Abstract
The title compound, [Na(C18H36N2O6)]ClO4, was isolated and crystallized to understand more fully the ligand’s binding specificity to cations. The cation and anion reside at an intersection of crystallographic twofold and threefold axes. The carbon atoms in the cation are disordered over two positions in a 3:2 ratio, and the anion is equally disordered over two positions. The geometries of the cation and anion are typical. The compound packs in alternating sheets of discrete cations and anions stacked along the c axis, separated by a distance equal to one-sixth the length of the c axis.
Related literature
For general background to the macrocyclic polyether 4,7,13,16,21,24-hexaoxa-1,10-diaza-bicyclo[8.8.8]hexacosane, see: Izatt et al. (1985 ▶); Tait et al. (1997 ▶); Varga et al. (1994 ▶); Trend et al. (1993 ▶); Hamacher et al. (1986 ▶); Su & Burnette (2008 ▶). For related structures, see: Belaj et al. (1997 ▶); Tehan et al. (1974 ▶). For a description of the Cambridge Structural Database, see: Allen (2002 ▶) and for Mogul, see: Bruno et al. (2004 ▶).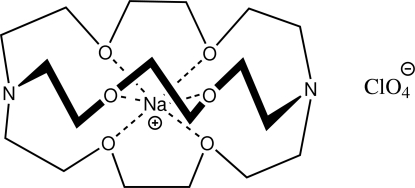
Experimental
Crystal data
[Na(C18H36N2O6)]ClO4
M r = 498.93
Rhombohedral,

a = 8.4730 (3) Å
c = 28.220 (3) Å
V = 1754.5 (2) Å3
Z = 3
Mo- Kα radiation
μ = 0.24 mm−1
T = 100 K
0.49 × 0.37 × 0.35 mm
Data collection
Bruker CCD-1000 area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2007 ▶) T min = 0.893, T max = 0.922
6885 measured reflections
805 independent reflections
765 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.026
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.037
wR(F 2) = 0.113
S = 1.11
805 reflections
85 parameters
144 restraints
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.28 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 319 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: 0.01 (15)
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 2007 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2007 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXTL; molecular graphics: SHELXTL, OLEX2 (Dolomanov et al., 2009 ▶) and DIAMOND (Brandenburg, 1999 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL, modiCIFer (Guzei, 2007 ▶) and publCIF (Westrip, 2009 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809039683/hk2757sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809039683/hk2757Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Selected geometric parameters (Å, °).
| Cl1—O2i | 1.422 (4) |
| Cl1—O2 | 1.422 (4) |
| Cl1—O3i | 1.434 (3) |
| Cl1—O3ii | 1.434 (3) |
| Cl1—O3 | 1.434 (3) |
| Cl1—O3iii | 1.434 (3) |
| Cl1—O3iv | 1.434 (3) |
| Cl1—O3v | 1.434 (3) |
| Na1—O1 | 2.5661 (15) |
| Na1—N1 | 2.684 (2) |
| O2—O3iii | 1.639 (5) |
| O3—O3v | 1.797 (10) |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  ; (iv)
; (iv)  ; (v)
; (v)  .
.
Acknowledgments
We thank the National Science Foundation for financial support.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
The macrocyclic polyether 4,7,13,16,21,24-hexaoxa-1,10-diaza-bicyclo[8.8.8]hexacosane (222) is a classic example of a host molecule possessing important clinical functions. 222 encapsulates 1:1 various alkali and alkaline earth metals, and features high selectivity for K+ and Sr2+ in solution (Izatt et al., 1985). Tait et al. (1997) formulated a cation exchange resin treated with 222 that sorbed more than 95% of the fallout nuclide 90Sr in liquid milk (295 K, pH 5.2, 4 h contact time, 1:50 resin to milk volume ratio). Varga et al. (1994) synthesized functionalized 222 for 85Sr2+ decorporation in the rat and mouse. J. E. Trend and co-workers (1993) formulated 222 with a covalently bound chromophore to assay clinical blood K+4. Hamacher et al. (1986) developed the use of [K+(222)]18F- as a phase transfer catalyst in synthesizing the clinically significant PET tracer 2-[18F]fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose. Due to 222 obvious industrial and clinical applications the relative binding characteristics of 222 to Li+, Na+ and K+ have been studied in order to more fully understand 222's binding specificity to cations (Su & Burnette, 2008).
