Abstract
The title molecule, C14H9ClN2OS, exists in the solid state in its amide form with a typical C=O bond length, as well as shortened C—N bonds. The plane containing the HNCO atoms subtends dihedral angles of 12.3 (4) and 8.1 (3)° with the planes of the phenyl ring and benzothiazole group, respectively, whereas the dihedral angle between the planes of the phenyl ring and the benzothiazole group is 5.96 (6)°. In the crystal, molecules form intermolecular N—H⋯N hydrogen bonds, generating independent scissor-like R 2 2(8) dimers.
Related literature
For geometric data, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶); For related structures, see: Garden et al. (2005 ▶); Wardell et al. (2005 ▶).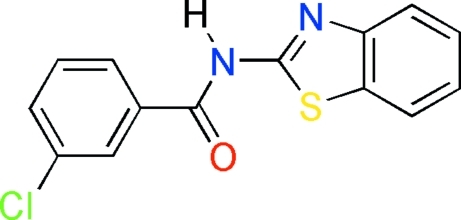
Experimental
Crystal data
C14H9ClN2OS
M r = 288.74
Monoclinic,

a = 26.6613 (19) Å
b = 7.5766 (5) Å
c = 12.6729 (10) Å
β = 99.729 (6)°
V = 2523.1 (3) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.46 mm−1
T = 173 K
0.39 × 0.38 × 0.35 mm
Data collection
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.028
wR(F 2) = 0.079
S = 1.03
2352 reflections
177 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.29 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3
Data collection: X-AREA (Stoe & Cie, 2001 ▶); cell refinement: X-AREA; data reduction: X-AREA; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶) and XP in SHELXTL-Plus (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809016481/hg2508sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809016481/hg2508Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N1—H1⋯N2i | 0.94 (2) | 2.02 (2) | 2.9429 (18) | 168.9 (17) |
Symmetry code: (i) 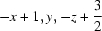 .
.
Acknowledgments
MKR is grateful to the HEC, Pakistan, for financial support of the PhD program under scholarship No. ILC-0363104.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
We report here the structure of the title compound, (I) (Fig. 1), which has been separated from an impure sample of thiourea by column chromatography as a by-product, a part of our ongoing studies related to N,N'-disubstituted thioureas and heterocyclic compounds. These include N—H···N hydrogen bonds, with possible oxygen-sulfur intramolecular interactions (Fig. 2). In this class of componds, N—H···O, C—H···O and N—H···N hydrogen bonds, and weak π–π stacking interactions are the only direction-specific intermolecular interactions (Garden et al., 2005; Wardell et al., 2005). The molecules of (I) are nearly planar, as shown by the leading torsion angles [C11—C1—N1—C2 174.90 (12) and C1—N1—C2—N2 -171.57 (13)°], and the amide group adopts the usual trans conformation; the bond lengths and inter-bond angles present no unusual values (Allen et al., 1987).
Experimental
Freshly prepared and steam-distilled 3-chlorobenzoyl isothiocyanate (1.98 g, 10 mmol) was stirred in acetone (30 ml) for 20 min. Neat 2-aminobenzothiazole (1.50 g, 10 mmol) was then added and the resulting mixture was stirred for 1 h. The reaction mixture was then poured into 300 ml (approx.) acidified (pH 4) water and stirred well. The solid product was separated and washed with deionized water. One of the fraction obtained as a by-product during the column chromatography of the target thiourea was recrystallized from methanol/1,1-dichloromethane (1:10 v/v) to give fine crystals of (I), with an overall fractional yield of 15%.
