Abstract
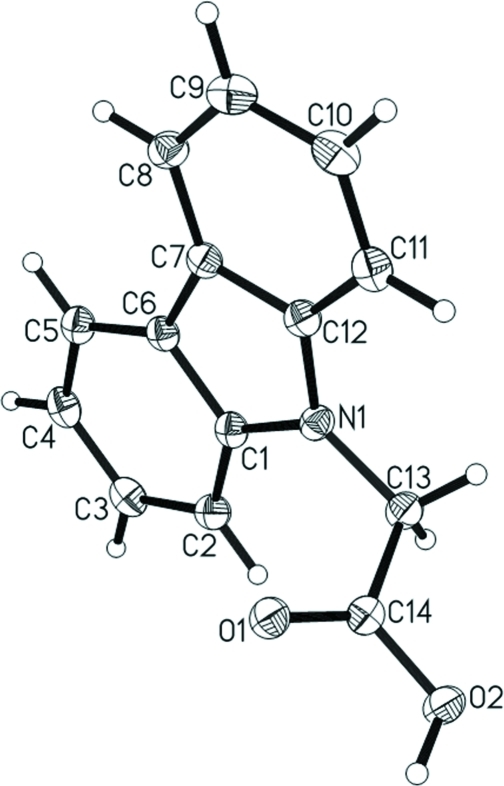
In the title compound, C14H11NO2, the tricyclic aromatic ring system is essentially planar [maximum deviation = 0.025 (2) Å]. The dihedral angle between the two benzene rings is 2.8 (5)°, while the carboxyl group forms a dihedral angle of 88.5 (1)° with the pyrrole ring. Intermolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds may contribute to the overall stabilization of the crystal structure.
Related literature
For the use of the title compound in high-performance liquid chromatography, see: Jinmao et al. (2001 ▶). For synthesis: Xie et al. (2006 ▶).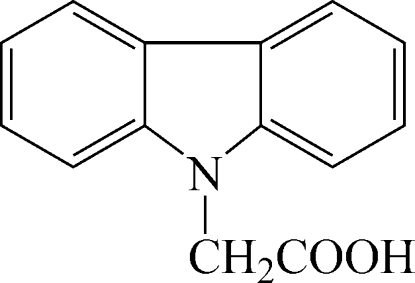
Experimental
Crystal data
C14H11NO2
M r = 225.24
Monoclinic,
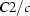
a = 32.067 (19) Å
b = 5.340 (3) Å
c = 13.134 (7) Å
β = 97.756 (8)°
V = 2229 (2) Å3
Z = 8
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 93 K
0.40 × 0.30 × 0.08 mm
Data collection
Rigaku SPIDER diffractometer
Absorption correction: none
8360 measured reflections
2534 independent reflections
1749 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.067
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.048
wR(F 2) = 0.093
S = 1.00
2534 reflections
159 parameters
H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement
Δρmax = 0.22 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3
Data collection: RAPID-AUTO (Rigaku, 2004 ▶); cell refinement: RAPID-AUTO; data reduction: RAPID-AUTO; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809043463/cs2123sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809043463/cs2123Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O2—H2O⋯O1i | 0.95 (3) | 1.70 (3) | 2.645 (2) | 171 (2) |
Symmetry code: (i) 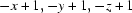 .
.
Acknowledgments
The Key Laboratory of Nuclear Medicine of the Ministry Health of China is thanked for supporting this work.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Carbazoles are ubiquitous structural subunits of numerous naturally occurring compounds as well as synthetic materials. The title molecule (Fig. 1), is useful as an important agent for determination of alcohols by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorimetric detection after pre-column derivatization (Jinmao et al., 2001; Xie et al., 2006). The crystal structure shows that the tricyclic aromatic ring system is coplanar. The dihedral angle between the two benzene rings is 2.8 (5)°. The pyrrole ring makes dihedral angles of 1.5 (5)° and 1.3 (5)° with the benzene rings, respectively. The pyrrole ring and the carboxylic acid group (O1/C14/O2) are twisted to each other by a torsion angles of 88.5 (1)°. The crystal structure may be stabilized by intermolecular O2–H2O···O1i [i= 1-x, 1-y, 1-z] hydrogen bonds.
Experimental
The title compound was prepared by a method reported earlier (Xie et al., 2006). The pure product (0.1 g) obtained was dissolved in 50% ethanol (10 ml). The solution was evaporated in air affording colourless platelet crystals suitable for X-ray analysis (yield: 67.2%).
