Abstract
The quinoline fused-ring system of the title compound, C11H8ClNO, is planar (r.m.s. deviation = 0.007 Å); the formyl group is bent slightly out of the plane [C—C—C—O torsion angles = −9.6 (5) and 170.4 (3)°].
Related literature
For a review of the synthesis of quinolines by the Vilsmeier–Haack reaction, see: Meth-Cohn (1993 ▶).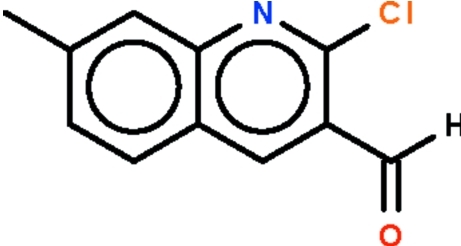
Experimental
Crystal data
C11H8ClNO
M r = 205.63
Monoclinic,

a = 15.458 (3) Å
b = 3.9382 (8) Å
c = 16.923 (3) Å
β = 112.854 (3)°
V = 949.3 (3) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.36 mm−1
T = 290 K
0.24 × 0.18 × 0.06 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.918, T max = 0.979
6484 measured reflections
1796 independent reflections
1356 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.042
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.078
wR(F 2) = 0.209
S = 1.13
1796 reflections
128 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.78 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.49 e Å−3
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2004 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2004 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: X-SEED (Barbour, 2001 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: publCIF (Westrip, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809040823/xu2629sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809040823/xu2629Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Acknowledgments
We thank the Department of Science and Technology, India, for use of the diffraction facility at IISc under the IRHPA–DST program; FNK thanks the DST for Fast Track Proposal funding. We also thank VIT University and the University of Malaya for supporting this study.
supplementary crystallographic information
Experimental
A Vilsmeier-Haack adduct prepared from phosphorus oxytrichloride (6.5 ml, 70 mmol) and N,N-dimethylformamide (2.3 ml, 30 mmol) at 273 K was added N-(3-tolyl)acetamide (1.49 g, 10 mmol). The mixture was heated at 353 K for 15 h. The mixture was poured onto ice; the white product was collected and dried. The compound was purified by recrystallization from a petroleum ether/ethyl acetate mixture.
Refinement
Carbon-bound H-atoms were placed in calculated positions (C–H 0.93–0.96 Å) and were included in the refinement in the riding model approximation, with U(H) set to 1.2–1.5U(C).
Figures
Fig. 1.
Thermal ellipsoid plot (Barbour, 2001) of C11H8ClNO at the 50% probability level; hydrogen atoms are drawn as spheres of arbitrary radius.
Crystal data
| C11H8ClNO | F(000) = 424 |
| Mr = 205.63 | Dx = 1.439 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 973 reflections |
| a = 15.458 (3) Å | θ = 1.3–24.9° |
| b = 3.9382 (8) Å | µ = 0.36 mm−1 |
| c = 16.923 (3) Å | T = 290 K |
| β = 112.854 (3)° | Block, colorless |
| V = 949.3 (3) Å3 | 0.24 × 0.18 × 0.06 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART area-detector diffractometer | 1796 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 1356 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.042 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 25.7°, θmin = 2.3° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −18→18 |