Refinement
H atoms bonded to C were included in calculated positions and refined as riding on their parent C atom with C—H = 0.95 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C). The H atom bonded to N was freely refined.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of (I) showing atom-numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
Packing diagram of (I) with view onto the ac plane. Hydrogen bonds shown as dashed lines. H atoms are omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| C14H9ClN2OS | F(000) = 1184 |
| Mr = 288.74 | Dx = 1.520 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -C 2yc | Cell parameters from 8429 reflections |
| a = 26.6613 (19) Å | θ = 3.6–25.9° |
| b = 7.5766 (5) Å | µ = 0.46 mm−1 |
| c = 12.6729 (10) Å | T = 173 K |
| β = 99.729 (6)° | Block, light yellow |
| V = 2523.1 (3) Å3 | 0.39 × 0.38 × 0.35 mm |
| Z = 8 |
Data collection
| Stoe IPDS II two-circle diffractometer | 2352 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2084 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.038 |
| ω scans | θmax = 25.6°, θmin = 3.6° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan [MULABS (Spek, 2009); Blessing, 1995)] | h = −32→32 |
| Tmin = 0.841, Tmax = 0.856 | k = −8→9 |
| 9132 measured reflections | l = −15→15 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.028 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.079 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.051P)2 + 0.8598P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.03 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 2352 reflections | Δρmax = 0.28 e Å−3 |
| 177 parameters | Δρmin = −0.22 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.0071 (6) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.762196 (14) | 0.69837 (6) | 0.65336 (3) | 0.03053 (14) | |
| S1 | 0.500738 (13) | 0.23662 (5) | 0.45176 (3) | 0.01915 (13) | |
| O1 | 0.58693 (4) | 0.40431 (15) | 0.51591 (8) | 0.0241 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.54529 (4) | 0.34541 (16) | 0.65241 (10) | 0.0178 (3) | |
| H1 | 0.5448 (7) | 0.325 (2) | 0.7252 (17) | 0.032 (5)* | |
| C1 | 0.58602 (5) | 0.41061 (19) | 0.61190 (11) | 0.0179 (3) | |
| N2 | 0.46256 (4) | 0.23590 (16) | 0.62817 (10) | 0.0185 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.50288 (5) | 0.27653 (19) | 0.58813 (11) | 0.0167 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.42583 (5) | 0.16277 (19) | 0.54925 (12) | 0.0185 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.44015 (5) | 0.15038 (19) | 0.44819 (12) | 0.0191 (3) | |
| C5 | 0.40794 (6) | 0.0750 (2) | 0.36146 (12) | 0.0242 (3) | |
| H5 | 0.4179 | 0.0661 | 0.2932 | 0.029* | |
| C6 | 0.36121 (6) | 0.0141 (2) | 0.37817 (13) | 0.0275 (4) | |
| H6 | 0.3388 | −0.0391 | 0.3207 | 0.033* | |
| C7 | 0.34626 (6) | 0.0292 (2) | 0.47829 (13) | 0.0273 (4) | |
| H7 | 0.3136 | −0.0118 | 0.4873 | 0.033* | |
| C8 | 0.37807 (5) | 0.1024 (2) | 0.56412 (12) | 0.0234 (3) | |
| H8 | 0.3677 | 0.1117 | 0.6320 | 0.028* | |
| C11 | 0.62782 (5) | 0.49568 (19) | 0.68791 (11) | 0.0188 (3) | |
| C12 | 0.67079 (5) | 0.5438 (2) | 0.64573 (12) | 0.0200 (3) | |
| H12 | 0.6734 | 0.5140 | 0.5740 | 0.024* | |
| C13 | 0.70955 (5) | 0.6348 (2) | 0.70855 (12) | 0.0213 (3) | |
