Abstract
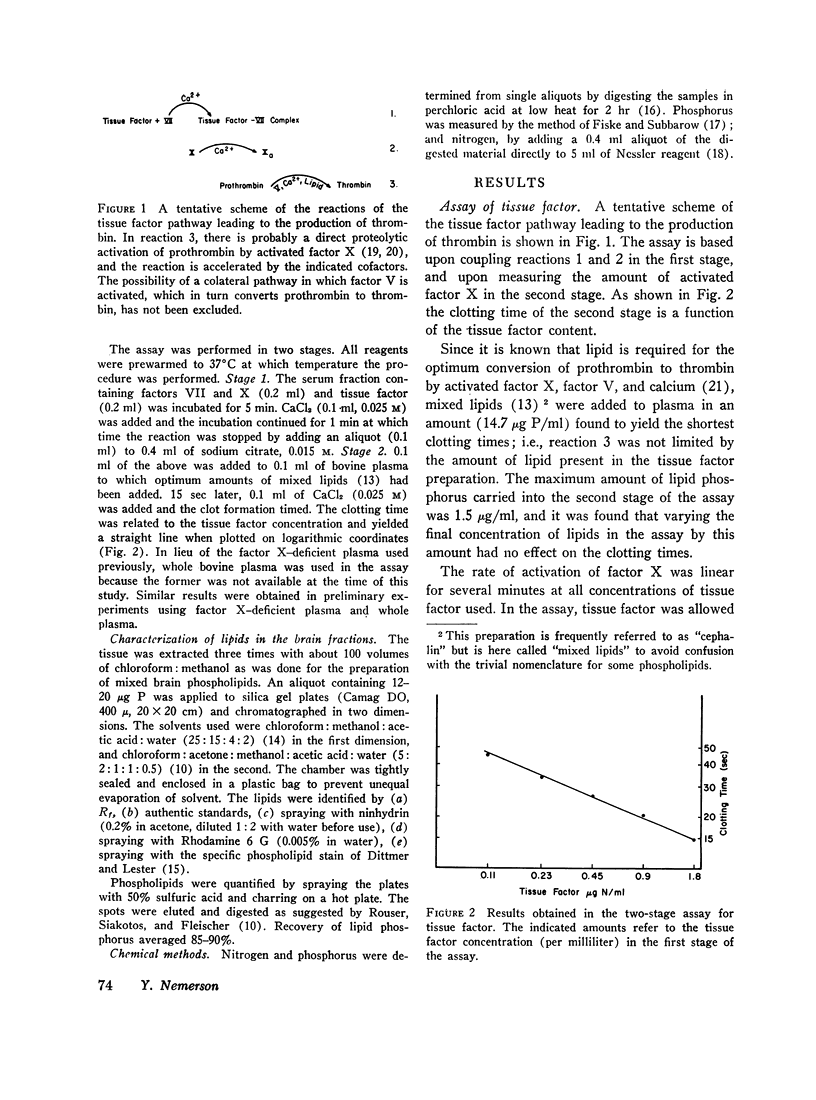
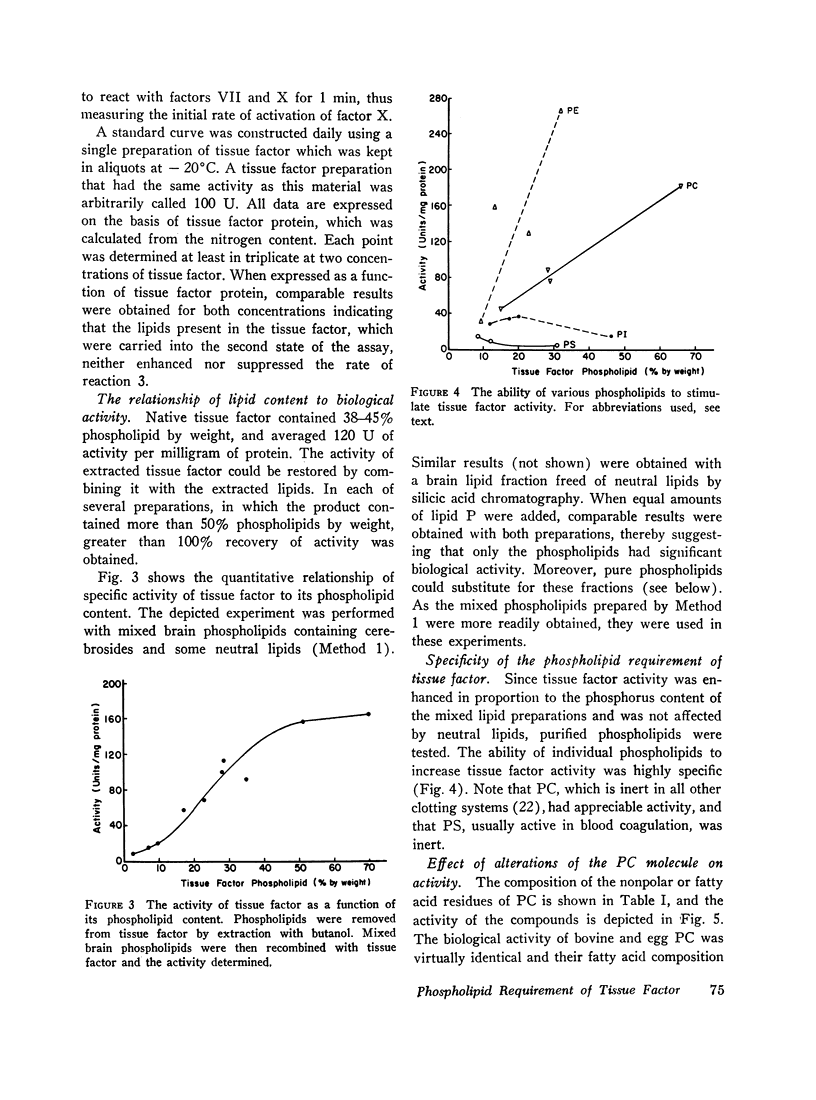
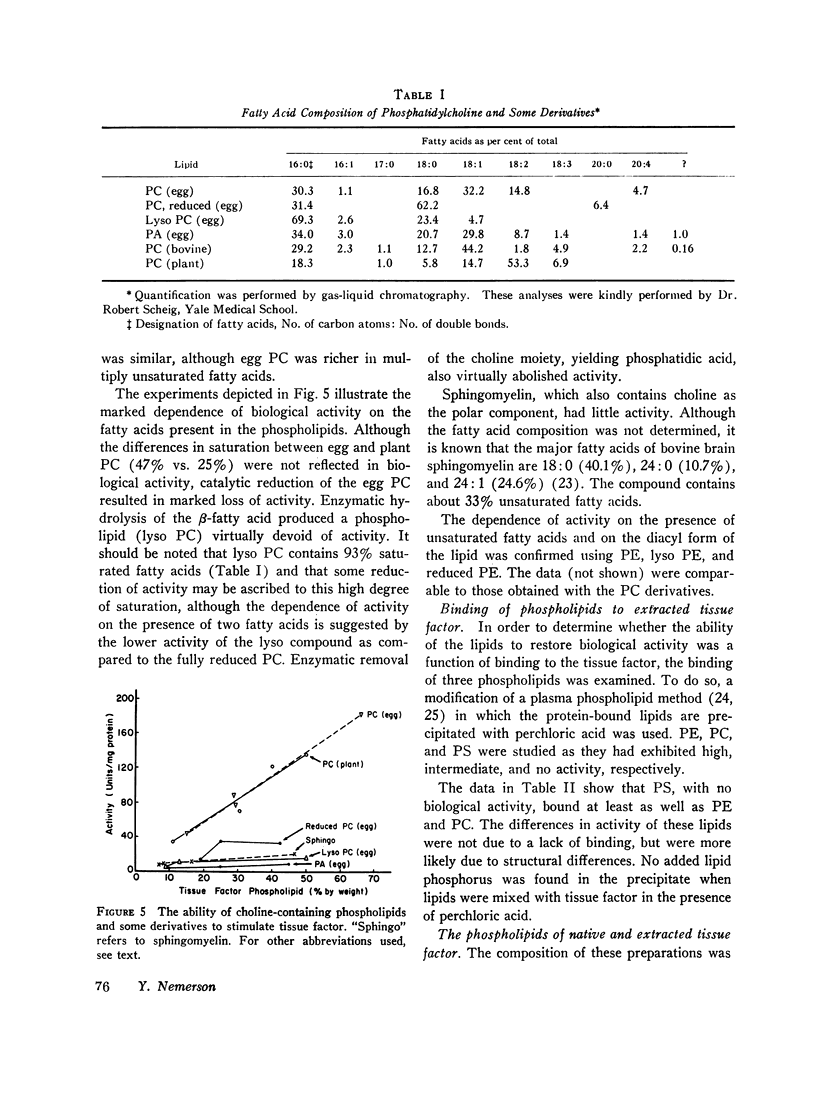
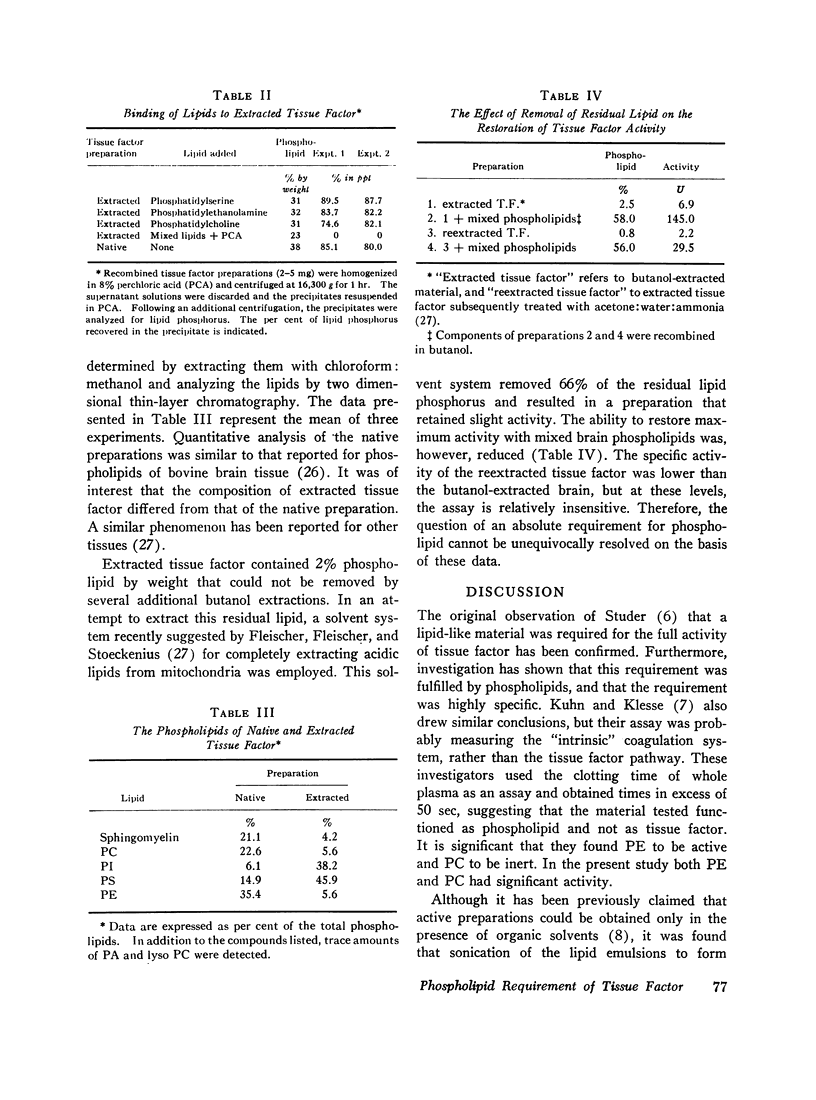
Using a coagulation assay specific for tissue factor, we found that removal of 95% of the tissue factor-phospholipid resulted in a loss of 98% of its biological activity. The activity could be restored, with yields in excess of 100% by combining the extracted tissue factor with either mixed brain phospholipids or highly purified phospholipids. Phosphatidylethanolamine was the most active, followed by phosphatidylcholine. Phosphatidylserine, phosphatidylinositol, and sphingomyelin had little or no activity. In addition, a requirement for unsaturation and the presence of two fatty acids was demonstrated. The activity of phosphatidylcholine was also dependent on the presence of the base. Furthermore, it was shown that activity was not a function of binding of phospholipids to tissue factor, as both active and inactive lipids were equally bound.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABRAMSON M. B., KATZMAN R., WILSON C. E., GREGOR H. P. IONIC PROPERTIES OF AQUEOUS DISPERSIONS OF PHOSPHATIDIC ACID. J Biol Chem. 1964 Dec;239:4066–4072. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aronson D. L., Ménaché D. Chromatographic analysis of the activation of human prothrombin with human thrombokinase. Biochemistry. 1966 Aug;5(8):2635–2640. doi: 10.1021/bi00872a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BANGHAM A. D., DAWSON R. M. The relation between the activity of a lecithinase and the electrophoretic charge of the substrate. Biochem J. 1959 Jul;72:486–492. doi: 10.1042/bj0720486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BELL W. N., ALTON H. G. A brain extract as a substitute for platelet suspensions in the thromboplastin generation test. Nature. 