Abstract
In the title compound, C12H15BrN2O2, the dihedral angle between the benzene ring and the mean plane of the amide grouping is 77.7 (8)°. In the crystal, inversion dimers linked by pairs of N—H⋯O hydrogen bonds occur, and the packing is further supported by C—H⋯O and C—H⋯Br interactions and weak π–π ring stacking interactions.
Related literature
Hydrazides and their corresponding Schiff bases are useful precursors in the synthesis of several heterocyclic systems, see: Narayana et al. (2005 ▶; 2005a
▶). For the biological activity of substituted hydrazides, see: Cajocorius et al. (1977 ▶). Hydrazides are intermediates in the production of many pharmaceutically important compounds, see: Liu et al. (2006 ▶). For related structures, see: Butcher et al. (2007 ▶); Hou (2009 ▶); Li & Ban (2009 ▶); Sarojini et al. (2007a
▶,b
▶,c
▶,d
▶). For the MOPAC AM1 calculations, see: Schmidt & Polik (2007 ▶).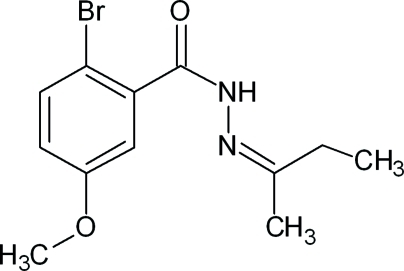
Experimental
Crystal data
C12H15BrN2O2
M r = 299.17
Monoclinic,
a = 8.0942 (1) Å
b = 14.2475 (2) Å
c = 11.2974 (2) Å
β = 91.1519 (13)°
V = 1302.58 (3) Å3
Z = 4
Cu Kα radiation
μ = 4.25 mm−1
T = 200 K
0.56 × 0.47 × 0.35 mm
Data collection
Oxford Diffraction Gemini R CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction, 2007 ▶) T min = 0.452, T max = 1.000
7962 measured reflections
2577 independent reflections
2484 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.023
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.044
wR(F 2) = 0.122
S = 1.07
2577 reflections
157 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.73 e Å−3
Δρmin = −1.07 e Å−3
Data collection: CrysAlis Pro (Oxford Diffraction, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: CrysAlis Pro; data reduction: CrysAlis Pro; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809044869/ds2010sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809044869/ds2010Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C7—H7B⋯O2i | 0.98 | 2.60 | 3.561 (4) | 166 |
| C10—H10A⋯Brii | 0.98 | 3.07 | 3.949 (5) | 151 |
| C10—H10A⋯O2iii | 0.98 | 2.55 | 3.231 (4) | 127 |
| C11—H11A⋯O1iv | 0.99 | 2.55 | 3.373 (4) | 141 |
| N1—H1A⋯O2iii | 0.88 | 2.07 | 2.932 (3) | 165 |
Symmetry codes: (i) 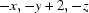 ; (ii)
; (ii) 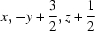 ; (iii)
; (iii) 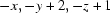 ; (iv)
; (iv) 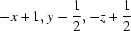 .
.
Acknowledgments
LPS thanks the University of Mysore for use of their research facilities under the MPhil programme in Chemistry for the year 2008–2009. RJB acknowledges the NSF MRI program (grant No. CHE-0619278) for funds to purchase an X-ray diffractometer.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Hydrazides and the corresponding Schiff bases are useful precursors in the synthesis of several heterocyclic systems (Narayana et al. 2005; 2005a). Some substituted hydrazides are reported to exhibit carcinostatic activity against several types of tumors (Cajocorius et al. 1977) and also possess antimicrobial activity. It is also used as an intermediate in many pharmaceutically important compounds (Liu et al. 2006). In continuation with our studies on the structures of hydrazides and their Schiff bases (Sarojini et al. 2007a, 2007b, 2007c, 2007d; Butcher et al. 2007) a new Schiff base, (I), C12H15BrN2O2, has been synthesized and its crystal structure is now reported.