| C14 | 0.70650 (6) | 0.6824 (2) | 0.81238 (12) | 0.0245 (3) | |
| H14 | 0.7333 | 0.7463 | 0.8547 | 0.029* | |
| C15 | 0.66341 (6) | 0.6349 (2) | 0.85358 (12) | 0.0249 (3) | |
| H15 | 0.6607 | 0.6672 | 0.9248 | 0.030* | |
| C16 | 0.62434 (6) | 0.5413 (2) | 0.79260 (12) | 0.0220 (3) | |
| H16 | 0.5953 | 0.5083 | 0.8222 | 0.026* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0200 (2) | 0.0423 (3) | 0.0307 (2) | −0.00460 (15) | 0.00835 (16) | 0.00331 (17) |
| S1 | 0.0228 (2) | 0.0232 (2) | 0.0121 (2) | 0.00280 (14) | 0.00466 (14) | 0.00001 (13) |
| O1 | 0.0263 (6) | 0.0325 (6) | 0.0148 (6) | −0.0019 (4) | 0.0074 (4) | −0.0004 (4) |
| N1 | 0.0188 (6) | 0.0221 (7) | 0.0128 (6) | 0.0014 (5) | 0.0041 (5) | 0.0011 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0199 (7) | 0.0189 (7) | 0.0161 (8) | 0.0046 (5) | 0.0061 (5) | 0.0018 (5) |
| N2 | 0.0183 (6) | 0.0227 (7) | 0.0143 (6) | 0.0024 (5) | 0.0019 (5) | 0.0000 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0207 (7) | 0.0178 (7) | 0.0121 (7) | 0.0050 (5) | 0.0040 (5) | 0.0019 (5) |
| C3 | 0.0203 (7) | 0.0188 (7) | 0.0156 (7) | 0.0042 (6) | 0.0008 (5) | 0.0014 (5) |
| C4 | 0.0220 (7) | 0.0184 (7) | 0.0167 (7) | 0.0044 (6) | 0.0024 (6) | 0.0011 (6) |
| C5 | 0.0322 (8) | 0.0214 (8) | 0.0172 (8) | 0.0050 (6) | −0.0009 (6) | −0.0020 (6) |
| C6 | 0.0301 (8) | 0.0230 (8) | 0.0256 (9) | 0.0001 (6) | −0.0060 (6) | −0.0029 (6) |
| C7 | 0.0233 (8) | 0.0253 (9) | 0.0311 (9) | −0.0005 (6) | −0.0015 (6) | 0.0036 (7) |
| C8 | 0.0225 (7) | 0.0260 (9) | 0.0215 (8) | 0.0026 (6) | 0.0030 (6) | 0.0032 (6) |
| C11 | 0.0220 (7) | 0.0182 (7) | 0.0170 (7) | 0.0033 (6) | 0.0053 (6) | 0.0021 (6) |
| C12 | 0.0220 (7) | 0.0228 (8) | 0.0162 (7) | 0.0034 (6) | 0.0061 (6) | 0.0008 (6) |
| C13 | 0.0198 (7) | 0.0231 (8) | 0.0221 (8) | 0.0012 (6) | 0.0067 (6) | 0.0048 (6) |
| C14 | 0.0280 (8) | 0.0240 (8) | 0.0202 (8) | −0.0027 (6) | 0.0004 (6) | 0.0010 (6) |
| C15 | 0.0337 (8) | 0.0259 (8) | 0.0159 (7) | −0.0028 (7) | 0.0063 (6) | 0.0000 (6) |
| C16 | 0.0267 (8) | 0.0241 (8) | 0.0173 (8) | −0.0004 (6) | 0.0095 (6) | 0.0027 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cl1—C13 | 1.7386 (15) | C6—C7 | 1.397 (2) |
| S1—C4 | 1.7360 (15) | C6—H6 | 0.9500 |
| S1—C2 | 1.7459 (14) | C7—C8 | 1.378 (2) |
| O1—C1 | 1.2216 (18) | C7—H7 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C1 | 1.3696 (18) | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| N1—C2 | 1.3794 (18) | C11—C16 | 1.389 (2) |
| N1—H1 | 0.94 (2) | C11—C12 | 1.392 (2) |
| C1—C11 | 1.491 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.378 (2) |
| N2—C2 | 1.3008 (19) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| N2—C3 | 1.3912 (18) | C13—C14 | 1.380 (2) |
| C3—C8 | 1.395 (2) | C14—C15 | 1.388 (2) |
| C3—C4 | 1.400 (2) | C14—H14 | 0.9500 |
| C4—C5 | 1.397 (2) | C15—C16 | 1.383 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.378 (2) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| C4—S1—C2 | 88.03 (7) | C8—C7—H7 | 119.4 |
| C1—N1—C2 | 122.53 (12) | C6—C7—H7 | 119.4 |
| C1—N1—H1 | 125.0 (11) | C7—C8—C3 | 118.64 (14) |
| C2—N1—H1 | 111.8 (11) | C7—C8—H8 | 120.7 |
| O1—C1—N1 | 120.63 (13) | C3—C8—H8 | 120.7 |
| O1—C1—C11 | 121.46 (13) | C16—C11—C12 | 119.59 (14) |
| N1—C1—C11 | 117.86 (12) | C16—C11—C1 | 124.15 (13) |
