Abstract
In the title salt, C11H13N2 +·C6H2N3O7 −, the dihedral angles between the benzene ring in the cation and the imidazolium ring and the benzene ring of the picrate anion are 113.7 (2) and 116.3 (2)°, respectively. The imidazolium ring is nearly parallel to the benzene ring of the picrate anion, the dihedral angle between the planes being 2.6 (1)°. The nitro groups in the picrate anions are disordered (occupancy ratio 0.54:0.46). The crystal packing is stabilized by weak C—H⋯O interactions between the cation–anion pairs.
Related literature
For civilian and military applications of energetic materials, see: Sikder & Sikder (2004 ▶). Heterocyclic organic salts with low melting points are a new class of energetic materials, which have attracted considerable interest because of their ‘green chemistry’ properties, see: Singh et al. (2006 ▶). Picric acid is a polynitrogen compound with explosive character and imidazolium-based cation picrate salts are good candidates for energetic ionic salts, see: Jin et al. (2005 ▶).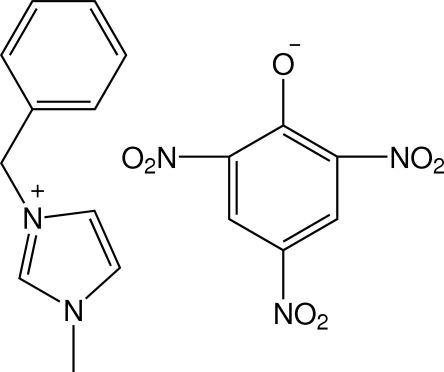
Experimental
Crystal data
C11H13N2 +·C6H2N3O7 −
M r = 401.34
Triclinic,
a = 9.1322 (6) Å
b = 10.2060 (7) Å
c = 10.8744 (7) Å
α = 63.6190 (10)°
β = 80.1660 (10)°
γ = 86.4820 (10)°
V = 894.52 (10) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.12 mm−1
T = 298 K
0.20 × 0.10 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.986, T max = 0.988
5623 measured reflections
3447 independent reflections
2610 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.046
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.056
wR(F 2) = 0.144
S = 1.04
3447 reflections
320 parameters
15 restraints
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.35 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.24 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2001 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT-Plus (Bruker, 2001 ▶); data reduction: SAINT-Plus; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809035454/jj2007sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809035454/jj2007Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C17—H17C⋯O7i | 0.96 | 2.42 | 3.346 (10) | 162 |
| C14—H14⋯O5ii | 0.93 | 2.39 | 3.283 (11) | 161 |
| C17—H17A⋯O2iii | 0.96 | 2.32 | 3.205 (11) | 153 |
| C16—H16⋯O2iii | 0.93 | 2.39 | 3.159 (9) | 140 |
| C16—H16⋯O1iii | 0.93 | 2.19 | 3.021 (2) | 149 |
| C13—H13A⋯O1iii | 0.97 | 2.58 | 3.382 (3) | 140 |
| C17—H17C⋯O7i | 0.96 | 2.42 | 3.346 (10) | 162 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 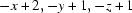 ; (ii)
; (ii) 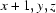 ; (iii)
; (iii) 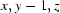 .
.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the financial support of the National Science Funds for Distinguished Young Scholars of Hubei Province (grant No. 2006ABB038), the Outstanding Mid-young Scholars’ Programs, Hubei Provincial Department of Education (Q20072203) and the project sponsored by SRF for ROCS, SEM (200724).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Energetic materials are used extensively for both civilian and military applications (Sikder & Sikder, 2004). Heterocyclic organic salts with low melting points are a new class of energetic materials that has attracted considerable interest because of their "green chemistry" properties (Singh et al., 2006). Picric acid is a polynitrogen compound with explosive character and imidazolium-based cation picrate salts are good candidates for energetic ionic salts (Jin et al., 2005). Based on our continued interest in these compounds, the title organic salt (scheme 1) was prepared and its structure is reported.
