) | 0.10587 (18) | 0.0460 (5) | |
| H16 | 0.6039 | 0.5181 | 0.1600 | 0.055* | |
| C17 | 0.6772 (2) | 0.2108 (2) | 0.32443 (17) | 0.0423 (5) | |
| C18 | 0.7603 (2) | 0.1025 (2) | 0.59690 (16) | 0.0352 (4) | |
| C19 | 0.6856 (2) | 0.0176 (2) | 0.58127 (17) | 0.0385 (4) | |
| H19 | 0.6682 | 0.0056 | 0.5054 | 0.046* | |
| C20 | 0.6833 (2) | −0.0028 (2) | 0.78422 (17) | 0.0380 (4) | |
| C21 | 0.6582 (2) | −0.0376 (2) | 0.90989 (18) | 0.0476 (5) | |
| H21 | 0.6081 | −0.1001 | 0.9444 | 0.057* | |
| C22 | 0.7105 (3) | 0.0240 (3) | 0.98141 (19) | 0.0568 (6) | |
| H22 | 0.6957 | 0.0029 | 1.0663 | 0.068* | |
| C23 | 0.7851 (3) | 0.1175 (3) | 0.92946 (19) | 0.0601 (6) | |
| H23 | 0.8188 | 0.1581 | 0.9803 | 0.072* | |
| C24 | 0.8104 (2) | 0.1515 (3) | 0.80452 (18) | 0.0507 (5) | |
| H24 | 0.8605 | 0.2143 | 0.7711 | 0.061* | |
| C25 | 0.7595 (2) | 0.0901 (2) | 0.72879 (16) | 0.0366 (4) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| N1 | 0.0353 (8) | 0.0367 (9) | 0.0374 (8) | −0.0191 (7) | 0.0027 (7) | −0.0097 (7) |
| N2 | 0.0430 (9) | 0.0583 (11) | 0.0475 (9) | −0.0321 (8) | 0.0058 (8) | −0.0173 (8) |
| N3 | 0.0675 (12) | 0.0748 (13) | 0.0507 (10) | −0.0502 (11) | −0.0130 (9) | 0.0006 (9) |
| N4 | 0.0439 (9) | 0.0449 (9) | 0.0476 (9) | −0.0298 (8) | 0.0052 (7) | −0.0109 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0320 (9) | 0.0349 (10) | 0.0378 (10) | −0.0153 (8) | 0.0024 (8) | −0.0102 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0336 (9) | 0.0415 (11) | 0.0369 (10) | −0.0206 (8) | 0.0024 (8) | −0.0058 (8) |
| C3 | 0.0354 (10) | 0.0346 (10) | 0.0355 (10) | −0.0159 (8) | 0.0005 (8) | −0.0081 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0346 (9) | 0.0346 (10) | 0.0362 (10) | −0.0172 (8) | 0.0001 (8) | −0.0082 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0329 (9) | 0.0314 (9) | 0.0385 (10) | −0.0157 (8) | 0.0034 (8) | −0.0114 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0319 (9) | 0.0355 (10) | 0.0407 (10) | −0.0152 (8) | 0.0036 (8) | −0.0134 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0452 (11) | 0.0490 (12) | 0.0415 (11) | −0.0237 (10) | −0.0025 (9) | −0.0083 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0514 (12) | 0.0575 (13) | 0.0492 (12) | −0.0256 (11) | −0.0101 (10) | −0.0131 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0334 (10) | 0.0567 (13) | 0.0663 (14) | −0.0199 (10) | −0.0016 (10) | −0.0281 (11) |
| C10 | 0.0458 (12) | 0.0661 (14) | 0.0611 (13) | −0.0364 (11) | 0.0121 (10) | −0.0249 (11) |
| C11 | 0.0418 (10) | 0.0419 (11) | 0.0360 (10) | −0.0255 (9) | 0.0003 (8) | −0.0080 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0459 (11) | 0.0509 (12) | 0.0399 (11) | −0.0266 (10) | 0.0016 (9) | −0.0089 (9) |
| C13 | 0.0668 (14) | 0.0664 (15) | 0.0398 (11) | −0.0420 (13) | 0.0114 (10) | −0.0171 (10) |