1954 Nov 6;174(4436):880–881. doi: 10.1038/174880a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHUNG A. E., LAW J. H. CYCLOPROPANE FATTY ACID SYNTHETASE: PARTIAL PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES. Biochemistry. 1964 Jul;3:967–974. doi: 10.1021/bi00895a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEUTSCH E., IRSIGLER K., LOMOSCHITZ H. STUDIEN UEBER GEWEBETHROMBOPLASTIN. 1. REINIGUNG, CHEMISCHE CHARAKTERISIERUNG UND TRENNUNG IN EINEN EISWISS-UND LIPOIDANTEIL. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1964 Oct 15;12:12–34. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DITTMER J. C., LESTER R. L. A SIMPLE, SPECIFIC SPRAY FOR THE DETECTION OF PHOSPHOLIPIDS ON THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAMS. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jan;5:126–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLEISCHER S., BRIERLEY G., KLOUWEN H., SLAUTTERBACK D. B. Studies of the electron transfer system. 47. The role of phospholipids in electron transfer. J Biol Chem. 1962 Oct;237:3264–3272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleischer S., Fleischer B., Stoeckenius W. Fine structure of lipid-depleted mitochondria. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jan;32(1):193–208. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.1.193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobin F., Esnouf M. P. Studies on the formation of the prothrombin-converting complex. Biochem J. 1967 Mar;102(3):666–674. doi: 10.1042/bj1020666. