Abstract
In the crystal of the title compound, C12H15N5O3·H2O, the component species are linked by N—H⋯N, N—H⋯O, O—H⋯N and O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, forming a three-dimesnional network.
Related literature
For background, see: Czarnik (2008 ▶).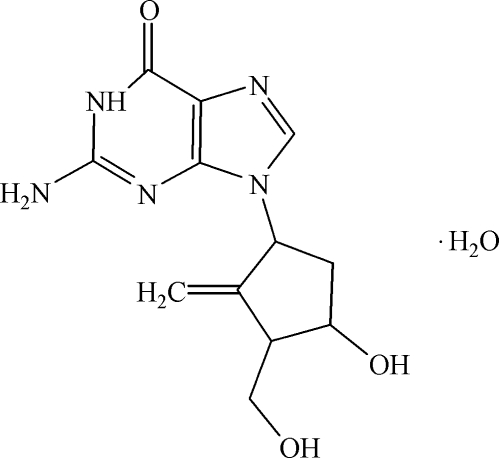
Experimental
Crystal data
C12H15N5O3·H2O
M r = 295.31
Orthorhombic,

a = 6.9986 (10) Å
b = 11.6229 (10) Å
c = 33.932 (3) Å
V = 2760.1 (5) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.11 mm−1
T = 273 K
0.12 × 0.10 × 0.08 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2004 ▶) T min = 0.987, T max = 0.991
6725 measured reflections
1377 independent reflections
1270 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.030
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.030
wR(F 2) = 0.079
S = 1.00
1377 reflections
204 parameters
4 restraints
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.16 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2004 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT-Plus (Bruker, 2004 ▶); data reduction: SAINT-Plus; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809032966/hb5032sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809032966/hb5032Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1⋯N4i | 0.82 | 2.04 | 2.857 (2) | 172 |
| O2—H2A⋯O1Wii | 0.82 | 1.83 | 2.639 (3) | 169 |
| N3—H3B⋯O3iii | 0.86 | 2.24 | 3.039 (3) | 154 |
| N5—H5C⋯N2iii | 0.97 (3) | 1.86 (3) | 2.829 (3) | 177 (3) |
| O1W—H2W⋯O1iv | 0.819 (19) | 2.113 (10) | 2.900 (3) | 161 (3) |
| O1W—H1W⋯O2v | 0.821 (12) | 2.000 (16) | 2.783 (3) | 159 (4) |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  ; (v)
; (v)  .
.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Chinese Academy of Sciences (‘Hundred Talents Program’) and the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (project of ‘973’ plan, No. 2007CB607606).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The research of anti-hepatitis B virus (anti-HBV) drug has long been one of the serious diseases threatening human's health, and thus searching for effective medicines to cure such illness has led to significant interest over the past decades (Czarnik, 2008). In this article, we report the crystal structural characterization of 2-Amino-1,9-dihydro-9-[(1S,3R,4S)-4-hydroxy-3- (hydroxymethyl)-2-methylenecyclopentyl]-6H-purin-6-one.
As shown in figure 1, the asymmetrical unit contains one 2-Amino-1,9-dihydro-9-[(1S,3R,4S)-4-hydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)-2 -methylenecyclopentyl]-6H-purin-6-one and one water molecule. In addition, it is noteworthy that the multipoint hydrogen-bonding links also exist between the hydrogen atoms including N3—H3B···O3, 3.039 (3) Å; O1—H1···N4, 2.861 (2) Å; O2—H2A···O1W, 2.634 (2) Å; O1W—H2W···O1, 2.899 (3) Å; O1W—H1W···O2, 2.786 (3) Å; this may make a contribution to stabilizing the chain structure, shown in figure 2.
Experimental
The reaction was performed in a 25-ml Teflon-lined stainless steel vessel. The powder of 2-amino-1,9-dihydro-9-[(1S,3R,4S)-4-hydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)-2 -methylenecyclopentyl]-6H-purin-6-one (1 mmol) in 5 ml water and 5 ml etanol was heated to 443 K and kept at this temperature for one day. Upon cooling, colourless blocks of (I) were recovered. Anal. Calc. for C12H17N5O4: C 48.76, H 5.08, N 23.70%; Found: 48.68, H 5.05, N 23.66%.
Refinement
Anomalous dispersion was negligible and Friedel pairs were merged before refinement.
All hydrogen atoms bound to carbon were refined using a riding model with C—H = 0.93 (aryl), 0.97 (methylene) or 0.96 Å (methyl), and with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) (aryl, methylene) or 1.5Ueq(C) (methyl). The water H atoms were refined with restraints of O—H = 0.82 (1)Å and H···H = 1.38 (1)Å.