In the title compound, (I), both the Na+(222) cation and the perchlorate anion of (I) reside at an intersection of crystallographic twofold and threefold axes. All the carbon atoms in the cation are disordered over two positions in a 3:2 ratio. The perchlorate anion is equally disordered over two positions. Multiple restraints were applied to ensure computational stability of the refinement.
The bond distances and angles within (I) are typical as confirmed by the Mogul structural check (Bruno et. al, 2004). Among 59 relevant compounds reported to the CSD (Allen, 2002), the most closely related is (4,7,13,16,21,24-hexaoxa-1,10-diazabicyclo(8.8.8)hexacosane)-sodium periodate which contains the same cation as (I) and a periodate anion instead of the perchlorate anion (Belaj et al., 1997), and sodium (2,2,2)-crypt-sodium (Tehan et al., 1974) which forms crystals in the same rhombohedral space group R32, as (I).
The packing structure of compound (I) consists of alternating sheets of cations and anions stacked along the c axis. The distance between these sheets is 4.70 Å, or one sixth of the length of the c axis.
Experimental
An equimolar mixture of 222 and NaClO4 was prepared in acetone. The mixture was allowed to evaporate slowly at room temperature until crystallization was observed.
Refinement
All H-atoms were placed in idealized locations and refined as riding with appropriate thermal displacement coefficients Uiso(H) = 1.2 times Ueq(bearing atom).
The following restraints (expressed as SHELXL commands) were used. Thus, we imposed distance similarity restraints on the C—C and C—N bonds involving disordered atoms and refined the ClO4- anion with an idealized geometry allowing the Cl—O distanct to refine as a free variable. The thermal displacement parameters for C3 and C3a were restrained to approximate isotropic behavior.
EQIV $3 Y+1/3, X-1/3, –Z+5/3 SADI 0.005 C1 C2 C1A C2A C3 C3_$3 C3A C3A_$3 SADI 0.005 N1 C1 N1 C1A SADI 0.005 O1 C2 O1 C2A O1 C3 O1 C3A DFIX 21 0.005 C L1 O3 CL1 O2 DFIX 21.633 0.005 O2 O3 SIMU DELU ISOR 0.02 C3 C3A FVAR 0.49309 1.43008 0.34032
Figures
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of (I). The thermal ellipsoids are shown at 50% probability level. Only the preferred orientation of the carbon atoms is shown and only tone orientation of the perchlorate molecule is shown. All hydrogen atoms were omitted for clarity. Symmetry transformations used to generate equivalent atoms: i: (-x + y+1,-x + 1,z) ii: (-y + 1,x-y,z) iii: (-x + 4/3,-x + y+2/3,-z + 5/3) iv: (y + 1/3,x - 1/3,-z + 5/3) v: (x-y + 1/3,-y + 2/3,-z + 5/3) vi: (-x + y+1,-x + 2,z) vii: (-y + 2,x-y + 1,z).