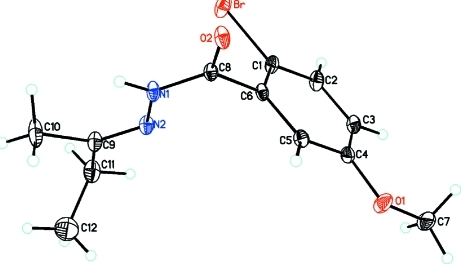
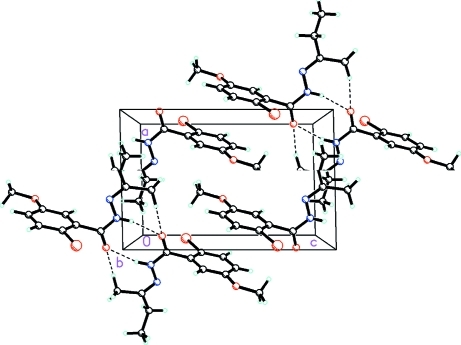
In the title compound, C12H15BrN2O2, (Fig. 1), the 2-bromo and 5-methoxy groups are in the plane of the benzene ring. The dihedral angle between the mean planes of the carbonyl group (–C6—C8(O2)—N1—N2-) and benzene ring is 77.7 (8)°. The C1—C6—C8—O2 and C1—C6—C8—N1 torsion angles (-101.1 (3)° & -103.7 (3)°) support this observation. Crystal packing is supported by a collection of intermediate N1—H1A—O2 (-x,-y + 2,-z + 1) intermolecular interactions (see Table 1) which produces a cooperative network of infinite O—H···O—H···O—H chains arranged diagonally along the (101) plane of the unit cell (Fig. 2). In addition, weak intermolecular C10—H10A···O2 (-x,-y + 2,-z + 1), C11—H11A···O1 (-x + 1, y - 1/2,-z + 1/2), C7—H7B···O2 (-x,-y + 2,-z) and C10—H10A···Br (x,-y + 3/2,z1/2) interactions (Table 1) along with Cg1···Cg1 π-π ring stacking interactions at 3.869 (1)Å (2 - x,1 - y,1 - z; slippage = 1.43 (2) Å, where Cg1 = C1—C6), collectively, slightly influence crystal packing in this crystalline environment.
After a MOPAC AM1 computational calculation (Schmidt, 2007), the dihedral angle between the mean planes of the carbonyl group (–C6—C8(O2)—N1—N2-) and benzene ring becomes 84.0 (8)°, significantly greater that the 77.7 (8)° seen in the crystal. This supports the observation of a collective action of the intermediate and weak hydrogen bond interactions along with weak intermolecular π-π stacking interactions which influence crystal packing stability.
Experimental
A mixture of 2-bromo-5-methoxybenzohydrazide (2.45 g, 0.01 mol) and ethyl methyl ketone(1.44 g, 0.02 mol) in 20 ml of ethanol containing a drop of dilute sulfuric acid was refluxed for about 2 h (Scheme 2). On cooling, the solid separated was filtered and recrystallized from ethyl methyl ketone. M.P.: 385 K. Analysis for C12H15BrN2O2: Found (Calculated): C: 48.14 (48.18); H: 5.02 (5.05%); N: 9.31 (9.36%).
Refinement
All of the H atoms were placed in their calculated positions and then refined using the riding model with N—H = 0.88, C—H = 0.95–0.99 Å, and with Uiso(H) = 1.2–1.5 Ueq(C,N).
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of C12H15BrN2O2 showing atom labeling scheme and 50% probability displacement ellipsoids.
Fig. 2.
Packing diagram of the title compound, (I), viewed down the b axis. Dashed lines indicate intermediate intermolecular N—H···O and C—H···O interactions which produces a network of infinite O—H···O—H···O—H chains arranged diagonally along the (101) plane of the unit cell.
