Abstract
In the molecular structure of the title compound, C21H25NO4, the dihydropyridine ring adopts a flattened boat conformation while the cyclohexenone ring is in an envelope conformation. In the crystal structure, molecules are linked into a two-dimensional network parallel to (10 ) by N—H⋯O and O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. The network is generated by R
4
4(30) and R
4
4(34) graph-set motifs.
) by N—H⋯O and O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds. The network is generated by R
4
4(30) and R
4
4(34) graph-set motifs.
Related literature
For general background to oxoquinoline derivatives, see: Baba (1997 ▶); Baba et al. (1997 ▶,1998 ▶); Koga et al. (1980 ▶); Qi et al. (2007 ▶). For a related structure, see: Czaun et al. (2002 ▶); For graph-set motifs, see: Etter et al. (1990 ▶).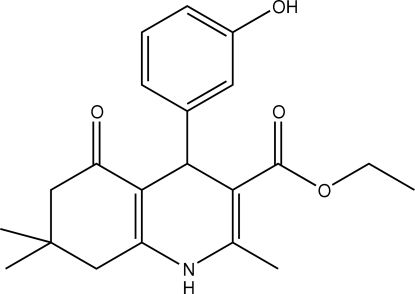
Experimental
Crystal data
C21H25NO4
M r = 355.42
Monoclinic,

a = 10.8721 (4) Å
b = 16.1255 (7) Å
c = 11.0856 (4) Å
β = 100.682 (2)°
V = 1909.83 (13) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.09 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.26 × 0.15 × 0.12 mm
Data collection
Bruker Kappa APEXII area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2004 ▶) T min = 0.93, T max = 0.95
14667 measured reflections
3163 independent reflections
2137 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.041
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.040
wR(F 2) = 0.115
S = 1.02
3163 reflections
236 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.15 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.15 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2004 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT-Plus (Bruker, 2004 ▶); data reduction: SAINT-Plus; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: PLATON (Spek, 2009 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809039877/ci2916sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809039877/ci2916Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O8C—H8C⋯O9Bi | 0.82 | 2.05 | 2.835 (2) | 162 |
| N1—H1⋯O6Aii | 0.86 | 2.16 | 2.970 (2) | 157 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Some oxoquinoline derivatives viz. 8-difluoromethoxy-1-ethyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-7-[4-(2-methoxyphenyl)- 1-πiperazinyl]- 4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid (K-12), 7-(3,4-dehydro-4-phenyl-1-piperidinyl)-1,4-dihydro-6-fluoro-1-methyl- 8-trifluoromethyl-4-oxoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid (K-37), 8-difluoromethoxy-1,4-dihydro-6-fluoro-7-(3,4-dehydro-4-phenyl- 1-piperidinyl)-1-[4,(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)methylphenyl]-4-oxoquinoline- 3-carboxylic acid (K-38) act as potent and selective inhibitor of human immunodeficiency virus type I (HIV-1) transcription (Baba, 1997; Baba et al., 1997,1998). Structure-activity relationships of antibacterial oxoquinolone-3-carboxylic acids have been studied (Koga et al., 1980). In view of the signficicant biological activitiy, precise single crystal structure determinations of these derivatives are expcted to provide insights in their design and function. The crystal structure of 1H-2-phenyl-3-hydroxy-4-oxoquinoline-dimethylsulfoxide has already been reported (Czaun et al., 2002). The expression, purification and crystallization of 1H-3-hydroxy-4-oxoquinoline 2,4-dioxygenase are reported elsewhere (Qi et al., 2007).
The dihydropyridine ring of the title molecule (Fig.1) adopts a flattened boat conformation. The cyclohexenone ring is in an envelope conformation with atom C4 at the flap. The 4-methoxyphenyl ring and the planar part of the dihydropyridine ring (C2/C7/C9/C10) are nearly perpendicular to each other, with a dihedral angle of 89.37 (6)°.