Refinement
Positional parameters of all the H atoms bonded to C atoms were calculated geometrically and were allowed to ride on the C atoms to which they are bonded,with C—H=0.95 and 0.99 Å for aromatic and methylene and with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(aromatic,methylene) parent atoms. The carboxylic H atom was taken from a differnce density map and refined.
Figures
Fig. 1.
A view of the title compound with the atomic numbering scheme. Displacement ellipsoids were drawn at the 30% probability level.
Crystal data
| C14H11NO2 | F(000) = 944 |
| Mr = 225.24 | Dx = 1.343 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, C2/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -C 2yc | Cell parameters from 2975 reflections |
| a = 32.067 (19) Å | θ = 3.1–27.5° |
| b = 5.340 (3) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 13.134 (7) Å | T = 93 K |
| β = 97.756 (8)° | Platelet, colorless |
| V = 2229 (2) Å3 | 0.40 × 0.30 × 0.08 mm |
| Z = 8 |
Data collection
| Rigaku SPIDER diffractometer | 1749 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: Rotating Anode | Rint = 0.067 |
| graphite | θmax = 27.5°, θmin = 3.1° |
| ω scans | h = −41→41 |
| 8360 measured reflections | k = −6→6 |
| 2534 independent reflections | l = −17→17 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.048 | H atoms treated by a mixture of independent and constrained refinement |
| wR(F2) = 0.093 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0136P)2 + 0.660P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.00 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 2534 reflections | Δρmax = 0.22 e Å−3 |
| 159 parameters | Δρmin = −0.25 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Extinction coefficient: 0.0006 (2) |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O1 | 0.45527 (4) | 0.3887 (2) | 0.43806 (10) | 0.0305 (3) | |
| O2 | 0.48708 (4) | 0.7517 (2) | 0.40940 (10) | 0.0322 (4) | |
| N1 | 0.38917 (5) | 0.4955 (3) | 0.28479 (11) | 0.0248 (4) | |
| C1 | 0.39216 (6) | 0.3113 (3) | 0.21154 (13) | 0.0240 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.42431 (6) | 0.2678 (3) | 0.15246 (14) | 0.0285 (5) | |
| H2 | 0.4486 | 0.3715 | 0.1582 | 0.034* | |
| C3 | 0.41955 (6) | 0.0674 (3) | 0.08487 (14) | 0.0309 (5) | |
| H3 | 0.4411 | 0.0330 | 0.0438 | 0.037* | |
| C4 | 0.38388 (6) | −0.0852 (4) | 0.07555 (14) | 0.0303 (5) | |
| H4 | 0.3814 | −0.2204 | 0.0281 | 0.036* | |
| C5 | 0.35211 (6) | −0.0411 (3) | 0.13498 (14) | 0.0281 (5) | |
| H5 | 0.3279 | −0.1456 | 0.1287 | 0.034* | |
| C6 | 0.35604 (6) | 0.1578 (3) | 0.20388 (13) | 0.0235 (4) | |
| C7 | 0.33048 (6) | 0.2527 (3) | 0.27875 (13) | 0.0245 (4) | |
| C8 | 0.29237 (6) | 0.1775 (4) | 0.30960 (14) | 0.0291 (5) | |
| H8 | 0.2775 | 0.0374 | 0.2785 | 0.035* | |
| C9 | 0.27678 (6) | 0.3113 (4) | 0.38653 (15) | 0.0338 (5) | |
| H9 | 0.2510 | 0.2615 | 0.4086 | 0.041* | |
| C10 | 0.29835 (6) | 0.5181 (4) | 0.43219 (15) | 0.0344 (5) | |
| H10 | 0.2867 | 0.6077 | 0.4841 | 0.041* | |
| C11 | 0.33618 (6) | 0.5962 (4) | 0.40406 (14) | 0.0303 (5) | |
| H11 | 0.3509 | 0.7360 | 0.4360 | 0.036* | |
| C12 | 0.35197 (6) | 0.4611 (3) | 0.32662 (14) | 0.0255 (4) | |
