Abstract
In the title compound, C17H17ClO4, the dihedral angle between the mean planes of the two benzene rings is 65.92 (5)°. The methyl ester group lies within the ring plane [deviations of O atoms from the plane = −0.051 (2) and 0.151 (2) Å] due to an intramolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bond. In the crystal, molecules are held together by rather weak non-classical intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds, resulting in dimeric units about inversion centers, forming eight- and ten-membered ring systems as R 2 2(8) and R 2 2(10) motifs.
Related literature
For the pharmacological relevance of 3-arylsalicylates, see: Buchanan et al. (1997 ▶); Huang et al. (1999 ▶); Lin, Lin & Kuo (1997 ▶); Lin, Wu & Kuo (1997 ▶). For the synthesis, see: Adeel et al. (2009 ▶); For hydrogen-bond motifs, see: Bernstein et al. (1994 ▶).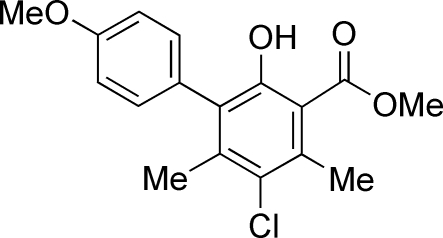
Experimental
Crystal data
C17H17ClO4
M r = 320.76
Triclinic,

a = 6.534 (4) Å
b = 9.574 (6) Å
c = 12.694 (8) Å
α = 97.420 (15)°
β = 100.56 (2)°
γ = 96.042 (14)°
V = 767.3 (8) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.26 mm−1
T = 173 K
0.55 × 0.27 × 0.01 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2004 ▶) T min = 0.868, T max = 0.997
14947 measured reflections
3964 independent reflections
3091 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.024
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.040
wR(F 2) = 0.125
S = 1.09
3964 reflections
207 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.31 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2003 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2003 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEP-3 (Farrugia, 1997 ▶) and DIAMOND (Brandenburg, 2005 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809031614/pv2189sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809031614/pv2189Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1⋯O2 | 0.94 (2) | 1.63 (2) | 2.5061 (18) | 153 (2) |
| C10—H10A⋯Cl1 | 0.98 | 2.45 | 3.003 (2) | 115 |
| C9—H9A⋯O2i | 0.98 | 2.73 | 3.242 (3) | 113 |
| C15—H15⋯O4ii | 0.95 | 2.50 | 3.437 (2) | 170 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
Financial support for MA from the Higher Education Commission of Pakistan (HEC) under the IPFP programe is gratefully acknowledged.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Functionalized biaryls containing a 3-arylsalicylate substructure occur in a variety of pharmacologically relevant natural products. The simple biaryls cynandione A—C have been isolated from many plant sources and show a considerable in vitro activity against hepatocytes, human bladder carcinoma T-24 cells, epidermoid carcinoma KB cells, and human hepatoma PLC/PRF/5 cells. For data on the pharmacological relevance of 3-arylsalicylates, see: Buchanan et al., (1997), Huang et al., (1999), Lin, Lin & Kuo (1997) and Lin, Wu & Kuo (1997). The sterically encumbered and functionalized biaryl, the title compound (I), was synthesized from 4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1,3-bis(trimethylsilyloxy)-1,3-butadiene which is not readily available by other methods. In this paper, the crystal structure of (I) has been presented.
In the title compound (Fig. 1), the the dihedral angle between the mean planes of the two benzene rings is 65.92 (5)°. The methoxy group and the methylester group lie within the planes of the benzene rings to which they are bonded (deviation from mean planes: O2, -0.051 (2); O3, 0.151 (2); (??), 0.143 (2) Å; the torsion angles are: C2—C3—C8—O2 -174.47 (12) and C17—O4—C14—C15 -176.38 (12)°). There is an intramolecular hydrogen bond between the hydroxyl group and the carbonyl O atom of the methylester group. There are weak intramolecular interactions of the types C—H···O between atom O3 of the ester group and the adjacent methyl group (C10) and C—H···Cl between Cl1 and the adjacent methyl groups (C7/C10).