Crystal data
| [Na(C18H36N2O6)]ClO4 | F(000) = 798 |
| Mr = 498.93 | Dx = 1.417 Mg m−3 |
| Rhombohedral, R32 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: R 3 2" | Cell parameters from 999 reflections |
| a = 8.4730 (3) Å | θ = 2.2–26.4° |
| c = 28.220 (3) Å | µ = 0.24 mm−1 |
| α = 90° | T = 100 K |
| γ = 120° | Block, colorless |
| V = 1754.5 (2) Å3 | 0.49 × 0.37 × 0.35 mm |
| Z = 3 |
Data collection
| Bruker CCD-1000 area-detector diffractometer | 805 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 765 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.026 |
| 0.30° ω scans | θmax = 26.4°, θmin = 2.2° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2007) | h = −10→10 |
| Tmin = 0.893, Tmax = 0.922 | k = −10→10 |
| 6885 measured reflections | l = −35→35 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.037 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.113 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0715P)2 + 1.1083P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.11 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 805 reflections | Δρmax = 0.28 e Å−3 |
| 85 parameters | Δρmin = −0.18 e Å−3 |
| 144 restraints | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 319 Friedel pairs |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Flack parameter: 0.01 (15) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| Cl1 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.0347 (3) | |
| Na1 | 0.6667 | 0.3333 | 0.8333 | 0.0246 (3) | |
| O1 | 0.9844 (2) | 0.5262 (3) | 0.86993 (4) | 0.0589 (6) | |
| O2 | 1.0000 | 1.0000 | 0.94963 (15) | 0.0768 (17) | 0.50 |
| O3 | 0.8972 (8) | 0.8167 (4) | 1.01732 (13) | 0.0762 (10) | 0.50 |
| N1 | 0.6667 | 0.3333 | 0.92846 (8) | 0.0420 (6) | |
| C1 | 0.8527 (6) | 0.3802 (11) | 0.9424 (2) | 0.0688 (15) | 0.60 |
| H1A | 0.8634 | 0.3967 | 0.9772 | 0.083* | 0.60 |
| H1B | 0.8694 | 0.2754 | 0.9348 | 0.083* | 0.60 |
| C1A | 0.8443 (7) | 0.4767 (11) | 0.9471 (3) | 0.0534 (16) | 0.40 |
| H1C | 0.8525 | 0.5973 | 0.9452 | 0.064* | 0.40 |
| H1D | 0.8581 | 0.4518 | 0.9807 | 0.064* | 0.40 |
| C2 | 1.0022 (10) | 0.5443 (10) | 0.92024 (13) | 0.0614 (18) | 0.60 |
| H2A | 0.9972 | 0.6535 | 0.9305 | 0.074* | 0.60 |
| H2B | 1.1210 | 0.5592 | 0.9301 | 0.074* | 0.60 |
| C2A | 0.9880 (17) | 0.475 (3) | 0.9180 (2) | 0.087 (4) | 0.40 |
