Abstract
The title compound, [FeCl3(C12H18N4)]·0.5CH3OH, contains an FeIII ion in a distorted octahedral coordination environment. The neutral N,N′,N′′-tridentate ligand adopts a fac coordination mode, and chloride ligands lie trans to each of the three coordinated N atoms. In the crystal, the complexes form columns extending parallel to the approximate local threefold axes of the FeN3Cl3 octahedra, and the columns are arranged so that the uncoordinated nitrile groups align in an antiparallel manner and the pyridyl rings form offset face-to-face arrangements [interplanar separations = 2.95 (1) and 3.11 (1) Å; centroid–centroid distances = 5.31 (1) and 4.92 (1) Å]. The methanol solvent molecule is disordered about a twofold rotation axis.
Related literature
For structures of similar FeIII complexes, see: Cowdell et al. (2004 ▶); Sundaravel et al. (2008 ▶); Velusamy et al. (2005 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
[FeCl3(C12H18N4)]·0.5CH4O
M r = 396.53
Monoclinic,

a = 34.243 (2) Å
b = 7.1331 (5) Å
c = 15.4835 (11) Å
β = 116.733 (3)°
V = 3377.8 (4) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 1.37 mm−1
T = 180 K
0.18 × 0.10 × 0.10 mm
Data collection
Bruker–Nonius X8 APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2004 ▶) T min = 0.744, T max = 0.875
38084 measured reflections
2937 independent reflections
2033 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.066
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.040
wR(F 2) = 0.105
S = 1.07
2937 reflections
196 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.48 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.45 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2004 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2004 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: SHELXTL; software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680904375X/hb5138sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680904375X/hb5138Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Selected bond lengths (Å).
| Fe1—N1 | 2.186 (3) |
| Fe1—N2 | 2.235 (3) |
| Fe1—N3 | 2.330 (3) |
| Fe1—Cl1 | 2.2873 (11) |
| Fe1—Cl2 | 2.2908 (11) |
| Fe1—Cl3 | 2.3284 (11) |
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the Danish Natural Sciences Research Council and the Carlsberg Foundation for provision of the X-ray equipment.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The ligand N,N'-dimethyl-N-(2-pyridylmethyl)ethylendiamine- N'-acetonitrile was prepared as a by-product during synthesis of N,N'-dimethyl-N-(2-pyridylmethyl)ethylendiamine- N'-acetic acid, as a result of contamination of the reagent bromoacetic acid with bromoacetonitrile.
Experimental
The ligand synthesis was undertaken in three steps:
(i) Picolinal (2.50 ml, 24 mmol) and N,N'-dimethylethylenediamine (2.22 ml, 24 mmol) in dry diethylether (20 ml) were stirred overnight under CaCl2 protection. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure to leave 1,3-dimethyl-2-(2-pyridylmethyl)imidazolidine as a thin yellow oil (3.9 g, yield 92%).
(ii) NaBH3CN (1.3925 g, 22 mmol) and CF3COOH (3.365 ml, 44 mmol) were added in small portions [CAUTION: possible formation of HCN!] to 1,3-dimethyl-2-(2-pyridylmethyl)imidazolidine (3.8944 g, 22 mmol) in methanol (80 ml) and the reaction mixture was stirred overnight under CaCl2 protection. NaOH (85 ml of a 4 M aqueous solution) was added. The reaction mixture was stirred overnight and extracted with CHCl2 (3 × 20 ml), then the organic phase was dried over Na2SO4 and filtered. The filtrate was evaporated in vacuo to leave N,N'-dimethyl-N-(2-pyridylmethyl)ethylenediamine as a thin yellow oil (3.2 g, yield 81%).
(iii) A mixture of N,N'-dimethyl-N-(2-pyridylmethyl)ethylenediamine (3.1602 g, 18 mmol), bromoacetic acid (2.4499 g, 18 mmol) and triethylamine (2.444 ml, 18 mmol) in absolute ethanol (10 ml) was heated overnight under reflux and N2. The solvent was removed under reduced pressure, then the residue was re-dissolved in water, adjusted to pH 8 with conc. NaOH and washed with CH2Cl2 (3 × 15 ml). The aqueous phase was adjusted to pH 4 with conc. HCl then evaporated in vacuo to leave a mixture of N,N'-dimethyl-N-(2-pyridylmethyl)ethylendiamine- N'-acetonitrile (L) and N,N'-dimethyl-N-(2-pyridylmethyl)ethylendiamine- N'-acetic acid as a brown oil (6.0 g, yield 139% due to impurities of triethylammonium bromide).
