Abstract
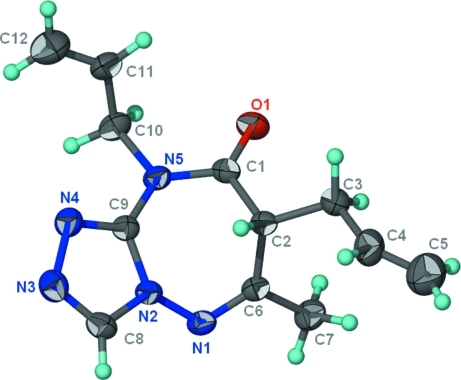
The title compound, C12H15N5O, features a triazolyl ring fused with a seven-membered triazepinyl ring; the latter ring adopts a boat conformation with the allyl-bearing C atom as the prow and the C and N fused-ring atoms as the stern.
Related literature
Triazepines are used in the treatment of neuronal disorders. They are also the reactants for the synthesis of other heterocyclic compounds; see, for example: Essassi et al. (1977 ▶); Richter & Sheefelot (1991 ▶).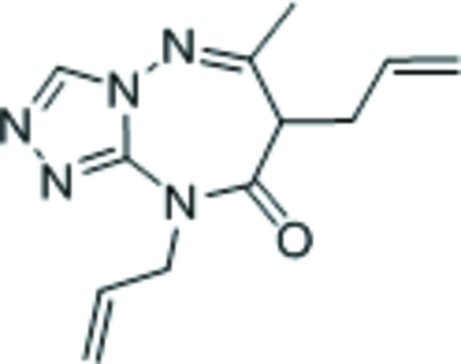
Experimental
Crystal data
C12H15N5O
M r = 245.29
Monoclinic,
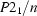
a = 7.4674 (3) Å
b = 8.3398 (3) Å
c = 20.2214 (6) Å
β = 95.174 (2)°
V = 1254.19 (8) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.3 × 0.3 × 0.3 mm
Data collection
Bruker APEX2 diffractometer
Absorption correction: none
11394 measured reflections
2435 independent reflections
1600 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.041
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.053
wR(F 2) = 0.176
S = 1.03
2435 reflections
164 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.62 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.31 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2005 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: X-SEED (Barbour, 2001 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: publCIF (Westrip, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680903133X/xu2583sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680903133X/xu2583Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
We thank Université Mohammed V-Agdal and the University of Malaya for supporting this study.
supplementary crystallographic information
Experimental
To a solution of 6-methyl-7H-[1,2,4]triazolo[4,3-b][1,2,4]triazepin-8(9H)-one (1 g, 6 mmol) in N,N-dimethylformamide (20 ml), potassium carbonate (1.26 g, 9 mmol), allyl bromide (0.8 ml, 9 mmol) and a catalytic amount of tetrabutyammonium bromide were added. The mixture was stirred for 12 h. After the completion of the reaction (as monitored by TLC), the solid material was removed by filtration and the solvent evaporated under vacuum. Dichloromethane (20 ml) was added and the solution filtered. The solvent was removed and the product purified by column chromatography (30% ethyl acetate/hexane) to afford colorless crystals in 30% yield; m.p. 423 K. The formulation was established by proton and carbon-13 NMR spectroscopy in DMSO-d6.
Refinement
Carbon-bound H-atoms were placed in calculated positions (C—H 0.93 to 0.97 Å) and were included in the refinement in the riding model approximation, with U(H) set to 1.2U(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
Thermal ellipsoid plot (Barbour, 2001) of C12H15N5O at the 50% probability level; hydrogen atoms are drawn as spheres of arbitrary radius.