| C13 | 0.42069 (6) | 0.6818 (3) | 0.31517 (14) | 0.0277 (5) | |
| H13A | 0.4072 | 0.8275 | 0.3440 | 0.033* | |
| H13B | 0.4326 | 0.7395 | 0.2535 | 0.033* | |
| C14 | 0.45600 (6) | 0.5897 (4) | 0.39346 (14) | 0.0257 (4) | |
| H2O | 0.5081 (8) | 0.687 (4) | 0.4603 (19) | 0.088 (9)* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O1 | 0.0316 (8) | 0.0297 (8) | 0.0293 (8) | −0.0020 (6) | 0.0000 (6) | 0.0064 (6) |
| O2 | 0.0290 (8) | 0.0318 (8) | 0.0337 (8) | −0.0065 (7) | −0.0034 (6) | 0.0074 (7) |
| N1 | 0.0252 (9) | 0.0249 (9) | 0.0238 (9) | −0.0024 (7) | 0.0011 (7) | 0.0003 (7) |
| C1 | 0.0286 (10) | 0.0238 (11) | 0.0187 (9) | 0.0017 (8) | 0.0001 (7) | 0.0037 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0285 (11) | 0.0308 (11) | 0.0262 (10) | 0.0003 (9) | 0.0038 (8) | 0.0068 (9) |
| C3 | 0.0373 (12) | 0.0344 (12) | 0.0214 (10) | 0.0081 (9) | 0.0057 (9) | 0.0053 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0405 (12) | 0.0283 (11) | 0.0211 (10) | 0.0068 (9) | 0.0004 (9) | 0.0011 (8) |
| C5 | 0.0330 (11) | 0.0264 (11) | 0.0235 (10) | 0.0003 (9) | −0.0009 (8) | 0.0019 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0262 (10) | 0.0241 (11) | 0.0190 (9) | 0.0030 (8) | −0.0018 (7) | 0.0031 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0252 (10) | 0.0259 (10) | 0.0210 (10) | 0.0022 (8) | −0.0015 (7) | 0.0040 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0261 (11) | 0.0326 (12) | 0.0274 (11) | −0.0014 (9) | −0.0004 (8) | 0.0034 (9) |
| C9 | 0.0287 (11) | 0.0460 (14) | 0.0270 (11) | 0.0019 (10) | 0.0047 (8) | 0.0056 (10) |
| C10 | 0.0354 (12) | 0.0405 (13) | 0.0275 (11) | 0.0080 (10) | 0.0043 (9) | −0.0007 (10) |
| C11 | 0.0356 (12) | 0.0298 (11) | 0.0240 (11) | 0.0038 (9) | −0.0009 (8) | −0.0005 (9) |
| C12 | 0.0266 (10) | 0.0269 (11) | 0.0220 (10) | 0.0015 (8) | −0.0001 (8) | 0.0054 (8) |
| C13 | 0.0281 (10) | 0.0275 (11) | 0.0264 (10) | −0.0021 (8) | −0.0005 (8) | 0.0033 (8) |
| C14 | 0.0282 (11) | 0.0273 (11) | 0.0221 (10) | −0.0015 (8) | 0.0048 (8) | −0.0015 (8) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O1—C14 | 1.224 (2) | C5—H5 | 0.9500 |
| O2—C14 | 1.315 (2) | C6—C7 | 1.454 (2) |
| O2—H2O | 0.95 (3) | C7—C8 | 1.397 (2) |
| N1—C1 | 1.388 (2) | C7—C12 | 1.411 (2) |
| N1—C12 | 1.391 (2) | C8—C9 | 1.385 (3) |
| N1—C13 | 1.436 (2) | C8—H8 | 0.9500 |
| C1—C2 | 1.391 (2) | C9—C10 | 1.395 (3) |
| C1—C6 | 1.412 (2) | C9—H9 | 0.9500 |
| C2—C3 | 1.386 (2) | C10—C11 | 1.379 (3) |
| C2—H2 | 0.9500 | C10—H10 | 0.9500 |
| C3—C4 | 1.397 (3) | C11—C12 | 1.397 (2) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9500 | C11—H11 | 0.9500 |
| C4—C5 | 1.385 (3) | C13—C14 | 1.506 (2) |
| C4—H4 | 0.9500 | C13—H13A | 0.9900 |
| C5—C6 | 1.390 (2) | C13—H13B | 0.9900 |
| C14—O2—H2O | 109.0 (14) | C9—C8—C7 | 118.62 (18) |
| C1—N1—C12 | 108.85 (15) | C9—C8—H8 | 120.7 |
| C1—N1—C13 | 124.87 (16) | C7—C8—H8 | 120.7 |
| C12—N1—C13 | 126.21 (16) | C8—C9—C10 | 121.03 (19) |
| N1—C1—C2 | 129.09 (17) | C8—C9—H9 | 119.5 |