The title compound was then prepared as follows:
Anhydrous FeCl3 (15.8 mg, 0.097 mmol) was added to the mixed ligand product from above (23.3 mg, 0.098 mmol) in methanol (1.75 ml), and a few yellow blocks of (I) were deposited overnight.
Refinement
H atoms bound to C atoms were placed in idealized positions with C—H = 0.95–0.99 Å and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = 1.2 or 1.5Ueq(C). The methanol molecule is disordered around a 2-fold rotation axis and all of its atoms have site occupancy factor 0.5. The H atom of the OH group was placed along the O1S—Cl3i vector [symmetry code (i): x, 1 - y, 1/2 + z], with O—H = 0.85 Å and refined as riding with Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(O).
Figures
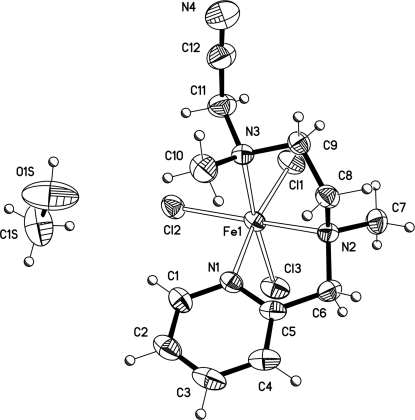
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of (I) with displacement ellipsoids shown at 50% probability for non-H atoms. The methanol molecule (C1S—O1S) is disordered around a 2-fold rotation axis.
Fig. 2.
Unit-cell contents of (I) projected along the b axis, which corresponds to the stacking directions of the "columns" referred to in the Abstract.
Crystal data
| [FeCl3(C12H18N4)]·0.5CH4O | F(000) = 1632 |
| Mr = 396.53 | Dx = 1.559 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -C 2yc | Cell parameters from 5350 reflections |
| a = 34.243 (2) Å | θ = 2.6–21.6° |
| b = 7.1331 (5) Å | µ = 1.37 mm−1 |
| c = 15.4835 (11) Å | T = 180 K |
| β = 116.733 (3)° | Block, yellow |
| V = 3377.8 (4) Å3 | 0.18 × 0.10 × 0.10 mm |
| Z = 8 |
Data collection
| Bruker–Nonius X8 APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2937 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2033 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.066 |
| Thin–slice ω and φ scans | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 3.7° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2004) | h = −37→40 |
| Tmin = 0.744, Tmax = 0.875 | k = −8→8 |
| 38084 measured reflections | l = −18→18 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.040 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.105 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.07 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0478P)2 + 6.352P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2937 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 196 parameters | Δρmax = 0.48 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.45 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| Fe1 | 0.132445 (17) | 0.50145 (7) | 0.14178 (4) | 0.02864 (18) | |
| Cl1 | 0.19634 (3) | 0.65429 (14) | 0.23597 (8) | 0.0446 (3) | |
