Abstract
In the title compound, [Zn(C12H11N2O)2], the ZnII atom, lying on an inversion center, is coordinated by two O atoms and two N atoms from two salicylal Schiff base ligands in a distorted square-planar geometry. A three-dimensional network is formed by intermolecular C—H⋯N hydrogen bonds and C—H⋯π contacts.
Related literature
For general background to Schiff base complexes, see: Qiu et al. (2006 ▶); Shi et al. (2007 ▶); Xiao et al. (2007a
▶,b
▶, 2008 ▶); You et al. (2006 ▶). For related structures, see: Qiu et al. (2004 ▶); You et al. (2004 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
[Zn(C12H11N2O)2]
M r = 463.83
Triclinic,
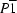
a = 5.3443 (4) Å
b = 9.8669 (8) Å
c = 10.1392 (8) Å
α = 104.108 (1)°
β = 95.830 (1)°
γ = 100.126 (1)°
V = 504.58 (7) Å3
Z = 1
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 1.25 mm−1
T = 200 K
0.30 × 0.30 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.706, T max = 0.789
6063 measured reflections
2455 independent reflections
2432 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.047
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.050
wR(F 2) = 0.144
S = 1.11
2455 reflections
142 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 1.07 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.73 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809034217/hy2222sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809034217/hy2222Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Selected bond lengths (Å).
| Zn1—O1 | 1.8967 (19) |
| Zn1—N1 | 2.001 (2) |
Table 2. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C8—H8A⋯O1i | 0.99 | 2.26 | 2.770 (3) | 111 |
| C7—H7⋯N2ii | 0.95 | 2.51 | 3.453 (3) | 170 |
| C6—H6⋯Cg1iii | 0.95 | 2.73 | 3.624 (3) | 158 |
| C11—H11⋯Cg2iv | 0.95 | 2.81 | 3.615 (3) | 143 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 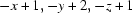 ; (ii)
; (ii) 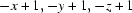 ; (iii)
; (iii) 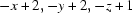 ; (iv)
; (iv) 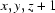 . Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the N2,C9–C12 and C1–C6 rings, respectively.
. Cg1 and Cg2 are the centroids of the N2,C9–C12 and C1–C6 rings, respectively.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
In preparing metal complexes, Schiff base ligands have been frequently employed (Qiu et al., 2004, 2006; Shi et al., 2007; Xiao et al., 2007a,b; Xiao et al., 2008; You et al., 2006). Zinc derivatives are particularly interesting owing to their essential importance in several biological processes (You et al., 2004, 2006; Xiao et al., 2007a,b; Xiao et al., 2008). We have reported the structures of a few zinc(II) complexes (You et al., 2004; Qiu et al., 2004). As an extension of our work, we report here the structure of a zinc(II) complex with salicylal Schiff base ligands.
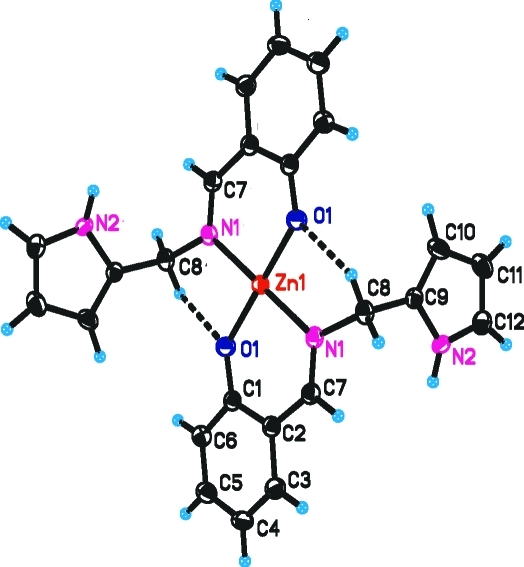
The title compound consists of a ZnII atom, lying on an inversion center, and two bidentate salicylal Schiff base ligands. The central ZnII atom is coordinated by two N atoms from the pyrrole groups and two O atoms from the phenolate groups, forming a slightly distorted square-planar geometry (Fig. 1). The distortion arises from the difference between Zn—O and Zn—N bonds (Table 1). The six-membered ring (Zn1, N1, C7, C2, C1, O1) and the benzene ring are almost co-planar with a mean deviation of 0.046 (1) Å.