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS M. L., WARE A. G. A simple procedure for separation of prothrombin and accelerator globulin from citrated human plasma. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Dec;84(3):636–640. doi: 10.3181/00379727-84-20737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILSTONE J. H. Fractionation of plasma globulin for prothrombin, thrombokinase, and accessory thromboplastin. J Gen Physiol. 1951 Sep;35(1):67–87. doi: 10.1085/jgp.35.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILSTONE J. H. THROMBOKINASE AS PRIME ACTIVATOR OF PROTHROMBIN: HISTORICAL PERSPECTIVES AND PRESENT STATUS. Fed Proc. 1964 Jul-Aug;23:742–748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A. J. The role of lipids in blood coagulation. Adv Lipid Res. 1966;4:1–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus A. J., Zucker-Franklin D., Safier L. B., Ullman H. L. Studies on human platelet granules and membranes. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jan;45(1):14–28. doi: 10.1172/JCI105318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEMERSON Y., SPAET T. H. THE ACTIVATION OF FACTOR X BY EXTRACTS OF RABBIT BRAIN. Blood. 1964 May;23:657–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemerson Y. The reaction between bovine brain tissue factor and factors VII and X. Biochemistry. 1966 Feb;5(2):601–608. doi: 10.1021/bi00866a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J. S., Fillerup D. L., Mead J. F. Quantification and fatty acid and fatty aldehyde composition of ethanolamine, choline, and serine glycerophosphatides in human cerebral grey and white matter. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jul;5(3):329–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J. S., Rouser G. The fatty acid composition of brain sphingolipids: sphingomyelin, ceramide, cerebroside, and cerebroside sulfate. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jul;5(3):339–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAPPORT M. M. Activation of phospholipid thromboplastin by lecithin. Nature. 1956 Sep 15;178(4533):591–592. doi: 10.1038/178591b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothfield L., Pearlman M. The role of cell envelope phospholipid in the enzymatic synthesis of bacterial lipopolysaccharide. Structural requirements of the phospholipid molecule. J Biol Chem. 1966 Mar 25;241(6):1386–1392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouser G., Siakotos A. N., Fleischer S. Quantitative analysis of phospholipids by thin-layer chromatography and phosphorus analysis of spots. Lipids. 1966 Jan;1(1):85–86. doi: 10.1007/BF02668129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skipski V. P., Peterson R. F., Barclay M. Quantitative analysis of phospholipids by thin-layer chromatography. Biochem J. 1964 Feb;90(2):374–378. doi: 10.1042/bj0900374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams W. J., Norris D. G. Purification of a bovine plasma protein (factor VII) which is required for the activity of lung microsomes in blood coagulation. J Biol Chem. 1966 Apr 25;241(8):1847–1856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZILVERSMIT D. B., DAVIS A. K. Microdetermination of plasma phospholipids by trichloroacetic acid precipitation. J Lab Clin Med. 1950 Jan;35(1):155–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ZILVERSMIT R. D., MARCUS A. J., ULLMAN H. L. Plasmalogen in human blood platelets. J Biol Chem. 1961 Jan;236:47–49. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