| C2—N2—C3 | 109.98 (12) | C12—C11—C1 | 116.03 (12) |
| N2—C2—N1 | 120.53 (13) | C13—C12—C11 | 119.64 (13) |
| N2—C2—S1 | 117.01 (11) | C13—C12—H12 | 120.2 |
| N1—C2—S1 | 122.45 (11) | C11—C12—H12 | 120.2 |
| N2—C3—C8 | 125.53 (13) | C12—C13—C14 | 121.49 (14) |
| N2—C3—C4 | 114.62 (13) | C12—C13—Cl1 | 118.93 (12) |
| C8—C3—C4 | 119.85 (14) | C14—C13—Cl1 | 119.52 (12) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 121.38 (14) | C13—C14—C15 | 118.48 (14) |
| C5—C4—S1 | 128.30 (12) | C13—C14—H14 | 120.8 |
| C3—C4—S1 | 110.32 (11) | C15—C14—H14 | 120.8 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 117.87 (15) | C16—C15—C14 | 121.08 (14) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 121.1 | C16—C15—H15 | 119.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 121.1 | C14—C15—H15 | 119.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 121.06 (14) | C15—C16—C11 | 119.71 (13) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.5 | C15—C16—H16 | 120.1 |
| C7—C6—H6 | 119.5 | C11—C16—H16 | 120.1 |
| C8—C7—C6 | 121.19 (15) | ||
| C2—N1—C1—O1 | −2.6 (2) | C5—C6—C7—C8 | −1.2 (2) |
| C2—N1—C1—C11 | 174.90 (12) | C6—C7—C8—C3 | 0.3 (2) |
| C3—N2—C2—N1 | −177.62 (12) | N2—C3—C8—C7 | −178.45 (14) |
| C3—N2—C2—S1 | 1.43 (16) | C4—C3—C8—C7 | 0.9 (2) |
| C1—N1—C2—N2 | −171.57 (13) | O1—C1—C11—C16 | 165.51 (14) |
| C1—N1—C2—S1 | 9.43 (19) | N1—C1—C11—C16 | −11.9 (2) |
| C4—S1—C2—N2 | −1.80 (12) | O1—C1—C11—C12 | −8.9 (2) |
| C4—S1—C2—N1 | 177.23 (12) | N1—C1—C11—C12 | 173.61 (12) |
| C2—N2—C3—C8 | 179.29 (14) | C16—C11—C12—C13 | 0.5 (2) |
| C2—N2—C3—C4 | −0.12 (18) | C1—C11—C12—C13 | 175.22 (13) |
| N2—C3—C4—C5 | 178.08 (13) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | −1.1 (2) |
| C8—C3—C4—C5 | −1.4 (2) | C11—C12—C13—Cl1 | −178.45 (11) |
| N2—C3—C4—S1 | −1.19 (16) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 0.7 (2) |
| C8—C3—C4—S1 | 179.37 (11) | Cl1—C13—C14—C15 | 178.04 (12) |
| C2—S1—C4—C5 | −177.64 (15) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | 0.3 (2) |
| C2—S1—C4—C3 | 1.56 (11) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | −0.8 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.5 (2) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | 0.4 (2) |
| S1—C4—C5—C6 | 179.62 (12) | C1—C11—C16—C15 | −173.83 (14) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | 0.8 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| N1—H1···N2i | 0.94 (2) | 2.02 (2) | 2.9429 (18) | 168.9 (17) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, y, −z+3/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HG2508).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Blessing, R. H. (1995). Acta Cryst. A51, 33–38. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Garden, S. J., Glidewell, C., Low, J. N., Skakle, J. M. S. & Wardell, J. L. (2005). Acta Cryst. C61, o450–o451. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Stoe & Cie (2001). X-AREA Stoe & Cie, Darmstadt, Germany.
- Wardell, J. L., Skakle, J. M. S., Low, J. N. & Glidewell, C. (2005). Acta Cryst. C61, o634–o638. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809016481/hg2508sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809016481/hg2508Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