| Cl2 | 0.09339 (3) | 0.60710 (15) | 0.21941 (7) | 0.0419 (3) | |
| Cl3 | 0.10936 (3) | 0.71324 (14) | 0.01386 (7) | 0.0449 (3) | |
| N1 | 0.07912 (9) | 0.3232 (4) | 0.0431 (2) | 0.0303 (7) | |
| N2 | 0.16333 (9) | 0.3137 (4) | 0.0744 (2) | 0.0301 (7) | |
| N3 | 0.15694 (10) | 0.2550 (4) | 0.2523 (2) | 0.0310 (7) | |
| C1 | 0.03944 (12) | 0.3100 (5) | 0.0400 (3) | 0.0362 (10) | |
| H1A | 0.0349 | 0.3647 | 0.0907 | 0.043* | |
| C2 | 0.00547 (13) | 0.2210 (6) | −0.0332 (3) | 0.0425 (11) | |
| H2A | −0.0225 | 0.2177 | −0.0343 | 0.051* | |
| C3 | 0.01180 (14) | 0.1367 (6) | −0.1051 (3) | 0.0476 (11) | |
| H3A | −0.0115 | 0.0715 | −0.1557 | 0.057* | |
| C4 | 0.05248 (14) | 0.1471 (6) | −0.1034 (3) | 0.0439 (11) | |
| H4A | 0.0576 | 0.0897 | −0.1527 | 0.053* | |
| C5 | 0.08561 (12) | 0.2433 (5) | −0.0281 (3) | 0.0334 (9) | |
| C6 | 0.12956 (13) | 0.2725 (6) | −0.0253 (3) | 0.0373 (10) | |
| H6A | 0.1379 | 0.1584 | −0.0494 | 0.045* | |
| H6B | 0.1279 | 0.3779 | −0.0684 | 0.045* | |
| C7 | 0.20174 (12) | 0.3989 (6) | 0.0690 (3) | 0.0399 (10) | |
| H7A | 0.2138 | 0.3098 | 0.0392 | 0.060* | |
| H7B | 0.2241 | 0.4296 | 0.1344 | 0.060* | |
| H7C | 0.1927 | 0.5134 | 0.0300 | 0.060* | |
| C8 | 0.17688 (12) | 0.1338 (5) | 0.1299 (3) | 0.0339 (9) | |
| H8A | 0.2007 | 0.0754 | 0.1197 | 0.041* | |
| H8B | 0.1518 | 0.0460 | 0.1058 | 0.041* | |
| C9 | 0.19227 (12) | 0.1686 (5) | 0.2357 (3) | 0.0310 (9) | |
| H9A | 0.2012 | 0.0485 | 0.2714 | 0.037* | |
| H9B | 0.2180 | 0.2528 | 0.2604 | 0.037* | |
| C10 | 0.12260 (14) | 0.1127 (6) | 0.2399 (3) | 0.0462 (11) | |
| H10A | 0.1354 | 0.0147 | 0.2891 | 0.069* | |
| H10B | 0.1114 | 0.0564 | 0.1754 | 0.069* | |
| H10C | 0.0986 | 0.1739 | 0.2471 | 0.069* | |
| C11 | 0.17554 (14) | 0.3223 (6) | 0.3534 (3) | 0.0466 (11) | |
| H11A | 0.1968 | 0.4236 | 0.3625 | 0.056* | |
| H11B | 0.1518 | 0.3759 | 0.3655 | 0.056* | |
| C12 | 0.19758 (15) | 0.1724 (7) | 0.4245 (3) | 0.0495 (12) | |
| N4 | 0.21605 (14) | 0.0568 (6) | 0.4803 (3) | 0.0660 (12) | |
| C1S | 0.0000 | 0.3867 (12) | 0.2500 | 0.081 (2) | |
| H1S1 | −0.0264 | 0.3589 | 0.1902 | 0.122* | 0.50 |
| H1S2 | 0.0177 | 0.4799 | 0.2369 | 0.122* | 0.50 |
| H1S3 | −0.0084 | 0.4363 | 0.2983 | 0.122* | 0.50 |
| O1S | 0.0231 (3) | 0.2310 (11) | 0.2834 (5) | 0.103 (3) | 0.50 |
| H1S | 0.0438 | 0.2424 | 0.3402 | 0.155* | 0.50 |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Fe1 | 0.0251 (3) | 0.0238 (3) | 0.0325 (3) | −0.0011 (2) | 0.0090 (2) | −0.0001 (2) |
| Cl1 | 0.0361 (6) | 0.0348 (6) | 0.0520 (7) | −0.0047 (5) | 0.0100 (5) | −0.0027 (5) |
| Cl2 | 0.0341 (6) | 0.0442 (6) | 0.0442 (6) | 0.0051 (5) | 0.0150 (5) | −0.0080 (5) |