In the crystal structure, molecules are linked into a two-dimensional network (Fig.2) parallel to the (101) by N—H···O and O—H···O hydrogen bonds (Table 1). The two-deimensional layer, resembiling a corrugated sheet, contains R44(30) and R44(34) graph-set motifs (Etter et al., 1990) as its fundamental repeating units. It is observed that these rings are assembled through centrosymmetrically related pairs of molecules with no direct hydrogen bonding between them.
Experimental
A 50 ml round-bottomed flask was charged with 3-hydroxybenzaldehyde (1.221 g, 10 mmol), 5,5-dimethyl-1,3-cyclohexanedione (1.402 g, 10 mmol), ethyl acetoacetate (1.265 ml, 10 mmol) and ammonium acetate (0.771 g, 10 mmol) followed by ethanol (10 ml). The mixture was stirred at 343 K for 1.5 h and left aside for a day. The solid separated out was filtered and washed with ethanol-diethyl ether mixture (1:4). It was recrystalyzed from 100% chloroform. Light yellow prismatic crystals of the title compound were obtained by slow evaporation of a methonolic solution. Pale yellow crystals with slab morphology were obtained by slow evaporation of a methonol-chloroform solution.
Refinement
H atoms were positioned geometrically [O-H = 0.82 Å, N-H = 0.86 Å and C-H = 0.93–0.98 Å] and refined using a riding model with Uiso(H) = 1.2Ueq(C) and 1.2Ueq(O and Cmethyl).
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound, with atom labels and 50% probability displacement ellipsoids for non-H atoms. H atoms have been omitted for clarity.
Fig. 2.
A view of the molecular aggregation down the a axis. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. C-bound H atoms have been omitted for clarity.
Fig. 3.
A view of the molecular aggregation down the b axis. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines. C-bound H atoms have been omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| C21H25NO4 | F(000) = 760 |
| Mr = 355.42 | Dx = 1.236 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/n | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2yn | Cell parameters from 5123 reflections |
| a = 10.8721 (4) Å | θ = 2.0–30.0° |
| b = 16.1255 (7) Å | µ = 0.09 mm−1 |
| c = 11.0856 (4) Å | T = 296 K |
| β = 100.682 (2)° | Prism, yellow |
| V = 1909.83 (13) Å3 | 0.26 × 0.15 × 0.12 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker Kappa APEXII area-detector diffractometer | 3163 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2137 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.041 |
| ω and φ scans | θmax = 24.5°, θmin = 2.3° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 2004) | h = −12→12 |