| Tmin = 0.918, Tmax = 0.979 | k = −4→4 |
| 6484 measured reflections | l = −20→20 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.078 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.209 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.13 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.1371P)2] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 1796 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 128 parameters | Δρmax = 0.78 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.49 e Å−3 |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cl1 | 0.37647 (6) | 0.6903 (3) | 0.18658 (6) | 0.0603 (4) | |
| O1 | 0.36833 (17) | 0.1214 (8) | 0.39875 (18) | 0.0705 (9) | |
| N1 | 0.55664 (19) | 0.6719 (7) | 0.27097 (16) | 0.0402 (7) | |
| C1 | 0.4781 (2) | 0.5835 (8) | 0.27548 (19) | 0.0393 (7) | |
| C2 | 0.4683 (2) | 0.4068 (8) | 0.34482 (19) | 0.0383 (7) | |
| C3 | 0.5497 (2) | 0.3312 (8) | 0.4129 (2) | 0.0387 (7) | |
| H3 | 0.5468 | 0.2182 | 0.4601 | 0.046* | |
| C4 | 0.6373 (2) | 0.4210 (7) | 0.41281 (18) | 0.0347 (7) | |
| C5 | 0.7243 (2) | 0.3490 (8) | 0.48060 (19) | 0.0407 (8) | |
| H5 | 0.7253 | 0.2376 | 0.5294 | 0.049* | |
| C6 | 0.8064 (2) | 0.4414 (8) | 0.47489 (19) | 0.0424 (8) | |
| H6 | 0.8628 | 0.3923 | 0.5201 | 0.051* | |
| C7 | 0.8080 (2) | 0.6125 (7) | 0.4009 (2) | 0.0394 (8) | |
| C8 | 0.7248 (2) | 0.6851 (8) | 0.3354 (2) | 0.0391 (7) | |
| H8 | 0.7252 | 0.7978 | 0.2872 | 0.047* | |
| C9 | 0.6379 (2) | 0.5927 (7) | 0.33897 (18) | 0.0341 (7) | |
| C10 | 0.3769 (2) | 0.3059 (9) | 0.3458 (2) | 0.0503 (9) | |
| H10 | 0.3228 | 0.3900 | 0.3029 | 0.060* | |
| C11 | 0.9001 (3) | 0.7114 (9) | 0.3968 (2) | 0.0523 (9) | |
| H11A | 0.8906 | 0.9001 | 0.3584 | 0.078* | |
| H11B | 0.9248 | 0.5226 | 0.3764 | 0.078* | |
| H11C | 0.9436 | 0.7746 | 0.4530 | 0.078* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0499 (6) | 0.0826 (8) | 0.0457 (6) | 0.0050 (4) | 0.0157 (4) | 0.0154 (4) |
| O1 | 0.0512 (17) | 0.103 (2) | 0.0731 (18) | −0.0030 (14) | 0.0416 (15) | 0.0286 (15) |
| N1 | 0.0478 (16) | 0.0474 (15) | 0.0341 (14) | 0.0010 (12) | 0.0252 (13) | 0.0033 (10) |
| C1 | 0.0427 (18) | 0.0452 (17) | 0.0380 (16) | 0.0017 (13) | 0.0245 (14) | 0.0012 (13) |
| C2 | 0.0407 (18) | 0.0452 (17) | 0.0395 (17) | 0.0026 (12) | 0.0272 (14) | 0.0014 (12) |
| C3 | 0.0476 (19) | 0.0439 (17) | 0.0383 (16) | 0.0018 (13) | 0.0316 (15) | 0.0017 (12) |
| C4 | 0.0424 (17) | 0.0396 (15) | 0.0323 (15) | 0.0025 (12) | 0.0257 (13) | −0.0005 (11) |
| C5 | 0.0439 (18) | 0.0549 (19) | 0.0338 (16) | 0.0035 (14) | 0.0267 (14) | 0.0011 (13) |
| C6 | 0.0390 (17) | 0.0560 (19) | 0.0386 (17) | 0.0053 (14) | 0.0221 (14) | −0.0053 (14) |
| C7 | 0.0467 (19) | 0.0403 (16) | 0.0449 (18) | −0.0047 (13) | 0.0328 (16) | −0.0095 (12) |
| C8 | 0.0477 (19) | 0.0440 (17) | 0.0400 (17) | −0.0032 (13) | 0.0327 (15) | −0.0016 (12) |
| C9 | 0.0423 (17) | 0.0391 (15) | 0.0322 (15) | −0.0007 (12) | 0.0268 (13) | −0.0019 (11) |
| C10 | 0.0388 (19) | 0.065 (2) | 0.055 (2) | 0.0019 (15) | 0.0272 (17) | 0.0066 (17) |