| Cl3 | 0.0434 (6) | 0.0320 (6) | 0.0460 (6) | −0.0021 (5) | 0.0083 (5) | 0.0112 (5) |
| N1 | 0.0254 (18) | 0.0280 (18) | 0.0329 (18) | 0.0023 (14) | 0.0090 (14) | 0.0036 (14) |
| N2 | 0.0262 (18) | 0.0366 (19) | 0.0250 (17) | −0.0030 (14) | 0.0095 (14) | −0.0019 (14) |
| N3 | 0.0283 (18) | 0.0358 (19) | 0.0262 (17) | −0.0009 (14) | 0.0098 (15) | −0.0019 (14) |
| C1 | 0.028 (2) | 0.033 (2) | 0.045 (2) | −0.0015 (18) | 0.014 (2) | 0.0012 (19) |
| C2 | 0.029 (2) | 0.040 (2) | 0.048 (3) | 0.0003 (19) | 0.008 (2) | 0.013 (2) |
| C3 | 0.033 (3) | 0.046 (3) | 0.042 (3) | −0.007 (2) | −0.002 (2) | 0.004 (2) |
| C4 | 0.044 (3) | 0.045 (3) | 0.029 (2) | −0.004 (2) | 0.0046 (19) | −0.0008 (19) |
| C5 | 0.032 (2) | 0.033 (2) | 0.027 (2) | −0.0023 (17) | 0.0048 (19) | 0.0036 (18) |
| C6 | 0.038 (2) | 0.046 (2) | 0.027 (2) | −0.0031 (19) | 0.0134 (19) | −0.0022 (18) |
| C7 | 0.035 (2) | 0.048 (3) | 0.042 (2) | −0.006 (2) | 0.022 (2) | 0.000 (2) |
| C8 | 0.030 (2) | 0.034 (2) | 0.035 (2) | 0.0039 (18) | 0.0116 (18) | −0.0020 (18) |
| C9 | 0.029 (2) | 0.028 (2) | 0.036 (2) | 0.0025 (17) | 0.0140 (18) | 0.0016 (17) |
| C10 | 0.042 (3) | 0.042 (3) | 0.055 (3) | −0.002 (2) | 0.022 (2) | 0.016 (2) |
| C11 | 0.051 (3) | 0.049 (3) | 0.034 (2) | 0.011 (2) | 0.014 (2) | −0.002 (2) |
| C12 | 0.056 (3) | 0.052 (3) | 0.041 (3) | 0.004 (2) | 0.022 (2) | 0.005 (2) |
| N4 | 0.071 (3) | 0.071 (3) | 0.054 (3) | 0.007 (2) | 0.027 (2) | 0.017 (2) |
| C1S | 0.073 (6) | 0.071 (6) | 0.119 (7) | 0.000 | 0.061 (5) | 0.000 |
| O1S | 0.121 (7) | 0.052 (5) | 0.074 (6) | 0.008 (5) | −0.012 (5) | 0.008 (4) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Fe1—N1 | 2.186 (3) | C6—H6A | 0.990 |
| Fe1—N2 | 2.235 (3) | C6—H6B | 0.990 |
| Fe1—N3 | 2.330 (3) | C7—H7A | 0.980 |
| Fe1—Cl1 | 2.2873 (11) | C7—H7B | 0.980 |
| Fe1—Cl2 | 2.2908 (11) | C7—H7C | 0.980 |
| Fe1—Cl3 | 2.3284 (11) | C8—C9 | 1.500 (5) |
| N1—C1 | 1.341 (5) | C8—H8A | 0.990 |
| N1—C5 | 1.345 (5) | C8—H8B | 0.990 |
| N2—C6 | 1.484 (5) | C9—H9A | 0.990 |
| N2—C7 | 1.484 (4) | C9—H9B | 0.990 |
| N2—C8 | 1.497 (5) | C10—H10A | 0.980 |
| N3—C9 | 1.479 (4) | C10—H10B | 0.980 |
| N3—C11 | 1.480 (5) | C10—H10C | 0.980 |
| N3—C10 | 1.499 (5) | C11—C12 | 1.476 (6) |
| C1—C2 | 1.362 (5) | C11—H11A | 0.990 |
| C1—H1A | 0.950 | C11—H11B | 0.990 |
| C2—C3 | 1.365 (6) | C12—N4 | 1.155 (5) |
| C2—H2A | 0.950 | C1S—O1S | 1.326 (9) |
| C3—C4 | 1.383 (6) | C1S—H1S1 | 0.980 |
| C3—H3A | 0.950 | C1S—H1S2 | 0.980 |
| C4—C5 | 1.388 (5) | C1S—H1S3 | 0.980 |
| C4—H4A | 0.950 | O1S—O1Si | 1.449 (16) |
| C5—C6 | 1.501 (5) | O1S—H1S | 0.850 |
| N1—Fe1—N2 | 75.33 (11) | N2—C6—H6A | 109.4 |
| N1—Fe1—Cl1 | 169.08 (9) | C5—C6—H6A | 109.4 |
