Abstract
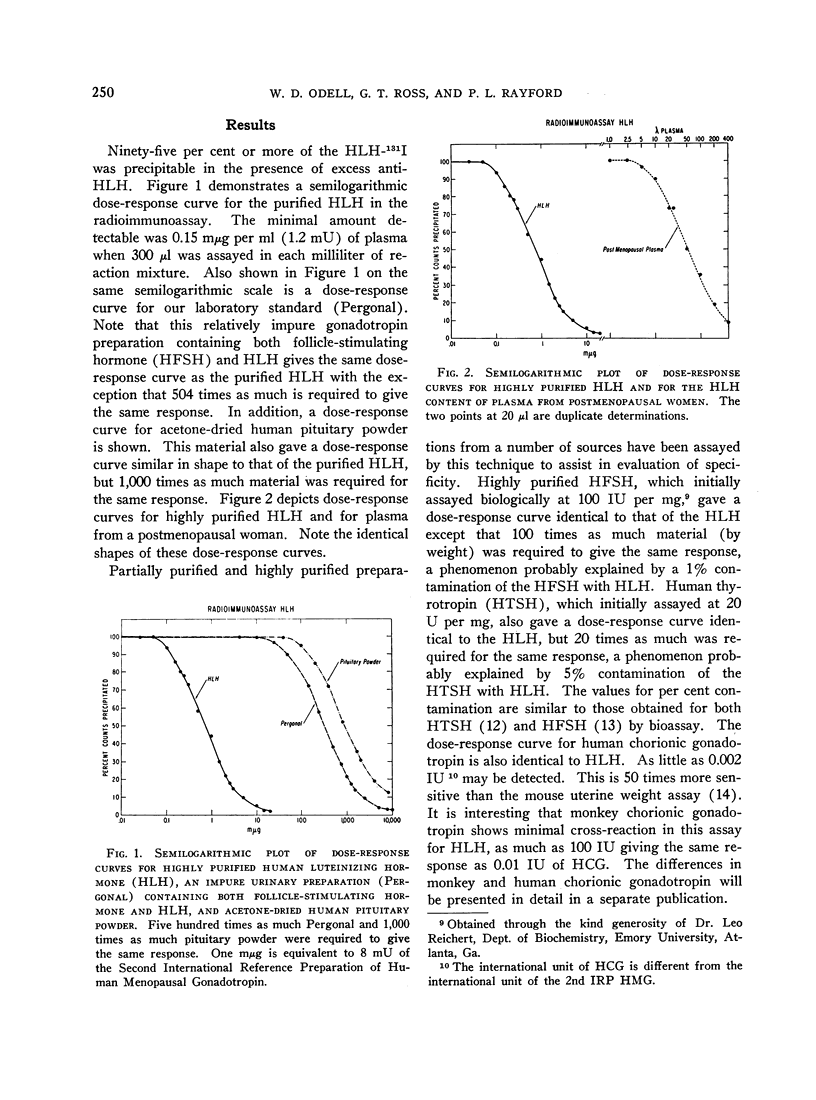
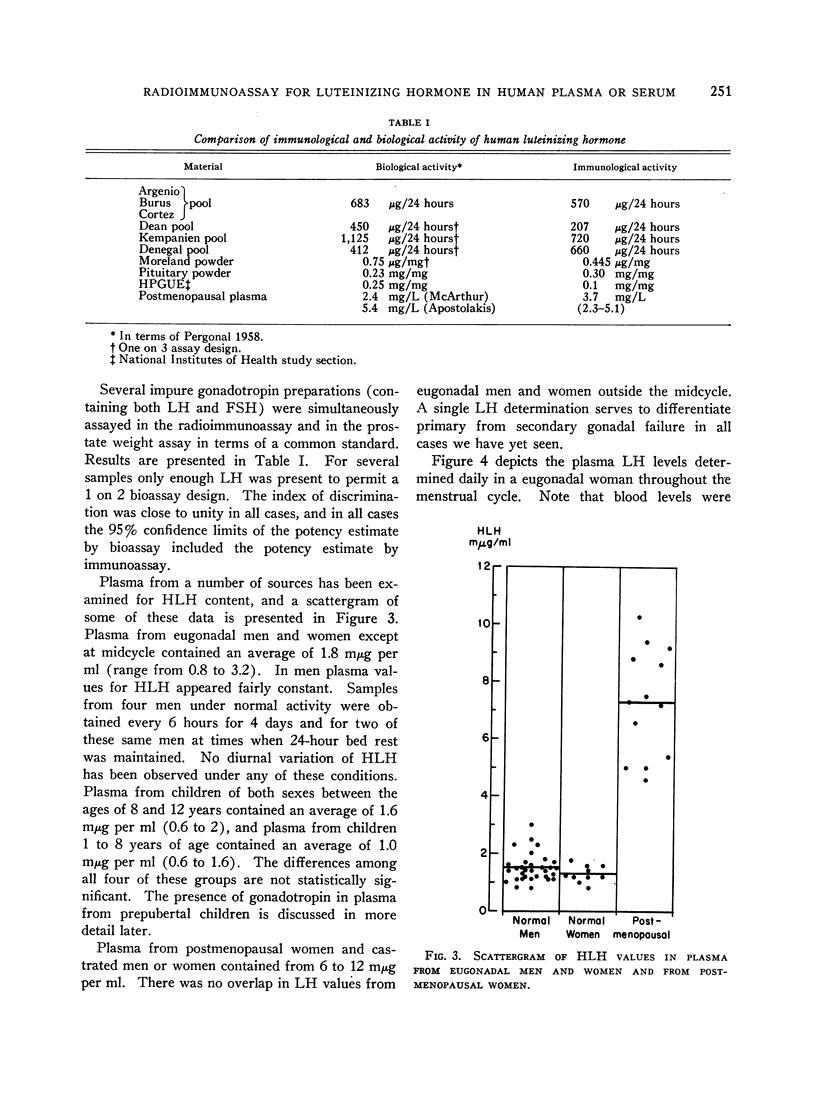
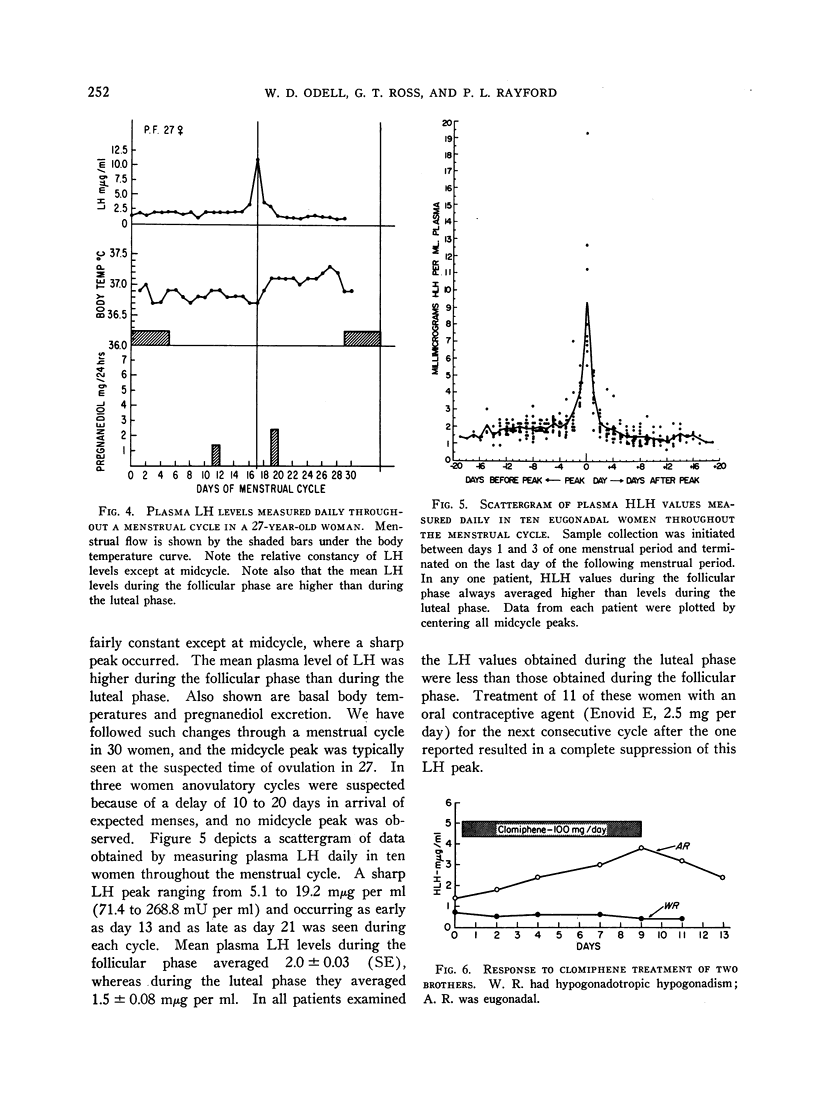
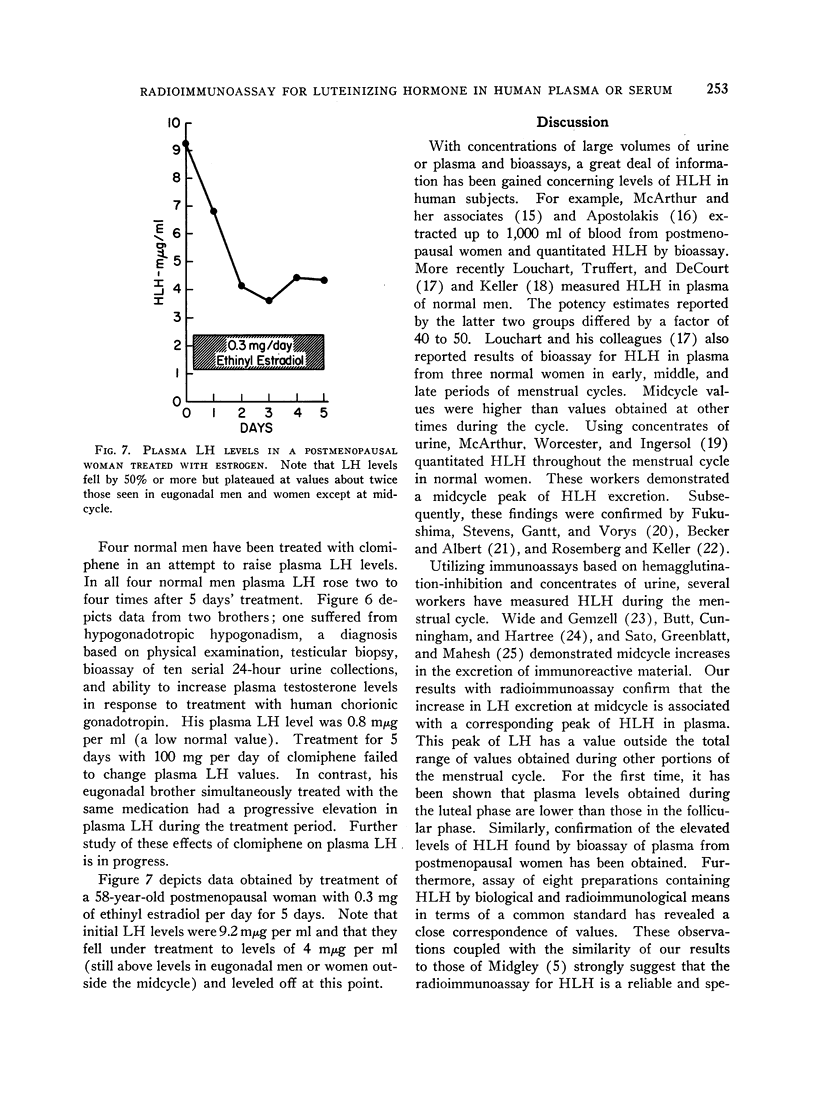
It is not practical to quantitate gonadotropin in the blood of normal men and women by utilizing bioassays. We have developed a method for sensitive, precise, and specific radioimmunoassay of luteinizing hormone (LH) in human serum or plasma. Antisera were developed against human chorionic gonadotropin, and one of these was selected for extensive cross-reaction with human LH. Highly purified LH was radioiodinated by the method of Greenwood, Hunter, and Glover. Separation of antibody-bound from free LH-131I was accomplished by a double antibody technique. Dose-response curves for the purifed LH, an impure urinary LH preparation, pituitary powder, and LH in plasma were all identical. Immunoassay and bioassay of impure urinary and pituitary gonadotropin preparations in terms of a common standard resulted in an index of discrimination of close to unity. LH levels in plasma from 32 adult men and 30 women outside the midcycle ranged from 0.6 to 3.2 mμg per ml (1 mμg of our laboratory LH standard is equivalent to 8 mU of the Second International Reference Preparation of Human Menopausal Gonadotropin). Levels were remarkably constant in men from day to day and in women except at midcycle, when a sharp peak occurred lasting less than 24 hours. In all women studied who had a midcycle LH peak, mean plasma LH levels during the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle were higher than mean values obtained during the luteal phase. Prepubertal children had detectable plasma LH, and mean values were only slightly less than in adults. Plasma from castrate men or women or postmenopausal women contained 4.5 to 10.5 mμg per ml. Clomiphene treatment of four men resulted in a doubling of plasma LH in 5 days.