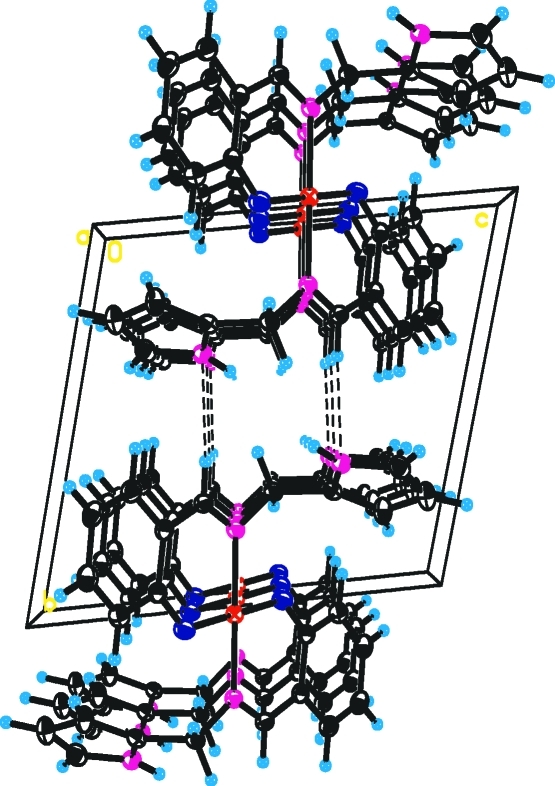
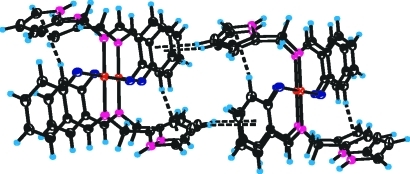
Intramolecular C—H···O hydrogen bond occours between H8A and O1 (Fig. 1 and Table 2). C—H···π contacts involving C6—H6···Cg1iii [Cg1 is the centroid of N2, C9–C12 ring; symmetry code: (iii) 2-x, 2-y, 1-z] and C11—H11···Cg2iv [Cg2 is the centroid of C1–C6 ring; (iv) x, y, 1+z] are observed (Fig. 3). These interactions as well as intermolecular C—H···N hydrogen bond (Fig. 2) connect the molecules into a three-dimensional network.
Experimental
Zinc oxide (0.5 mmol), salicylaldehyde (1 mmol) and (1H-pyrrol-yl)methanamine (1 mmol) were dissolved in 10 ml of methanol. After 3 ml ammonia was added, the resulting solution was heated to 423 K for 10 h. The reactor was cooled to room temperature at a rate of 10 K h-1. The mixture was filtered and held at room temperature for 10 d. Colorless block crystals were isolated (yield 38%).
Refinement
H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined as riding atoms, with C—H = 0.95 (CH), 0.99 (CH2) Å and N—H = 0.88 Å, and with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C,N).
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of the title compound. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level. Dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds. [Symmetry code: (i) 1-x, 2-y, 1-z.]
Fig. 2.
Packing diagram of the title compound. Dashed lines indicate C—H···N hydrogen bonds.
Fig. 3.
C—H···π interactions in the title compound (dashed lines).