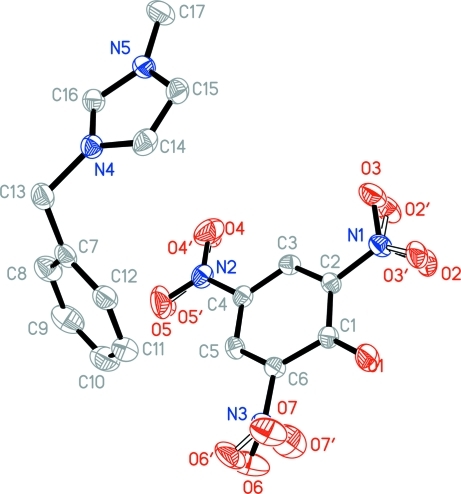
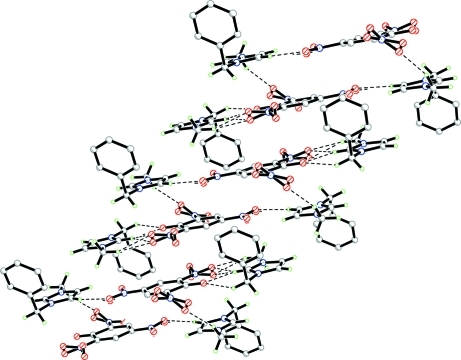
The asymmetric unit of the title compound contains one independent cation (1-methyl-3-benzenylimidazolium)-anion (picrate) pair (Fig. 1). The dihedral angle between the benzene ring in the cation and the imidazolium ring and the benzene ring of the picrate anion is 113.7 (2)° and 116.3 (2) °, respectively. The imidazolium ring is nearly parallel to the benzene ring of the picrate anion with the dihedral angle of separation being 2.6 (1)°. The oxygen atoms in the nitro groups of the picrate anion are disorderd with the o-NO2 major components (O2, O3, O4, O5) being 0.54 occupied and the p-NO2major components (O5, O6) at 0.58 occupancy . Crystal packing is stabilized by the weak C—H···O interactions between the cation-anion pairs (Fig. 2, Table 1).
Experimental
The title salt (C11H13N2)+.(C6H2N3O7)- was synthesized using a slightly modified literature mothod (Jin et al., 2005). It was crystallized by slow evaporation of an acetonitrile and methanol solution of the salt.
Refinement
H atoms were positioned geometrically with C—H bond lengths fixed to 0.93 (aromatic CH),0.97 (methylene CH2) or 0.96Å (methyl CH3). A riding model was used during the refinement process. The Uiso parameters for H atoms were constrained to be 1.2Ueq of the carrier C atom for aromatic and methylene groups, and 1.5Ueq of the carrier C atom for methyl groups. Measured Friedel pairs were merged before refinement.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The structure of (I) showing the atom-numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level and H atoms have been omitted for clarity. Only the predominate nitro oxygen atoms are displayed for the disordered nitro groups [O2,O3,O4,O5 (0.54); O6,O7 (0.58)].
Fig. 2.
The molecular packing diagram of the title compound. Dashed lines indicate weak C—H···O hydrogen bonding interactions between the cation-anion pairs (Table 1). Both of the disordered oxygen atoms in the nitro groups of the picrate anions are displayed.