In the crystal structure, the molecules of (I) are held together by rather weak intermolecular C—H···O type non-classical hydrogen bonds resulting in dimeric units about inversion centers, forming eight and ten membered ring systems which may be described in terms of graph set notations (Bernstein et al. 1994) as R22(8) and R22(10) motifs for the hydrogen bonds: C15–H15···O4ii and C9–H9A···O2i, respectively (details are given in Table 1 and Figure 2); leading to a zigzag chain arrangement.
Experimental
The title compound was prepared according to a previously published procedure (Adeel et al., 2009) using 3-chloro-4-trimethylsiloxy-pent-3-en-2-one (450 mg, 2.2 mmol), 4-(4-methoxyphenyl)-1,3-bis(silyloxy)-1,3-diene (806 mg, 2.2 mmol), and TiCl4 (0.241 ml, 2.2 mmol). (I) was isolated as a colourless crystalline solid. Re-crystallization from a saturated dichloromethane/methanol (9:1) solution at ambient temperature gave colourless crystals suitable for crystallographic studies.
Refinement
The H atom bonded to O1 was located in a difference map and refined freely. Other H atoms were positioned geometrically and refined using a riding model, with C—H = 0.98 (methyl groups) or 0.95 Å (aryl CH) and with Uiso(H) = 1.5 times Ueq(C) (methyl groups) or with Uiso(H) = 1.2 times Ueq(C) (aryl CH). Torsion angles of all methyl groups were allowed to refine.
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of (I), showing the atomic numbering scheme and displacement ellipsoids drawn at the 50% probability level.
Fig. 2.
Part of the packing diagram of (I). Unique O—H···O, C—H···O and C—H···Cl interactions represented by dashed lines are shown.
Crystal data
| C17H17ClO4 | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 320.76 | F(000) = 336 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.388 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Melting point: 367 K |
| a = 6.534 (4) Å | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| b = 9.574 (6) Å | Cell parameters from 7750 reflections |
| c = 12.694 (8) Å | θ = 6.4–59.5° |
| α = 97.420 (15)° | µ = 0.26 mm−1 |
| β = 100.56 (2)° | T = 173 K |
| γ = 96.042 (14)° | Plate, colourless |
| V = 767.3 (8) Å3 | 0.55 × 0.27 × 0.01 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII CCD diffractometer | 3964 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: sealed tube | 3091 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.024 |
| ω scans | θmax = 29.0°, θmin = 4.4° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2004) | h = −8→8 |
| Tmin = 0.868, Tmax = 0.997 | k = −13→13 |
| 14947 measured reflections | l = −17→17 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.040 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.125 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| S = 1.09 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.073P)2 + 0.0592P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3964 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 207 parameters | Δρmax = 0.31 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.23 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. Yield: 241 mg, 38%. m.p. = 367 (2) K. 1H NMR (250 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 2.10 (s, 3H, CH3), 2.56 (s, 3H, CH3), 3.77 (s, 3H, OCH3), 3.89 (s, 3H, OCH3), 6.89 (d, 2H, J = 8.8 Hz, ArH), 7.03 (d, 2H, J = 8.8 Hz, ArH), 10.54 (s, 1 H, OH). 