Crystal data
| [Zn(C12H11N2O)2] | Z = 1 |
| Mr = 463.83 | F(000) = 240 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.526 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 5.3443 (4) Å | Cell parameters from 2361 reflections |
| b = 9.8669 (8) Å | θ = 2.7–26.6° |
| c = 10.1392 (8) Å | µ = 1.25 mm−1 |
| α = 104.108 (1)° | T = 200 K |
| β = 95.830 (1)° | Block, colorless |
| γ = 100.126 (1)° | 0.30 × 0.30 × 0.20 mm |
| V = 504.58 (7) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD diffractometer | 2455 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2432 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.047 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 28.3°, θmin = 2.2° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −7→7 |
| Tmin = 0.706, Tmax = 0.789 | k = −13→13 |
| 6063 measured reflections | l = −13→13 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.050 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.144 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.11 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0948P)2 + 0.2435P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2455 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 142 parameters | Δρmax = 1.07 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.73 e Å−3 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| C1 | 0.8616 (5) | 0.9132 (3) | 0.3153 (2) | 0.0297 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.7761 (5) | 0.7658 (3) | 0.3046 (2) | 0.0306 (5) | |
| C3 | 0.8882 (6) | 0.6636 (3) | 0.2175 (3) | 0.0379 (6) | |
| H3 | 0.8295 | 0.5648 | 0.2088 | 0.045* | |
| C4 | 1.0792 (6) | 0.7055 (3) | 0.1461 (3) | 0.0392 (6) | |
| H4 | 1.1518 | 0.6367 | 0.0880 | 0.047* | |
| C5 | 1.1647 (6) | 0.8508 (4) | 0.1602 (3) | 0.0403 (6) | |
| H5 | 1.2984 | 0.8804 | 0.1120 | 0.048* | |
| C6 | 1.0611 (5) | 0.9518 (3) | 0.2417 (3) | 0.0363 (5) | |
| H6 | 1.1246 | 1.0500 | 0.2491 | 0.044* | |
| C7 | 0.5899 (5) | 0.7143 (3) | 0.3816 (3) | 0.0320 (5) | |
| H7 | 0.5492 | 0.6139 | 0.3688 | 0.038* | |
| C8 | 0.2983 (5) | 0.7075 (3) | 0.5401 (3) | 0.0331 (5) | |
| H8A | 0.1403 | 0.7464 | 0.5483 | 0.040* | |
| H8B | 0.2478 | 0.6061 | 0.4866 | 0.040* | |
| C9 | 0.4297 (5) | 0.7175 (3) | 0.6791 (3) | 0.0290 (5) | |
| C10 | 0.3985 (5) | 0.7807 (4) | 0.8078 (3) | 0.0398 (6) | |
| H10 | 0.2724 | 0.8349 | 0.8336 | 0.048* | |
| C11 | 0.5913 (6) | 0.7507 (4) | 0.8987 (3) | 0.0447 (7) | |
| H11 | 0.6185 | 0.7811 | 0.9964 | 0.054* | |
| C12 | 0.7259 (6) | 0.6713 (3) | 0.8190 (3) | 0.0405 (6) | |
| H12 | 0.8665 | 0.6354 | 0.8519 | 0.049* | |
| N1 | 0.4708 (4) | 0.7890 (2) | 0.4666 (2) | 0.0297 (4) | |
| N2 | 0.6319 (4) | 0.6496 (2) | 0.6837 (2) | 0.0291 (4) | |
| H2A | 0.6901 | 0.6011 | 0.6127 | 0.035* | |
| O1 | 0.7656 (4) | 1.0126 (2) | 0.3902 (2) | 0.0346 (4) | |
| Zn1 | 0.5000 | 1.0000 | 0.5000 | 0.02730 (17) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0298 (11) | 0.0310 (11) | 0.0267 (10) | 0.0055 (9) | −0.0013 (8) | 0.0079 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0311 (11) | 0.0325 (12) | 0.0263 (10) | 0.0053 (9) | −0.0014 (8) | 0.0075 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0413 (14) | 0.0378 (13) | 0.0334 (12) | 0.0112 (11) | 0.0002 (10) | 0.0074 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0384 (14) | 0.0478 (15) | 0.0307 (12) | 0.0177 (11) | 0.0042 (10) | 0.0035 (11) |