| H2C | 1.1084 | 0.5602 | 0.9319 | 0.104* | 0.40 |
| H2D | 0.9725 | 0.3514 | 0.9186 | 0.104* | 0.40 |
| C3 | 1.0622 (10) | 0.7167 (5) | 0.85941 (11) | 0.087 (2) | 0.60 |
| H3A | 1.1909 | 0.7854 | 0.8699 | 0.105* | 0.60 |
| H3B | 0.9934 | 0.7671 | 0.8756 | 0.105* | 0.60 |
| C3A | 1.1033 (9) | 0.6727 (12) | 0.8398 (4) | 0.094 (4) | 0.40 |
| H3C | 1.1327 | 0.6254 | 0.8110 | 0.113* | 0.40 |
| H3D | 1.2183 | 0.7554 | 0.8565 | 0.113* | 0.40 |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cl1 | 0.0316 (3) | 0.0316 (3) | 0.0408 (5) | 0.01580 (17) | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| Na1 | 0.0265 (4) | 0.0265 (4) | 0.0208 (6) | 0.0132 (2) | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| O1 | 0.0367 (7) | 0.0832 (14) | 0.0448 (8) | 0.0211 (8) | −0.0063 (6) | 0.0004 (7) |
| O2 | 0.093 (3) | 0.093 (3) | 0.045 (3) | 0.0464 (14) | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| O3 | 0.071 (3) | 0.0472 (18) | 0.109 (3) | 0.028 (2) | 0.015 (3) | 0.0307 (17) |
| N1 | 0.0486 (9) | 0.0486 (9) | 0.0289 (10) | 0.0243 (5) | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| C1 | 0.068 (3) | 0.087 (4) | 0.037 (2) | 0.028 (3) | −0.026 (2) | 0.003 (3) |
| C1A | 0.060 (4) | 0.058 (4) | 0.032 (3) | 0.022 (4) | −0.017 (3) | 0.000 (3) |
| C2 | 0.040 (3) | 0.077 (4) | 0.047 (3) | 0.014 (2) | −0.008 (2) | −0.0187 (19) |
| C2A | 0.046 (4) | 0.146 (12) | 0.054 (5) | 0.037 (6) | −0.025 (3) | 0.008 (5) |
| C3 | 0.067 (4) | 0.056 (3) | 0.088 (4) | −0.007 (3) | −0.033 (3) | 0.000 (3) |
| C3A | 0.041 (4) | 0.100 (7) | 0.089 (6) | −0.005 (4) | 0.009 (4) | −0.004 (5) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cl1—O2i | 1.422 (4) | O3—O3i | 1.533 (9) |
| Cl1—O2 | 1.422 (4) | O3—O3v | 1.797 (10) |
| Cl1—O3i | 1.434 (3) | N1—C1 | 1.474 (4) |
| Cl1—O3ii | 1.434 (3) | N1—C1vi | 1.474 (4) |
| Cl1—O3 | 1.434 (3) | N1—C1viii | 1.474 (4) |
| Cl1—O3iii | 1.434 (3) | N1—C1Avi | 1.480 (4) |
| Cl1—O3iv | 1.434 (3) | N1—C1A | 1.480 (4) |
| Cl1—O3v | 1.434 (3) | N1—C1Aviii | 1.480 (4) |
| Na1—O1 | 2.5661 (15) | C1—C2 | 1.473 (5) |
| Na1—O1vi | 2.5661 (15) | C1—H1A | 0.9900 |
| Na1—O1vii | 2.5661 (15) | C1—H1B | 0.9900 |
| Na1—O1viii | 2.5661 (15) | C1A—C2A | 1.476 (6) |
| Na1—O1ix | 2.5661 (15) | C1A—H1C | 0.9900 |
| Na1—O1x | 2.5661 (15) | C1A—H1D | 0.9900 |
| Na1—N1 | 2.684 (2) | C2—H2A | 0.9900 |