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- APOSTOLAKIS M. Detection and estimation of pituitary gonadotrophins in human plasma. J Endocrinol. 1959 Dec;19:377–388. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0190377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECKER K. L., ALBERT A. URINARY EXCRETION OF FOLLICLE-STIMULATING AND LUTEINIZING HORMONES. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Jul;25:962–974. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-7-962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTT W. R., CUNNINGHAM F. J., HARTREE A. S. GONADOTROPHINS. PREPARATION AND ASSAY OF HUMAN PITUITARY FSH AND LH. Proc R Soc Med. 1964 Feb;57:107–108. doi: 10.1177/003591576405700213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUTT W. R., CUNNINGHAM F. J., HARTREE A. S. GONADOTROPHINS. PREPARATION AND ASSAY OF HUMAN PITUITARY FSH AND LH. Proc R Soc Med. 1964 Feb;57:107–108. doi: 10.1177/003591576405700213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BYRNES W. W., MEYER R. K. The inhibition of gonadotrophic hormone secretion by physiological doses of estrogen. Endocrinology. 1951 Feb;48(2):133–136. doi: 10.1210/endo-48-2-133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITSCHEN W., CLAYTON B. E. URINARY EXCRETION OF GONADOTROPHINS WITH PARTICULAR REFERENCE TO CHILDREN. Arch Dis Child. 1965 Feb;40:16–26. doi: 10.1136/adc.40.209.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUKUSHIMA M., STEVENS V. C., GANTT C. L., VORYS N. URINARY FSH AND LH EXCRETION DURING THE NORMAL MENSTRUAL CYCLE. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Feb;24:205–213. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-2-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C. The use of non-castrate parabiotic rats for the evaluation of plasma gonadotrophins. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1966 Feb;51(2):269–280. