Abstract
In the molecule of the title compound, C19H17NO2, the quinoline ring system is planar [maximum deviation 0.021 (3) Å] and oriented with respect to the phenyl ring at a dihedral angle of 80.44 (4)°. Intramolecular C—H⋯O interactions result in the formation of five- and six-membered rings having planar and envelope conformations, respectively. In the crystal structure, intermolecular C—H⋯O interactions link the molecules into centrosymmetric dimers forming R 2 2(12) ring motifs. π–π contacts between the rings of the quinoline system [centroid-to-centroid distance = 3.812 (1) Å] may further stabilize the structure. Two weak C—H⋯π interactions are also found.
Related literature
For general background, see: Doube et al. (1998 ▶). For ring-motifs, see: Bernstein et al. (1995 ▶). For bond-length data, see: Allen et al. (1987 ▶).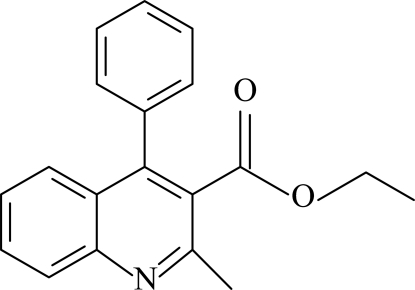
Experimental
Crystal data
C19H17NO2
M r = 291.34
Triclinic,

a = 9.0282 (10) Å
b = 9.362 (1) Å
c = 10.7258 (10) Å
α = 69.765 (8)°
β = 66.733 (8)°
γ = 70.605 (8)°
V = 761.08 (15) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.08 mm−1
T = 120 K
0.35 × 0.32 × 0.25 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: none
8164 measured reflections
3995 independent reflections
3410 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.044
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.065
wR(F 2) = 0.194
S = 1.09
3995 reflections
199 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.33 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.35 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 1998 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 1998 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶) and PLATON.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809018625/hk2681sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809018625/hk2681Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C16—H16A⋯O1 | 0.97 | 2.32 | 2.711 (3) | 103 |
| C19—H19B⋯O2i | 0.96 | 2.52 | 3.374 (3) | 147 |
| C19—H19C⋯O2 | 0.96 | 2.59 | 3.212 (3) | 122 |
| C12—H12⋯Cg2ii | 0.93 | 2.95 | 3.750 (3) | 145 |
| C17—H17C⋯Cg3iii | 0.96 | 2.97 | 3.883 (3) | 160 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  . Cg2 and Cg3 are the centroids of rings C1–C6 and C8–C13, respectively.
. Cg2 and Cg3 are the centroids of rings C1–C6 and C8–C13, respectively.
Acknowledgments
The author is grateful to the Islamic Azad University, Dorood Branch, for financial support.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The quinoline moiety is probably the most well known heterocycle, a common and important feature of a variety of natural products and medicinal agents. They have emerged as antimalarial, antiasthmatic, anti-inflamatory, antibacterial, antihypertensive and tyrosine kinase PDGF-RTK inhibiting agents (Doube et al., 1998). Moreover, polyquinolines are found to undergo hierarchical self-assembly into a variety of nano and meso structures with enhanced electronic and photonic functions. We report herein the synthesis and crystal structure of the title compound.
In the molecule of the title compound (Fig. 1), the bond lengths (Allen et al., 1987) and angles are within normal ranges. The quinoline ring system A (N1/C1–C7/C14/C18) is planar with a maximum deviaton of -0.021 (3) Å for atom C18, and oriented with respect to the phenyl ring B (C8–C13) at a dihedral angle of A/B = 80.44 (4)°. Intramolecular C—H···O interactions result in the formations of five- and six-membered rings C (O1/O2/C15/C16/H16A) and D (O2/C14/C15/C18/C19/H19C). Ring C is planar, while ring D adopts envelope conformation, with atom O2 displaced by -1.166 (4) Å from the plane of the other ring atoms.
In the crystal structure, intermolecular C—H···O interactions (Table 1) link the molecules into centrosymmetric dimers forming R22(12) ring motifs (Fig. 2) (Bernstein et al., 1995), in which they may be effective in the stabilization of the structure. The π–π contact between the rings of the quinoline ring system, Cg1···Cg2i [symmetry code: (i) 1 - x, -1 - y, 1 - z, where Cg1 and Cg2 are centroids of the rings (N1/C1/C6/C7/C14/C18) and (C1–C6), respectively] may further stabilize the structure, with centroid-centroid distance of 3.812 (1) Å. There also exist two weak C—H···π interactions (Table 1).
