Abstract
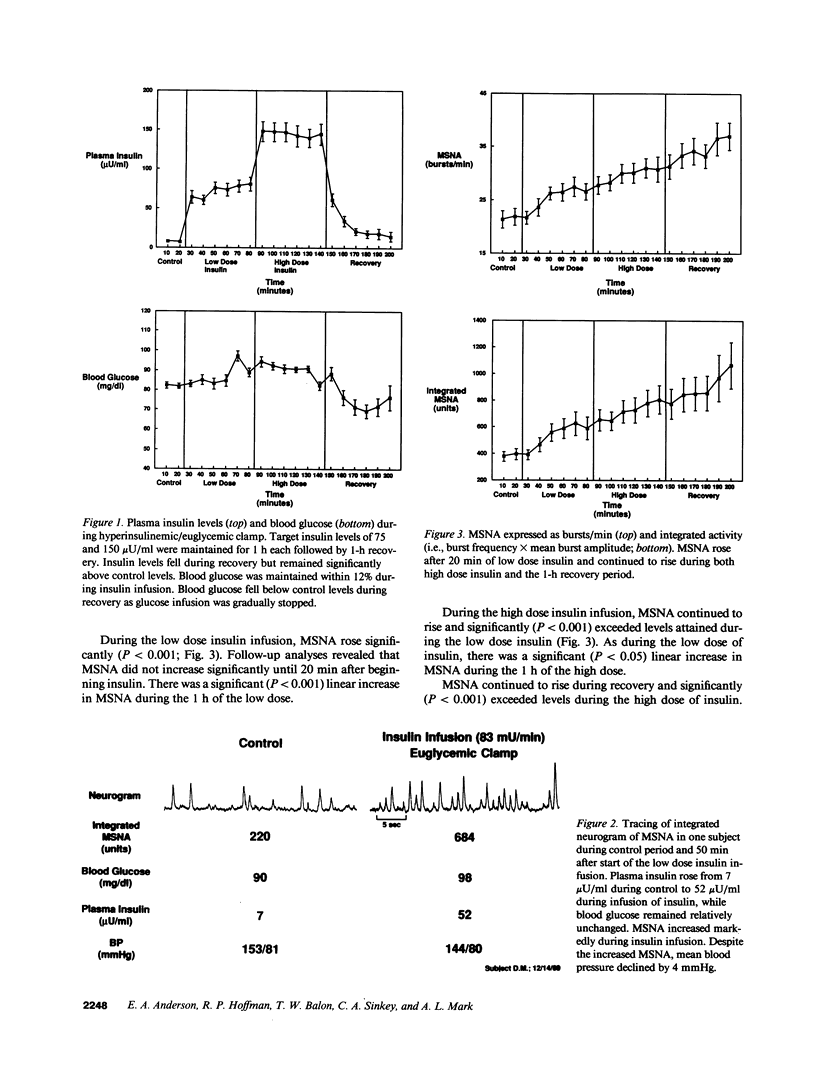
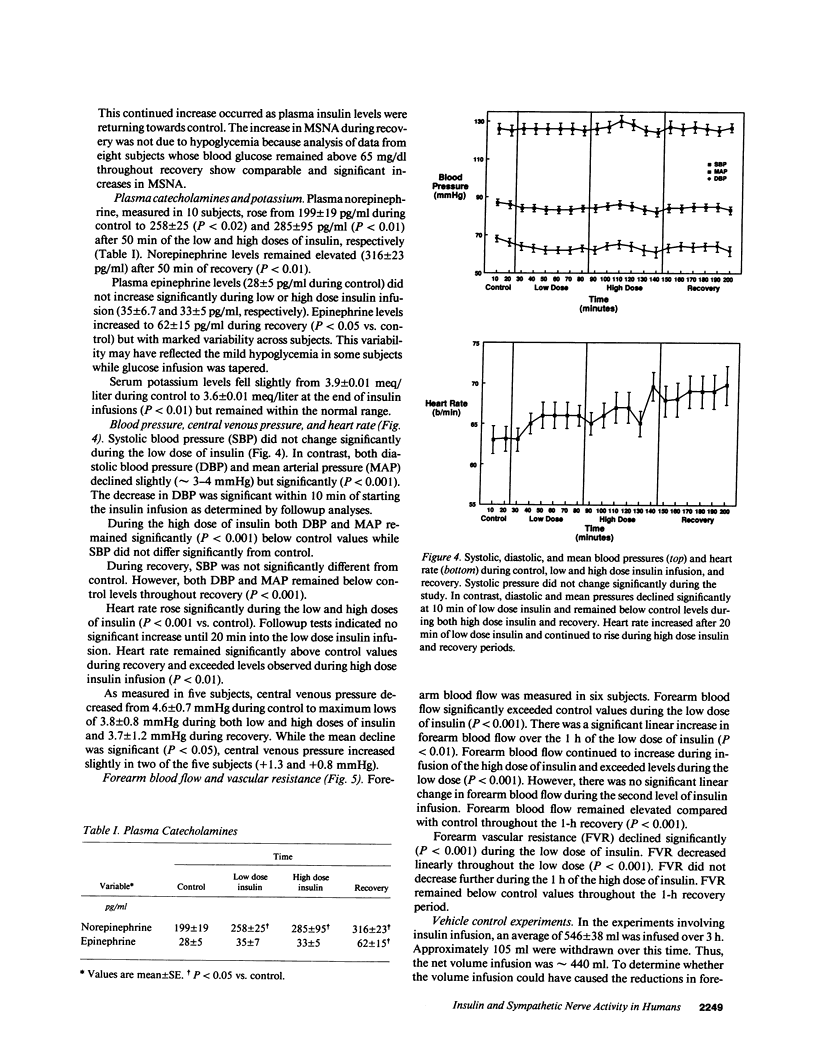
Hyperinsulinemia may contribute to hypertension by increasing sympathetic activity and vascular resistance. We sought to determine if insulin increases central sympathetic neural outflow and vascular resistance in humans. We recorded muscle sympathetic nerve activity (MSNA; microneurography, peroneal nerve), forearm blood flow (plethysmography), heart rate, and blood pressure in 14 normotensive males during 1-h infusions of low (38 mU/m2/min) and high (76 mU/m2/min) doses of insulin while holding blood glucose constant. Plasma insulin rose from 8 +/- 1 microU/ml during control, to 72 +/- 8 and 144 +/- 13 microU/ml during the low and high insulin doses, respectively, and fell to 15 +/- 6 microU/ml 1 h after insulin infusion was stopped. MSNA, which averaged 21.5 +/- 1.5 bursts/min in control, increased significantly (P less than 0.001) during both the low and high doses of insulin (+/- 5.4 and +/- 9.3 bursts/min, respectively) and further increased during 1-h recovery (+15.2 bursts/min). Plasma norepinephrine levels (119 +/- 19 pg/ml during control) rose during both low (258 +/- 25; P less than 0.02) and high (285 +/- 95; P less than 0.01) doses of insulin and recovery (316 +/- 23; P less than 0.01). Plasma epinephrine levels did not change during insulin infusion. Despite the increased MSNA and plasma norepinephrine, there were significant (P less than 0.001) increases in forearm blood flow and decreases in forearm vascular resistance during both doses of insulin. Systolic pressure did not change significantly during infusion of insulin and diastolic pressure fell approximately 4-5 mmHg (P less than 0.01). This study suggests that acute increases in plasma insulin within the physiological range elevate sympathetic neural outflow but produce forearm vasodilation and do not elevate arterial pressure in normal humans.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alexander W. D., Oake R. J. The effect of insulin on vascular reactivity to norepinephrine. Diabetes. 1977 Jul;26(7):611–614. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.7.611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson E. A., Sinkey C. A., Lawton W. J., Mark A. L. Elevated sympathetic nerve activity in borderline hypertensive humans. Evidence from direct intraneural recordings. Hypertension. 1989 Aug;14(2):177–183. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.14.2.177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berne C., Fagius J., Niklasson F. Sympathetic response to oral carbohydrate administration. Evidence from microelectrode nerve recordings. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1403–1409. doi: 10.1172/JCI114313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonora E., Zavaroni I., Alpi O., Pezzarossa A., Bruschi F., Dall'Aglio E., Guerra L., Coscelli C., Butturini U. Relationship between blood pressure and plasma insulin in non-obese and obese non-diabetic subjects. Diabetologia. 1987 Sep;30(9):719–723. doi: 10.1007/BF00296995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisholm D. J., Klassen G. A., Dupre J., Pozefsky T. Interaction of secretin and insulin on human forearm metabolism. Eur J Clin Invest. 1975 Nov 21;5(6):487–494. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1975.tb00481.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen N. J. Acute effects of insulin on cardiovascular function and noradrenaline uptake and release. Diabetologia. 