13C NMR (62 MHz, CDCl3): δ = 19.0, 19.4 (CH3), 51.4, 54.2 (OCH3), 111.5 (C), 112.9 (2 C, CH), 126.8, 127.6, 128.3 (C), 129.9 (2 C, CH), 135.3, 140.8, 156.1, 157.8 (C), 170.5 (C=O). IR (KBr, cm -1): ~ν = 3430 (m), 3050 (w), 3002 (w), 2959 (m), 2931 (m), 2837 (m), 1653 (s), 1607 (m), 1572 (w), 1514 (s), 1444 (s), 1373 (m), 1361 (s), 1297 (s), 1253 (s), 1220 (s), 1176 (m), 1092 (m), 1036 (m) 810 (m), 686 (m). GC—MS (EI, 70 eV): m/z (%): 322 (M+, 37Cl, 16), 320 (M+, 47), 288 (100), 260 (11), 245 (27), 225 (29), 181 (7), 152 (12). HRMS (EI, 70 eV): calcd for C17H17O4Cl [M, 35Cl]: 320.08099; found 320.08088. |
| Geometry. All s.u.'s (except the s.u. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell s.u.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of s.u.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between s.u.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell s.u.'s is used for estimating s.u.'s involving l.s. planes.Least-squares planes (x,y,z in crystal coordinates) and deviations from them (* indicates atom used to define plane)- 3.7416 (0.0035) x + 4.8249 (0.0051) y - 7.9961 (0.0069) z = 2.4746 (0.0052)* 0.0019 (0.0009) C1 * -0.0098 (0.0009) C2 * 0.0101 (0.0008) C3 * -0.0023 (0.0008) C4 * -0.0059 (0.0008) C5 * 0.0061 (0.0008) C6 0.0307 (0.0018) C8 - 0.0505 (0.0021) O2 0.1508 (0.0021) O3 0.1865 (0.0030) C9Rms deviation of fitted atoms = 0.00683.1094 (0.0040) x + 6.1432 (0.0055) y - 9.0638 (0.0075) z = 4.7524 (0.0041)Angle to previous plane (with approximate su) = 65.92 (0.05)* 0.0117 (0.0009) C11 * -0.0089 (0.0009) C12 * -0.0016 (0.0009) C13 * 0.0091 (0.0009) C14 * -0.0060 (0.0010) C15 * -0.0043 (0.0010) C16 0.0476 (0.0018) O4 0.1434 (0.0024) C17Rms deviation of fitted atoms = 0.0077 |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > 2σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | −0.09153 (15) | 0.87698 (10) | 0.26779 (8) | 0.0377 (2) | |
| H1 | −0.175 (3) | 0.892 (2) | 0.3196 (17) | 0.067 (6)* | |
| O2 | −0.25708 (18) | 0.99014 (12) | 0.41459 (9) | 0.0505 (3) | |
| O3 | −0.16796 (18) | 1.21628 (12) | 0.48417 (9) | 0.0491 (3) | |
| O4 | 0.23627 (16) | 0.52864 (10) | −0.09022 (8) | 0.0405 (2) | |
| Cl1 | 0.48249 (6) | 1.39934 (4) | 0.30599 (3) | 0.05110 (15) | |
| C1 | 0.3067 (2) | 1.24545 (14) | 0.29830 (10) | 0.0313 (3) | |
| C2 | 0.1636 (2) | 1.24546 (14) | 0.36668 (10) | 0.0310 (3) | |
| C3 | 0.02086 (19) | 1.11978 (13) | 0.35519 (9) | 0.0279 (3) | |
| C4 | 0.03415 (19) | 1.00141 (13) | 0.27908 (10) | 0.0272 (3) | |
| C5 | 0.18323 (18) | 1.00544 (13) | 0.21221 (9) | 0.0265 (3) | |
| C6 | 0.32076 (19) | 1.12961 (13) | 0.22127 (9) | 0.0282 (3) | |
| C7 | 0.4785 (2) | 1.14192 (16) | 0.14895 (11) | 0.0386 (3) | |
| H7A | 0.4538 | 1.0572 | 0.0937 | 0.058* | |
| H7B | 0.6207 | 1.1501 | 0.1925 | 0.058* | |
| H7C | 0.4637 | 1.2265 | 0.1136 | 0.058* | |
| C8 | −0.1451 (2) | 1.10217 (14) | 0.41965 (10) | 0.0318 (3) | |
| C9 | −0.3311 (3) | 1.20118 (19) | 0.54694 (14) | 0.0515 (4) | |