Experimental
For the preparation of the title compound, a mixture of ethyl acetoacetate (0.13 g, 1 mmol), (2-aminophenyl)(phenyl)methanone (0.20 g, 1 mmol) and p-toluene sulfonic acid (0.1 g, 5.8 mmol) in water (5 ml) was stirred at reflux for 4 h. After completion of reaction (monitored by TLC) the reaction mixture was filtered and the precipitate washed with water (15 ml) and then recrystallized from EtOH/water (1:2) to afford the pure product (yield; 75%, 0.218 g).
Refinement
H atoms were positioned geometrically, with C—H = 0.93, 0.97 and 0.96 Å for aromatic, methylene and methyl H, respectively, and constrained to ride on their parent atoms, with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title molecule, with the atom-numbering scheme. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dotted lines.
Fig. 2.
A partial packing diagram of the title compound. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| C19H17NO2 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 291.34 | F(000) = 308 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.271 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 9.0282 (10) Å | Cell parameters from 1548 reflections |
| b = 9.362 (1) Å | θ = 2.4–29.2° |
| c = 10.7258 (10) Å | µ = 0.08 mm−1 |
| α = 69.765 (8)° | T = 120 K |
| β = 66.733 (8)° | Block, colourless |
| γ = 70.605 (8)° | 0.35 × 0.32 × 0.25 mm |
| V = 761.08 (15) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer | Rint = 0.044 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 29.2°, θmin = 2.4° |
| 8164 measured reflections | h = −12→12 |
| 3995 independent reflections | k = −12→12 |
| 3410 reflections with I > 2σ(I) | l = −13→14 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | 0 restraints |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.065 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0955P)2 + 0.1587P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.194 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.01 |
| S = 1.09 | Δρmax = 0.33 e Å−3 |
| 3995 reflections | Δρmin = −0.35 e Å−3 |
| 199 parameters |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.6903 (3) | −0.70878 (17) | 0.11893 (14) | 0.0879 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.6965 (2) | −0.95151 (14) | 0.24871 (13) | 0.0696 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.44256 (15) | −0.71135 (15) | 0.57975 (13) | 0.0470 (3) | |
| C1 | 0.56342 (18) | −0.68228 (16) | 0.60840 (15) | 0.0438 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.5192 (2) | −0.6418 (2) | 0.73600 (17) | 0.0551 (4) | |
| H2 | 0.4104 | −0.6328 | 0.7953 | 0.066* | |
| C3 | 0.6347 (3) | −0.6159 (2) | 0.77284 (19) | 0.0622 (5) | |
| H3 | 0.6046 | −0.5907 | 0.8575 | 0.075* | |
| C4 | 0.7988 (2) | −0.6273 (2) | 0.6834 (2) | 0.0615 (4) | |
| H4 | 0.8767 | −0.6096 | 0.7094 | 0.074* | |
| C5 | 0.8456 (2) | −0.66413 (19) | 0.55808 (18) | 0.0523 (4) | |
| H5 | 0.9545 | −0.6702 | 0.4994 | 0.063* | |
| C6 | 0.72854 (17) | −0.69295 (15) | 0.51769 (15) | 0.0420 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.76870 (17) | −0.73393 (15) | 0.38991 (14) | 0.0402 (3) | |
| C8 | 0.94211 (17) | −0.75008 (16) | 0.29187 (15) | 0.0423 (3) | |
| C9 | 1.0023 (2) | −0.61966 (19) | 0.20110 (18) | 0.0546 (4) | |
| H9 | 0.9326 | −0.5206 | 0.1985 | 0.066* | |