| Na1—N1ix | 2.685 (2) | C2—H2B | 0.9900 |
| O1—C2 | 1.428 (4) | C2A—H2C | 0.9900 |
| O1—C2A | 1.428 (4) | C2A—H2D | 0.9900 |
| O1—C3 | 1.436 (4) | C3—C3ix | 1.483 (6) |
| O1—C3A | 1.425 (5) | C3—H3A | 0.9900 |
| O2—O3iii | 1.639 (5) | C3—H3B | 0.9900 |
| O2—O3v | 1.639 (5) | C3A—C3Aix | 1.474 (6) |
| O2—O3i | 1.639 (5) | C3A—H3C | 0.9900 |
| O3—O2i | 1.639 (5) | C3A—H3D | 0.9900 |
| O2i—Cl1—O2 | 180.000 (4) | C3—O1—Na1 | 112.2 (3) |
| O2i—Cl1—O3i | 109.92 (16) | Cl1—O2—O3iii | 55.32 (15) |
| O2—Cl1—O3i | 70.08 (16) | Cl1—O2—O3v | 55.32 (15) |
| O2i—Cl1—O3ii | 70.08 (16) | O3iii—O2—O3v | 90.8 (2) |
| O2—Cl1—O3ii | 109.92 (16) | Cl1—O2—O3i | 55.32 (15) |
| O3i—Cl1—O3ii | 172.5 (5) | O3iii—O2—O3i | 90.8 (2) |
| O2i—Cl1—O3 | 70.08 (16) | O3v—O2—O3i | 90.8 (2) |
| O2—Cl1—O3 | 109.92 (16) | Cl1—O3—O3i | 57.7 (2) |
| O3i—Cl1—O3 | 64.6 (5) | Cl1—O3—O2i | 54.60 (16) |
| O3ii—Cl1—O3 | 109.01 (16) | O3i—O3—O2i | 94.9 (4) |
| O2i—Cl1—O3iii | 109.92 (16) | Cl1—O3—O3v | 51.2 (2) |
| O2—Cl1—O3iii | 70.08 (16) | O3i—O3—O3v | 88.7 (3) |
| O3i—Cl1—O3iii | 109.01 (16) | O2i—O3—O3v | 85.6 (3) |
| O3ii—Cl1—O3iii | 77.6 (5) | C1—N1—C1vi | 113.1 (2) |
| O3—Cl1—O3iii | 172.5 (5) | C1—N1—C1viii | 113.1 (2) |
| O2i—Cl1—O3iv | 70.08 (16) | C1vi—N1—C1viii | 113.1 (2) |
| O2—Cl1—O3iv | 109.92 (16) | C1Avi—N1—C1A | 108.0 (3) |
| O3i—Cl1—O3iv | 77.6 (5) | C1Avi—N1—C1Aviii | 108.0 (3) |
| O3ii—Cl1—O3iv | 109.01 (16) | C1A—N1—C1Aviii | 108.0 (3) |
| O3—Cl1—O3iv | 109.01 (16) | C1—N1—Na1 | 105.5 (2) |
| O3iii—Cl1—O3iv | 64.6 (4) | C1vi—N1—Na1 | 105.5 (3) |
| O2i—Cl1—O3v | 109.92 (16) | C1viii—N1—Na1 | 105.5 (2) |
| O2—Cl1—O3v | 70.08 (16) | C1Avi—N1—Na1 | 110.9 (3) |
| O3i—Cl1—O3v | 109.01 (16) | C1A—N1—Na1 | 110.9 (3) |
| O3ii—Cl1—O3v | 64.6 (5) | C1Aviii—N1—Na1 | 110.9 (3) |
| O3—Cl1—O3v | 77.6 (5) | C2—C1—N1 | 116.1 (6) |
| O3iii—Cl1—O3v | 109.01 (16) | C2—C1—H1A | 108.3 |
| O3iv—Cl1—O3v | 172.5 (5) | N1—C1—H1A | 108.3 |
| O1—Na1—O1vi | 104.90 (3) | C2—C1—H1B | 108.3 |
| O1—Na1—O1vii | 167.11 (9) | N1—C1—H1B | 108.3 |
| O1vi—Na1—O1vii | 86.11 (9) | H1A—C1—H1B | 107.4 |
| O1—Na1—O1viii | 104.90 (3) | C2A—C1A—N1 | 107.4 (8) |
| O1vi—Na1—O1viii | 104.90 (3) | C2A—C1A—H1C | 110.2 |
| O1vii—Na1—O1viii | 65.09 (7) | N1—C1A—H1C | 110.2 |
| O1—Na1—O1ix | 65.09 (7) | C2A—C1A—H1D | 110.2 |
| O1vi—Na1—O1ix | 167.11 (9) | N1—C1A—H1D | 110.2 |