| H9A | −0.4673 | 1.1710 | 0.4978 | 0.077* | |
| H9B | −0.3346 | 1.2925 | 0.5910 | 0.077* | |
| H9C | −0.3018 | 1.1298 | 0.5945 | 0.077* | |
| C10 | 0.1683 (3) | 1.37309 (18) | 0.45028 (13) | 0.0513 (4) | |
| H10A | 0.2995 | 1.4367 | 0.4576 | 0.077* | |
| H10B | 0.1599 | 1.3421 | 0.5202 | 0.077* | |
| H10C | 0.0487 | 1.4235 | 0.4275 | 0.077* | |
| C11 | 0.18957 (19) | 0.87662 (13) | 0.13357 (9) | 0.0277 (3) | |
| C12 | 0.0254 (2) | 0.82784 (14) | 0.04645 (10) | 0.0310 (3) | |
| H12 | −0.0962 | 0.8750 | 0.0389 | 0.037* | |
| C13 | 0.0333 (2) | 0.71183 (14) | −0.03026 (10) | 0.0320 (3) | |
| H13 | −0.0805 | 0.6811 | −0.0899 | 0.038* | |
| C14 | 0.2094 (2) | 0.64160 (13) | −0.01864 (10) | 0.0312 (3) | |
| C15 | 0.3732 (2) | 0.68633 (15) | 0.06955 (11) | 0.0366 (3) | |
| H15 | 0.4927 | 0.6372 | 0.0785 | 0.044* | |
| C16 | 0.3628 (2) | 0.80242 (15) | 0.14448 (11) | 0.0348 (3) | |
| H16 | 0.4760 | 0.8322 | 0.2046 | 0.042* | |
| C17 | 0.0787 (3) | 0.48428 (16) | −0.18492 (11) | 0.0427 (3) | |
| H17A | −0.0537 | 0.4516 | −0.1644 | 0.064* | |
| H17B | 0.1213 | 0.4064 | −0.2306 | 0.064* | |
| H17C | 0.0596 | 0.5642 | −0.2252 | 0.064* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0325 (5) | 0.0332 (5) | 0.0465 (5) | −0.0037 (4) | 0.0149 (4) | −0.0005 (4) |
| O2 | 0.0459 (6) | 0.0494 (7) | 0.0592 (7) | −0.0045 (5) | 0.0307 (5) | −0.0012 (5) |
| O3 | 0.0522 (7) | 0.0473 (6) | 0.0545 (6) | 0.0061 (5) | 0.0337 (5) | −0.0003 (5) |
| O4 | 0.0479 (6) | 0.0350 (5) | 0.0402 (5) | 0.0133 (4) | 0.0143 (4) | −0.0022 (4) |
| Cl1 | 0.0526 (3) | 0.0427 (2) | 0.0526 (2) | −0.01755 (17) | 0.02060 (18) | −0.00782 (16) |
| C1 | 0.0298 (6) | 0.0316 (7) | 0.0294 (6) | −0.0037 (5) | 0.0050 (5) | 0.0013 (5) |
| C2 | 0.0305 (7) | 0.0336 (7) | 0.0270 (6) | 0.0029 (5) | 0.0054 (5) | −0.0007 (5) |
| C3 | 0.0247 (6) | 0.0327 (6) | 0.0268 (6) | 0.0058 (5) | 0.0056 (5) | 0.0045 (5) |
| C4 | 0.0221 (6) | 0.0296 (6) | 0.0289 (6) | 0.0029 (5) | 0.0032 (4) | 0.0039 (4) |
| C5 | 0.0236 (6) | 0.0299 (6) | 0.0256 (5) | 0.0056 (5) | 0.0030 (4) | 0.0034 (4) |
| C6 | 0.0246 (6) | 0.0345 (7) | 0.0246 (5) | 0.0022 (5) | 0.0042 (4) | 0.0040 (5) |
| C7 | 0.0358 (7) | 0.0452 (8) | 0.0354 (7) | −0.0010 (6) | 0.0149 (6) | 0.0024 (6) |
| C8 | 0.0274 (6) | 0.0408 (7) | 0.0293 (6) | 0.0080 (6) | 0.0074 (5) | 0.0075 (5) |
| C9 | 0.0509 (9) | 0.0617 (11) | 0.0531 (9) | 0.0171 (8) | 0.0336 (8) | 0.0092 (7) |
| C10 | 0.0572 (10) | 0.0446 (9) | 0.0485 (8) | −0.0076 (7) | 0.0249 (7) | −0.0150 (7) |
| C11 | 0.0268 (6) | 0.0287 (6) | 0.0282 (6) | 0.0045 (5) | 0.0072 (5) | 0.0032 (5) |
| C12 | 0.0291 (6) | 0.0308 (6) | 0.0325 (6) | 0.0086 (5) | 0.0040 (5) | 0.0023 (5) |
| C13 | 0.0337 (7) | 0.0318 (7) | 0.0292 (6) | 0.0058 (5) | 0.0038 (5) | 0.0016 (5) |
| C14 | 0.0370 (7) | 0.0267 (6) | 0.0336 (6) | 0.0071 (5) | 0.0152 (5) | 0.0046 (5) |
| C15 | 0.0317 (7) | 0.0418 (8) | 0.0401 (7) | 0.0154 (6) | 0.0108 (6) | 0.0061 (6) |
| C16 | 0.0274 (7) | 0.0412 (8) | 0.0348 (6) | 0.0082 (6) | 0.0038 (5) | 0.0027 (5) |
| C17 | 0.0569 (9) | 0.0345 (7) | 0.0368 (7) | 0.0054 (6) | 0.0154 (6) | −0.0030 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C4 | 1.3495 (17) | C7—H7C | 0.9800 |
| O1—H1 | 0.94 (2) | C9—H9A | 0.9800 |