| N2—Fe1—Cl1 | 93.76 (8) | N2—C6—H6B | 109.4 |
| N1—Fe1—Cl2 | 93.27 (8) | C5—C6—H6B | 109.4 |
| N2—Fe1—Cl2 | 162.33 (8) | H6A—C6—H6B | 108.0 |
| Cl1—Fe1—Cl2 | 97.20 (4) | N2—C7—H7A | 109.5 |
| N1—Fe1—Cl3 | 85.73 (8) | N2—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| N2—Fe1—Cl3 | 92.44 (8) | H7A—C7—H7B | 109.5 |
| Cl1—Fe1—Cl3 | 95.42 (4) | N2—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| Cl2—Fe1—Cl3 | 100.25 (4) | H7A—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| N1—Fe1—N3 | 89.21 (10) | H7B—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| N2—Fe1—N3 | 78.53 (10) | N2—C8—C9 | 110.6 (3) |
| Cl1—Fe1—N3 | 88.06 (8) | N2—C8—H8A | 109.5 |
| Cl2—Fe1—N3 | 88.00 (8) | C9—C8—H8A | 109.5 |
| Cl3—Fe1—N3 | 170.54 (8) | N2—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| C1—N1—C5 | 118.7 (3) | C9—C8—H8B | 109.5 |
| C1—N1—Fe1 | 125.4 (3) | H8A—C8—H8B | 108.1 |
| C5—N1—Fe1 | 115.2 (2) | N3—C9—C8 | 110.2 (3) |
| C6—N2—C7 | 108.6 (3) | N3—C9—H9A | 109.6 |
| C6—N2—C8 | 108.8 (3) | C8—C9—H9A | 109.6 |
| C7—N2—C8 | 109.2 (3) | N3—C9—H9B | 109.6 |
| C6—N2—Fe1 | 107.1 (2) | C8—C9—H9B | 109.6 |
| C7—N2—Fe1 | 113.4 (2) | H9A—C9—H9B | 108.1 |
| C8—N2—Fe1 | 109.6 (2) | N3—C10—H10A | 109.5 |
| C9—N3—C11 | 108.8 (3) | N3—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C9—N3—C10 | 110.5 (3) | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C11—N3—C10 | 107.1 (3) | N3—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C9—N3—Fe1 | 103.9 (2) | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C11—N3—Fe1 | 111.9 (2) | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C10—N3—Fe1 | 114.5 (2) | C12—C11—N3 | 112.8 (3) |
| N1—C1—C2 | 122.3 (4) | C12—C11—H11A | 109.0 |
| N1—C1—H1A | 118.9 | N3—C11—H11A | 109.0 |
| C2—C1—H1A | 118.9 | C12—C11—H11B | 109.0 |
| C1—C2—C3 | 119.6 (4) | N3—C11—H11B | 109.0 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 120.2 | H11A—C11—H11B | 107.8 |
| C3—C2—H2A | 120.2 | N4—C12—C11 | 177.8 (5) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.3 (4) | O1S—C1S—H1S1 | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 120.4 | O1S—C1S—H1S2 | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 120.4 | H1S1—C1S—H1S2 | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 118.5 (4) | O1S—C1S—H1S3 | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—H4A | 120.7 | H1S1—C1S—H1S3 | 109.5 |
| C5—C4—H4A | 120.7 | H1S2—C1S—H1S3 | 109.5 |
| N1—C5—C4 | 121.6 (4) | C1S—O1S—O1Si | 56.9 (4) |
| N1—C5—C6 | 116.8 (3) | C1S—O1S—H1S | 113.4 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 121.5 (4) | O1Si—O1S—H1S | 150.8 |
| N2—C6—C5 | 111.1 (3) | ||