| O1vii—Na1—O1ix | 104.90 (3) | H1C—C1A—H1D | 108.5 |
| O1viii—Na1—O1ix | 86.11 (9) | O1—C2—C1 | 109.0 (4) |
| O1—Na1—O1x | 86.11 (9) | O1—C2—H2A | 109.9 |
| O1vi—Na1—O1x | 65.09 (7) | C1—C2—H2A | 109.9 |
| O1vii—Na1—O1x | 104.89 (3) | O1—C2—H2B | 109.9 |
| O1viii—Na1—O1x | 167.11 (9) | C1—C2—H2B | 109.9 |
| O1ix—Na1—O1x | 104.89 (3) | H2A—C2—H2B | 108.3 |
| O1—Na1—N1 | 66.27 (3) | O1—C2A—C1A | 112.6 (7) |
| O1vi—Na1—N1 | 66.27 (3) | O1—C2A—H2C | 109.1 |
| O1vii—Na1—N1 | 113.73 (3) | C1A—C2A—H2C | 109.1 |
| O1viii—Na1—N1 | 66.27 (3) | O1—C2A—H2D | 109.1 |
| O1ix—Na1—N1 | 113.73 (3) | C1A—C2A—H2D | 109.1 |
| O1x—Na1—N1 | 113.73 (3) | H2C—C2A—H2D | 107.8 |
| O1—Na1—N1ix | 113.73 (3) | O1—C3—C3ix | 105.9 (4) |
| O1vi—Na1—N1ix | 113.73 (3) | O1—C3—H3A | 110.5 |
| O1vii—Na1—N1ix | 66.27 (3) | C3ix—C3—H3A | 110.5 |
| O1viii—Na1—N1ix | 113.73 (3) | O1—C3—H3B | 110.5 |
| O1ix—Na1—N1ix | 66.27 (3) | C3ix—C3—H3B | 110.5 |
| O1x—Na1—N1ix | 66.27 (3) | H3A—C3—H3B | 108.7 |
| N1—Na1—N1ix | 180.0 | O1—C3A—C3Aix | 106.5 (5) |
| C3A—O1—C2A | 135.9 (9) | O1—C3A—H3C | 110.4 |
| C2—O1—C3 | 96.9 (4) | C3Aix—C3A—H3C | 110.4 |
| C3A—O1—Na1 | 112.0 (4) | O1—C3A—H3D | 110.4 |
| C2A—O1—Na1 | 111.3 (6) | C3Aix—C3A—H3D | 110.4 |
| C2—O1—Na1 | 119.3 (3) | H3C—C3A—H3D | 108.6 |
| O3i—Cl1—O2—O3iii | 120.000 (5) | O1x—Na1—O1—C3 | 126.9 (3) |
| O3ii—Cl1—O2—O3iii | −68.0 (5) | N1—Na1—O1—C3 | −115.1 (3) |
| O3—Cl1—O2—O3iii | 172.0 (5) | N1ix—Na1—O1—C3 | 64.9 (3) |
| O3iv—Cl1—O2—O3iii | 52.0 (5) | O1—Na1—N1—C1 | −23.0 (4) |
| O3v—Cl1—O2—O3iii | −120.000 (5) | O1vi—Na1—N1—C1 | 97.0 (4) |
| O3i—Cl1—O2—O3v | −120.000 (14) | O1vii—Na1—N1—C1 | 171.1 (3) |
| O3ii—Cl1—O2—O3v | 52.0 (5) | O1viii—Na1—N1—C1 | −143.0 (4) |
| O3—Cl1—O2—O3v | −68.0 (5) | O1ix—Na1—N1—C1 | −68.9 (3) |
| O3iii—Cl1—O2—O3v | 120.000 (13) | O1x—Na1—N1—C1 | 51.1 (3) |
| O3iv—Cl1—O2—O3v | 172.0 (5) | O1—Na1—N1—C1vi | −143.0 (3) |
| O3ii—Cl1—O2—O3i | 172.0 (5) | O1vi—Na1—N1—C1vi | −23.0 (3) |
| O3—Cl1—O2—O3i | 52.0 (5) | O1vii—Na1—N1—C1vi | 51.1 (3) |
| O3iii—Cl1—O2—O3i | −120.000 (3) | O1viii—Na1—N1—C1vi | 97.0 (3) |
| O3iv—Cl1—O2—O3i | −68.0 (5) | O1ix—Na1—N1—C1vi | 171.1 (3) |
| O3v—Cl1—O2—O3i | 120.000 (2) | O1x—Na1—N1—C1vi | −68.9 (3) |
| O2i—Cl1—O3—O3i | 125.0 (4) | O1—Na1—N1—C1viii | 97.0 (4) |
| O2—Cl1—O3—O3i | −55.0 (4) | O1vi—Na1—N1—C1viii | −143.0 (4) |