| O2—C8 | 1.2205 (18) | C9—H9B | 0.9800 |
| O3—C8 | 1.3170 (18) | C9—H9C | 0.9800 |
| O3—C9 | 1.4496 (19) | C10—H10A | 0.9800 |
| O4—C14 | 1.3678 (16) | C10—H10B | 0.9800 |
| O4—C17 | 1.4169 (19) | C10—H10C | 0.9800 |
| Cl1—C1 | 1.7510 (16) | C11—C12 | 1.3850 (18) |
| C1—C2 | 1.3870 (19) | C11—C16 | 1.3937 (19) |
| C1—C6 | 1.4033 (18) | C12—C13 | 1.3914 (18) |
| C2—C3 | 1.417 (2) | C12—H12 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C10 | 1.505 (2) | C13—C14 | 1.3869 (19) |
| C3—C4 | 1.4121 (18) | C13—H13 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C8 | 1.4821 (19) | C14—C15 | 1.387 (2) |
| C4—C5 | 1.4052 (18) | C15—C16 | 1.382 (2) |
| C5—C6 | 1.3913 (19) | C15—H15 | 0.9500 |
| C5—C11 | 1.4925 (18) | C16—H16 | 0.9500 |
| C6—C7 | 1.5061 (19) | C17—H17A | 0.9800 |
| C7—H7A | 0.9800 | C17—H17B | 0.9800 |
| C7—H7B | 0.9800 | C17—H17C | 0.9800 |
| C4—O1—H1 | 104.4 (13) | O3—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C8—O3—C9 | 116.73 (12) | H9A—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C14—O4—C17 | 118.03 (11) | H9B—C9—H9C | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 124.48 (12) | C2—C10—H10A | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—Cl1 | 118.94 (10) | C2—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—Cl1 | 116.58 (10) | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 116.76 (12) | C2—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—C10 | 120.28 (13) | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C10 | 122.94 (12) | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.62 (12) | C12—C11—C16 | 117.68 (12) |
| C4—C3—C8 | 116.31 (12) | C12—C11—C5 | 121.30 (11) |
| C2—C3—C8 | 124.06 (12) | C16—C11—C5 | 121.01 (11) |
| O1—C4—C5 | 115.99 (11) | C11—C12—C13 | 121.91 (12) |
| O1—C4—C3 | 122.28 (12) | C11—C12—H12 | 119.0 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 121.72 (12) | C13—C12—H12 | 119.0 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 118.97 (11) | C14—C13—C12 | 119.20 (12) |
| C6—C5—C11 | 121.90 (11) | C14—C13—H13 | 120.4 |
| C4—C5—C11 | 119.13 (11) | C12—C13—H13 | 120.4 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 118.42 (12) | O4—C14—C15 | 115.94 (12) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 121.32 (12) | O4—C14—C13 | 124.23 (12) |
| C1—C6—C7 | 120.25 (12) | C15—C14—C13 | 119.83 (12) |
| C6—C7—H7A | 109.5 | C16—C15—C14 | 120.05 (12) |
| C6—C7—H7B | 109.5 | C16—C15—H15 | 120.0 |
| H7A—C7—H7B | 109.5 | C14—C15—H15 | 120.0 |
| C6—C7—H7C | 109.5 | C15—C16—C11 | 121.29 (12) |
| H7A—C7—H7C | 109.5 | C15—C16—H16 | 119.4 |
| H7B—C7—H7C | 109.5 | C11—C16—H16 | 119.4 |
| O2—C8—O3 | 120.57 (12) | O4—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| O2—C8—C3 | 123.38 (12) | O4—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| O3—C8—C3 | 116.05 (12) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| O3—C9—H9A | 109.5 | O4—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| O3—C9—H9B | 109.5 | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| H9A—C9—H9B | 109.5 | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | −1.3 (2) | Cl1—C1—C6—C7 | −1.06 (16) |
| Cl1—C1—C2—C3 | 178.26 (9) | C9—O3—C8—O2 | −0.3 (2) |