| C10 | 1.1658 (2) | −0.6361 (2) | 0.11427 (19) | 0.0619 (4) | |
| H10 | 1.2049 | −0.5483 | 0.0535 | 0.074* | |
| C11 | 1.2697 (2) | −0.7819 (2) | 0.11829 (18) | 0.0612 (5) | |
| H11 | 1.3796 | −0.7925 | 0.0614 | 0.073* | |
| C12 | 1.2116 (2) | −0.9125 (2) | 0.20633 (19) | 0.0622 (4) | |
| H12 | 1.2818 | −1.0112 | 0.2081 | 0.075* | |
| C13 | 1.0480 (2) | −0.89658 (18) | 0.29248 (17) | 0.0526 (4) | |
| H13 | 1.009 | −0.9851 | 0.3512 | 0.063* | |
| C14 | 0.64476 (17) | −0.76184 (16) | 0.36344 (14) | 0.0410 (3) | |
| C15 | 0.67936 (18) | −0.80112 (17) | 0.22859 (15) | 0.0451 (3) | |
| C16 | 0.7336 (3) | −1.0130 (2) | 0.12943 (19) | 0.0640 (5) | |
| H16A | 0.7594 | −0.9331 | 0.0428 | 0.077* | |
| H16B | 0.6389 | −1.0461 | 0.1365 | 0.077* | |
| C17 | 0.8780 (3) | −1.1482 (3) | 0.1307 (2) | 0.0694 (5) | |
| H17A | 0.8511 | −1.2265 | 0.2168 | 0.083* | |
| H17B | 0.9711 | −1.114 | 0.1231 | 0.083* | |
| H17C | 0.905 | −1.1913 | 0.0532 | 0.083* | |
| C18 | 0.48148 (18) | −0.75086 (17) | 0.46289 (15) | 0.0441 (3) | |
| C19 | 0.3470 (2) | −0.7867 (2) | 0.43737 (19) | 0.0577 (4) | |
| H19A | 0.2567 | −0.6965 | 0.4356 | 0.069* | |
| H19B | 0.3086 | −0.8727 | 0.511 | 0.069* | |
| H19C | 0.3897 | −0.8138 | 0.3491 | 0.069* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.1583 (17) | 0.0598 (8) | 0.0463 (7) | −0.0329 (9) | −0.0344 (9) | −0.0036 (6) |
| O2 | 0.1184 (12) | 0.0481 (6) | 0.0487 (6) | −0.0242 (7) | −0.0284 (7) | −0.0121 (5) |
| N1 | 0.0443 (6) | 0.0499 (7) | 0.0454 (6) | −0.0124 (5) | −0.0135 (5) | −0.0091 (5) |
| C1 | 0.0471 (7) | 0.0398 (6) | 0.0437 (7) | −0.0072 (5) | −0.0161 (6) | −0.0096 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0607 (9) | 0.0556 (9) | 0.0460 (8) | −0.0086 (7) | −0.0143 (7) | −0.0166 (6) |
| C3 | 0.0786 (12) | 0.0623 (10) | 0.0558 (9) | −0.0085 (8) | −0.0288 (9) | −0.0248 (8) |
| C4 | 0.0684 (11) | 0.0631 (10) | 0.0709 (11) | −0.0092 (8) | −0.0375 (9) | −0.0251 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0494 (8) | 0.0540 (8) | 0.0629 (9) | −0.0071 (6) | −0.0261 (7) | −0.0203 (7) |
| C6 | 0.0437 (7) | 0.0376 (6) | 0.0472 (7) | −0.0052 (5) | −0.0191 (6) | −0.0117 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0408 (6) | 0.0364 (6) | 0.0433 (7) | −0.0082 (5) | −0.0146 (5) | −0.0087 (5) |
| C8 | 0.0411 (6) | 0.0440 (7) | 0.0442 (7) | −0.0097 (5) | −0.0151 (5) | −0.0119 (5) |
| C9 | 0.0563 (9) | 0.0464 (8) | 0.0594 (9) | −0.0154 (6) | −0.0170 (7) | −0.0090 (6) |
| C10 | 0.0627 (10) | 0.0744 (11) | 0.0509 (9) | −0.0347 (9) | −0.0119 (7) | −0.0071 (8) |
| C11 | 0.0454 (8) | 0.0894 (13) | 0.0472 (8) | −0.0166 (8) | −0.0103 (6) | −0.0190 (8) |
| C12 | 0.0497 (9) | 0.0676 (10) | 0.0589 (9) | 0.0023 (7) | −0.0163 (7) | −0.0192 (8) |
| C13 | 0.0499 (8) | 0.0455 (7) | 0.0544 (8) | −0.0070 (6) | −0.0147 (6) | −0.0086 (6) |
| C14 | 0.0442 (7) | 0.0394 (6) | 0.0405 (6) | −0.0110 (5) | −0.0151 (5) | −0.0075 (5) |
| C15 | 0.0476 (7) | 0.0471 (7) | 0.0435 (7) | −0.0142 (6) | −0.0163 (6) | −0.0089 (5) |
| C16 | 0.0854 (13) | 0.0621 (10) | 0.0558 (9) | −0.0166 (9) | −0.0259 (9) | −0.0238 (8) |
| C17 | 0.0650 (11) | 0.0801 (13) | 0.0642 (11) | −0.0162 (9) | −0.0143 (9) | −0.0266 (9) |
| C18 | 0.0433 (7) | 0.0452 (7) | 0.0439 (7) | −0.0124 (5) | −0.0162 (5) | −0.0060 (5) |
| C19 | 0.0497 (8) | 0.0728 (11) | 0.0576 (9) | −0.0221 (8) | −0.0213 (7) | −0.0115 (8) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—N1 | 1.3708 (19) | C11—H11 | 0.93 |