| C14 | 0.0770 (16) | 0.0650 (15) | 0.0357 (11) | −0.0472 (13) | −0.0048 (11) | −0.0026 (10) |
| C15 | 0.0566 (13) | 0.0545 (13) | 0.0463 (12) | −0.0306 (11) | −0.0118 (11) | 0.0018 (10) |
| C16 | 0.0448 (11) | 0.0539 (12) | 0.0410 (10) | −0.0260 (10) | −0.0005 (9) | −0.0085 (9) |
| C17 | 0.0457 (11) | 0.0469 (12) | 0.0382 (10) | −0.0283 (10) | 0.0001 (9) | −0.0042 (9) |
| C18 | 0.0334 (9) | 0.0345 (10) | 0.0388 (10) | −0.0164 (8) | 0.0030 (8) | −0.0098 (8) |
| C19 | 0.0408 (10) | 0.0398 (11) | 0.0387 (10) | −0.0215 (9) | 0.0030 (8) | −0.0109 (8) |
| C20 | 0.0339 (10) | 0.0373 (10) | 0.0436 (11) | −0.0174 (8) | 0.0041 (8) | −0.0105 (8) |
| C21 | 0.0476 (12) | 0.0545 (13) | 0.0449 (11) | −0.0305 (10) | 0.0111 (9) | −0.0091 (10) |
| C22 | 0.0709 (15) | 0.0729 (15) | 0.0377 (11) | −0.0436 (13) | 0.0129 (10) | −0.0146 (11) |
| C23 | 0.0815 (16) | 0.0805 (16) | 0.0432 (12) | −0.0570 (14) | 0.0122 (11) | −0.0205 (11) |
| C24 | 0.0656 (14) | 0.0626 (13) | 0.0424 (11) | −0.0457 (12) | 0.0096 (10) | −0.0145 (10) |
| C25 | 0.0356 (10) | 0.0374 (10) | 0.0394 (10) | −0.0199 (8) | 0.0033 (8) | −0.0091 (8) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| N1—C1 | 1.339 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.385 (3) |
| N1—C5 | 1.347 (2) | C11—C16 | 1.391 (3) |
| N2—C10 | 1.334 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.384 (3) |
| N2—C6 | 1.341 (2) | C12—H12 | 0.9300 |
| N3—C17 | 1.144 (2) | C13—C14 | 1.378 (3) |
| N4—C19 | 1.354 (2) | C13—H13 | 0.9300 |
| N4—C20 | 1.377 (2) | C14—C15 | 1.369 (3) |
| N4—H4 | 0.8600 | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C1—C2 | 1.381 (2) | C15—C16 | 1.384 (3) |
| C1—C6 | 1.490 (2) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C2—C3 | 1.385 (2) | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C18—C19 | 1.375 (2) |
| C3—C4 | 1.404 (2) | C18—C25 | 1.451 (2) |
| C3—C11 | 1.484 (2) | C19—H19 | 0.9300 |
| C4—C5 | 1.420 (2) | C20—C21 | 1.384 (3) |
| C4—C17 | 1.432 (2) | C20—C25 | 1.405 (2) |
| C5—C18 | 1.465 (2) | C21—C22 | 1.372 (3) |
| C6—C7 | 1.388 (2) | C21—H21 | 0.9300 |
| C7—C8 | 1.377 (3) | C22—C23 | 1.389 (3) |
| C7—H7 | 0.9300 | C22—H22 | 0.9300 |
| C8—C9 | 1.368 (3) | C23—C24 | 1.376 (3) |
| C8—H8 | 0.9300 | C23—H23 | 0.9300 |
| C9—C10 | 1.371 (3) | C24—C25 | 1.398 (3) |
| C9—H9 | 0.9300 | C24—H24 | 0.9300 |
| C10—H10 | 0.9300 | ||
| C1—N1—C5 | 119.18 (15) | C13—C12—H12 | 119.7 |
| C10—N2—C6 | 117.30 (17) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.7 |
| C19—N4—C20 | 109.41 (15) | C14—C13—C12 | 120.1 (2) |
| C19—N4—H4 | 125.3 | C14—C13—H13 | 119.9 |
| C20—N4—H4 | 125.3 | C12—C13—H13 | 119.9 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 123.09 (15) | C15—C14—C13 | 119.85 (19) |