Crystal data
| C11H13N2+·C6H2N3O7− | Z = 2 |
| Mr = 401.34 | F(000) = 416 |
| Triclinic, P1 | Dx = 1.490 Mg m−3 |
| Hall symbol: -P 1 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| a = 9.1322 (6) Å | Cell parameters from 1924 reflections |
| b = 10.2060 (7) Å | θ = 2.2–26.5° |
| c = 10.8744 (7) Å | µ = 0.12 mm−1 |
| α = 63.619 (1)° | T = 298 K |
| β = 80.166 (1)° | Block, yellow |
| γ = 86.482 (1)° | 0.20 × 0.10 × 0.10 mm |
| V = 894.52 (10) Å3 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEX CCD area-detector diffractometer | 3447 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2610 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.046 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 26.0°, θmin = 2.2° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −10→11 |
| Tmin = 0.986, Tmax = 0.988 | k = −12→12 |
| 5623 measured reflections | l = −11→13 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.056 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.144 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.04 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0707P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3447 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 320 parameters | Δρmax = 0.35 e Å−3 |
| 15 restraints | Δρmin = −0.24 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| C1 | 0.6669 (2) | 0.9523 (2) | 0.3757 (2) | 0.0412 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.5960 (2) | 0.8381 (2) | 0.50638 (19) | 0.0391 (5) | |
| C3 | 0.4985 (2) | 0.7359 (2) | 0.5166 (2) | 0.0417 (5) | |
| H3 | 0.4582 | 0.6639 | 0.6035 | 0.050* | |
| C4 | 0.4602 (2) | 0.7397 (2) | 0.3977 (2) | 0.0421 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.5191 (2) | 0.8461 (2) | 0.2678 (2) | 0.0435 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.4912 | 0.8496 | 0.1881 | 0.052* | |
| C6 | 0.6182 (2) | 0.9453 (2) | 0.25820 (19) | 0.0409 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.9029 (2) | 0.4665 (2) | 0.16740 (19) | 0.0448 (5) | |
| C8 | 0.7605 (3) | 0.4513 (3) | 0.1476 (2) | 0.0602 (6) | |
| H8 | 0.7217 | 0.3584 | 0.1754 | 0.072* | |
| C9 | 0.6758 (3) | 0.5720 (4) | 0.0873 (3) | 0.0767 (8) | |
| H9 | 0.5803 | 0.5606 | 0.0741 | 0.092* | |
| C10 | 0.7316 (3) | 0.7092 (3) | 0.0466 (2) | 0.0736 (8) | |
| H10 | 0.6740 | 0.7908 | 0.0058 | 0.088* | |
| C11 | 0.8721 (3) | 0.7263 (3) | 0.0659 (2) | 0.0670 (7) | |
| H11 | 0.9097 | 0.8194 | 0.0390 | 0.080* | |
| C12 | 0.9572 (3) | 0.6063 (2) | 0.1247 (2) | 0.0525 (6) | |
| H12 | 1.0532 | 0.6188 | 0.1362 | 0.063* | |
| C13 | 0.9942 (3) | 0.3344 (2) | 0.2325 (2) | 0.0516 (6) | |
| H13A | 0.9526 | 0.2525 | 0.2267 | 0.062* | |
| H13B | 1.0944 | 0.3526 | 0.1807 | 0.062* | |
| C14 | 1.0841 (2) | 0.3658 (2) | 0.4261 (2) | 0.0495 (5) | |
| H14 | 1.1477 | 0.4457 | 0.3713 | 0.059* | |
| C15 | 1.0570 (2) | 0.2983 (2) | 0.5651 (2) | 0.0492 (5) | |
| H15 | 1.0988 | 0.3221 | 0.6249 | 0.059* | |