| C5 | 0.0349 (13) | 0.0527 (17) | 0.0340 (13) | 0.0124 (11) | 0.0044 (10) | 0.0110 (12) |
| C6 | 0.0331 (12) | 0.0405 (13) | 0.0353 (12) | 0.0057 (10) | 0.0047 (9) | 0.0118 (10) |
| C7 | 0.0370 (12) | 0.0265 (11) | 0.0300 (11) | 0.0048 (9) | 0.0000 (9) | 0.0062 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0350 (12) | 0.0292 (11) | 0.0318 (11) | −0.0022 (9) | −0.0009 (9) | 0.0108 (9) |
| C9 | 0.0282 (11) | 0.0285 (11) | 0.0320 (11) | 0.0050 (8) | 0.0041 (8) | 0.0123 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0311 (12) | 0.0613 (18) | 0.0306 (12) | 0.0152 (12) | 0.0082 (9) | 0.0140 (12) |
| C11 | 0.0368 (14) | 0.069 (2) | 0.0317 (13) | 0.0110 (13) | 0.0041 (10) | 0.0206 (13) |
| C12 | 0.0392 (14) | 0.0448 (15) | 0.0402 (14) | 0.0106 (11) | −0.0011 (11) | 0.0182 (12) |
| N1 | 0.0334 (10) | 0.0272 (9) | 0.0269 (9) | 0.0031 (7) | 0.0000 (7) | 0.0085 (7) |
| N2 | 0.0327 (10) | 0.0275 (9) | 0.0292 (9) | 0.0129 (8) | 0.0035 (7) | 0.0074 (7) |
| O1 | 0.0368 (9) | 0.0299 (9) | 0.0384 (9) | 0.0067 (7) | 0.0114 (7) | 0.0096 (7) |
| Zn1 | 0.0300 (2) | 0.0258 (2) | 0.0259 (2) | 0.00531 (15) | 0.00390 (14) | 0.00714 (15) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—O1 | 1.302 (3) | C8—N1 | 1.491 (3) |
| C1—C6 | 1.413 (4) | C8—H8A | 0.9900 |
| C1—C2 | 1.419 (4) | C8—H8B | 0.9900 |
| C2—C7 | 1.425 (4) | C9—C10 | 1.344 (4) |
| C2—C3 | 1.429 (4) | C9—N2 | 1.371 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.373 (4) | C10—C11 | 1.430 (4) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C10—H10 | 0.9500 |
| C4—C5 | 1.393 (5) | C11—C12 | 1.339 (5) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| C5—C6 | 1.367 (4) | C12—N2 | 1.363 (3) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9500 | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C6—H6 | 0.9500 | N2—H2A | 0.8800 |
| C7—N1 | 1.287 (3) | Zn1—O1 | 1.8967 (19) |
| C7—H7 | 0.9500 | Zn1—N1 | 2.001 (2) |
| C8—C9 | 1.481 (3) | ||
| O1—C1—C6 | 119.4 (2) | H8A—C8—H8B | 108.1 |
| O1—C1—C2 | 122.8 (2) | C10—C9—N2 | 109.4 (2) |
| C6—C1—C2 | 117.8 (3) | C10—C9—C8 | 134.5 (2) |
| C1—C2—C7 | 123.0 (2) | N2—C9—C8 | 116.1 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.1 (2) | C9—C10—C11 | 106.9 (3) |
| C7—C2—C3 | 117.8 (2) | C9—C10—H10 | 126.6 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 121.3 (3) | C11—C10—H10 | 126.6 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.4 | C12—C11—C10 | 106.5 (3) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.4 | C12—C11—H11 | 126.8 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 118.8 (3) | C10—C11—H11 | 126.8 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.6 | C11—C12—N2 | 110.1 (2) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.6 | C11—C12—H12 | 124.9 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 121.7 (3) | N2—C12—H12 | 124.9 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.2 | C7—N1—C8 | 115.6 (2) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.2 | C7—N1—Zn1 | 124.25 (18) |
| C5—C6—C1 | 121.3 (3) | C8—N1—Zn1 | 120.09 (17) |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.3 | C12—N2—C9 | 107.1 (2) |
| C1—C6—H6 | 119.3 | C12—N2—H2A | 126.4 |