| N1—C1—C6 | 116.67 (15) | C15—C14—H14 | 120.1 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 120.24 (16) | C13—C14—H14 | 120.1 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.94 (16) | C14—C15—C16 | 120.5 (2) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 120.0 | C14—C15—H15 | 119.8 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 120.0 | C16—C15—H15 | 119.8 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 117.25 (16) | C15—C16—C11 | 120.2 (2) |
| C2—C3—C11 | 119.47 (16) | C15—C16—H16 | 119.9 |
| C4—C3—C11 | 123.25 (15) | C11—C16—H16 | 119.9 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.12 (15) | N3—C17—C4 | 179.5 (2) |
| C3—C4—C17 | 118.82 (15) | C19—C18—C25 | 105.64 (15) |
| C5—C4—C17 | 121.05 (16) | C19—C18—C5 | 128.12 (16) |
| N1—C5—C4 | 120.37 (15) | C25—C18—C5 | 126.18 (15) |
| N1—C5—C18 | 115.71 (15) | N4—C19—C18 | 110.50 (16) |
| C4—C5—C18 | 123.91 (15) | N4—C19—H19 | 124.7 |
| N2—C6—C7 | 122.15 (16) | C18—C19—H19 | 124.7 |
| N2—C6—C1 | 115.83 (15) | N4—C20—C21 | 129.29 (17) |
| C7—C6—C1 | 122.01 (16) | N4—C20—C25 | 107.56 (15) |
| C8—C7—C6 | 118.82 (18) | C21—C20—C25 | 123.15 (17) |
| C8—C7—H7 | 120.6 | C22—C21—C20 | 117.15 (18) |
| C6—C7—H7 | 120.6 | C22—C21—H21 | 121.4 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 119.50 (19) | C20—C21—H21 | 121.4 |
| C9—C8—H8 | 120.2 | C21—C22—C23 | 121.23 (19) |
| C7—C8—H8 | 120.2 | C21—C22—H22 | 119.4 |
| C8—C9—C10 | 118.03 (18) | C23—C22—H22 | 119.4 |
| C8—C9—H9 | 121.0 | C24—C23—C22 | 121.5 (2) |
| C10—C9—H9 | 121.0 | C24—C23—H23 | 119.2 |
| N2—C10—C9 | 124.20 (19) | C22—C23—H23 | 119.2 |
| N2—C10—H10 | 117.9 | C23—C24—C25 | 118.88 (18) |
| C9—C10—H10 | 117.9 | C23—C24—H24 | 120.6 |
| C12—C11—C16 | 118.78 (17) | C25—C24—H24 | 120.6 |
| C12—C11—C3 | 119.99 (16) | C24—C25—C20 | 118.06 (17) |
| C16—C11—C3 | 121.11 (17) | C24—C25—C18 | 135.01 (17) |
| C13—C12—C11 | 120.51 (19) | C20—C25—C18 | 106.88 (15) |
| C5—N1—C1—C2 | 0.0 (3) | C16—C11—C12—C13 | −0.3 (3) |
| C5—N1—C1—C6 | −179.68 (15) | C3—C11—C12—C13 | −176.21 (17) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 2.0 (3) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 1.0 (3) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −178.34 (16) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | −0.7 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −2.2 (3) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −0.1 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C11 | 175.87 (17) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | 0.8 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.7 (3) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | −0.5 (3) |
| C11—C3—C4—C5 | −177.30 (16) | C3—C11—C16—C15 | 175.28 (17) |
| C2—C3—C4—C17 | −178.14 (16) | N1—C5—C18—C19 | −157.15 (17) |
| C11—C3—C4—C17 | 3.8 (3) | C4—C5—C18—C19 | 24.1 (3) |
| C1—N1—C5—C4 | −1.6 (2) | N1—C5—C18—C25 | 19.5 (3) |
| C1—N1—C5—C18 | 179.67 (15) | C4—C5—C18—C25 | −159.21 (17) |