Crystal data
| C12H15BrN2O2 | F(000) = 608 |
| Mr = 299.17 | Dx = 1.526 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Cu Kα radiation, λ = 1.54184 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 8517 reflections |
| a = 8.0942 (1) Å | θ = 5.0–73.4° |
| b = 14.2475 (2) Å | µ = 4.25 mm−1 |
| c = 11.2974 (2) Å | T = 200 K |
| β = 91.1519 (13)° | Chunk, colorless |
| V = 1302.58 (3) Å3 | 0.56 × 0.47 × 0.35 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Oxford Diffraction Gemini R CCD diffractometer | 2577 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2484 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.023 |
| Detector resolution: 10.5081 pixels mm-1 | θmax = 73.6°, θmin = 5.0° |
| φ and ω scans | h = −10→9 |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (CrysAlis RED; Oxford Diffraction, 2007) | k = −16→17 |
| Tmin = 0.452, Tmax = 1.000 | l = −9→13 |
| 7962 measured reflections |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.044 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.122 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.07 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0673P)2 + 1.7115P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 2577 reflections | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 157 parameters | Δρmax = 0.73 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −1.07 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Br | −0.00062 (5) | 0.75926 (3) | 0.23886 (3) | 0.05362 (18) | |
| O1 | 0.3113 (3) | 1.07458 (17) | −0.03054 (18) | 0.0478 (6) | |
| O2 | −0.0433 (2) | 1.01275 (15) | 0.35066 (16) | 0.0358 (5) | |
| N1 | 0.1775 (3) | 0.93324 (16) | 0.42004 (18) | 0.0306 (5) | |
| H1A | 0.1550 | 0.9465 | 0.4941 | 0.037* | |
| N2 | 0.3148 (3) | 0.87860 (17) | 0.39363 (19) | 0.0318 (5) | |
| C1 | 0.0954 (3) | 0.85866 (18) | 0.1528 (2) | 0.0305 (5) | |
| C2 | 0.1316 (4) | 0.8445 (2) | 0.0351 (2) | 0.0361 (6) | |
| H2A | 0.1073 | 0.7858 | −0.0012 | 0.043* | |
| C3 | 0.2033 (3) | 0.9154 (2) | −0.0303 (2) | 0.0316 (6) | |
| H3A | 0.2285 | 0.9056 | −0.1111 | 0.038* | |
| C4 | 0.2379 (3) | 1.00067 (19) | 0.0234 (2) | 0.0294 (5) | |
| C5 | 0.1981 (3) | 1.01479 (18) | 0.1415 (2) | 0.0285 (5) | |
| H5A | 0.2195 | 1.0739 | 0.1775 | 0.034* | |
| C6 | 0.1282 (3) | 0.94403 (17) | 0.2066 (2) | 0.0244 (5) | |
| C7 | 0.3619 (4) | 1.0618 (3) | −0.1501 (3) | 0.0525 (9) | |
| H7A | 0.4202 | 1.1181 | −0.1766 | 0.079* | |
| H7B | 0.2644 | 1.0512 | −0.2012 | 0.079* | |
| H7C | 0.4357 | 1.0075 | −0.1544 | 0.079* | |
| C8 | 0.0802 (3) | 0.96538 (18) | 0.3318 (2) | 0.0258 (5) | |
| C9 | 0.4048 (3) | 0.8504 (2) | 0.4794 (2) | 0.0357 (6) | |
| C10 | 0.3829 (5) | 0.8738 (3) | 0.6083 (3) | 0.0624 (12) | |
| H10A | 0.2676 | 0.8632 | 0.6295 | 0.094* | |
| H10B | 0.4118 | 0.9397 | 0.6221 | 0.094* | |
| H10C | 0.4551 | 0.8336 | 0.6570 | 0.094* | |
| C11 | 0.5478 (4) | 0.7880 (3) | 0.4479 (3) | 0.0485 (8) | |
| H11A | 0.5308 | 0.7253 | 0.4835 | 0.058* | |
| H11B | 0.5486 | 0.7800 | 0.3609 | 0.058* | |
| C12 | 0.7109 (5) | 0.8246 (4) | 0.4882 (5) | 0.0764 (13) | |
| H12A | 0.7969 | 0.7786 | 0.4702 | 0.115* | |
| H12B | 0.7097 | 0.8357 | 0.5738 | 0.115* | |
| H12C | 0.7339 | 0.8837 | 0.4472 | 0.115* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Br | 0.0949 (4) | 0.0345 (2) | 0.0315 (2) | −0.01786 (16) | 0.00182 (18) | 0.00284 (12) |
| O1 | 0.0666 (14) | 0.0508 (13) | 0.0261 (11) | −0.0214 (11) | 0.0079 (9) | −0.0005 (9) |
