Abstract
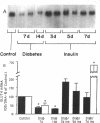
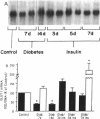
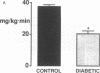
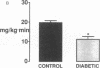
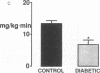
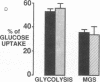
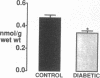
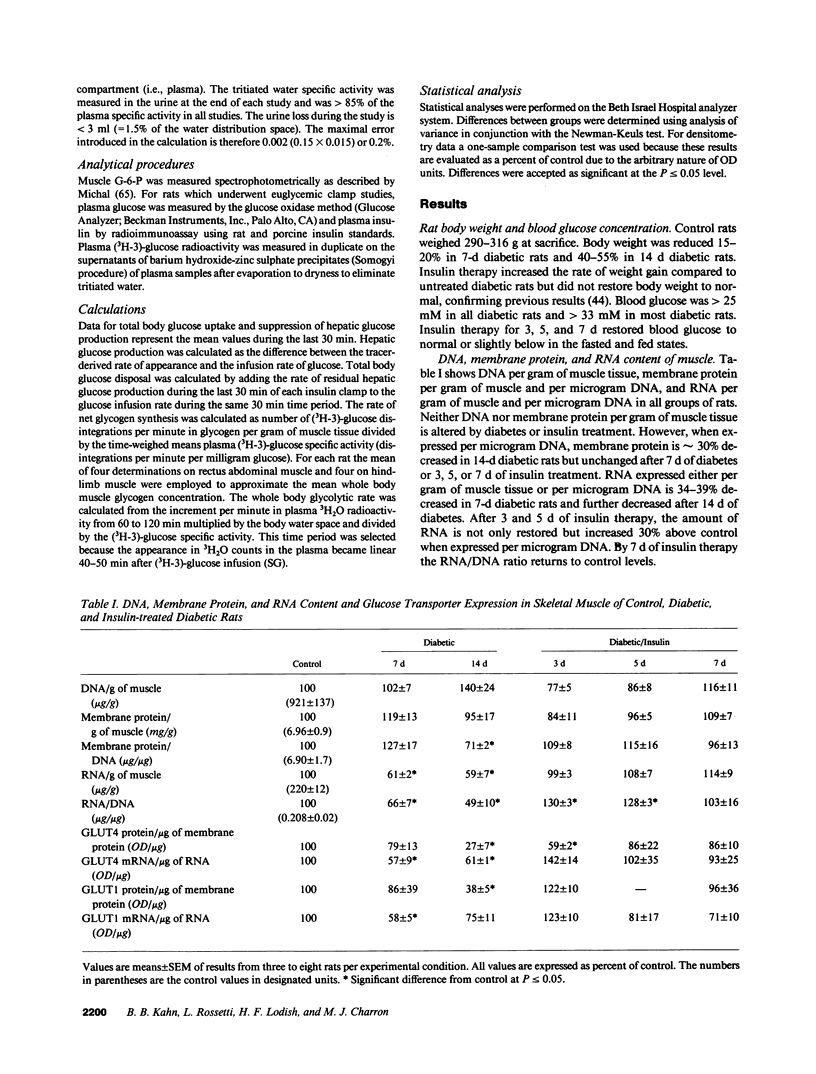
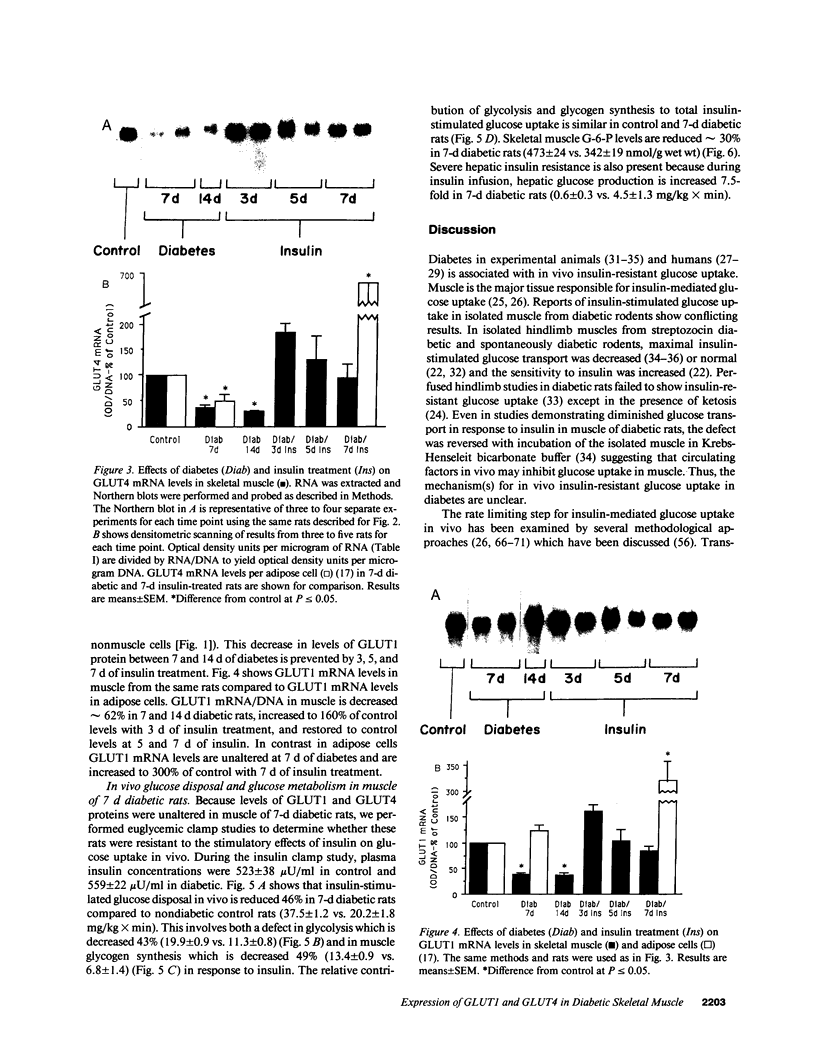
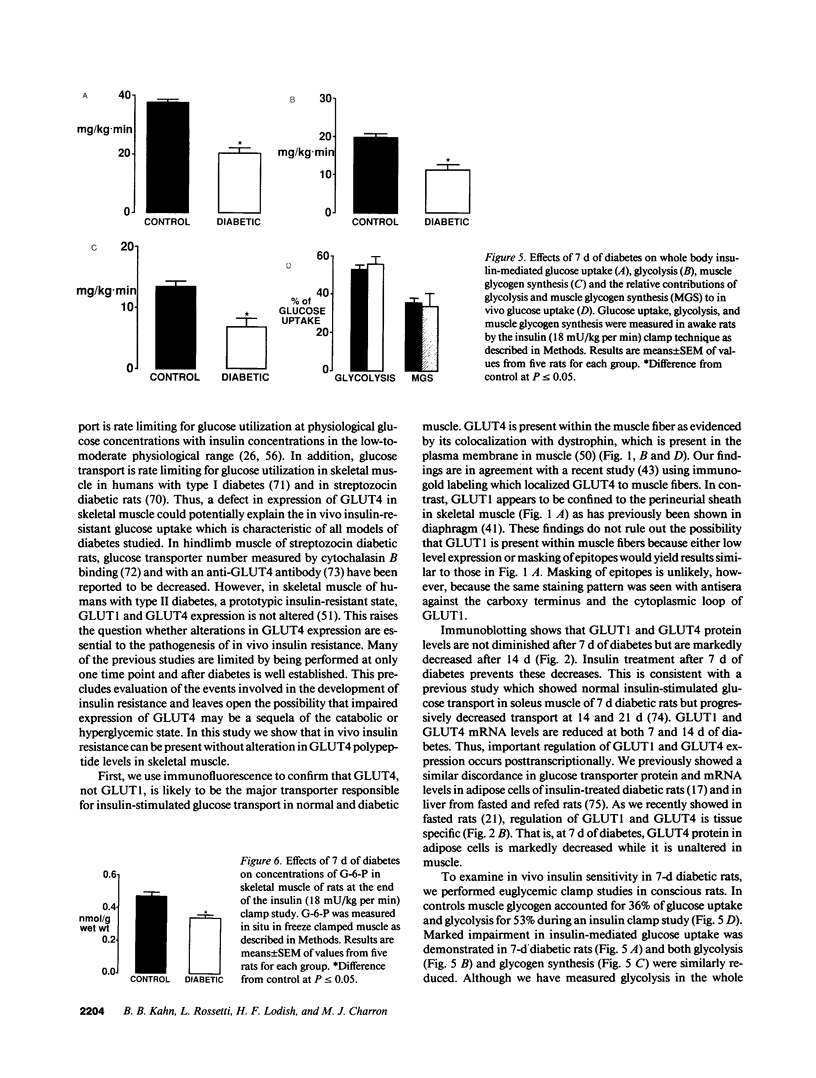
This study was designed to determine whether altered glucose transporter expression is essential for the in vivo insulin-resistant glucose uptake characteristic of streptozocin-induced diabetes. Immunofluorescence in rat skeletal muscle colocalizes GLUT4 with dystrophin, both intrinsic to muscle fibers. In contrast, GLUT1 is extrinsic to muscle fibers, probably in perineurial sheath. Immunoblotting shows that levels of GLUT1 and GLUT4 protein per DNA in hindlimb muscle are unaltered from control levels at 7 d of diabetes but decrease to approximately 20% of control at 14 d of diabetes. This decrease is prevented by insulin treatment. In adipose cells of 7 d diabetic rats, GLUT4 levels are depressed. Thus, GLUT4 undergoes tissue-specific regulation in response to diabetes. GLUT4 and GLUT1 mRNA levels in muscle are decreased 62-70% at both 7 and 14 d of diabetes and are restored by insulin treatment. At 7 d of diabetes, when GLUT4 protein levels in muscle are unaltered, in vivo insulin-stimulated glucose uptake measured by euglycemic clamp is 54% of control. This reflects impairment in both glycogen synthesis and glycolysis and the substrate common to these two pathways, glucose-6-phosphate, is decreased approximately 30% in muscle of diabetic rats. These findings suggest a defect early in the pathway of glucose utilization, probably at the step of glucose transport. Because GLUT1 and GLUT4 levels are unaltered at 7 d of diabetes, reduced glucose uptake in muscle probably reflects impaired glucose transporter translocation or intrinsic activity. Later, at 14 d of diabetes, GLUT1 and GLUT4 protein levels are reduced, suggesting that sequential defects may contribute to the insulin-resistant glucose transport characteristic of diabetes.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amara J. F., Lederkremer G., Lodish H. F. Intracellular degradation of unassembled asialoglycoprotein receptor subunits: a pre-Golgi, nonlysosomal endoproteolytic cleavage. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3315–3324. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnard R. J., Youngren J. F., Kartel D. S., Martin D. A. Effects of streptozotocin-induced diabetes on glucose transport in skeletal muscle. Endocrinology. 1990 Apr;126(4):1921–1926. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-4-1921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell G. I., Kayano T., Buse J. B., Burant C. F., Takeda J., Lin D., Fukumoto H., Seino S. Molecular biology of mammalian glucose transporters. Diabetes Care. 1990 Mar;13(3):198–208. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.3.198. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger J., Biswas C., Vicario P. P., Strout H. V., Saperstein R., Pilch P. F. Decreased expression of the insulin-responsive glucose transporter in diabetes and fasting. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):70–72. doi: 10.1038/340070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum M. J., Haspel H. C., Rosen O. M. Cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding the rat brain glucose-transporter protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5784–5788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum M. J. Identification of a novel gene encoding an insulin-responsive glucose transporter protein. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):305–315. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90968-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff J., Lodish H. F. Two asialoglycoprotein receptor polypeptides in human hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11825–11832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boström M., Nie Z., Goertz G., Henriksson J., Wallberg-Henriksson H. Indirect effect of catecholamines on development of insulin resistance in skeletal muscle from diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1989 Jul;38(7):906–910. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.7.906. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron M. J., Brosius F. C., 3rd, Alper S. L., Lodish H. F. A glucose transport protein expressed predominately in insulin-responsive tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2535–2539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charron M. J., Kahn B. B. Divergent molecular mechanisms for insulin-resistant glucose transport in muscle and adipose cells in vivo. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):7994–8000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiasson J. L., Germain L., Srivastava A. K., Dupuis P. Hormonal regulation of glucose transport in contracting skeletal muscle from normal and diabetic rats. Metabolism. 1984 Jul;33(7):617–621. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(84)90059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Hendler R., Simonson D. Insulin resistance is a prominent feature of insulin-dependent diabetes. Diabetes. 1982 Sep;31(9):795–801. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.9.795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Jacot E., Jequier E., Maeder E., Wahren J., Felber J. P. The effect of insulin on the disposal of intravenous glucose. Results from indirect calorimetry and hepatic and femoral venous catheterization. Diabetes. 1981 Dec;30(12):1000–1007. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.12.1000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohm G. L., Tapscott E. B., Pories W. J., Dabbs D. J., Flickinger E. G., Meelheim D., Fushiki T., Atkinson S. M., Elton C. W., Caro J. F. An in vitro human muscle preparation suitable for metabolic studies. Decreased insulin stimulation of glucose transport in muscle from morbidly obese and diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1988 Aug;82(2):486–494. doi: 10.1172/JCI113622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrannini E., Smith J. D., Cobelli C., Toffolo G., Pilo A., DeFronzo R. A. Effect of insulin on the distribution and disposition of glucose in man. J Clin Invest. 1985 Jul;76(1):357–364. doi: 10.1172/JCI111969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foley J. E., Huecksteadt T. P. Glucose 6-phosphate effects on deoxyglucose, glucose and methylglucose transport in rat adipocytes. Evidence for intracellular regulation of sugar transport by glucose metabolites. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Nov 13;805(3):313–316. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(84)90088-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froehner S. C., Davies A., Baldwin S. A., Lienhard G. E. The blood-nerve barrier is rich in glucose transporter. J Neurocytol. 1988 Apr;17(2):173–178. doi: 10.1007/BF01674204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumoto H., Kayano T., Buse J. B., Edwards Y., Pilch P. F., Bell G. I., Seino S. Cloning and characterization of the major insulin-responsive glucose transporter expressed in human skeletal muscle and other insulin-responsive tissues. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):7776–7779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukumoto H., Seino S., Imura H., Seino Y., Eddy R. L., Fukushima Y., Byers M. G., Shows T. B., Bell G. I. Sequence, tissue distribution, and chromosomal localization of mRNA encoding a human glucose transporter-like protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(15):5434–5438. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.15.5434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia A. M., Lodish H. F. Lysine 539 of human band 3 is not essential for ion transport or inhibition by stilbene disulfonates. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 25;264(33):19607–19613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garvey W. T., Huecksteadt T. P., Birnbaum M. J. Pretranslational suppression of an insulin-responsive glucose transporter in rats with diabetes mellitus. Science. 1989 Jul 7;245(4913):60–63. doi: 10.1126/science.2662408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman M. N., Berger M., Ruderman N. B. Glucose metabolism in rat skeletal muscle at rest. Effect of starvation, diabetes, ketone bodies and free fatty acids. Diabetes. 1974 Nov;23(11):881–888. doi: 10.2337/diab.23.11.881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman I., Mandarino L., Verdonk C., Rizza R., Gerich J. Insulin increases the maximum velocity for glucose uptake without altering the Michaelis constant in man. Evidence that insulin increases glucose uptake merely by providing additional transport sites. J Clin Invest. 1982 Dec;70(6):1310–1314. doi: 10.1172/JCI110731. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N., Alexander H., Olson A., Alexander S., Shinnick T. M., Sutcliffe J. G., Lerner R. A. Immunogenic structure of the influenza virus hemagglutinin. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90202-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossbard L., Schimke R. T. Multiple hexokinases of rat tissues. Purification and comparison of soluble forms. J Biol Chem. 1966 Aug 10;241(15):3546–3560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen I. L., Cryer P. E., Rizza R. A. Comparison of insulin-mediated and glucose-mediated glucose disposal in patients with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and in nondiabetic subjects. Diabetes. 1985 Aug;34(8):751–755. doi: 10.2337/diab.34.8.751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman E. P., Beggs A. H., Koenig M., Kunkel L. M., Angelini C. Cross-reactive protein in Duchenne muscle. Lancet. 