| C11 | 0.0469 (19) | 0.060 (2) | 0.063 (2) | −0.0075 (15) | 0.0351 (17) | −0.0042 (16) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cl1—C1 | 1.753 (3) | C5—H5 | 0.9300 |
| O1—C10 | 1.200 (4) | C6—C7 | 1.430 (4) |
| N1—C1 | 1.293 (4) | C6—H6 | 0.9300 |
| N1—C9 | 1.370 (4) | C7—C8 | 1.363 (4) |
| C1—C2 | 1.422 (4) | C7—C11 | 1.502 (5) |
| C2—C3 | 1.369 (4) | C8—C9 | 1.416 (4) |
| C2—C10 | 1.473 (4) | C8—H8 | 0.9300 |
| C3—C4 | 1.400 (4) | C10—H10 | 0.9300 |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C11—H11A | 0.9600 |
| C4—C5 | 1.417 (4) | C11—H11B | 0.9600 |
| C4—C9 | 1.424 (4) | C11—H11C | 0.9600 |
| C5—C6 | 1.359 (4) | ||
| C1—N1—C9 | 117.7 (3) | C8—C7—C6 | 118.6 (3) |
| N1—C1—C2 | 125.7 (3) | C8—C7—C11 | 121.3 (3) |
| N1—C1—Cl1 | 115.7 (2) | C6—C7—C11 | 120.1 (3) |
| C2—C1—Cl1 | 118.5 (2) | C7—C8—C9 | 121.5 (3) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 116.3 (3) | C7—C8—H8 | 119.3 |
| C3—C2—C10 | 120.2 (3) | C9—C8—H8 | 119.3 |
| C1—C2—C10 | 123.5 (3) | N1—C9—C8 | 118.8 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 121.2 (3) | N1—C9—C4 | 121.9 (3) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 119.4 | C8—C9—C4 | 119.3 (3) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 119.4 | O1—C10—C2 | 123.8 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 124.3 (3) | O1—C10—H10 | 118.1 |
| C3—C4—C9 | 117.2 (3) | C2—C10—H10 | 118.1 |
| C5—C4—C9 | 118.5 (3) | C7—C11—H11A | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 120.5 (3) | C7—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5 | 119.7 | H11A—C11—H11B | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 119.7 | C7—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—C7 | 121.5 (3) | H11A—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C5—C6—H6 | 119.3 | H11B—C11—H11C | 109.5 |
| C7—C6—H6 | 119.3 | ||
| C9—N1—C1—C2 | −0.7 (5) | C5—C6—C7—C11 | 179.9 (3) |
| C9—N1—C1—Cl1 | −179.8 (2) | C6—C7—C8—C9 | −0.5 (4) |
| N1—C1—C2—C3 | 1.3 (5) | C11—C7—C8—C9 | −180.0 (3) |
| Cl1—C1—C2—C3 | −179.6 (2) | C1—N1—C9—C8 | 179.6 (3) |
| N1—C1—C2—C10 | −178.7 (3) | C1—N1—C9—C4 | −0.4 (4) |
| Cl1—C1—C2—C10 | 0.5 (4) | C7—C8—C9—N1 | −179.8 (3) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | −0.8 (4) | C7—C8—C9—C4 | 0.2 (4) |
| C10—C2—C3—C4 | 179.2 (3) | C3—C4—C9—N1 | 0.8 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −179.5 (3) | C5—C4—C9—N1 | −179.8 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—C9 | −0.2 (4) | C3—C4—C9—C8 | −179.2 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5—C6 | 179.1 (3) | C5—C4—C9—C8 | 0.1 (4) |
| C9—C4—C5—C6 | −0.2 (4) | C3—C2—C10—O1 | −9.6 (5) |
| C4—C5—C6—C7 | −0.1 (5) | C1—C2—C10—O1 | 170.4 (3) |
| C5—C6—C7—C8 | 0.5 (5) |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: XU2629).
References
- Barbour, L. J. (2001). J. Supramol. Chem.1, 189–191.
- Bruker (2004). SAINT and SMART Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Meth-Cohn, O. (1993). Heterocycles, 35, 539–557.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2009). publCIF In preparation.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809040823/xu2629sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809040823/xu2629Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