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0510269. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller P. J. Studies on pituitary gonadotrophins in human plasma. II. Follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormone in male and postmenopausal plasma. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1966 Jul;52(3):348–356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOUCHART J., TRUFFERT J., DECOURT J. DOSAGE DE L'HORMONE LUTEINISANTE DANS LE PLASMA HUMAIN. RESULTATS CHEZ LES SUJETS NORMAUX DES DEUX SEXES. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1965 Jun;49:293–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCARTHUR J. W., ANTONIADES H. N., LARSON L. H., PENNELL R. B., INGERSOLL F. M., ULFELDER H. FOLLICLE-STIMULATING HORMONE AND LUTEINIZING HORMONE CONTENT OF POOLED HUMAN MENOPAUSAL PLASMA AND OF SUBFRACTIONS PREPARED BY COHN METHODS 6 AND 9. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 May;24:425–431. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-5-425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORGAN C. R., SORENSON R. L., LAZAROW A. STUDIES OF AN INHIBITOR OF THE TWO ANTIBODY IMMUNOASSAY SYSTEM. Diabetes. 1964 Jan-Feb;13:1–5. doi: 10.2337/diab.13.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McARTHUR J. W., WORCESTER J., INGERSOLL F. M. The urinary excretion of interstitial-cell and follicle-stimulating hormone activity during the normal menstrual cycle. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1958 Nov;18(11):1186–1201. doi: 10.1210/jcem-18-11-1186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midgley A. R., Jr Radioimmunoassay: a method for human chorionic gonadotropin and human luteinizing hormone. Endocrinology. 1966 Jul;79(1):10–18. doi: 10.1210/endo-79-1-10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odell W. D., Ross G. T., Rayford P. L. Radioimmunoassay for human luteinizing hormone. Metabolism. 