| C1—C6 | 1.415 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.388 (2) |
| C1—C2 | 1.415 (2) | C12—H12 | 0.93 |
| C2—C3 | 1.365 (3) | C13—H13 | 0.93 |
| C2—H2 | 0.93 | C14—C18 | 1.433 (2) |
| C3—C4 | 1.403 (3) | C14—C15 | 1.5031 (19) |
| C3—H3 | 0.93 | C15—O1 | 1.1841 (19) |
| C4—C5 | 1.371 (2) | C15—O2 | 1.3132 (19) |
| C4—H4 | 0.93 | C16—O2 | 1.457 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.417 (2) | C16—C17 | 1.485 (3) |
| C5—H5 | 0.93 | C16—H16A | 0.97 |
| C6—C7 | 1.4268 (19) | C16—H16B | 0.97 |
| C7—C14 | 1.3775 (19) | C17—H17A | 0.96 |
| C7—C8 | 1.4939 (19) | C17—H17B | 0.96 |
| C8—C13 | 1.387 (2) | C17—H17C | 0.96 |
| C8—C9 | 1.391 (2) | C18—N1 | 1.311 (2) |
| C9—C10 | 1.390 (2) | C18—C19 | 1.503 (2) |
| C9—H9 | 0.93 | C19—H19A | 0.96 |
| C10—C11 | 1.373 (3) | C19—H19B | 0.96 |
| C10—H10 | 0.93 | C19—H19C | 0.96 |
| C11—C12 | 1.378 (3) | ||
| N1—C1—C6 | 123.08 (13) | C11—C12—H12 | 120 |
| N1—C1—C2 | 117.62 (14) | C13—C12—H12 | 120 |
| C6—C1—C2 | 119.30 (14) | C8—C13—C12 | 120.70 (15) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 120.59 (16) | C8—C13—H13 | 119.7 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.7 | C12—C13—H13 | 119.7 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.7 | C7—C14—C18 | 120.33 (13) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 120.20 (16) | C7—C14—C15 | 120.08 (12) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.9 | C18—C14—C15 | 119.58 (12) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.9 | O1—C15—O2 | 124.63 (15) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 120.81 (15) | O1—C15—C14 | 124.46 (14) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.6 | O2—C15—C14 | 110.91 (12) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.6 | O2—C16—C17 | 107.69 (15) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 120.21 (16) | O2—C16—H16A | 110.2 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.9 | C17—C16—H16A | 110.2 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.9 | O2—C16—H16B | 110.2 |
| C1—C6—C5 | 118.89 (13) | C17—C16—H16B | 110.2 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 117.77 (12) | H16A—C16—H16B | 108.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 123.35 (13) | C16—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| C14—C7—C6 | 117.96 (12) | C16—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C14—C7—C8 | 122.12 (12) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 119.89 (12) | C16—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C13—C8—C9 | 118.59 (14) | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C13—C8—C7 | 120.19 (13) | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C9—C8—C7 | 121.21 (13) | N1—C18—C14 | 122.27 (13) |
| C10—C9—C8 | 120.56 (16) | N1—C18—C19 | 117.00 (14) |
| C10—C9—H9 | 119.7 | C14—C18—C19 | 120.73 (13) |
| C8—C9—H9 | 119.7 | C18—C19—H19A | 109.5 |
| C11—C10—C9 | 120.00 (16) | C18—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C11—C10—H10 | 120 | H19A—C19—H19B | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—H10 | 120 | C18—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C10—C11—C12 | 120.20 (16) | H19A—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C10—C11—H11 | 119.9 | H19B—C19—H19C | 109.5 |