Crystal data
| C12H15N5O | F(000) = 520 |
| Mr = 245.29 | Dx = 1.299 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 2666 reflections |
| a = 7.4674 (3) Å | θ = 2.6–23.2° |
| b = 8.3398 (3) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 20.2214 (6) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 95.174 (2)° | Block, colorless |
| V = 1254.19 (8) Å3 | 0.3 × 0.3 × 0.3 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker APEXII diffractometer | 1600 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.041 |
| graphite | θmax = 25.9°, θmin = 2.0° |
| φ and ω scans | h = −9→9 |
| 11394 measured reflections | k = −10→10 |
| 2435 independent reflections | l = −22→24 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.053 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.176 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.03 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.1011P)2 + 0.1814P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2435 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 164 parameters | Δρmax = 0.62 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.31 e Å−3 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.6016 (3) | 0.9072 (2) | 0.62240 (9) | 0.0504 (5) | |
| N1 | 0.6575 (3) | 0.4291 (2) | 0.67475 (9) | 0.0372 (5) | |
| N2 | 0.6714 (3) | 0.4126 (2) | 0.60624 (9) | 0.0346 (5) | |
| N3 | 0.7253 (3) | 0.2937 (3) | 0.51391 (10) | 0.0486 (6) | |
| N4 | 0.7390 (3) | 0.4593 (3) | 0.50437 (9) | 0.0424 (6) | |
| N5 | 0.7149 (3) | 0.6893 (2) | 0.57403 (9) | 0.0360 (5) | |
| C1 | 0.5941 (3) | 0.7634 (3) | 0.61190 (10) | 0.0353 (6) | |
| C2 | 0.4588 (3) | 0.6533 (3) | 0.63974 (10) | 0.0328 (6) | |
| H2 | 0.4112 | 0.5834 | 0.6033 | 0.039* | |
| C3 | 0.3002 (3) | 0.7447 (3) | 0.66310 (12) | 0.0460 (7) | |
| H3A | 0.3402 | 0.8057 | 0.7025 | 0.055* | |
| H3B | 0.2560 | 0.8200 | 0.6289 | 0.055* | |
| C4 | 0.1488 (4) | 0.6348 (4) | 0.67861 (16) | 0.0600 (8) | |
| H4 | 0.1127 | 0.5587 | 0.6465 | 0.072* | |
| C5 | 0.0662 (5) | 0.6348 (5) | 0.73019 (19) | 0.0877 (12) | |
| H5A | 0.0969 | 0.7084 | 0.7639 | 0.105* | |
| H5B | −0.0256 | 0.5613 | 0.7346 | 0.105* | |
| C6 | 0.5616 (3) | 0.5471 (3) | 0.69075 (10) | 0.0338 (6) | |
| C7 | 0.5614 (4) | 0.5818 (3) | 0.76328 (11) | 0.0480 (7) | |
| H7A | 0.6349 | 0.5044 | 0.7882 | 0.072* | |
| H7B | 0.4406 | 0.5759 | 0.7758 | 0.072* | |
| H7C | 0.6086 | 0.6874 | 0.7724 | 0.072* | |
| C8 | 0.6870 (3) | 0.2708 (3) | 0.57428 (13) | 0.0433 (6) | |
| H8 | 0.6722 | 0.1707 | 0.5933 | 0.052* | |
| C9 | 0.7056 (3) | 0.5264 (3) | 0.56022 (11) | 0.0334 (6) | |
| C10 | 0.8431 (3) | 0.7867 (3) | 0.53946 (12) | 0.0449 (7) | |
| H10A | 0.9421 | 0.7191 | 0.5286 | 0.054* | |
| H10B | 0.8920 | 0.8704 | 0.5692 | 0.054* | |
| C11 | 0.7587 (4) | 0.8618 (3) | 0.47735 (13) | 0.0519 (7) | |
| H11 | 0.6702 | 0.9388 | 0.4813 | 0.062* | |
| C12 | 0.8000 (5) | 0.8273 (4) | 0.41876 (16) | 0.0779 (11) | |
| H12A | 0.8880 | 0.7509 | 0.4130 | 0.093* | |