| C16 | 0.9239 (2) | 0.1884 (2) | 0.4886 (2) | 0.0428 (5) | |
| H16 | 0.8581 | 0.1243 | 0.4855 | 0.051* | |
| C17 | 0.9006 (3) | 0.0830 (3) | 0.7460 (2) | 0.0630 (7) | |
| H17A | 0.8231 | 0.0235 | 0.7460 | 0.094* | |
| H17B | 0.8617 | 0.1349 | 0.7993 | 0.094* | |
| H17C | 0.9802 | 0.0218 | 0.7866 | 0.094* | |
| N1 | 0.6315 (2) | 0.8244 (2) | 0.63649 (18) | 0.0492 (5) | |
| N2 | 0.3603 (2) | 0.6289 (2) | 0.4097 (2) | 0.0525 (5) | |
| N3 | 0.6791 (2) | 1.0516 (2) | 0.11900 (19) | 0.0537 (5) | |
| N4 | 1.00040 (18) | 0.29513 (17) | 0.37987 (16) | 0.0416 (4) | |
| N5 | 0.95646 (18) | 0.18786 (18) | 0.60292 (16) | 0.0436 (4) | |
| O1 | 0.75553 (19) | 1.04635 (18) | 0.36201 (16) | 0.0646 (5) | |
| O2 | 0.6926 (10) | 0.9248 (11) | 0.6410 (15) | 0.064 (2) | 0.54 |
| O3 | 0.6079 (6) | 0.7030 (6) | 0.7381 (6) | 0.0693 (15) | 0.54 |
| O4 | 0.3127 (14) | 0.5302 (14) | 0.5267 (10) | 0.091 (4) | 0.54 |
| O5 | 0.3362 (16) | 0.6282 (15) | 0.3029 (9) | 0.093 (4) | 0.54 |
| O6 | 0.5945 (15) | 1.1147 (16) | 0.0366 (15) | 0.104 (4) | 0.58 |
| O7 | 0.8115 (7) | 1.0704 (12) | 0.0890 (11) | 0.075 (2) | 0.58 |
| O2' | 0.5492 (7) | 0.7504 (8) | 0.7465 (7) | 0.0700 (18) | 0.46 |
| O3' | 0.7363 (11) | 0.8962 (12) | 0.6320 (17) | 0.060 (2) | 0.46 |
| O5' | 0.3250 (14) | 0.6386 (14) | 0.3006 (8) | 0.061 (3) | 0.46 |
| O4' | 0.3061 (11) | 0.5414 (13) | 0.5233 (7) | 0.047 (2) | 0.46 |
| O6' | 0.616 (2) | 1.073 (2) | 0.027 (2) | 0.094 (5) | 0.42 |
| O7' | 0.7953 (14) | 1.1148 (18) | 0.0970 (19) | 0.114 (6) | 0.42 |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0384 (10) | 0.0434 (11) | 0.0450 (11) | −0.0048 (9) | −0.0101 (9) | −0.0205 (9) |
| C2 | 0.0363 (10) | 0.0451 (11) | 0.0391 (11) | 0.0023 (9) | −0.0108 (8) | −0.0197 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0372 (11) | 0.0410 (11) | 0.0427 (11) | −0.0032 (9) | −0.0058 (9) | −0.0143 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0377 (10) | 0.0424 (11) | 0.0492 (12) | −0.0051 (9) | −0.0082 (9) | −0.0218 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0415 (11) | 0.0514 (12) | 0.0448 (11) | −0.0017 (9) | −0.0117 (9) | −0.0257 (10) |
| C6 | 0.0392 (11) | 0.0431 (11) | 0.0383 (10) | −0.0037 (9) | −0.0064 (8) | −0.0155 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0523 (12) | 0.0520 (12) | 0.0282 (10) | −0.0094 (10) | 0.0025 (9) | −0.0177 (9) |
| C8 | 0.0590 (15) | 0.0666 (16) | 0.0465 (13) | −0.0155 (13) | −0.0010 (11) | −0.0180 (12) |
| C9 | 0.0572 (16) | 0.106 (2) | 0.0563 (16) | 0.0023 (16) | −0.0112 (13) | −0.0260 (16) |
| C10 | 0.085 (2) | 0.0757 (19) | 0.0474 (14) | 0.0179 (16) | −0.0074 (14) | −0.0192 (13) |
| C11 | 0.097 (2) | 0.0537 (15) | 0.0442 (13) | −0.0012 (14) | −0.0074 (13) | −0.0168 (11) |
| C12 | 0.0646 (14) | 0.0521 (14) | 0.0380 (11) | −0.0117 (11) | −0.0067 (10) | −0.0164 (10) |
| C13 | 0.0612 (14) | 0.0543 (13) | 0.0407 (11) | −0.0084 (11) | 0.0008 (10) | −0.0242 (10) |
| C14 | 0.0472 (12) | 0.0419 (12) | 0.0629 (14) | −0.0066 (10) | −0.0119 (10) | −0.0242 (11) |