| O2 | 0.0396 (10) | 0.0467 (12) | 0.0210 (9) | 0.0198 (8) | −0.0009 (7) | −0.0063 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0373 (11) | 0.0386 (12) | 0.0159 (10) | 0.0145 (9) | 0.0007 (8) | −0.0042 (8) |
| N2 | 0.0371 (11) | 0.0346 (12) | 0.0238 (11) | 0.0125 (9) | 0.0026 (9) | −0.0023 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0452 (14) | 0.0245 (12) | 0.0219 (12) | 0.0002 (10) | 0.0004 (10) | −0.0003 (10) |
| C2 | 0.0576 (17) | 0.0292 (13) | 0.0212 (13) | 0.0033 (12) | −0.0032 (11) | −0.0081 (10) |
| C3 | 0.0397 (13) | 0.0395 (15) | 0.0157 (11) | 0.0066 (11) | 0.0019 (9) | −0.0066 (10) |
| C4 | 0.0322 (12) | 0.0352 (14) | 0.0206 (12) | −0.0005 (10) | −0.0021 (10) | −0.0007 (10) |
| C5 | 0.0342 (12) | 0.0283 (12) | 0.0230 (12) | 0.0015 (10) | −0.0020 (9) | −0.0070 (10) |
| C6 | 0.0281 (11) | 0.0275 (12) | 0.0175 (11) | 0.0092 (9) | −0.0018 (8) | −0.0033 (9) |
| C7 | 0.0564 (19) | 0.076 (2) | 0.0250 (15) | −0.0218 (17) | 0.0066 (13) | 0.0033 (15) |
| C8 | 0.0327 (12) | 0.0255 (12) | 0.0192 (11) | 0.0047 (9) | −0.0004 (9) | −0.0039 (9) |
| C9 | 0.0391 (14) | 0.0418 (15) | 0.0263 (13) | 0.0132 (12) | 0.0014 (10) | 0.0018 (11) |
| C10 | 0.060 (2) | 0.104 (3) | 0.0233 (15) | 0.040 (2) | −0.0041 (14) | 0.0002 (17) |
| C11 | 0.0513 (18) | 0.0549 (19) | 0.0393 (17) | 0.0250 (15) | 0.0012 (13) | 0.0036 (15) |
| C12 | 0.050 (2) | 0.100 (4) | 0.079 (3) | 0.016 (2) | 0.004 (2) | 0.004 (3) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Br—C1 | 1.894 (3) | C5—H5A | 0.9500 |
| O1—C4 | 1.359 (3) | C6—C8 | 1.506 (3) |
| O1—C7 | 1.431 (4) | C7—H7A | 0.9800 |
| O2—C8 | 1.228 (3) | C7—H7B | 0.9800 |
| N1—C8 | 1.338 (3) | C7—H7C | 0.9800 |
| N1—N2 | 1.394 (3) | C9—C10 | 1.507 (4) |
| N1—H1A | 0.8800 | C9—C11 | 1.508 (4) |
| N2—C9 | 1.266 (4) | C10—H10A | 0.9800 |
| C1—C2 | 1.382 (4) | C10—H10B | 0.9800 |
| C1—C6 | 1.383 (3) | C10—H10C | 0.9800 |
| C2—C3 | 1.386 (4) | C11—C12 | 1.482 (6) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9500 | C11—H11A | 0.9900 |
| C3—C4 | 1.383 (4) | C11—H11B | 0.9900 |
| C3—H3A | 0.9500 | C12—H12A | 0.9800 |
| C4—C5 | 1.393 (4) | C12—H12B | 0.9800 |
| C5—C6 | 1.376 (4) | C12—H12C | 0.9800 |
| C4—O1—C7 | 117.4 (2) | H7A—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C8—N1—N2 | 119.4 (2) | H7B—C7—H7C | 109.5 |
| C8—N1—H1A | 120.3 | O2—C8—N1 | 121.9 (2) |
| N2—N1—H1A | 120.3 | O2—C8—C6 | 120.0 (2) |
| C9—N2—N1 | 117.5 (2) | N1—C8—C6 | 118.2 (2) |
| C2—C1—C6 | 120.6 (2) | N2—C9—C10 | 126.3 (3) |
| C2—C1—Br | 118.8 (2) | N2—C9—C11 | 116.0 (3) |
| C6—C1—Br | 120.59 (19) | C10—C9—C11 | 117.6 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3 | 120.3 (2) | C9—C10—H10A | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 119.9 | C9—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—H2A | 119.9 | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 119.4 (2) | C9—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 120.3 | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 120.3 | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| O1—C4—C3 | 124.8 (2) | C12—C11—C9 | 113.8 (3) |
| O1—C4—C5 | 115.4 (2) | C12—C11—H11A | 108.8 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 119.8 (2) | C9—C11—H11A | 108.8 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 120.8 (2) | C12—C11—H11B | 108.8 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 119.6 | C9—C11—H11B | 108.8 |