| O3ii—Cl1—O3—O3i | −175.6 (3) | O1vii—Na1—N1—C1viii | −68.9 (4) |
| O3iv—Cl1—O3—O3i | 65.5 (5) | O1viii—Na1—N1—C1viii | −23.0 (4) |
| O3v—Cl1—O3—O3i | −118.2 (4) | O1ix—Na1—N1—C1viii | 51.1 (4) |
| O2—Cl1—O3—O2i | 180.000 (4) | O1x—Na1—N1—C1viii | 171.1 (4) |
| O3i—Cl1—O3—O2i | −125.0 (4) | O1—Na1—N1—C1Avi | −107.5 (4) |
| O3ii—Cl1—O3—O2i | 59.45 (19) | O1vi—Na1—N1—C1Avi | 12.5 (4) |
| O3iv—Cl1—O3—O2i | −59.45 (19) | O1vii—Na1—N1—C1Avi | 86.6 (4) |
| O3v—Cl1—O3—O2i | 116.8 (3) | O1viii—Na1—N1—C1Avi | 132.5 (4) |
| O2i—Cl1—O3—O3v | −116.8 (3) | O1ix—Na1—N1—C1Avi | −153.4 (4) |
| O2—Cl1—O3—O3v | 63.2 (3) | O1x—Na1—N1—C1Avi | −33.4 (4) |
| O3i—Cl1—O3—O3v | 118.2 (4) | O1—Na1—N1—C1A | 12.5 (4) |
| O3ii—Cl1—O3—O3v | −57.3 (4) | O1vi—Na1—N1—C1A | 132.5 (4) |
| O3iv—Cl1—O3—O3v | −176.2 (2) | O1vii—Na1—N1—C1A | −153.4 (4) |
| O1vi—Na1—O1—C3A | 153.1 (4) | O1viii—Na1—N1—C1A | −107.5 (4) |
| O1vii—Na1—O1—C3A | −58.9 (4) | O1ix—Na1—N1—C1A | −33.4 (4) |
| O1viii—Na1—O1—C3A | −96.7 (4) | O1x—Na1—N1—C1A | 86.6 (4) |
| O1ix—Na1—O1—C3A | −18.3 (4) | O1—Na1—N1—C1Aviii | 132.5 (5) |
| O1x—Na1—O1—C3A | 90.1 (4) | O1vi—Na1—N1—C1Aviii | −107.5 (5) |
| N1—Na1—O1—C3A | −151.8 (4) | O1vii—Na1—N1—C1Aviii | −33.4 (4) |
| N1ix—Na1—O1—C3A | 28.2 (4) | O1viii—Na1—N1—C1Aviii | 12.5 (5) |
| O1vi—Na1—O1—C2A | −35.5 (7) | O1ix—Na1—N1—C1Aviii | 86.6 (5) |
| O1vii—Na1—O1—C2A | 112.5 (7) | O1x—Na1—N1—C1Aviii | −153.4 (5) |
| O1viii—Na1—O1—C2A | 74.8 (7) | C3—O1—C2—C1 | 149.0 (7) |
| O1ix—Na1—O1—C2A | 153.2 (7) | Na1—O1—C2—C1 | 28.7 (9) |
| O1x—Na1—O1—C2A | −98.4 (7) | C3A—O1—C2A—C1A | 115.5 (10) |
| N1—Na1—O1—C2A | 19.7 (7) | Na1—O1—C2A—C1A | −53.0 (13) |
| N1ix—Na1—O1—C2A | −160.3 (7) | C2—O1—C3—C3ix | −177.7 (7) |
| O1vi—Na1—O1—C2 | −58.0 (5) | Na1—O1—C3—C3ix | −52.1 (8) |
| O1vii—Na1—O1—C2 | 90.0 (5) | C2A—O1—C3A—C3Aix | −116.9 (11) |
| O1viii—Na1—O1—C2 | 52.3 (5) | Na1—O1—C3A—C3Aix | 51.6 (10) |
| O1ix—Na1—O1—C2 | 130.7 (5) | C1vi—N1—C1—C2 | 166.0 (5) |
| O1x—Na1—O1—C2 | −120.9 (5) | C1viii—N1—C1—C2 | −63.7 (9) |
| N1—Na1—O1—C2 | −2.8 (5) | Na1—N1—C1—C2 | 51.2 (6) |
| N1ix—Na1—O1—C2 | 177.2 (5) | C1Avi—N1—C1A—C2A | 79.9 (10) |
| O1vi—Na1—O1—C3 | −170.2 (3) | C1Aviii—N1—C1A—C2A | −163.5 (7) |
| O1vii—Na1—O1—C3 | −22.2 (3) | Na1—N1—C1A—C2A | −41.8 (8) |
| O1viii—Na1—O1—C3 | −59.9 (3) | N1—C1—C2—O1 | −55.6 (9) |