| C15 | 0.0530 (13) | 0.0469 (12) | 0.0599 (14) | 0.0027 (10) | −0.0239 (11) | −0.0293 (11) |
| C16 | 0.0446 (11) | 0.0424 (11) | 0.0447 (11) | −0.0041 (9) | −0.0116 (9) | −0.0199 (9) |
| C17 | 0.0752 (16) | 0.0644 (15) | 0.0433 (13) | −0.0063 (13) | −0.0174 (11) | −0.0147 (11) |
| N1 | 0.0475 (11) | 0.0565 (12) | 0.0424 (10) | −0.0041 (9) | −0.0111 (8) | −0.0188 (9) |
| N2 | 0.0482 (11) | 0.0498 (12) | 0.0635 (13) | −0.0084 (9) | −0.0101 (11) | −0.0272 (11) |
| N3 | 0.0581 (13) | 0.0584 (12) | 0.0426 (11) | −0.0144 (10) | −0.0124 (10) | −0.0170 (9) |
| N4 | 0.0448 (9) | 0.0405 (9) | 0.0417 (9) | −0.0045 (8) | −0.0063 (7) | −0.0196 (8) |
| N5 | 0.0471 (10) | 0.0443 (10) | 0.0427 (10) | 0.0013 (8) | −0.0156 (8) | −0.0191 (8) |
| O1 | 0.0735 (11) | 0.0697 (11) | 0.0521 (9) | −0.0361 (9) | −0.0076 (8) | −0.0242 (8) |
| O2 | 0.083 (5) | 0.064 (4) | 0.055 (3) | −0.012 (4) | −0.016 (4) | −0.032 (3) |
| O3 | 0.081 (4) | 0.077 (4) | 0.039 (2) | −0.019 (3) | −0.011 (3) | −0.013 (2) |
| O4 | 0.099 (7) | 0.054 (5) | 0.108 (7) | −0.019 (5) | −0.016 (5) | −0.023 (5) |
| O5 | 0.119 (8) | 0.103 (7) | 0.089 (8) | −0.022 (5) | −0.024 (5) | −0.066 (6) |
| O6 | 0.086 (4) | 0.118 (8) | 0.062 (5) | 0.003 (5) | −0.028 (3) | 0.005 (4) |
| O7 | 0.044 (2) | 0.096 (5) | 0.056 (3) | −0.021 (2) | 0.0098 (19) | −0.011 (3) |
| O2' | 0.068 (4) | 0.094 (5) | 0.040 (2) | −0.026 (3) | 0.000 (3) | −0.022 (3) |
| O3' | 0.064 (5) | 0.067 (5) | 0.058 (4) | −0.014 (4) | −0.021 (4) | −0.031 (3) |
| O5' | 0.063 (5) | 0.059 (5) | 0.058 (6) | −0.037 (4) | −0.017 (4) | −0.014 (4) |
| O4' | 0.048 (4) | 0.053 (5) | 0.039 (4) | −0.031 (4) | 0.005 (3) | −0.018 (4) |
| O6' | 0.127 (11) | 0.104 (9) | 0.047 (4) | −0.047 (7) | −0.034 (6) | −0.017 (5) |
| O7' | 0.126 (9) | 0.122 (11) | 0.080 (5) | −0.060 (8) | −0.017 (6) | −0.026 (6) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—O1 | 1.235 (2) | C13—H13B | 0.9700 |
| C1—C2 | 1.451 (3) | C14—C15 | 1.336 (3) |
| C1—C6 | 1.454 (3) | C14—N4 | 1.371 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.368 (3) | C14—H14 | 0.9300 |
| C2—N1 | 1.450 (2) | C15—N5 | 1.367 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.379 (3) | C15—H15 | 0.9300 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C16—N4 | 1.319 (2) |
| C4—C5 | 1.383 (3) | C16—N5 | 1.325 (2) |
| C4—N2 | 1.443 (3) | C16—H16 | 0.9300 |
| C5—C6 | 1.357 (3) | C17—N5 | 1.464 (3) |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | C17—H17A | 0.9600 |
| C6—N3 | 1.451 (3) | C17—H17B | 0.9600 |
| C7—C8 | 1.383 (3) | C17—H17C | 0.9600 |
| C7—C12 | 1.385 (3) | N1—O2 | 1.220 (9) |
| C7—C13 | 1.493 (3) | N1—O3' | 1.222 (10) |
| C8—C9 | 1.373 (4) | N1—O2' | 1.235 (7) |
| C8—H8 | 0.9300 | N1—O3 | 1.240 (6) |
| C9—C10 | 1.369 (4) | N2—O4' | 1.197 (7) |
| C9—H9 | 0.9300 | N2—O5 | 1.222 (9) |
| C10—C11 | 1.368 (4) | N2—O5' | 1.243 (9) |
| C10—H10 | 0.9300 | N2—O4 | 1.245 (9) |
| C11—C12 | 1.367 (3) | N3—O6' | 1.168 (11) |