| H12B | 0.7420 | 0.8788 | 0.3820 | 0.093* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0657 (13) | 0.0282 (11) | 0.0585 (11) | −0.0048 (9) | 0.0122 (9) | −0.0007 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0448 (12) | 0.0352 (12) | 0.0313 (10) | −0.0009 (10) | 0.0013 (8) | 0.0048 (8) |
| N2 | 0.0407 (12) | 0.0290 (11) | 0.0341 (10) | 0.0007 (9) | 0.0037 (8) | 0.0025 (8) |
| N3 | 0.0564 (15) | 0.0419 (14) | 0.0482 (13) | 0.0010 (11) | 0.0084 (11) | −0.0081 (10) |
| N4 | 0.0485 (13) | 0.0417 (13) | 0.0376 (11) | −0.0001 (10) | 0.0073 (9) | −0.0018 (9) |
| N5 | 0.0391 (12) | 0.0314 (12) | 0.0381 (10) | −0.0050 (9) | 0.0063 (9) | 0.0049 (8) |
| C1 | 0.0424 (15) | 0.0303 (14) | 0.0327 (12) | 0.0003 (11) | −0.0005 (10) | 0.0010 (10) |
| C2 | 0.0363 (13) | 0.0296 (13) | 0.0324 (12) | −0.0009 (10) | 0.0016 (10) | 0.0014 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0504 (17) | 0.0422 (15) | 0.0461 (14) | 0.0071 (13) | 0.0087 (12) | 0.0053 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0377 (16) | 0.081 (2) | 0.0619 (18) | 0.0146 (15) | 0.0103 (13) | 0.0091 (16) |
| C5 | 0.066 (2) | 0.106 (3) | 0.093 (3) | 0.009 (2) | 0.018 (2) | 0.018 (2) |
| C6 | 0.0360 (14) | 0.0328 (13) | 0.0323 (12) | −0.0049 (11) | 0.0018 (10) | 0.0028 (10) |
| C7 | 0.0541 (17) | 0.0556 (18) | 0.0340 (13) | 0.0011 (14) | 0.0022 (11) | 0.0019 (11) |
| C8 | 0.0489 (16) | 0.0299 (14) | 0.0510 (15) | 0.0011 (12) | 0.0038 (12) | −0.0002 (11) |
| C9 | 0.0323 (13) | 0.0331 (14) | 0.0342 (12) | −0.0008 (10) | 0.0004 (9) | 0.0016 (10) |
| C10 | 0.0443 (16) | 0.0436 (16) | 0.0475 (14) | −0.0111 (13) | 0.0080 (12) | 0.0063 (11) |
| C11 | 0.0567 (18) | 0.0493 (18) | 0.0519 (16) | −0.0001 (14) | 0.0166 (13) | 0.0142 (13) |
| C12 | 0.100 (3) | 0.079 (3) | 0.0560 (19) | 0.009 (2) | 0.0132 (18) | 0.0164 (17) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C1 | 1.218 (3) | C3—H3B | 0.9700 |
| N1—C6 | 1.276 (3) | C4—C5 | 1.259 (4) |
| N1—N2 | 1.405 (3) | C4—H4 | 0.9300 |
| N2—C8 | 1.358 (3) | C5—H5A | 0.9300 |
| N2—C9 | 1.369 (3) | C5—H5B | 0.9300 |
| N3—C8 | 1.293 (3) | C6—C7 | 1.495 (3) |
| N3—N4 | 1.400 (3) | C7—H7A | 0.9600 |
| N4—C9 | 1.304 (3) | C7—H7B | 0.9600 |
| N5—C1 | 1.381 (3) | C7—H7C | 0.9600 |
| N5—C9 | 1.388 (3) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| N5—C10 | 1.479 (3) | C10—C11 | 1.491 (4) |
| C1—C2 | 1.511 (3) | C10—H10A | 0.9700 |
| C2—C6 | 1.514 (3) | C10—H10B | 0.9700 |
| C2—C3 | 1.519 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.283 (4) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9800 | C11—H11 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.510 (4) | C12—H12A | 0.9300 |
| C3—H3A | 0.9700 | C12—H12B | 0.9300 |
| C6—N1—N2 | 114.74 (18) | H5A—C5—H5B | 120.0 |
| C8—N2—C9 | 104.5 (2) | N1—C6—C7 | 116.6 (2) |
| C8—N2—N1 | 124.87 (19) | N1—C6—C2 | 122.7 (2) |
| C9—N2—N1 | 129.60 (19) | C7—C6—C2 | 120.7 (2) |
| C8—N3—N4 | 107.47 (19) | C6—C7—H7A | 109.5 |