1983 Nov;25(5):377–381. doi: 10.1007/BF00282513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creager M. A., Liang C. S., Coffman J. D. Beta adrenergic-mediated vasodilator response to insulin in the human forearm. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Dec;235(3):709–714. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Orléans-Juste P., Dion S., Mizrahi J., Regoli D. Effects of peptides and non-peptides on isolated arterial smooth muscles: role of endothelium. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Aug 7;114(1):9–21. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Tobin J. D., Andres R. Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am J Physiol. 1979 Sep;237(3):E214–E223. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1979.237.3.E214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delius W., Hagbarth K. E., Hongell A., Wallin B. G. General characteristics of sympathetic activity in human muscle nerves. Acta Physiol Scand. 1972 Jan;84(1):65–81. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1972.tb05158.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards J. G., Tipton C. M. Influences of exogenous insulin on arterial blood pressure measurements of the rat. J Appl Physiol (1985) 1989 Dec;67(6):2335–2342. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1989.67.6.2335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier R. D., Chiueh C. C., Kopin I. J., Knapka J. J., DiPette D., Preuss H. G. Refined carbohydrate increases blood pressure and catecholamine excretion in SHR and WKY. Am J Physiol. 1986 Apr;250(4 Pt 1):E381–E385. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1986.250.4.E381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagbarth K. E., Vallbo A. B. Pulse and respiratory grouping of sympathetic impulses in human muscle-nerves. Acta Physiol Scand. 1968 Sep-Oct;74(1):96–108. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1968.tb04218.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. E., Brands M. W., Kivlighn S. D., Mizelle H. L., Hildebrandt D. A., Gaillard C. A. Chronic hyperinsulinemia and blood pressure. Interaction with catecholamines? Hypertension. 1990 May;15(5):519–527. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.15.5.519. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang I. S., Huang W. C., Wu J. N., Shian L. R., Reaven G. M. Effect of fructose-induced hypertension on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and atrial natriuretic factor. Am J Hypertens. 1989 Jun;2(6 Pt 1):424–427. doi: 10.1093/ajh/2.6.424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insel P. A., Liljenquist J. E., Tobin J. D., Sherwin R. S., Watkins P., Andres R., Berman M. Insulin control of glucose metabolism in man: a new kinetic analysis. J Clin Invest. 1975 May;55(5):1057–1066. doi: 10.1172/JCI108006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laakso M., Edelman S. V., Brechtel G., Baron A. D. Decreased effect of insulin to stimulate skeletal muscle blood flow in obese man. A novel mechanism for insulin resistance. J Clin Invest. 1990 Jun;85(6):1844–1852. doi: 10.1172/JCI114644. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landsberg L. Diet, obesity and hypertension: an hypothesis involving insulin, the sympathetic nervous system, and adaptive thermogenesis. Q J Med. 1986 Dec;61(236):1081–1090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landsberg L., Krieger D. R. Obesity, metabolism, and the sympathetic nervous system. Am J Hypertens. 1989 Mar;2(3 Pt 2):125S–132S. doi: 10.1093/ajh/2.3.125s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas C. P., Estigarribia J. A., Darga L. L., Reaven G. M. Insulin and blood pressure in obesity. Hypertension. 