| C11—H11 | 0.9300 | N3—O7 | 1.201 (7) |
| C12—H12 | 0.9300 | N3—O7' | 1.208 (11) |
| C13—N4 | 1.480 (3) | N3—O6 | 1.215 (10) |
| C13—H13A | 0.9700 | ||
| O1—C1—C2 | 126.06 (18) | N4—C14—H14 | 126.5 |
| O1—C1—C6 | 122.83 (18) | C14—C15—N5 | 107.38 (18) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 111.10 (16) | C14—C15—H15 | 126.3 |
| C3—C2—N1 | 116.05 (17) | N5—C15—H15 | 126.3 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 124.07 (18) | N4—C16—N5 | 108.52 (17) |
| N1—C2—C1 | 119.85 (17) | N4—C16—H16 | 125.7 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.81 (18) | N5—C16—H16 | 125.7 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.1 | N5—C17—H17A | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.1 | N5—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.79 (18) | H17A—C17—H17B | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—N2 | 119.28 (18) | N5—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—N2 | 119.92 (19) | H17A—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 119.12 (19) | H17B—C17—H17C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.4 | O2—N1—O2' | 112.3 (8) |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.4 | O3'—N1—O2' | 122.1 (8) |
| C5—C6—N3 | 116.53 (18) | O2—N1—O3 | 122.5 (7) |
| C5—C6—C1 | 125.09 (18) | O3'—N1—O3 | 116.7 (8) |
| N3—C6—C1 | 118.38 (17) | O2—N1—C2 | 120.6 (7) |
| C8—C7—C12 | 118.2 (2) | O3'—N1—C2 | 118.2 (8) |
| C8—C7—C13 | 120.1 (2) | O2'—N1—C2 | 119.5 (4) |
| C12—C7—C13 | 121.7 (2) | O3—N1—C2 | 116.6 (3) |
| C9—C8—C7 | 120.6 (2) | O4'—N2—O5 | 123.1 (7) |
| C9—C8—H8 | 119.7 | O4'—N2—O5' | 123.6 (5) |
| C7—C8—H8 | 119.7 | O5—N2—O4 | 122.0 (7) |
| C10—C9—C8 | 120.2 (3) | O5'—N2—O4 | 123.2 (7) |
| C10—C9—H9 | 119.9 | O4'—N2—C4 | 118.7 (4) |
| C8—C9—H9 | 119.9 | O5—N2—C4 | 118.2 (5) |
| C11—C10—C9 | 120.1 (3) | O5'—N2—C4 | 117.4 (4) |
| C11—C10—H10 | 120.0 | O4—N2—C4 | 119.5 (6) |
| C9—C10—H10 | 120.0 | O6'—N3—O7 | 115.7 (13) |
| C12—C11—C10 | 119.9 (2) | O6'—N3—O7' | 120.1 (12) |
| C12—C11—H11 | 120.0 | O7—N3—O6 | 122.8 (9) |
| C10—C11—H11 | 120.0 | O7'—N3—O6 | 115.6 (13) |
| C11—C12—C7 | 121.1 (2) | O6'—N3—C6 | 119.1 (10) |
| C11—C12—H12 | 119.5 | O7—N3—C6 | 118.5 (5) |
| C7—C12—H12 | 119.5 | O7'—N3—C6 | 120.8 (9) |
| N4—C13—C7 | 112.48 (16) | O6—N3—C6 | 118.6 (8) |
| N4—C13—H13A | 109.1 | C16—N4—C14 | 108.63 (17) |
| C7—C13—H13A | 109.1 | C16—N4—C13 | 125.71 (16) |
| N4—C13—H13B | 109.1 | C14—N4—C13 | 125.65 (17) |
| C7—C13—H13B | 109.1 | C16—N5—C15 | 108.46 (17) |
| H13A—C13—H13B | 107.8 | C16—N5—C17 | 126.17 (18) |
| C15—C14—N4 | 107.00 (18) | C15—N5—C17 | 125.31 (18) |
| C15—C14—H14 | 126.5 | ||
| O1—C1—C2—C3 | −179.9 (2) | C3—C2—N1—O2' | −18.1 (4) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 1.3 (3) | C1—C2—N1—O2' | 164.1 (4) |
| O1—C1—C2—N1 | −2.2 (3) | C3—C2—N1—O3 | 20.3 (4) |
| C6—C1—C2—N1 | 178.93 (17) | C1—C2—N1—O3 | −157.5 (3) |