1966 Apr;15(4):287–289. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(66)90142-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARLOW A. F., CONDLIFFE P. G., REICHERT L. E., Jr, WILHELMI A. E. RECOVERY AND PARTIAL PURIFICATION OF FSH AND LH DURING THE PURIFICATION OF TSH FROM HUMAN PITUITARY GLANDS. Endocrinology. 1965 Jan;76:27–34. doi: 10.1210/endo-76-1-27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAUL W. E., ODELL W. D. RADIATION INACTIVATION OF THE IMMUNOLOGICAL AND BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITIES OF HUMAN CHORIONIC GONADOTROPIN. Nature. 1964 Aug 29;203:979–980. doi: 10.1038/203979a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosemberg E., Keller P. J. Studies on the urinary excretion of follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormone activity during the menstrual cycle. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Sep;25(9):1262–1274. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-9-1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SATO T., GREENBLATT R. B., MAHESH V. B. LEVELS OF LUTEINIZING HORMONE DURING THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE DETERMINED BY IMMUNOLOGIC TECHNICS. Fertil Steril. 1965 Mar-Apr;16:223–228. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)35529-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullner W. W., Hertz R. Chorionic gonadotropin levels in the rhesus monkey during early pregnancy. Endocrinology. 1966 Jan;78(1):204–207. doi: 10.1210/endo-78-1-204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIDE L., GEMZELL C. Immunological determination of pituitary luteinizing hormone in the urine of fertile and post-menopausal women and adult men. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1962 Apr;39:539–546. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0390539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