1989 Nov 18;2(8673):1211–1212. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91812-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostetler K. Y., Landau B. R. Estimation of the pentose cycle contribution to glucose metabolism in tissue in vivo. Biochemistry. 1967 Oct;6(10):2961–2964. doi: 10.1021/bi00862a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Strube M., Mueckler M. Molecular cloning and characterization of an insulin-regulatable glucose transporter. Nature. 1989 Mar 2;338(6210):83–87. doi: 10.1038/338083a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaestner K. H., Christy R. J., McLenithan J. C., Braiterman L. T., Cornelius P., Pekala P. H., Lane M. D. Sequence, tissue distribution, and differential expression of mRNA for a putative insulin-responsive glucose transporter in mouse 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3150–3154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B. B., Charron M. J., Lodish H. F., Cushman S. W., Flier J. S. Differential regulation of two glucose transporters in adipose cells from diabetic and insulin-treated diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1989 Aug;84(2):404–411. doi: 10.1172/JCI114180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B. B., Cushman S. W., Flier J. S. Regulation of glucose transporter-specific mRNA levels in rat adipose cells with fasting and refeeding. Implications for in vivo control of glucose transporter number. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jan;83(1):199–204. doi: 10.1172/JCI113859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B. B., Cushman S. W. Mechanism for markedly hyperresponsive insulin-stimulated glucose transport activity in adipose cells from insulin-treated streptozotocin diabetic rats. Evidence for increased glucose transporter intrinsic activity. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 15;262(11):5118–5124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B. B., Flier J. S. Regulation of glucose-transporter gene expression in vitro and in vivo. Diabetes Care. 1990 Jun;13(6):548–564. doi: 10.2337/diacare.13.6.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn B. B., Shulman G. I., DeFronzo R. A., Cushman S. W., Rossetti L. Normalization of blood glucose in diabetic rats with phlorizin treatment reverses insulin-resistant glucose transport in adipose cells without restoring glucose transporter gene expression. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):561–570. doi: 10.1172/JCI115031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlander S., Roovete A., Vranić M., Efendić S. Glucose and fructose 6-phosphate cycle in humans. Am J Physiol. 1986 Nov;251(5 Pt 1):E530–E536. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.251.5.E530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz A., Nyomba B. L., Bogardus C. No accumulation of glucose in human skeletal muscle during euglycemic hyperinsulinemia. Am J Physiol. 1988 Dec;255(6 Pt 1):E942–E945. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1988.255.6.E942. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kayano T., Fukumoto H., Eddy R. L., Fan Y. S., Byers M. G., Shows T. B., Bell G. I. Evidence for a family of human glucose transporter-like proteins. Sequence and gene localization of a protein expressed in fetal skeletal muscle and other tissues. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 25;263(30):15245–15248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klip A., Ramlal T., Young D. A., Holloszy J. O. Insulin-induced translocation of glucose transporters in rat hindlimb muscles. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 16;224(1):224–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80452-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubo K., Foley J. E. Rate-limiting steps for insulin-mediated glucose uptake into perfused rat hindlimb. Am J Physiol. 1986 Jan;250(1 Pt 1):E100–E102. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.250.1.E100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca C., Paigen K. A simple, rapid, and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Marchand-Brustel Y., Freychet P. Effect of fasting and streptozotocin diabetes on insulin binding and action in the isolated mouse soleus muscle. J Clin Invest. 1979 Nov;64(5):1505–1515. doi: 10.1172/JCI109609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maegawa H., Kobayashi M., Watanabe N., Ishibashi O., Takata Y., Kitamura E., Shigeta Y. Effect of duration of diabetic state on insulin action in isolated rat soleus muscles. Metabolism. 1986 Jun;35(6):499–504. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(86)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandarino L. J., Madar Z., Kolterman O. G., Bell J. M., Olefsky J. M. Adipocyte glycogen synthase and pyruvate dehydrogenase in obese and type II diabetic subjects. Am J Physiol. 1986 Oct;251(4 Pt 1):E489–E496. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.251.4.E489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueckler M., Caruso C., Baldwin S. A., Panico M., Blench I., Morris H. R., Allard W. J., Lienhard G. E., Lodish H. F. Sequence and structure of a human glucose transporter. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):941–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3839598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka Y., Asano T., Shibasaki Y., Kasuga M., Kanazawa Y., Takaku F. Studies with antipeptide antibody suggest the presence of at least two types of glucose transporter in rat brain and adipocyte. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13432–13439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J. M., Kolterman O. G., Scarlett J. A. Insulin action and resistance in obesity and noninsulin-dependent type II diabetes mellitus. Am J Physiol. 1982 Jul;243(1):E15–E30. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1982.243.1.E15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen O., Bak J. F., Andersen P. H., Lund S., Moller D. E., Flier J. S., Kahn B. B. Evidence against altered expression of GLUT1 or GLUT4 in skeletal muscle of patients with obesity or NIDDM. Diabetes. 1990 Jul;39(7):865–870. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.7.865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramlal T., Rastogi S., Vranic M., Klip A. Decrease in glucose transporter number in skeletal muscle of mildly diabetic (streptozotocin-treated) rats. Endocrinology. 