| N2—Fe1—N1—C1 | 168.7 (3) | Cl2—Fe1—N3—C11 | −51.8 (2) |
| Cl1—Fe1—N1—C1 | 165.9 (3) | N1—Fe1—N3—C10 | −22.9 (3) |
| Cl2—Fe1—N1—C1 | 2.4 (3) | N2—Fe1—N3—C10 | −98.1 (3) |
| Cl3—Fe1—N1—C1 | −97.6 (3) | Cl1—Fe1—N3—C10 | 167.7 (3) |
| N3—Fe1—N1—C1 | 90.4 (3) | Cl2—Fe1—N3—C10 | 70.4 (2) |
| N2—Fe1—N1—C5 | −21.2 (2) | C5—N1—C1—C2 | −0.9 (5) |
| Cl1—Fe1—N1—C5 | −24.1 (6) | Fe1—N1—C1—C2 | 168.8 (3) |
| Cl2—Fe1—N1—C5 | 172.5 (2) | N1—C1—C2—C3 | 2.0 (6) |
| Cl3—Fe1—N1—C5 | 72.4 (2) | C1—C2—C3—C4 | −1.6 (6) |
| N3—Fe1—N1—C5 | −99.6 (3) | C2—C3—C4—C5 | 0.1 (6) |
| N1—Fe1—N2—C6 | 32.1 (2) | C1—N1—C5—C4 | −0.6 (5) |
| Cl1—Fe1—N2—C6 | −148.5 (2) | Fe1—N1—C5—C4 | −171.3 (3) |
| Cl2—Fe1—N2—C6 | 83.2 (3) | C1—N1—C5—C6 | 176.0 (3) |
| Cl3—Fe1—N2—C6 | −52.9 (2) | Fe1—N1—C5—C6 | 5.3 (4) |
| N3—Fe1—N2—C6 | 124.3 (2) | C3—C4—C5—N1 | 1.0 (6) |
| N1—Fe1—N2—C7 | 151.8 (3) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | −175.5 (4) |
| Cl1—Fe1—N2—C7 | −28.7 (2) | C7—N2—C6—C5 | −162.3 (3) |
| Cl2—Fe1—N2—C7 | −157.0 (2) | C8—N2—C6—C5 | 78.9 (4) |
| Cl3—Fe1—N2—C7 | 66.9 (2) | Fe1—N2—C6—C5 | −39.5 (4) |
| N3—Fe1—N2—C7 | −116.0 (2) | N1—C5—C6—N2 | 24.1 (5) |
| N1—Fe1—N2—C8 | −85.8 (2) | C4—C5—C6—N2 | −159.3 (4) |
| Cl1—Fe1—N2—C8 | 93.7 (2) | C6—N2—C8—C9 | −152.1 (3) |
| Cl2—Fe1—N2—C8 | −34.7 (4) | C7—N2—C8—C9 | 89.5 (4) |
| Cl3—Fe1—N2—C8 | −170.7 (2) | Fe1—N2—C8—C9 | −35.3 (3) |
| N3—Fe1—N2—C8 | 6.4 (2) | C11—N3—C9—C8 | −168.7 (3) |
| N1—Fe1—N3—C9 | 97.7 (2) | C10—N3—C9—C8 | 74.0 (4) |
| N2—Fe1—N3—C9 | 22.5 (2) | Fe1—N3—C9—C8 | −49.3 (3) |
| Cl1—Fe1—N3—C9 | −71.7 (2) | N2—C8—C9—N3 | 59.5 (4) |
| Cl2—Fe1—N3—C9 | −169.0 (2) | C9—N3—C11—C12 | −56.6 (4) |
| N1—Fe1—N3—C11 | −145.1 (3) | C10—N3—C11—C12 | 62.9 (4) |
| N2—Fe1—N3—C11 | 139.7 (3) | Fe1—N3—C11—C12 | −170.8 (3) |
| Cl1—Fe1—N3—C11 | 45.5 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, y, −z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HB5138).
References
- Bruker (2004). APEX2, SAINT and SADABS Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cowdell, R., Davies, C. J., Hilton, S. T., Marechal, J.-D., Solan, G. A., Thomas, O. & Fawcett, J. (2004). Dalton Trans. pp. 3231–3240. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Sundaravel, K., Dhanalakshmi, T., Suresh, E. & Palaniandavar, M. (2008). Dalton Trans. pp. 7012–7025. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Velusamy, M., Mayilmurugan, R. & Palaniandavar, M. (2005). J. Inorg. Biochem.99, 1032–1042. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680904375X/hb5138sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680904375X/hb5138Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report