| N1—C7—C2 | 127.1 (2) | C9—N2—H2A | 126.4 |
| N1—C7—H7 | 116.4 | C1—O1—Zn1 | 130.68 (18) |
| C2—C7—H7 | 116.4 | O1i—Zn1—O1 | 180.000 (1) |
| C9—C8—N1 | 110.58 (19) | O1i—Zn1—N1 | 88.44 (9) |
| C9—C8—H8A | 109.5 | O1—Zn1—N1 | 91.56 (9) |
| N1—C8—H8A | 109.5 | O1i—Zn1—N1i | 91.56 (9) |
| C9—C8—H8B | 109.5 | O1—Zn1—N1i | 88.44 (9) |
| N1—C8—H8B | 109.5 | N1—Zn1—N1i | 180.00 (12) |
| O1—C1—C2—C7 | −4.2 (4) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | −0.1 (4) |
| C6—C1—C2—C7 | 175.2 (2) | C10—C11—C12—N2 | 0.3 (4) |
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | 178.6 (2) | C2—C7—N1—C8 | −176.0 (2) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −2.0 (3) | C2—C7—N1—Zn1 | 5.3 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.1 (4) | C9—C8—N1—C7 | 98.0 (3) |
| C7—C2—C3—C4 | −176.3 (2) | C9—C8—N1—Zn1 | −83.2 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.4 (4) | C11—C12—N2—C9 | −0.4 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.8 (4) | C10—C9—N2—C12 | 0.3 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.1 (4) | C8—C9—N2—C12 | 179.9 (2) |
| O1—C1—C6—C5 | −179.0 (2) | C6—C1—O1—Zn1 | 179.70 (17) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 1.6 (4) | C2—C1—O1—Zn1 | −0.9 (4) |
| C1—C2—C7—N1 | 1.6 (4) | C1—O1—Zn1—N1 | 5.4 (2) |
| C3—C2—C7—N1 | 178.9 (2) | C1—O1—Zn1—N1i | −174.6 (2) |
| N1—C8—C9—C10 | 111.4 (3) | C7—N1—Zn1—O1i | 172.7 (2) |
| N1—C8—C9—N2 | −68.1 (3) | C8—N1—Zn1—O1i | −5.97 (17) |
| N2—C9—C10—C11 | −0.1 (3) | C7—N1—Zn1—O1 | −7.3 (2) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | −179.6 (3) | C8—N1—Zn1—O1 | 174.03 (17) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+2, −z+1.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C8—H8A···O1i | 0.99 | 2.26 | 2.770 (3) | 111 |
| C7—H7···N2ii | 0.95 | 2.51 | 3.453 (3) | 170 |
| C6—H6···Cg1iii | 0.95 | 2.73 | 3.624 (3) | 158 |
| C11—H11···Cg2iv | 0.95 | 2.81 | 3.615 (3) | 143 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+2, −z+1; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1; (iii) −x+2, −y+2, −z+1; (iv) x, y, z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HY2222).
References
- Bruker (2007). SMART and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Qiu, X.-Y., Liu, W.-S., Hao, F.-Y. & Zhu, H.-L. (2006). Synth. React. Inorg. Met.36, 595–597.
- Qiu, X.-Y., Liu, Q.-X., Wang, Z.-G., Lin, Y.-S., Zeng, W.-J., Fun, H.-K. & Zhu, H.-L. (2004). Z. Kristallogr. New Cryst. Struct.219, 150–152.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Shi, D.-H., You, Z.-L., Xu, C., Zhang, Q. & Zhu, H.-L. (2007). Inorg. Chem. Commun.10, 404–406.
- Xiao, Z.-P., Fang, R.-Q., Shi, L., Ding, H., Xu, C. & Zhu, H.-L. (2007a). Can. J. Chem.85, 951–957.
- Xiao, Z.-P., Li, H.-Q., Xue, J.-Y., Shi, L. & Zhu, H.-L. (2008). Synth. Commun.38, 525–529.
- Xiao, Z.-P., Shi, D.-H., Li, H.-Q., Zhang, L.-N., Xu, C. & Zhu, H.-L. (2007b). Bioorg. Med. Chem.15, 3703–3710. [DOI] [PubMed]
- You, Z.-L., Shi, D.-H. & Zhu, H.-L. (2006). Inorg. Chem. Commun.9, 642–644.
- You, Z.-L., Zhu, H.-L. & Liu, W.-S. (2004). Acta Cryst. E60, m560–m562.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809034217/hy2222sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809034217/hy2222Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report