1989 Aug;125(2):890–897. doi: 10.1210/endo-125-2-890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossetti L., Giaccari A. Relative contribution of glycogen synthesis and glycolysis to insulin-mediated glucose uptake. A dose-response euglycemic clamp study in normal and diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1785–1792. doi: 10.1172/JCI114636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossetti L., Lauglin M. R. Correction of chronic hyperglycemia with vanadate, but not with phlorizin, normalizes in vivo glycogen repletion and in vitro glycogen synthase activity in diabetic skeletal muscle. J Clin Invest. 1989 Sep;84(3):892–899. doi: 10.1172/JCI114250. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossetti L. Normalization of insulin sensitivity with lithium in diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1989 May;38(5):648–652. doi: 10.2337/diab.38.5.648. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossetti L., Rothman D. L., DeFronzo R. A., Shulman G. I. Effect of dietary protein on in vivo insulin action and liver glycogen repletion. Am J Physiol. 1989 Aug;257(2 Pt 1):E212–E219. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1989.257.2.E212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossetti L., Smith D., Shulman G. I., Papachristou D., DeFronzo R. A. Correction of hyperglycemia with phlorizin normalizes tissue sensitivity to insulin in diabetic rats. J Clin Invest. 1987 May;79(5):1510–1515. doi: 10.1172/JCI112981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruderman N. B., Goodman M. N., Berger M., Hagg S. Effect of starvation on muscle glucose metabolism: studies with the isolated perfused rat hindquarter. Fed Proc. 1977 Feb;36(2):171–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman G. I., Rossetti L., Rothman D. L., Blair J. B., Smith D. Quantitative analysis of glycogen repletion by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the conscious rat. J Clin Invest. 1987 Aug;80(2):387–393. doi: 10.1172/JCI113084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Cushman S. W. Hormonal regulation of mammalian glucose transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1059–1089. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Sonne O. A simple, rapid, and sensitive method for measuring protein concentration in subcellular membrane fractions prepared by sucrose density ultracentrifugation. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 15;119(2):424–427. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90608-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sivitz W. I., DeSautel S. L., Kayano T., Bell G. I., Pessin J. E. Regulation of glucose transporter messenger RNA in insulin-deficient states. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):72–74. doi: 10.1038/340072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slot J. W., Moxley R., Geuze H. J., James D. E. No evidence for expression of the insulin-regulatable glucose transporter in endothelial cells. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):369–371. doi: 10.1038/346369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spence J. T., Koudelka A. P. Pathway of glycogen synthesis from glucose in hepatocytes maintained in primary culture. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1521–1526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strout H. V., Vicario P. P., Biswas C., Saperstein R., Brady E. J., Pilch P. F., Berger J. Vanadate treatment of streptozotocin diabetic rats restores expression of the insulin-responsive glucose transporter in skeletal muscle. Endocrinology. 1990 May;126(5):2728–2732. doi: 10.1210/endo-126-5-2728. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Flier J. S., Lodish H. F., Kahn B. B. Differential regulation of two glucose transporters in rat liver by fasting and refeeding and by diabetes and insulin treatment. Diabetes. 1990 Jun;39(6):712–719. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.6.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorens B., Sarkar H. K., Kaback H. R., Lodish H. F. Cloning and functional expression in bacteria of a novel glucose transporter present in liver, intestine, kidney, and beta-pancreatic islet cells. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):281–290. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vilaró S., Palacín M., Pilch P. F., Testar X., Zorzano A. Expression of an insulin-regulatable glucose carrier in muscle and fat endothelial cells. Nature. 1989 Dec 14;342(6251):798–800. doi: 10.1038/342798a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallberg-Henriksson H., Zetan N., Henriksson J. Reversibility of decreased insulin-stimulated glucose transport capacity in diabetic muscle with in vitro incubation. Insulin is not required. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7665–7671. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yki-Järvinen H., Koivisto V. A. Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion therapy decreases insulin resistance in type 1 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1984 Apr;58(4):659–666. doi: 10.1210/jcem-58-4-659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yki-Järvinen H., Sahlin K., Ren J. M., Koivisto V. A. Localization of rate-limiting defect for glucose disposal in skeletal muscle of insulin-resistant type I diabetic patients. Diabetes. 1990 Feb;39(2):157–167. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.2.157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yki-Järvinen H., Young A. A., Lamkin C., Foley J. E. Kinetics of glucose disposal in whole body and across the forearm in man. J Clin Invest. 1987 Jun;79(6):1713–1719. doi: 10.1172/JCI113011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young A. A., Bogardus C., Wolfe-Lopez D., Mott D. M. Muscle glycogen synthesis and disposition of infused glucose in humans with reduced rates of insulin-mediated carbohydrate storage. Diabetes. 1988 Mar;37(3):303–308. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.3.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziel F. H., Venkatesan N., Davidson M. B. Glucose transport is rate limiting for skeletal muscle glucose metabolism in normal and STZ-induced diabetic rats. Diabetes. 1988 Jul;37(7):885–890. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.7.885. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorzano A., Wilkinson W., Kotliar N., Thoidis G., Wadzinkski B. E., Ruoho A. E., Pilch P. F. Insulin-regulated glucose uptake in rat adipocytes is mediated by two transporter isoforms present in at least two vesicle populations. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12358–12363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]