1985 Sep-Oct;7(5):702–706. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.7.5.702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marigliano A., Tedde R., Sechi L. A., Pala A., Pisanu G., Pacifico A. Insulinemia and blood pressure. Relationships in patients with primary and secondary hypertension, and with or without glucose metabolism impairment. Am J Hypertens. 1990 Jul;3(7):521–526. doi: 10.1093/ajh/3.7.521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modan M., Halkin H., Almog S., Lusky A., Eshkol A., Shefi M., Shitrit A., Fuchs Z. Hyperinsulinemia. A link between hypertension obesity and glucose intolerance. J Clin Invest. 1985 Mar;75(3):809–817. doi: 10.1172/JCI111776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natali A., Buzzigoli G., Taddei S., Santoro D., Cerri M., Pedrinelli R., Ferrannini E. Effects of insulin on hemodynamics and metabolism in human forearm. Diabetes. 1990 Apr;39(4):490–500. doi: 10.2337/diab.39.4.490. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PENHOS J. C., KRAHL M. E. Insulin stimulus of leucine incorporation in rat liver protein. Am J Physiol. 1962 Feb;202:249–252. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1962.202.2.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rea R. F., Hamdan M. Baroreflex control of muscle sympathetic nerve activity in borderline hypertension. Circulation. 1990 Sep;82(3):856–862. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.82.3.856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reaven G. M. Banting lecture 1988. Role of insulin resistance in human disease. Diabetes. 1988 Dec;37(12):1595–1607. doi: 10.2337/diab.37.12.1595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe J. W., Young J. B., Minaker K. L., Stevens A. L., Pallotta J., Landsberg L. Effect of insulin and glucose infusions on sympathetic nervous system activity in normal man. Diabetes. 1981 Mar;30(3):219–225. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.3.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi T., Bray G. A. The effect of intrahypothalamic injections of glucose on sympathetic efferent firing rate. Brain Res Bull. 1987 May;18(5):591–595. doi: 10.1016/0361-9230(87)90128-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders J. S., Mark A. L., Ferguson D. W. Evidence for cholinergically mediated vasodilation at the beginning of isometric exercise in humans. Circulation. 1989 Apr;79(4):815–824. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.79.4.815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauter A., Goldstein M., Engel J., Ueta K. Effect of insulin on central catecholamines. Brain Res. 1983 Feb 7;260(2):330–333. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)90691-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen D. C., Shieh S. M., Fuh M. M., Wu D. A., Chen Y. D., Reaven G. M. Resistance to insulin-stimulated-glucose uptake in patients with hypertension. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1988 Mar;66(3):580–583. doi: 10.1210/jcem-66-3-580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Houten M., Posner B. I. Circumventricular organs: receptors and mediators of direct peptide hormone action on brain. Adv Metab Disord. 1983;10:269–289. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-027310-2.50015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. Immunoassay of endogenous plasma insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jul;39:1157–1175. doi: 10.1172/JCI104130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