Figures
Fig. 1.
A view of (I) with displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 30% probability level.
Fig. 2.
A view of (I) packing strcuture.
Crystal data
| C12H15N5O3·H2O | F(000) = 1248 |
| Mr = 295.31 | Dx = 1.421 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, C2221 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: C 2c 2 | Cell parameters from 1377 reflections |
| a = 6.9986 (10) Å | θ = 3.4–25.0° |
| b = 11.6229 (10) Å | µ = 0.11 mm−1 |
| c = 33.932 (3) Å | T = 273 K |
| V = 2760.1 (5) Å3 | Block, colorless |
| Z = 8 | 0.12 × 0.10 × 0.08 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 1377 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1270 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.030 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 3.4° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2004) | h = −8→8 |
| Tmin = 0.987, Tmax = 0.991 | k = −11→13 |
| 6725 measured reflections | l = −33→40 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.030 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.079 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.00 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.055P)2 + 0.4836P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 1377 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 204 parameters | Δρmax = 0.16 e Å−3 |
| 4 restraints | Δρmin = −0.17 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.5675 (3) | −0.0420 (2) | 0.57539 (7) | 0.0345 (5) | |
| H1A | 0.5960 | −0.1042 | 0.5573 | 0.041* | |
| H1B | 0.6267 | −0.0597 | 0.6005 | 0.041* | |
| C2 | 0.6493 (3) | 0.0717 (2) | 0.55918 (6) | 0.0297 (5) | |
| H2 | 0.5838 | 0.0930 | 0.5347 | 0.036* | |
| C3 | 0.6333 (3) | 0.16870 (18) | 0.58921 (6) | 0.0269 (5) | |
| C4 | 0.8242 (3) | 0.18411 (18) | 0.60945 (6) | 0.0267 (5) | |
| H4 | 0.8800 | 0.2562 | 0.5999 | 0.032* | |
| C5 | 0.9461 (3) | 0.0841 (2) | 0.59303 (7) | 0.0314 (5) | |
| H5A | 1.0796 | 0.1060 | 0.5911 | 0.038* | |
| H5B | 0.9355 | 0.0164 | 0.6096 | 0.038* | |
| C6 | 0.8611 (3) | 0.0616 (2) | 0.55207 (6) | 0.0306 (5) | |
| H6 | 0.8961 | −0.0146 | 0.5420 | 0.037* | |
| C7 | 0.7957 (4) | 0.10135 (19) | 0.67986 (7) | 0.0364 (6) | |
| H7 | 0.7995 | 0.0242 | 0.6727 | 0.044* | |
| C8 | 0.8003 (3) | 0.29145 (18) | 0.67510 (6) | 0.0293 (5) | |
| C9 | 0.7746 (4) | 0.25703 (19) | 0.71395 (7) | 0.0338 (5) | |
| C10 | 0.7892 (3) | 0.48170 (19) | 0.68899 (6) | 0.0327 (5) | |
| C11 | 0.7511 (4) | 0.34291 (19) | 0.74423 (7) | 0.0353 (5) | |
| C12 | 0.4843 (4) | 0.2341 (2) | 0.59666 (9) | 0.0445 (6) | |
| H12A | 0.4935 | 0.2931 | 0.6151 | 0.053* | |
| H12B | 0.3697 | 0.2215 | 0.5835 | 0.053* | |
| N1 | 0.8142 (3) | 0.19086 (16) | 0.65304 (5) | 0.0310 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.7723 (3) | 0.13654 (16) | 0.71662 (6) | 0.0395 (5) | |
| N3 | 0.7949 (3) | 0.59520 (16) | 0.67918 (6) | 0.0424 (5) | |
| H3A | 0.8106 | 0.6153 | 0.6550 | 0.051* | |
| H3B | 0.7829 | 0.6468 | 0.6972 | 0.051* | |
| N4 | 0.8083 (3) | 0.40206 (16) | 0.66034 (5) | 0.0331 (5) | |
| N5 | 0.7614 (3) | 0.45538 (16) | 0.72814 (5) | 0.0362 (5) | |
| O1 | 0.3698 (2) | −0.03239 (15) | 0.58020 (5) | 0.0387 (4) | |
| H1 | 0.3405 | −0.0525 | 0.6026 | 0.058* | |