| N1—C2—C3—C4 | −179.13 (17) | C3—C4—N2—O4' | 4.4 (8) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −1.4 (3) | C5—C4—N2—O4' | −177.1 (7) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.0 (3) | C3—C4—N2—O5 | −174.9 (10) |
| C2—C3—C4—N2 | 178.38 (18) | C5—C4—N2—O5 | 3.6 (10) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 1.5 (3) | C3—C4—N2—O5' | 177.9 (9) |
| N2—C4—C5—C6 | −176.96 (18) | C5—C4—N2—O5' | −3.6 (9) |
| C4—C5—C6—N3 | 178.34 (19) | C3—C4—N2—O4 | −1.4 (8) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −1.5 (3) | C5—C4—N2—O4 | 177.0 (8) |
| O1—C1—C6—C5 | −178.7 (2) | C5—C6—N3—O6' | 19.6 (10) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | 0.2 (3) | C1—C6—N3—O6' | −160.5 (10) |
| O1—C1—C6—N3 | 1.4 (3) | C5—C6—N3—O7 | −130.6 (6) |
| C2—C1—C6—N3 | −179.67 (17) | C1—C6—N3—O7 | 49.3 (7) |
| C12—C7—C8—C9 | −0.1 (3) | C5—C6—N3—O7' | −158.5 (9) |
| C13—C7—C8—C9 | −179.7 (2) | C1—C6—N3—O7' | 21.4 (9) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | −0.3 (4) | C5—C6—N3—O6 | 47.4 (7) |
| C8—C9—C10—C11 | 0.0 (4) | C1—C6—N3—O6 | −132.7 (7) |
| C9—C10—C11—C12 | 0.6 (4) | N5—C16—N4—C14 | −0.4 (2) |
| C10—C11—C12—C7 | −1.0 (3) | N5—C16—N4—C13 | −178.99 (17) |
| C8—C7—C12—C11 | 0.7 (3) | C15—C14—N4—C16 | 0.5 (2) |
| C13—C7—C12—C11 | −179.68 (19) | C15—C14—N4—C13 | 179.14 (19) |
| C8—C7—C13—N4 | −102.8 (2) | C7—C13—N4—C16 | 102.4 (2) |
| C12—C7—C13—N4 | 77.6 (2) | C7—C13—N4—C14 | −76.0 (2) |
| N4—C14—C15—N5 | −0.4 (2) | N4—C16—N5—C15 | 0.1 (2) |
| C3—C2—N1—O2 | −165.4 (5) | N4—C16—N5—C17 | −177.20 (19) |
| C1—C2—N1—O2 | 16.8 (5) | C14—C15—N5—C16 | 0.2 (2) |
| C3—C2—N1—O3' | 167.5 (6) | C14—C15—N5—C17 | 177.5 (2) |
| C1—C2—N1—O3' | −10.3 (6) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C17—H17C···O7i | 0.96 | 2.42 | 3.346 (10) | 162 |
| C14—H14···O5ii | 0.93 | 2.39 | 3.283 (11) | 161 |
| C17—H17A···O2iii | 0.96 | 2.32 | 3.205 (11) | 153 |
| C16—H16···O2iii | 0.93 | 2.39 | 3.159 (9) | 140 |
| C16—H16···O1iii | 0.93 | 2.19 | 3.021 (2) | 149 |
| C13—H13A···O1iii | 0.97 | 2.58 | 3.382 (3) | 140 |
| C17—H17C···O7i | 0.96 | 2.42 | 3.346 (10) | 162 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+2, −y+1, −z+1; (ii) x+1, y, z; (iii) x, y−1, z.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: JJ2007).
References
- Bruker (2001). SAINT-Plus and SMART Bruker AXS, Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Jin, C. M., Ye, C., Piekarski, C., Twamley, B. & Shreeve, J. M. (2005). Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. pp. 3760–3767.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sikder, A. K. & Sikder, N. J. (2004). J. Hazardous Materials A, 112, 1–15. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Singh, R. P., Verma, R. D., Meshri, D. T. & Shreeve, J. M. (2006). Angew. Chem. Int. Ed.45, 3584–3601. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809035454/jj2007sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809035454/jj2007Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report