| Tmin = 0.93, Tmax = 0.95 | k = −18→17 |
| 14667 measured reflections | l = −11→12 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.040 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.115 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.02 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.048P)2 + 0.4479P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 3163 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| 236 parameters | Δρmax = 0.15 e Å−3 |
| 0 restraints | Δρmin = −0.15 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| O9A | 1.01275 (14) | 0.04777 (9) | 0.71484 (12) | 0.0559 (4) | |
| O6A | 1.21908 (13) | 0.29658 (10) | 0.59297 (11) | 0.0577 (4) | |
| O9B | 0.84079 (15) | −0.01070 (9) | 0.60571 (13) | 0.0618 (4) | |
| O8C | 0.72595 (19) | 0.37790 (12) | 0.71929 (17) | 0.0969 (7) | |
| H8C | 0.7098 | 0.4009 | 0.7804 | 0.145* | |
| N1 | 0.85621 (15) | 0.18610 (10) | 0.34959 (13) | 0.0444 (4) | |
| H1 | 0.7990 | 0.1933 | 0.2857 | 0.053* | |
| C7 | 1.03735 (16) | 0.23880 (11) | 0.47694 (14) | 0.0346 (4) | |
| C2 | 0.95697 (17) | 0.23874 (11) | 0.36798 (15) | 0.0365 (4) | |
| C8 | 1.01637 (17) | 0.18488 (12) | 0.58296 (15) | 0.0376 (5) | |
| H8 | 1.0962 | 0.1583 | 0.6176 | 0.045* | |
| C9 | 0.92188 (17) | 0.11633 (11) | 0.53752 (15) | 0.0368 (4) | |
| C6 | 1.14473 (17) | 0.29327 (12) | 0.49410 (15) | 0.0394 (5) | |
| C10 | 0.84203 (17) | 0.12208 (12) | 0.42851 (15) | 0.0384 (5) | |
| C9A | 0.91749 (19) | 0.04511 (13) | 0.61867 (17) | 0.0433 (5) | |
| C4 | 1.04698 (18) | 0.37054 (12) | 0.29899 (16) | 0.0435 (5) | |
| C8B | 0.8704 (2) | 0.28573 (13) | 0.65967 (17) | 0.0509 (6) | |
| H8B | 0.8260 | 0.2893 | 0.5796 | 0.061* | |
| C3 | 0.97318 (19) | 0.29188 (13) | 0.26167 (15) | 0.0471 (5) | |
| H3A | 0.8913 | 0.3068 | 0.2159 | 0.057* | |
| H3B | 1.0157 | 0.2600 | 0.2075 | 0.057* | |
| C5 | 1.16617 (19) | 0.34564 (14) | 0.38772 (17) | 0.0537 (6) | |
| H5A | 1.2199 | 0.3154 | 0.3424 | 0.064* | |
| H5B | 1.2103 | 0.3956 | 0.4196 | 0.064* | |
| C8A | 0.97467 (19) | 0.23549 (12) | 0.68484 (15) | 0.0421 (5) | |
| C10A | 0.7372 (2) | 0.06394 (14) | 0.37939 (18) | 0.0536 (6) | |
| H10A | 0.7707 | 0.0101 | 0.3675 | 0.080* | |
| H10B | 0.6924 | 0.0845 | 0.3024 | 0.080* | |
| H10C | 0.6813 | 0.0600 | 0.4368 | 0.080* | |
| C8F | 1.0398 (2) | 0.23138 (15) | 0.80510 (17) | 0.0608 (6) | |
| H8F | 1.1111 | 0.1986 | 0.8241 | 0.073* | |
| C8C | 0.8307 (2) | 0.33082 (14) | 0.7515 (2) | 0.0608 (6) | |
| C9B | 1.0157 (2) | −0.01484 (16) | 0.8081 (2) | 0.0682 (7) | |
| H91B | 1.0250 | −0.0694 | 0.7740 | 0.082* | |