| C3—C4—C5—N1 | 1.2 (3) | C20—N4—C19—C18 | 0.8 (2) |
| C17—C4—C5—N1 | −179.95 (17) | C25—C18—C19—N4 | −0.5 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C18 | 179.84 (16) | C5—C18—C19—N4 | 176.68 (17) |
| C17—C4—C5—C18 | −1.3 (3) | C19—N4—C20—C21 | 178.41 (19) |
| C10—N2—C6—C7 | 0.0 (3) | C19—N4—C20—C25 | −0.8 (2) |
| C10—N2—C6—C1 | −179.08 (16) | N4—C20—C21—C22 | −178.64 (19) |
| N1—C1—C6—N2 | −179.21 (15) | C25—C20—C21—C22 | 0.5 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—N2 | 1.1 (3) | C20—C21—C22—C23 | 0.1 (3) |
| N1—C1—C6—C7 | 1.7 (3) | C21—C22—C23—C24 | −0.3 (4) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | −178.01 (17) | C22—C23—C24—C25 | 0.0 (4) |
| N2—C6—C7—C8 | 0.0 (3) | C23—C24—C25—C20 | 0.6 (3) |
| C1—C6—C7—C8 | 179.07 (17) | C23—C24—C25—C18 | 177.8 (2) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | −0.3 (3) | N4—C20—C25—C24 | 178.46 (16) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | 0.4 (3) | C21—C20—C25—C24 | −0.8 (3) |
| C6—N2—C10—C9 | 0.2 (3) | N4—C20—C25—C18 | 0.5 (2) |
| C8—C9—C10—N2 | −0.4 (3) | C21—C20—C25—C18 | −178.79 (17) |
| C2—C3—C11—C12 | 54.4 (2) | C19—C18—C25—C24 | −177.5 (2) |
| C4—C3—C11—C12 | −127.63 (19) | C5—C18—C25—C24 | 5.3 (3) |
| C2—C3—C11—C16 | −121.39 (19) | C19—C18—C25—C20 | 0.0 (2) |
| C4—C3—C11—C16 | 56.6 (3) | C5—C18—C25—C20 | −177.27 (16) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N4—H4···N3i | 0.86 | 2.23 | 3.066 (2) | 164 |
| C12—H12···Cg5ii | 0.93 | 2.84 | 3.649 (3) | 146 |
| C23—H23···Cg4iii | 0.93 | 2.91 | 3.711 (3) | 145 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y, −z+1; (ii) −x, −y+2, −z+1; (iii) x, y, z−1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HK2679).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl.34, 1555–1573.
- Jacobson, R. (1998). ABSCOR Private communication to the Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Johnson, C. K. (1976). ORTEPII Report ORNL-5138. Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Tennessee, USA.
- Joshi, K. C. & Chand, P. (1982). Pharmazie, 37, 1–12. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Namba, K., Cui, S., Wang, J. & Kishi, Y. (2005). Org. Lett.7, 5417–5419. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Rigaku/MSC (2001). CrystalClear Rigaku/MSC, The Woodlands, Texas, USA.
- Rigaku/MSC (2004). CrystalStructure Rigaku/MSC, The Woodlands, Texas, USA.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Silva, J. F. M. da, Garden, S. J. & Pinto, A. C. (2001). J. Braz. Chem. Soc.12, 273–324.
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Zhu, S. L., Ji, S. J., Zhao, K. & Liu, Y. (2008). Tetrahedron Lett.49, 2578–2582.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809016195/hk2679sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809016195/hk2679Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report