| O2 | 0.9107 (3) | 0.15191 (15) | 0.52463 (5) | 0.0422 (5) | |
| H2A | 1.0233 | 0.1455 | 0.5183 | 0.063* | |
| O3 | 0.7248 (3) | 0.32814 (15) | 0.78032 (5) | 0.0499 (5) | |
| O1W | 0.2565 (3) | 0.13435 (18) | 0.49421 (6) | 0.0500 (5) | |
| H2W | 0.274 (5) | 0.0919 (17) | 0.4753 (5) | 0.069 (12)* | |
| H1W | 0.274 (7) | 0.2029 (6) | 0.4897 (8) | 0.102 (16)* | |
| H5C | 0.754 (5) | 0.518 (2) | 0.7470 (8) | 0.080 (10)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0340 (12) | 0.0315 (13) | 0.0380 (13) | −0.0029 (10) | −0.0012 (10) | −0.0008 (11) |
| C2 | 0.0331 (12) | 0.0313 (12) | 0.0246 (10) | −0.0001 (10) | −0.0015 (9) | 0.0007 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0304 (11) | 0.0236 (11) | 0.0269 (10) | 0.0008 (9) | 0.0050 (9) | 0.0052 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0325 (11) | 0.0223 (11) | 0.0252 (10) | −0.0022 (9) | 0.0036 (8) | −0.0009 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0267 (11) | 0.0321 (12) | 0.0355 (12) | 0.0022 (10) | 0.0017 (9) | −0.0033 (10) |
| C6 | 0.0371 (12) | 0.0267 (11) | 0.0282 (11) | 0.0004 (10) | 0.0072 (9) | −0.0033 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0539 (15) | 0.0242 (11) | 0.0312 (12) | 0.0028 (11) | 0.0004 (11) | 0.0012 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0357 (12) | 0.0269 (11) | 0.0255 (11) | −0.0007 (10) | 0.0004 (9) | −0.0028 (9) |
| C9 | 0.0461 (13) | 0.0291 (11) | 0.0260 (11) | −0.0006 (11) | 0.0023 (11) | 0.0004 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0390 (13) | 0.0317 (12) | 0.0272 (11) | −0.0021 (11) | 0.0011 (10) | −0.0027 (9) |
| C11 | 0.0455 (13) | 0.0346 (11) | 0.0258 (12) | −0.0019 (12) | 0.0012 (10) | 0.0007 (9) |
| C12 | 0.0395 (14) | 0.0359 (14) | 0.0580 (17) | 0.0044 (12) | 0.0021 (12) | −0.0019 (12) |
| N1 | 0.0416 (11) | 0.0256 (9) | 0.0260 (9) | −0.0015 (9) | 0.0005 (8) | −0.0019 (8) |
| N2 | 0.0594 (13) | 0.0299 (10) | 0.0292 (10) | −0.0009 (10) | 0.0029 (10) | 0.0047 (8) |
| N3 | 0.0707 (15) | 0.0281 (10) | 0.0284 (10) | −0.0006 (11) | 0.0061 (10) | −0.0004 (8) |
| N4 | 0.0477 (12) | 0.0273 (10) | 0.0243 (9) | −0.0005 (9) | 0.0033 (9) | −0.0017 (8) |
| N5 | 0.0544 (12) | 0.0298 (10) | 0.0242 (9) | −0.0007 (10) | 0.0036 (9) | −0.0041 (8) |
| O1 | 0.0332 (9) | 0.0438 (10) | 0.0389 (9) | −0.0070 (8) | 0.0015 (7) | 0.0058 (8) |
| O2 | 0.0431 (10) | 0.0434 (10) | 0.0401 (9) | 0.0010 (8) | 0.0184 (8) | 0.0074 (8) |
| O3 | 0.0824 (14) | 0.0433 (10) | 0.0239 (8) | −0.0004 (10) | 0.0077 (8) | 0.0016 (7) |
| O1W | 0.0490 (11) | 0.0500 (12) | 0.0512 (12) | 0.0011 (11) | 0.0141 (9) | 0.0074 (10) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—O1 | 1.398 (3) | C8—N4 | 1.381 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.542 (3) | C8—C9 | 1.389 (3) |
| C1—H1A | 0.9700 | C8—N1 | 1.392 (3) |
| C1—H1B | 0.9700 | C9—N2 | 1.403 (3) |
| C2—C6 | 1.506 (3) | C9—C11 | 1.442 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.524 (3) | C10—N4 | 1.349 (3) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9800 | C10—N3 | 1.361 (3) |
| C3—C12 | 1.316 (3) | C10—N5 | 1.377 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.513 (3) | C11—O3 | 1.250 (3) |