| C9—N4—N3 | 106.37 (19) | C6—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| C1—N5—C9 | 121.80 (19) | H7A—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| C1—N5—C10 | 119.9 (2) | C6—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C9—N5—C10 | 117.75 (19) | H7A—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| O1—C1—N5 | 121.0 (2) | H7B—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| O1—C1—C2 | 123.7 (2) | N3—C8—N2 | 110.9 (2) |
| N5—C1—C2 | 115.2 (2) | N3—C8—H8 | 124.5 |
| C1—C2—C6 | 107.12 (18) | N2—C8—H8 | 124.5 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 112.1 (2) | N4—C9—N2 | 110.7 (2) |
| C6—C2—C3 | 116.29 (18) | N4—C9—N5 | 125.7 (2) |
| C1—C2—H2 | 106.9 | N2—C9—N5 | 123.41 (19) |
| C6—C2—H2 | 106.9 | N5—C10—C11 | 112.7 (2) |
| C3—C2—H2 | 106.9 | N5—C10—H10A | 109.0 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 112.3 (2) | C11—C10—H10A | 109.0 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 109.1 | N5—C10—H10B | 109.0 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 109.1 | C11—C10—H10B | 109.0 |
| C4—C3—H3B | 109.1 | H10A—C10—H10B | 107.8 |
| C2—C3—H3B | 109.1 | C12—C11—C10 | 124.4 (3) |
| H3A—C3—H3B | 107.9 | C12—C11—H11 | 117.8 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 127.1 (4) | C10—C11—H11 | 117.8 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 116.4 | C11—C12—H12A | 120.0 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 116.4 | C11—C12—H12B | 120.0 |
| C4—C5—H5A | 120.0 | H12A—C12—H12B | 120.0 |
| C4—C5—H5B | 120.0 | ||
| C6—N1—N2—C8 | −147.4 (2) | C1—C2—C6—C7 | 101.0 (2) |
| C6—N1—N2—C9 | 46.1 (3) | C3—C2—C6—C7 | −25.3 (3) |
| C8—N3—N4—C9 | −0.7 (3) | N4—N3—C8—N2 | 0.8 (3) |
| C9—N5—C1—O1 | −178.4 (2) | C9—N2—C8—N3 | −0.6 (3) |
| C10—N5—C1—O1 | −6.7 (3) | N1—N2—C8—N3 | −170.0 (2) |
| C9—N5—C1—C2 | 3.0 (3) | N3—N4—C9—N2 | 0.3 (3) |
| C10—N5—C1—C2 | 174.68 (19) | N3—N4—C9—N5 | 176.1 (2) |
| O1—C1—C2—C6 | −110.7 (2) | C8—N2—C9—N4 | 0.2 (3) |
| N5—C1—C2—C6 | 67.9 (2) | N1—N2—C9—N4 | 168.8 (2) |
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | 18.0 (3) | C8—N2—C9—N5 | −175.7 (2) |
| N5—C1—C2—C3 | −163.40 (19) | N1—N2—C9—N5 | −7.1 (4) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 169.1 (2) | C1—N5—C9—N4 | 142.8 (2) |
| C6—C2—C3—C4 | −67.2 (3) | C10—N5—C9—N4 | −29.0 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 130.9 (3) | C1—N5—C9—N2 | −41.9 (3) |
| N2—N1—C6—C7 | −172.6 (2) | C10—N5—C9—N2 | 146.2 (2) |
| N2—N1—C6—C2 | 4.6 (3) | C1—N5—C10—C11 | −78.4 (3) |
| C1—C2—C6—N1 | −76.1 (3) | C9—N5—C10—C11 | 93.6 (3) |
| C3—C2—C6—N1 | 157.6 (2) | N5—C10—C11—C12 | −114.4 (3) |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: XU2583).
References
- Barbour, L. J. (2001). J. Supramol. Chem.1, 189–191.
- Bruker (2005). APEX2 and SAINT Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Essassi, E. M., Lavergne, J. P. & Vialleffont, P. (1977). Tetrahedron, 33, 2807–2812.
- Richter, P. & Sheefelot, U. (1991). Pharmazie, 46, 701–705.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2009). publCIF In preparation.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680903133X/xu2583sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680903133X/xu2583Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report