| C12—C11—H11 | 119.9 | C18—N1—C1 | 118.58 (13) |
| C11—C12—C13 | 119.94 (16) | C15—O2—C16 | 119.11 (13) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 178.06 (15) | C10—C11—C12—C13 | −0.8 (3) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −1.1 (2) | C9—C8—C13—C12 | 1.3 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.8 (3) | C7—C8—C13—C12 | −177.08 (15) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.1 (3) | C11—C12—C13—C8 | −0.5 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.6 (3) | C6—C7—C14—C18 | −0.5 (2) |
| N1—C1—C6—C5 | −178.56 (13) | C8—C7—C14—C18 | 177.58 (12) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.6 (2) | C6—C7—C14—C15 | 178.33 (11) |
| N1—C1—C6—C7 | 0.9 (2) | C8—C7—C14—C15 | −3.6 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | −179.97 (12) | C7—C14—C15—O1 | −76.8 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.3 (2) | C18—C14—C15—O1 | 102.0 (2) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −179.12 (14) | C7—C14—C15—O2 | 102.89 (16) |
| C1—C6—C7—C14 | −0.56 (19) | C18—C14—C15—O2 | −78.24 (17) |
| C5—C6—C7—C14 | 178.85 (13) | C7—C14—C18—N1 | 1.5 (2) |
| C1—C6—C7—C8 | −178.70 (12) | C15—C14—C18—N1 | −177.41 (13) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 0.7 (2) | C7—C14—C18—C19 | −177.80 (14) |
| C14—C7—C8—C13 | −79.78 (18) | C15—C14—C18—C19 | 3.3 (2) |
| C6—C7—C8—C13 | 98.29 (17) | C14—C18—N1—C1 | −1.1 (2) |
| C14—C7—C8—C9 | 101.92 (17) | C19—C18—N1—C1 | 178.13 (13) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | −80.01 (18) | C6—C1—N1—C18 | 0.0 (2) |
| C13—C8—C9—C10 | −0.8 (2) | C2—C1—N1—C18 | −179.18 (13) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | 177.53 (15) | O1—C15—O2—C16 | 0.8 (3) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | −0.4 (3) | C14—C15—O2—C16 | −178.93 (15) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | 1.2 (3) | C17—C16—O2—C15 | 129.54 (19) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C16—H16A···O1 | 0.97 | 2.32 | 2.711 (3) | 103 |
| C19—H19B···O2i | 0.96 | 2.52 | 3.374 (3) | 147 |
| C19—H19C···O2 | 0.96 | 2.59 | 3.212 (3) | 122 |
| C12—H12···Cg2ii | 0.93 | 2.95 | 3.750 (3) | 145 |
| C17—H17C···Cg3iii | 0.96 | 2.97 | 3.883 (3) | 160 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y−2, −z+1; (ii) −x+2, −y, −z+1; (iii) −x+2, −y, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HK2681).
References
- Allen, F. H., Kennard, O., Watson, D. G., Brammer, L., Orpen, A. G. & Taylor, R. (1987). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 2, pp. S1–19.
- Bernstein, J., Davis, R. E., Shimoni, L. & Chang, N.-L. (1995). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl.34, 1555–1573.
- Bruker (1998). SMART and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Doube, D., Blouin, M., Brideau, C., Chan, C., Desmarais, S., Eithier, D., Falgueyert, J. P., Freisen, R. W., Girrard, M., Girrard, J., Tagari, P. & Yang, R. N. (1998). Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett.8, 1255–1260. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst.30, 565.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst.32, 837–838.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809018625/hk2681sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809018625/hk2681Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