| C4—N1 | 1.483 (2) | C11—N5 | 1.418 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.546 (3) | C12—H12A | 0.9300 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9800 | C12—H12B | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.534 (3) | N3—H3A | 0.8600 |
| C5—H5A | 0.9700 | N3—H3B | 0.8600 |
| C5—H5B | 0.9700 | N5—H5C | 0.97 (3) |
| C6—O2 | 1.445 (3) | O1—H1 | 0.8200 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9800 | O2—H2A | 0.8200 |
| C7—N2 | 1.323 (3) | O1W—H2W | 0.819 (19) |
| C7—N1 | 1.388 (3) | O1W—H1W | 0.821 (12) |
| C7—H7 | 0.9300 | ||
| O1—C1—C2 | 109.91 (19) | N2—C7—N1 | 113.4 (2) |
| O1—C1—H1A | 109.7 | N2—C7—H7 | 123.3 |
| C2—C1—H1A | 109.7 | N1—C7—H7 | 123.3 |
| O1—C1—H1B | 109.7 | N4—C8—C9 | 128.1 (2) |
| C2—C1—H1B | 109.7 | N4—C8—N1 | 125.74 (19) |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 108.2 | C9—C8—N1 | 106.11 (19) |
| C6—C2—C3 | 103.73 (19) | C8—C9—N2 | 110.5 (2) |
| C6—C2—C1 | 110.8 (2) | C8—C9—C11 | 119.4 (2) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 111.62 (18) | N2—C9—C11 | 130.0 (2) |
| C6—C2—H2 | 110.2 | N4—C10—N3 | 119.1 (2) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 110.2 | N4—C10—N5 | 123.8 (2) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 110.2 | N3—C10—N5 | 117.10 (19) |
| C12—C3—C4 | 123.0 (2) | O3—C11—N5 | 120.7 (2) |
| C12—C3—C2 | 127.9 (2) | O3—C11—C9 | 128.3 (2) |
| C4—C3—C2 | 109.04 (18) | N5—C11—C9 | 110.97 (18) |
| N1—C4—C3 | 114.69 (17) | C3—C12—H12A | 120.0 |
| N1—C4—C5 | 115.16 (18) | C3—C12—H12B | 120.0 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 103.58 (17) | H12A—C12—H12B | 120.0 |
| N1—C4—H4 | 107.7 | C7—N1—C8 | 105.70 (17) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 107.7 | C7—N1—C4 | 128.21 (18) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 107.7 | C8—N1—C4 | 125.75 (18) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 103.91 (17) | C7—N2—C9 | 104.25 (19) |
| C6—C5—H5A | 111.0 | C10—N3—H3A | 120.0 |
| C4—C5—H5A | 111.0 | C10—N3—H3B | 120.0 |
| C6—C5—H5B | 111.0 | H3A—N3—H3B | 120.0 |
| C4—C5—H5B | 111.0 | C10—N4—C8 | 111.93 (18) |
| H5A—C5—H5B | 109.0 | C10—N5—C11 | 125.68 (18) |
| O2—C6—C2 | 106.42 (19) | C10—N5—H5C | 118 (2) |
| O2—C6—C5 | 111.52 (19) | C11—N5—H5C | 116 (2) |
| C2—C6—C5 | 102.89 (18) | C1—O1—H1 | 109.5 |
| O2—C6—H6 | 111.8 | C6—O2—H2A | 109.5 |
| C2—C6—H6 | 111.8 | H2W—O1W—H1W | 115 (2) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 111.8 |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1···N4i | 0.82 | 2.04 | 2.857 (2) | 172 |
| O2—H2A···O1Wii | 0.82 | 1.83 | 2.639 (3) | 169 |
| N3—H3B···O3iii | 0.86 | 2.24 | 3.039 (3) | 154 |
| N5—H5C···N2iii | 0.97 (3) | 1.86 (3) | 2.829 (3) | 177 (3) |
| O1W—H2W···O1iv | 0.82 (2) | 2.11 (1) | 2.900 (3) | 161 (3) |
| O1W—H1W···O2v | 0.82 (1) | 2.00 (2) | 2.783 (3) | 159 (4) |
Symmetry codes: (i) x−1/2, y−1/2, z; (ii) x+1, y, z; (iii) −x+3/2, y+1/2, −z+3/2; (iv) x, −y, −z+1; (v) x−1/2, −y+1/2, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HB5032).
References
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809032966/hb5032sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809032966/hb5032Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




