Abstract
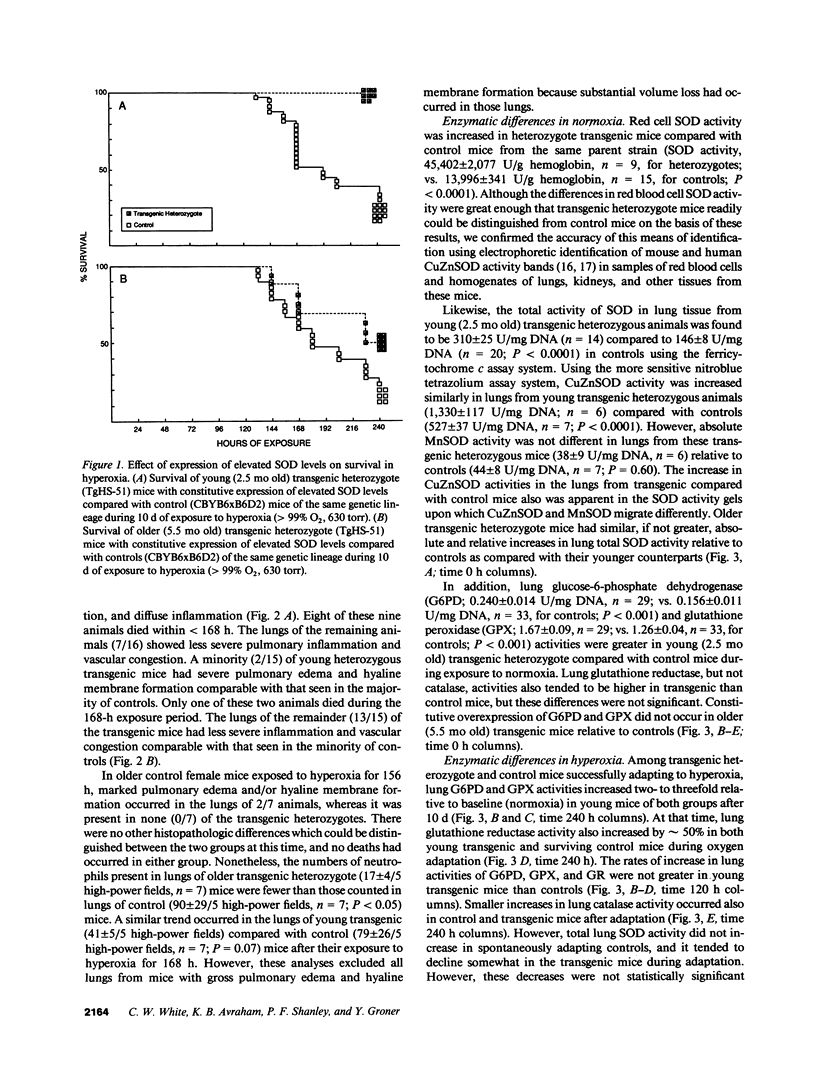
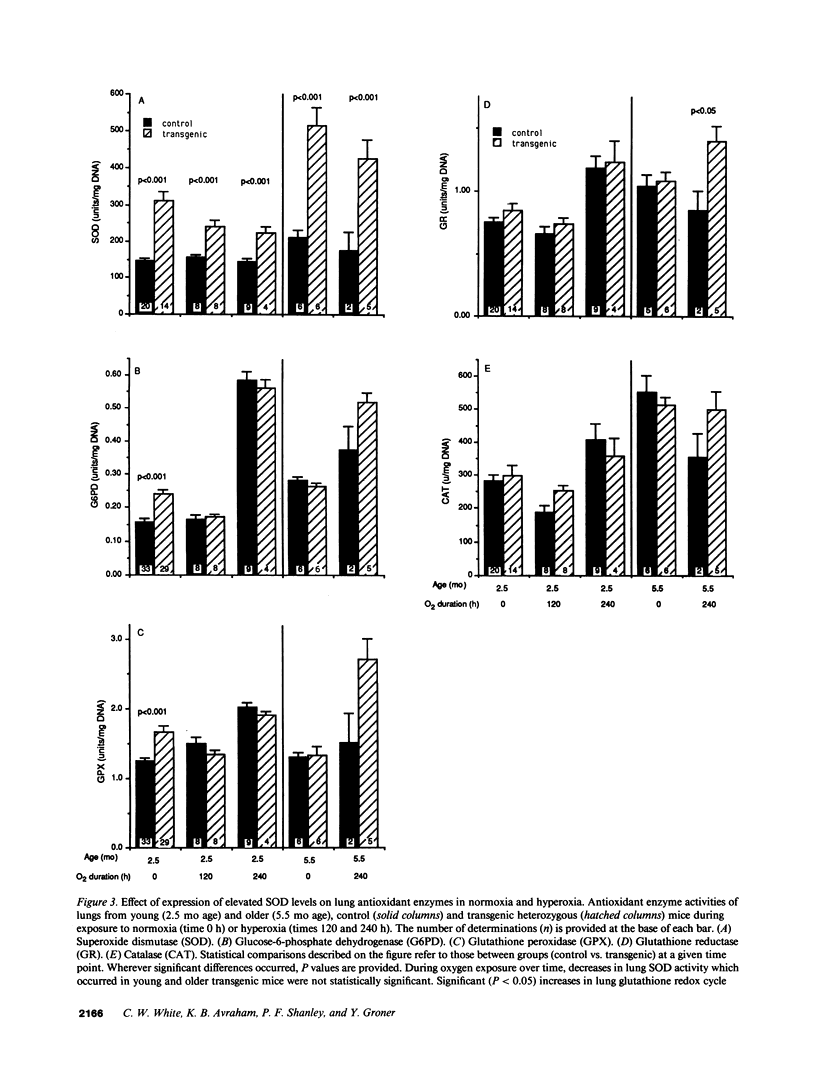
To test the hypothesis that increases in lung superoxide dismutase can cause tolerance to pulmonary oxygen toxicity, we studied transgenic mice which constitutively express elevated levels of the human copper-zinc SOD (CuZnSOD). Upon exposure to hyperoxia (greater than 99% O2, 630 torr) the transgenic CuZnSOD mice showed increased survival, decreased morphologic evidence of lung damage such as edema and hyaline membrane formation, and reduction in the number of lung neutrophils. During continuous exposure to oxygen, both control and transgenic animals who successfully adapted to hyperoxia showed increased activity of lung antioxidant enzymes such as glutathione peroxidase (GPX), glutathione reductase (GR), and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD), whereas superoxide dismutase activity remained unchanged. The results show that expression of elevated levels of CuZnSOD decreases pulmonary oxygen toxicity and associated histologic damage and mortality.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Avraham K. B., Schickler M., Sapoznikov D., Yarom R., Groner Y. Down's syndrome: abnormal neuromuscular junction in tongue of transgenic mice with elevated levels of human Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):823–829. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91153-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGMEYER H. U. Zur Messung von Katalase-Aktivitäten. Biochem Z. 1955;327(4):255–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beauchamp C., Fridovich I. Superoxide dismutase: improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1971 Nov;44(1):276–287. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90370-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crapo J. D., McCord J. M., Fridovich I. Preparation and assay of superoxide dismutases. Methods Enzymol. 1978;53:382–393. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)53044-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crapo J. D., Tierney D. F. Superoxide dismutase and pulmonary oxygen toxicity. Am J Physiol. 1974 Jun;226(6):1401–1407. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1974.226.6.1401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross C. E., Watanabe T. T., Hasegawa G. K., Goralnik G. N., Roertgen K. E., Kaizu T., Reiser K. M., Gorin A. B., Last J. A. Biochemical assays in lung homogenates: artifacts caused by trapped blood after perfusion. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1979 Mar 30;48(1 Pt 1):99–109. doi: 10.1016/s0041-008x(79)80012-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein C. J., Avraham K. B., Lovett M., Smith S., Elroy-Stein O., Rotman G., Bry C., Groner Y. Transgenic mice with increased Cu/Zn-superoxide dismutase activity: animal model of dosage effects in Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8044–8048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank L., Bucher J. R., Roberts R. J. Oxygen toxicity in neonatal and adult animals of various species. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1978 Nov;45(5):699–704. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1978.45.5.699. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank L., Summerville J., Massaro D. Potection from oxygen toxicity with endotoxin. Role of the endogenous antioxidant enzymes of the lung. J Clin Invest. 1980 May;65(5):1104–1110. doi: 10.1172/JCI109763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman B. A., Crapo J. D. Hyperoxia increases oxygen radical production in rat lungs and lung mitochondria. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):10986–10992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman B. A., Young S. L., Crapo J. D. Liposome-mediated augmentation of superoxide dismutase in endothelial cells prevents oxygen injury. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12534–12542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hass M. A., Iqbal J., Clerch L. B., Frank L., Massaro D. Rat lung Cu,Zn superoxide dismutase. Isolation and sequence of a full-length cDNA and studies of enzyme induction. J Clin Invest. 1989 Apr;83(4):1241–1246. doi: 10.1172/JCI114007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelner M. J., Bagnell R. Alteration of endogenous glutathione peroxidase, manganese superoxide dismutase, and glutathione transferase activity in cells transfected with a copper-zinc superoxide dismutase expression vector. Explanation for variations in paraquat resistance. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 5;265(19):10872–10875. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padmanabhan R. V., Gudapaty R., Liener I. E., Schwartz B. A., Hoidal J. R. Protection against pulmonary oxygen toxicity in rats by the intratracheal administration of liposome-encapsulated superoxide dismutase or catalase. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1985 Jul;132(1):164–167. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1985.132.1.164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrish D. A., Mitchell B. C., Henson P. M., Larsen G. L. Pulmonary response of fifth component of complement-sufficient and -deficient mice to hyperoxia. J Clin Invest. 1984 Sep;74(3):956–965. doi: 10.1172/JCI111515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petrone W. F., English D. K., Wong K., McCord J. M. Free radicals and inflammation: superoxide-dependent activation of a neutrophil chemotactic factor in plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1159–1163. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards G. M. Modifications of the diphenylamine reaction giving increased sensitivity and simplicity in the estimation of DNA. Anal Biochem. 1974 Feb;57(2):369–376. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90091-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld W., Evans H., Concepcion L., Jhaveri R., Schaeffer H., Friedman A. Prevention of bronchopulmonary dysplasia by administration of bovine superoxide dismutase in preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome. J Pediatr. 1984 Nov;105(5):781–785. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(84)80307-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaffer S. G., O'Neill D. H., Thibeault D. W. Administration of bovine superoxide dismutase fails to prevent chronic pulmonary sequelae of neonatal oxygen exposure in the rat. J Pediatr. 1987 Jun;110(6):942–946. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(87)80419-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sjostrom K., Crapo J. D. Structural and biochemical adaptive changes in rat lungs after exposure to hypoxia. Lab Invest. 1983 Jan;48(1):68–79. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanswell A. K., Freeman B. A. Liposome-entrapped antioxidant enzymes prevent lethal O2 toxicity in the newborn rat. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1987 Jul;63(1):347–352. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1987.63.1.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanswell A. K., Olson D. M., Freeman B. A. Liposome-mediated augmentation of antioxidant defenses in fetal rat pneumocytes. Am J Physiol. 1990 Apr;258(4 Pt 1):L165–L172. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.1990.258.4.L165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White C. W., Ghezzi P., Dinarello C. A., Caldwell S. A., McMurtry I. F., Repine J. E. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor/cachectin and interleukin 1 pretreatment decreases lung oxidized glutathione accumulation, lung injury, and mortality in rats exposed to hyperoxia. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jun;79(6):1868–1873. doi: 10.1172/JCI113029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White C. W., Ghezzi P., McMahon S., Dinarello C. A., Repine J. E. Cytokines increase rat lung antioxidant enzymes during exposure to hyperoxia. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Feb;66(2):1003–1007. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.66.2.1003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White C. W., Jackson J. H., Abuchowski A., Kazo G. M., Mimmack R. F., Berger E. M., Freeman B. A., McCord J. M., Repine J. E. Polyethylene glycol-attached antioxidant enzymes decrease pulmonary oxygen toxicity in rats. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Feb;66(2):584–590. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.66.2.584. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White C. W., Jackson J. H., McMurtry I. F., Repine J. E. Hypoxia increases glutathione redox cycle and protects rat lungs against oxidants. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1988 Dec;65(6):2607–2616. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1988.65.6.2607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]