| H92B | 0.9384 | −0.0139 | 0.8400 | 0.082* | |
| C4A | 1.0813 (2) | 0.41285 (15) | 0.18658 (18) | 0.0673 (7) | |
| H41A | 1.1279 | 0.4625 | 0.2115 | 0.101* | |
| H42A | 1.0063 | 0.4268 | 0.1298 | 0.101* | |
| H43A | 1.1313 | 0.3759 | 0.1477 | 0.101* | |
| C8E | 0.9988 (3) | 0.27565 (18) | 0.8960 (2) | 0.0777 (8) | |
| H8E | 1.0422 | 0.2714 | 0.9763 | 0.093* | |
| C8D | 0.8956 (3) | 0.32578 (17) | 0.8710 (2) | 0.0717 (8) | |
| H8D | 0.8697 | 0.3559 | 0.9333 | 0.086* | |
| C4B | 0.9704 (3) | 0.43009 (15) | 0.3613 (2) | 0.0796 (8) | |
| H41B | 1.0181 | 0.4796 | 0.3844 | 0.119* | |
| H42B | 0.9502 | 0.4043 | 0.4332 | 0.119* | |
| H43B | 0.8947 | 0.4440 | 0.3056 | 0.119* | |
| C9C | 1.1234 (3) | 0.0034 (2) | 0.9074 (2) | 0.0993 (11) | |
| H91C | 1.1276 | −0.0374 | 0.9710 | 0.149* | |
| H92C | 1.1130 | 0.0574 | 0.9407 | 0.149* | |
| H93C | 1.1993 | 0.0022 | 0.8749 | 0.149* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| O9A | 0.0679 (10) | 0.0550 (9) | 0.0430 (7) | 0.0030 (7) | 0.0057 (7) | 0.0178 (7) |
| O6A | 0.0501 (9) | 0.0749 (11) | 0.0390 (7) | −0.0106 (8) | −0.0157 (7) | 0.0038 (7) |
| O9B | 0.0681 (11) | 0.0521 (10) | 0.0667 (10) | −0.0076 (8) | 0.0164 (8) | 0.0124 (8) |
| O8C | 0.1049 (15) | 0.1028 (16) | 0.0858 (13) | 0.0344 (13) | 0.0246 (11) | −0.0337 (11) |
| N1 | 0.0460 (10) | 0.0493 (10) | 0.0313 (8) | −0.0099 (8) | −0.0099 (7) | 0.0028 (8) |
| C7 | 0.0365 (10) | 0.0380 (11) | 0.0272 (9) | 0.0017 (8) | 0.0006 (7) | −0.0014 (8) |
| C2 | 0.0402 (11) | 0.0380 (11) | 0.0286 (9) | −0.0024 (9) | −0.0005 (8) | −0.0028 (8) |
| C8 | 0.0390 (11) | 0.0427 (11) | 0.0282 (9) | 0.0027 (9) | −0.0011 (8) | 0.0036 (8) |
| C9 | 0.0438 (11) | 0.0356 (11) | 0.0325 (9) | 0.0021 (9) | 0.0107 (8) | −0.0012 (8) |
| C6 | 0.0375 (11) | 0.0456 (12) | 0.0312 (9) | 0.0008 (9) | −0.0034 (8) | −0.0018 (9) |
| C10 | 0.0438 (11) | 0.0374 (11) | 0.0338 (9) | −0.0024 (9) | 0.0068 (8) | −0.0046 (9) |
| C9A | 0.0479 (12) | 0.0432 (12) | 0.0418 (11) | 0.0067 (10) | 0.0160 (10) | 0.0002 (9) |
| C4 | 0.0519 (12) | 0.0440 (12) | 0.0312 (9) | −0.0051 (10) | −0.0009 (9) | 0.0020 (9) |
| C8B | 0.0619 (14) | 0.0548 (14) | 0.0351 (10) | 0.0008 (11) | 0.0063 (10) | −0.0091 (10) |
| C3 | 0.0542 (13) | 0.0540 (13) | 0.0282 (9) | −0.0119 (10) | −0.0052 (9) | 0.0032 (9) |
| C5 | 0.0508 (13) | 0.0627 (14) | 0.0429 (11) | −0.0151 (11) | −0.0037 (10) | 0.0060 (10) |
| C8A | 0.0538 (13) | 0.0429 (12) | 0.0285 (9) | −0.0071 (10) | 0.0046 (8) | −0.0019 (8) |
| C10A | 0.0579 (14) | 0.0541 (14) | 0.0472 (11) | −0.0153 (11) | 0.0058 (10) | −0.0075 (10) |
| C8F | 0.0772 (16) | 0.0680 (15) | 0.0326 (11) | −0.0053 (13) | −0.0016 (10) | −0.0034 (11) |