| O1ix—Na1—O1—C3 | 18.5 (3) | N1—C1A—C2A—O1 | 65.1 (14) |
Symmetry codes: (i) y, x, −z+2; (ii) −y+2, x−y+1, z; (iii) x−y+1, −y+2, −z+2; (iv) −x+y+1, −x+2, z; (v) −x+2, −x+y+1, −z+2; (vi) −x+y+1, −x+1, z; (vii) −x+4/3, −x+y+2/3, −z+5/3; (viii) −y+1, x−y, z; (ix) y+1/3, x−1/3, −z+5/3; (x) x−y+1/3, −y+2/3, −z+5/3.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: HK2757).
References
- Allen, F. H. (2002). Acta Cryst. B58, 380–388. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Belaj, F., Trnoska, A. & Nachbaur, E. (1997). Z. Kristallogr.212, 355–361.
- Brandenburg, K. (1999). DIAMOND Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Bruker (2007). SADABS, SAINT and SMART Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruno, I. J., Cole, J. C., Kessler, M., Luo, J., Motherwell, W. D. S., Purkis, L. H., Smith, B. R., Taylor, R., Cooper, R. I., Harris, S. E. & Orpen, A. G. (2004). J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci.44, 2133–2144. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Dolomanov, O. V., Bourhis, L. J., Gildea, R. J., Howard, J. A. K. & Puschmann, H. (2009). J. Appl. Cryst.42, 339–341.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Guzei, I. A. (2007). modiCIFer University of Wisconsin–Madison, USA.
- Hamacher, K., Coenen, H. H. & Stocklin, G. (1986). J. Nucl. Med.27, 235–238. [PubMed]
- Izatt, R. M., Bradshaw, J. S., Nielsen, B. L., Lamb, J. D. & Christensen, J. J. (1985). Chem. Rev.85, 271–339.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Su, J. W. & Burnette, R. R. (2008). ChemPhysChem, 9, 1989–1996. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Tait, D., Haase, G. & Wiechen, A. (1997). J. Radioanal. Nucl. Chem.226, 225–228.
- Tehan, F. J., Barnett, B. L. & Dye, J. L. (1974). J. Am. Chem. Soc.96, 7203–7208.
- Trend, J. E., Kipke, C. A., Rossmann, M., Yafuso, M. & Patil, S. L. (1993). US Patent No. 5 474 743.
- Varga, L. P., Sztanyik, L. B., Ronai, E., Bodo, K., Brucher, E., Gyori, B., Emri, J. & Kovacs, Z. (1994). Int. J. Radiat. Biol.66, 399–405. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Westrip, S. P. (2009). publCIF. In preparation.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809039683/hk2757sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809039683/hk2757Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