| C4—C5—H5A | 119.6 | H11A—C11—H11B | 107.7 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 119.1 (2) | C11—C12—H12A | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C8 | 118.1 (2) | C11—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| C1—C6—C8 | 122.7 (2) | H12A—C12—H12B | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—H7A | 109.5 | C11—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—H7B | 109.5 | H12A—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| H7A—C7—H7B | 109.5 | H12B—C12—H12C | 109.5 |
| O1—C7—H7C | 109.5 | ||
| C8—N1—N2—C9 | 179.2 (3) | Br—C1—C6—C5 | 179.97 (19) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.8 (4) | C2—C1—C6—C8 | 175.6 (2) |
| Br—C1—C2—C3 | −179.4 (2) | Br—C1—C6—C8 | −4.2 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.2 (4) | N2—N1—C8—O2 | 179.0 (3) |
| C7—O1—C4—C3 | −2.5 (4) | N2—N1—C8—C6 | −2.5 (4) |
| C7—O1—C4—C5 | 177.0 (3) | C5—C6—C8—O2 | 74.8 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—O1 | 178.4 (3) | C1—C6—C8—O2 | −101.1 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −1.0 (4) | C5—C6—C8—N1 | −103.7 (3) |
| O1—C4—C5—C6 | −177.9 (2) | C1—C6—C8—N1 | 80.4 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 1.6 (4) | N1—N2—C9—C10 | −3.0 (5) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | −0.9 (4) | N1—N2—C9—C11 | 177.4 (3) |
| C4—C5—C6—C8 | −177.0 (2) | N2—C9—C11—C12 | 122.5 (4) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.3 (4) | C10—C9—C11—C12 | −57.1 (5) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C7—H7B···O2i | 0.98 | 2.60 | 3.561 (4) | 166 |
| C10—H10A···Brii | 0.98 | 3.07 | 3.949 (5) | 151 |
| C10—H10A···O2iii | 0.98 | 2.55 | 3.231 (4) | 127 |
| C11—H11A···O1iv | 0.99 | 2.55 | 3.373 (4) | 141 |
| N1—H1A···O2iii | 0.88 | 2.07 | 2.932 (3) | 165 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x, −y+2, −z; (ii) x, −y+3/2, z+1/2; (iii) −x, −y+2, −z+1; (iv) −x+1, y−1/2, −z+1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: DS2010).
References
- Butcher, R. J., Jasinski, J. P., Narayana, B., Sunil, K. & Yathirajan, H. S. (2007). Acta Cryst. E63, o3652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Cajocorius, J., Cojocarius, Z. & Niester, C. (1977). Rev. Chim.28, 15–18.
- Hou, J.-L. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Li, C.-M. & Ban, H.-Y. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, o883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Liu, F., Stephen, A. G., Adainson, C. S., Gousset, K., Aman, M. J., Freed, E. O., Fisher, R. J. & Burke, T. R. Jr (2006). Org. Lett.8, 5165–5168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Narayana, B., Ashalatha, B. V., Vijayaraj, K. K., Fernandes, J. & Sarojini, B. K. (2005). Bioorg. Med. Chem.13, 4638–4644. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Narayana, B., Vijayaraj, K. K., Ashalatha, B. V. & Suchetha Kumari, N. (2005a). Pharmazie, 338, 373–377.
- Oxford Diffraction (2007). CrysAlis Pro and CrysAlis RED Oxford Diffraction Ltd, Abingdon, Oxfordshire, England.
- Sarojini, B. K., Mustafa, K., Narayana, B., Yathirajan, H. S. & Bolte, M. (2007a). Acta Cryst. E63, o4419.
- Sarojini, B. K., Narayana, B., Sunil, K., Yathirajan, H. S. & Bolte, M. (2007b). Acta Cryst. E63, o3551.
- Sarojini, B. K., Narayana, B., Sunil, K., Yathirajan, H. S. & Bolte, M. (2007c). Acta Cryst. E63, o3862–o3863.
- Sarojini, B. K., Yathirajan, H. S., Sunil, K., Narayana, B. & Bolte, M. (2007d). Acta Cryst. E63, o3487.
- Schmidt, J. R. & Polik, W. F. (2007). WebMO Pro. WebMO, LLC: Holland, MI, USA; available from http://www.webmo.net.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809044869/ds2010sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809044869/ds2010Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report