| C8C | 0.0738 (16) | 0.0540 (15) | 0.0586 (14) | −0.0031 (13) | 0.0229 (12) | −0.0155 (12) |
| C9B | 0.0835 (18) | 0.0674 (16) | 0.0571 (13) | 0.0206 (13) | 0.0220 (13) | 0.0296 (12) |
| C4A | 0.0850 (18) | 0.0689 (16) | 0.0438 (12) | −0.0258 (14) | 0.0008 (11) | 0.0110 (11) |
| C8E | 0.109 (2) | 0.089 (2) | 0.0303 (11) | −0.0111 (18) | 0.0015 (13) | −0.0135 (12) |
| C8D | 0.101 (2) | 0.0724 (18) | 0.0468 (13) | −0.0194 (16) | 0.0261 (14) | −0.0260 (13) |
| C4B | 0.117 (2) | 0.0556 (16) | 0.0675 (15) | 0.0266 (15) | 0.0204 (15) | 0.0067 (13) |
| C9C | 0.0805 (19) | 0.148 (3) | 0.0679 (16) | 0.0255 (19) | 0.0092 (15) | 0.0560 (19) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| O9A—C9A | 1.342 (2) | C3—H3A | 0.97 |
| O9A—C9B | 1.442 (2) | C3—H3B | 0.97 |
| O6A—C6 | 1.237 (2) | C5—H5A | 0.97 |
| O9B—C9A | 1.217 (2) | C5—H5B | 0.97 |
| O8C—C8C | 1.361 (3) | C8A—C8F | 1.390 (3) |
| O8C—H8C | 0.82 | C10A—H10A | 0.96 |
| N1—C2 | 1.371 (2) | C10A—H10B | 0.96 |
| N1—C10 | 1.380 (2) | C10A—H10C | 0.96 |
| N1—H1 | 0.86 | C8F—C8E | 1.374 (3) |
| C7—C2 | 1.353 (2) | C8F—H8F | 0.93 |
| C7—C6 | 1.445 (3) | C8C—C8D | 1.383 (3) |
| C7—C8 | 1.513 (2) | C9B—C9C | 1.480 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.494 (3) | C9B—H91B | 0.97 |
| C8—C9 | 1.529 (3) | C9B—H92B | 0.97 |
| C8—C8A | 1.529 (3) | C4A—H41A | 0.96 |
| C8—H8 | 0.98 | C4A—H42A | 0.96 |
| C9—C10 | 1.354 (2) | C4A—H43A | 0.96 |
| C9—C9A | 1.465 (3) | C8E—C8D | 1.369 (4) |
| C6—C5 | 1.503 (3) | C8E—H8E | 0.93 |
| C10—C10A | 1.498 (3) | C8D—H8D | 0.93 |
| C4—C3 | 1.517 (3) | C4B—H41B | 0.96 |
| C4—C4B | 1.518 (3) | C4B—H42B | 0.96 |
| C4—C4A | 1.526 (3) | C4B—H43B | 0.96 |
| C4—C5 | 1.528 (3) | C9C—H91C | 0.96 |
| C8B—C8A | 1.379 (3) | C9C—H92C | 0.96 |
| C8B—C8C | 1.383 (3) | C9C—H93C | 0.96 |
| C8B—H8B | 0.93 | ||
| C9A—O9A—C9B | 117.31 (17) | C4—C5—H5B | 108.6 |
| C8C—O8C—H8C | 109.5 | H5A—C5—H5B | 107.6 |
| C2—N1—C10 | 123.30 (14) | C8B—C8A—C8F | 118.38 (19) |
| C2—N1—H1 | 118.4 | C8B—C8A—C8 | 120.62 (15) |
| C10—N1—H1 | 118.4 | C8F—C8A—C8 | 120.99 (19) |
| C2—C7—C6 | 119.35 (16) | C10—C10A—H10A | 109.5 |
| C2—C7—C8 | 121.84 (17) | C10—C10A—H10B | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—C8 | 118.79 (14) | H10A—C10A—H10B | 109.5 |
| C7—C2—N1 | 119.95 (17) | C10—C10A—H10C | 109.5 |
| C7—C2—C3 | 123.56 (17) | H10A—C10A—H10C | 109.5 |
| N1—C2—C3 | 116.47 (14) | H10B—C10A—H10C | 109.5 |
| C7—C8—C9 | 110.38 (14) | C8E—C8F—C8A | 120.1 (2) |
| C7—C8—C8A | 112.04 (15) | C8E—C8F—H8F | 120.0 |
| C9—C8—C8A | 110.86 (15) | C8A—C8F—H8F | 120.0 |
| C7—C8—H8 | 107.8 | O8C—C8C—C8B | 117.4 (2) |