| C6—C1—C2—C10 | 177.07 (13) | C9—O3—C8—C3 | 179.38 (12) |
| Cl1—C1—C2—C10 | −3.41 (19) | C4—C3—C8—O2 | 4.94 (19) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 1.98 (18) | C2—C3—C8—O2 | −174.47 (12) |
| C10—C2—C3—C4 | −176.30 (12) | C4—C3—C8—O3 | −174.73 (10) |
| C1—C2—C3—C8 | −178.63 (11) | C2—C3—C8—O3 | 5.86 (19) |
| C10—C2—C3—C8 | 3.1 (2) | C6—C5—C11—C12 | −113.50 (15) |
| C2—C3—C4—O1 | 177.11 (11) | C4—C5—C11—C12 | 66.49 (17) |
| C8—C3—C4—O1 | −2.32 (17) | C6—C5—C11—C16 | 65.53 (17) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −1.34 (18) | C4—C5—C11—C16 | −114.48 (14) |
| C8—C3—C4—C5 | 179.22 (10) | C16—C11—C12—C13 | −2.1 (2) |
| O1—C4—C5—C6 | −178.70 (10) | C5—C11—C12—C13 | 176.99 (12) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | −0.15 (18) | C11—C12—C13—C14 | 0.9 (2) |
| O1—C4—C5—C11 | 1.31 (16) | C17—O4—C14—C15 | −176.38 (12) |
| C3—C4—C5—C11 | 179.86 (10) | C17—O4—C14—C13 | 2.97 (19) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.91 (17) | C12—C13—C14—O4 | −178.45 (11) |
| C11—C5—C6—C1 | −179.10 (10) | C12—C13—C14—C15 | 0.87 (19) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −177.74 (11) | O4—C14—C15—C16 | 178.07 (12) |
| C11—C5—C6—C7 | 2.25 (18) | C13—C14—C15—C16 | −1.3 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.19 (19) | C14—C15—C16—C11 | 0.0 (2) |
| Cl1—C1—C6—C5 | −179.72 (9) | C12—C11—C16—C15 | 1.6 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | 178.47 (12) | C5—C11—C16—C15 | −177.44 (12) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1···O2 | 0.94 (2) | 1.63 (2) | 2.5061 (18) | 153 (2) |
| C7—H7C···Cl1 | 0.98 | 2.74 | 2.957 (2) | 93 |
| C10—H10A···Cl1 | 0.98 | 2.45 | 3.003 (2) | 115 |
| C10—H10B···O3 | 0.98 | 2.28 | 2.662 (2) | 102 |
| C10—H10C···O3 | 0.98 | 2.57 | 2.662 (2) | 85 |
| C9—H9A···O2i | 0.98 | 2.73 | 3.242 (3) | 113 |
| C9—H9C···O2i | 0.98 | 2.96 | 3.242 (3) | 98 |
| C15—H15···O4ii | 0.95 | 2.50 | 3.437 (2) | 170 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x−1, −y+2, −z+1; (ii) −x+1, −y+1, −z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: PV2189).
References
- Adeel, M., Rashid, M. A., Rasool, N., Ahmad, R., Villinger, A., Reinke, H., Fischer, C. & Langer, P. (2009). Synthesis, pp. 243–250.
- Bernstein, J., Etter, M. C. & Leiserowitz, L. (1994). Structure Correlation, edited by H.-B. Bürgi & J. D. Dunitz, Vol. 2, pp. 431–507. New York: VCH.
- Brandenburg, K. (2005). DIAMOND Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Bruker (2003). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Buchanan, M. S., Gill, M. & Yu, J. (1997). J. Chem. Soc. Perkin Trans. 1, pp. 919–926.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst 30, 565.
- Huang, P.-L., Won, S.-J., Day, S.-H. & Lin, C.-N. (1999). Helv. Chim. Acta, 82, 1716–1720.
- Lin, Y.-L., Lin, T.-C. & Kuo, Y.-H. (1997). J. Nat. Prod 60, 368–370.
- Lin, Y.-L., Wu, Y.-M. & Kuo, Y.-H. (1997). Phytochemistry, 45, 1057–1061.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2004). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809031614/pv2189sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809031614/pv2189Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report