| N1—C1—C6 | 109.17 (16) | C10—C9—H9 | 119.5 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 121.74 (17) | C11—C10—C9 | 121.81 (19) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 117.42 (18) | C11—C10—H10 | 119.1 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 121.3 | C9—C10—H10 | 119.1 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 121.3 | C10—C11—C12 | 117.21 (18) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 121.67 (18) | C10—C11—H11 | 121.4 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.2 | C12—C11—H11 | 121.4 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.2 | N1—C12—C11 | 129.33 (18) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 120.51 (18) | N1—C12—C7 | 108.75 (17) |
| C5—C4—H4 | 119.7 | C11—C12—C7 | 121.91 (18) |
| C3—C4—H4 | 119.7 | N1—C13—C14 | 113.56 (15) |
| C4—C5—C6 | 119.20 (18) | N1—C13—H13A | 108.9 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 120.4 | C14—C13—H13A | 108.9 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 120.4 | N1—C13—H13B | 108.9 |
| C5—C6—C1 | 119.46 (17) | C14—C13—H13B | 108.9 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 134.18 (18) | H13A—C13—H13B | 107.7 |
| C1—C6—C7 | 106.34 (16) | O1—C14—O2 | 124.31 (18) |
| C8—C7—C12 | 119.41 (18) | O1—C14—C13 | 123.49 (17) |
| C8—C7—C6 | 133.70 (18) | O2—C14—C13 | 112.19 (16) |
| C12—C7—C6 | 106.88 (16) | ||
| C12—N1—C1—C2 | −177.99 (18) | C12—C7—C8—C9 | 0.2 (3) |
| C13—N1—C1—C2 | −0.9 (3) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | 178.84 (18) |
| C12—N1—C1—C6 | 1.23 (19) | C7—C8—C9—C10 | 0.4 (3) |
| C13—N1—C1—C6 | 178.30 (15) | C8—C9—C10—C11 | −0.9 (3) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 179.41 (16) | C9—C10—C11—C12 | 0.8 (3) |
| C6—C1—C2—C3 | 0.3 (3) | C1—N1—C12—C11 | 178.33 (18) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 0.3 (3) | C13—N1—C12—C11 | 1.3 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −0.6 (3) | C1—N1—C12—C7 | −0.6 (2) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 0.3 (3) | C13—N1—C12—C7 | −177.59 (15) |
| C4—C5—C6—C1 | 0.3 (3) | C10—C11—C12—N1 | −178.94 (17) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −177.68 (18) | C10—C11—C12—C7 | −0.2 (3) |
| N1—C1—C6—C5 | −179.87 (15) | C8—C7—C12—N1 | 178.71 (15) |
| C2—C1—C6—C5 | −0.6 (3) | C6—C7—C12—N1 | −0.3 (2) |
| N1—C1—C6—C7 | −1.38 (19) | C8—C7—C12—C11 | −0.3 (3) |
| C2—C1—C6—C7 | 177.91 (16) | C6—C7—C12—C11 | −179.28 (16) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 0.4 (4) | C1—N1—C13—C14 | −82.2 (2) |
| C1—C6—C7—C8 | −177.79 (19) | C12—N1—C13—C14 | 94.4 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7—C12 | 179.19 (19) | N1—C13—C14—O1 | −9.8 (3) |
| C1—C6—C7—C12 | 1.01 (19) | N1—C13—C14—O2 | 171.34 (15) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O2—H2O···O1i | 0.95 (3) | 1.70 (3) | 2.645 (2) | 171 (2) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: CS2123).
References
- Jinmao, Y., Bo, Zh. & Weibing, Zh. (2001). J. Chromatogr. A, 909, 171–182.
- Rigaku (2004). RAPID-AUTO Rigaku Corporation, Tokyo, Japan.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Xie, M. H., Qiu, A. Y., He, Y. J., Wu, J., Zhou, X. Q., Zou, P., Liu, Y. L. & Luo, S. N. (2006). Chin. J. Anal. Chem.34, S131–134.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809043463/cs2123sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809043463/cs2123Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report