| C9—C8—H8 | 107.8 | O8C—C8C—C8D | 122.5 (2) |
| C8A—C8—H8 | 107.8 | C8B—C8C—C8D | 120.1 (2) |
| C10—C9—C9A | 120.87 (17) | O9A—C9B—C9C | 107.7 (2) |
| C10—C9—C8 | 121.66 (16) | O9A—C9B—H91B | 110.2 |
| C9A—C9—C8 | 117.43 (15) | C9C—C9B—H91B | 110.2 |
| O6A—C6—C7 | 121.49 (17) | O9A—C9B—H92B | 110.2 |
| O6A—C6—C5 | 120.01 (17) | C9C—C9B—H92B | 110.2 |
| C7—C6—C5 | 118.50 (14) | H91B—C9B—H92B | 108.5 |
| C9—C10—N1 | 119.23 (16) | C4—C4A—H41A | 109.5 |
| C9—C10—C10A | 126.89 (18) | C4—C4A—H42A | 109.5 |
| N1—C10—C10A | 113.86 (15) | H41A—C4A—H42A | 109.5 |
| O9B—C9A—O9A | 121.89 (18) | C4—C4A—H43A | 109.5 |
| O9B—C9A—C9 | 127.35 (18) | H41A—C4A—H43A | 109.5 |
| O9A—C9A—C9 | 110.76 (17) | H42A—C4A—H43A | 109.5 |
| C3—C4—C4B | 110.26 (19) | C8D—C8E—C8F | 121.6 (2) |
| C3—C4—C4A | 110.37 (15) | C8D—C8E—H8E | 119.2 |
| C4B—C4—C4A | 109.04 (18) | C8F—C8E—H8E | 119.2 |
| C3—C4—C5 | 107.36 (16) | C8E—C8D—C8C | 118.8 (2) |
| C4B—C4—C5 | 110.14 (17) | C8E—C8D—H8D | 120.6 |
| C4A—C4—C5 | 109.66 (17) | C8C—C8D—H8D | 120.6 |
| C8A—C8B—C8C | 121.09 (19) | C4—C4B—H41B | 109.5 |
| C8A—C8B—H8B | 119.5 | C4—C4B—H42B | 109.5 |
| C8C—C8B—H8B | 119.5 | H41B—C4B—H42B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 113.47 (14) | C4—C4B—H43B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3A | 108.9 | H41B—C4B—H43B | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3A | 108.9 | H42B—C4B—H43B | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3B | 108.9 | C9B—C9C—H91C | 109.5 |
| C4—C3—H3B | 108.9 | C9B—C9C—H92C | 109.5 |
| H3A—C3—H3B | 107.7 | H91C—C9C—H92C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—C4 | 114.60 (16) | C9B—C9C—H93C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5A | 108.6 | H91C—C9C—H93C | 109.5 |
| C4—C5—H5A | 108.6 | H92C—C9C—H93C | 109.5 |
| C6—C5—H5B | 108.6 | ||
| C6—C7—C2—N1 | 178.61 (17) | C10—C9—C9A—O9A | 173.47 (17) |
| C8—C7—C2—N1 | −3.0 (3) | C8—C9—C9A—O9A | −8.8 (2) |
| C6—C7—C2—C3 | 0.7 (3) | C7—C2—C3—C4 | −26.3 (3) |
| C8—C7—C2—C3 | 179.07 (17) | N1—C2—C3—C4 | 155.73 (17) |
| C10—N1—C2—C7 | −11.5 (3) | C4B—C4—C3—C2 | −70.4 (2) |
| C10—N1—C2—C3 | 166.61 (17) | C4A—C4—C3—C2 | 169.08 (18) |
| C2—C7—C8—C9 | 17.0 (2) | C5—C4—C3—C2 | 49.6 (2) |
| C6—C7—C8—C9 | −164.56 (16) | O6A—C6—C5—C4 | −150.90 (19) |
| C2—C7—C8—C8A | −107.0 (2) | C7—C6—C5—C4 | 30.1 (3) |
| C6—C7—C8—C8A | 71.4 (2) | C3—C4—C5—C6 | −52.3 (2) |
| C7—C8—C9—C10 | −19.7 (2) | C4B—C4—C5—C6 | 67.8 (2) |
| C8A—C8—C9—C10 | 105.08 (19) | C4A—C4—C5—C6 | −172.20 (18) |
| C7—C8—C9—C9A | 162.58 (16) | C8C—C8B—C8A—C8F | −0.2 (3) |
| C8A—C8—C9—C9A | −72.7 (2) | C8C—C8B—C8A—C8 | 179.03 (19) |
| C2—C7—C6—O6A | 178.46 (18) | C7—C8—C8A—C8B | 55.7 (2) |
| C8—C7—C6—O6A | 0.0 (3) | C9—C8—C8A—C8B | −68.1 (2) |
| C2—C7—C6—C5 | −2.5 (3) | C7—C8—C8A—C8F | −125.0 (2) |
| C8—C7—C6—C5 | 179.01 (17) | C9—C8—C8A—C8F | 111.2 (2) |
| C9A—C9—C10—N1 | −174.18 (17) | C8B—C8A—C8F—C8E | 1.0 (3) |
| C8—C9—C10—N1 | 8.1 (3) | C8—C8A—C8F—C8E | −178.3 (2) |
| C9A—C9—C10—C10A | 4.3 (3) | C8A—C8B—C8C—O8C | −179.0 (2) |
| C8—C9—C10—C10A | −173.38 (18) | C8A—C8B—C8C—C8D | −0.2 (4) |
| C2—N1—C10—C9 | 8.7 (3) | C9A—O9A—C9B—C9C | −176.61 (19) |
| C2—N1—C10—C10A | −169.93 (18) | C8A—C8F—C8E—C8D | −1.3 (4) |
| C9B—O9A—C9A—O9B | −4.7 (3) | C8F—C8E—C8D—C8C | 0.8 (4) |
| C9B—O9A—C9A—C9 | 175.31 (17) | O8C—C8C—C8D—C8E | 178.7 (2) |
| C10—C9—C9A—O9B | −6.5 (3) | C8B—C8C—C8D—C8E | 0.0 (4) |
| C8—C9—C9A—O9B | 171.30 (19) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O8C—H8C···O9Bi | 0.82 | 2.05 | 2.835 (2) | 162 |
| N1—H1···O6Aii | 0.86 | 2.16 | 2.970 (2) | 157 |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+3/2, y+1/2, −z+3/2; (ii) x−1/2, −y+1/2, z−1/2.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: CI2916).
References
- Baba, M. (1997). Antivir. Res.33, 141–152. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Baba, M., Okamoto, M., Kawamura, M., Makino, M., Higashida, T., Takashi, T., Kimura, Y., Ikeuchi, T., Tetsuka, T. & Okamoto, T. (1998). Mol. Pharm.53, 1097–1103. [PubMed]
- Baba, M., Okamoto, M., Makino, M., Kimura, Y., Ikeuchi, T., Sakaguchi, T. & Okamoto, T. (1997). Antimicrob. Agents Chemother.41, 1250–1255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Bruker (2004). APEX2 and SAINT-Plus Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Czaun, M., Ganszky, I., Speier, G. & Parkanyi, L. (2002). Z. Kristallogr. New Cryst. Struct.217, 379–380.
- Etter, M. C., MacDonald, J. C. & Bernstein, J. (1990). Acta Cryst. B46, 256–262. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Koga, H., Itoh, A., murayama, S., Suzue, S. & Irikura, T. (1980). J. Med. Chem.23, 1358–1363. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Qi, R., Fetzner, S. & Oakley, A. J. (2007). Acta Cryst. F63, 378–381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2004). SADABS University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Spek, A. L. (2009). Acta Cryst. D65, 148–155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks I, global. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809039877/ci2916sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809039877/ci2916Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report





