Abstract
The function of the proximal and distal tubule was studied in the rhesus monkey during antidiuresis and during the diuresis after furosemide administration (during which extracellular fluid volume was maintained).
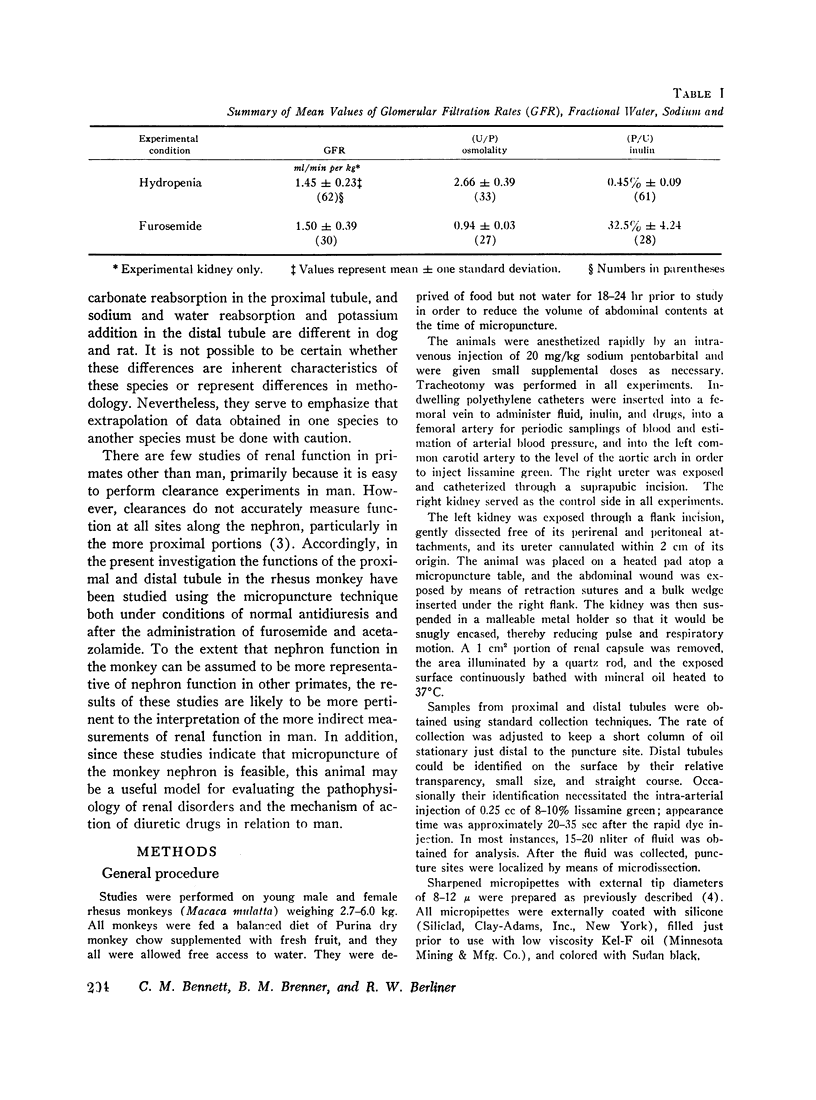
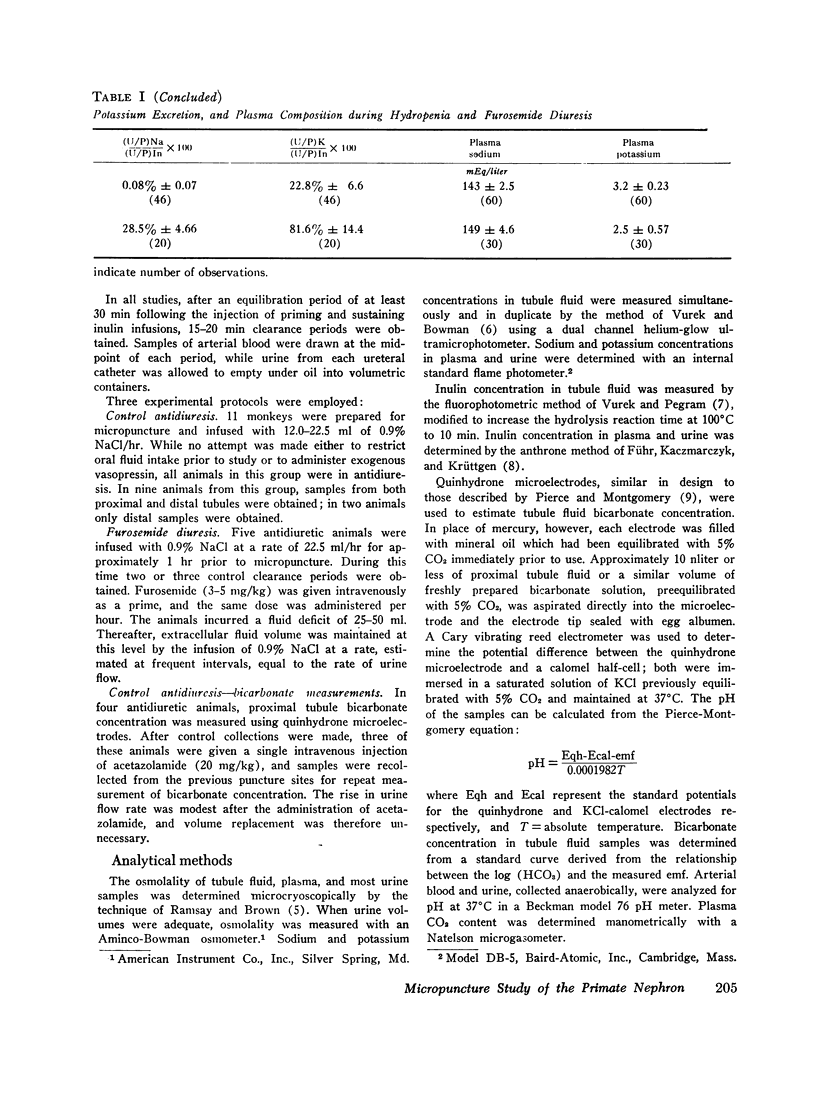
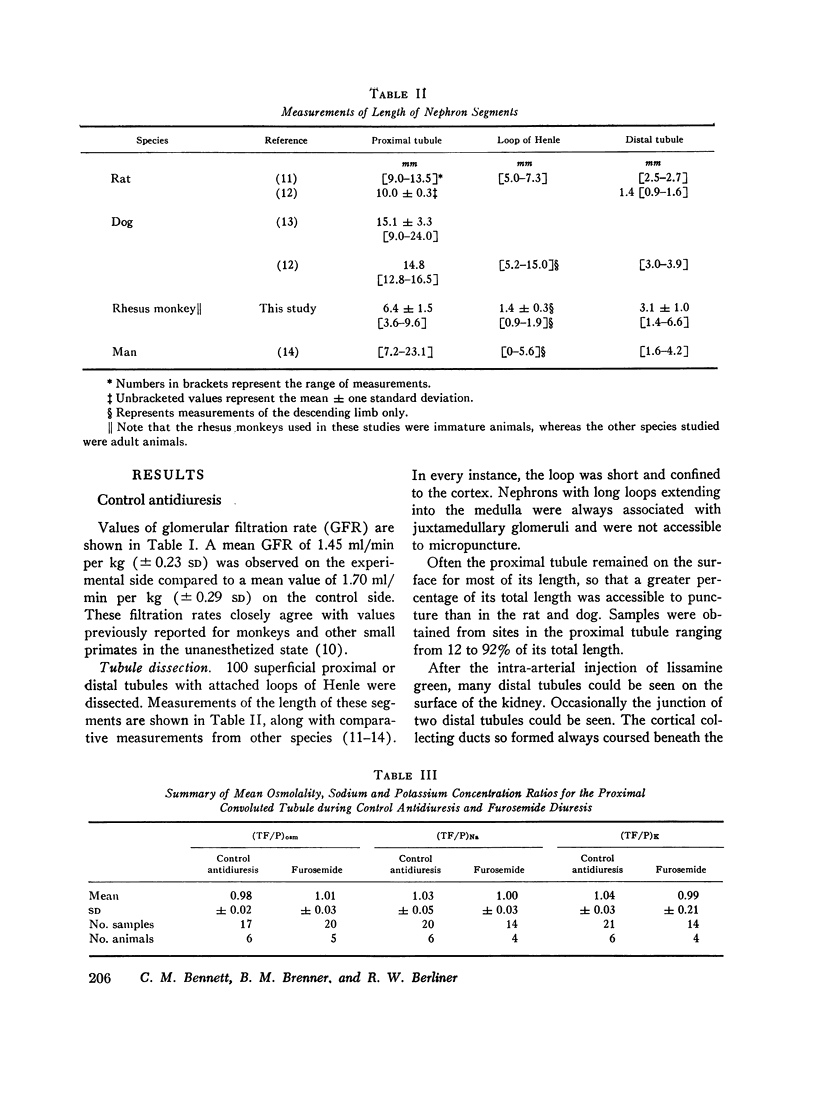
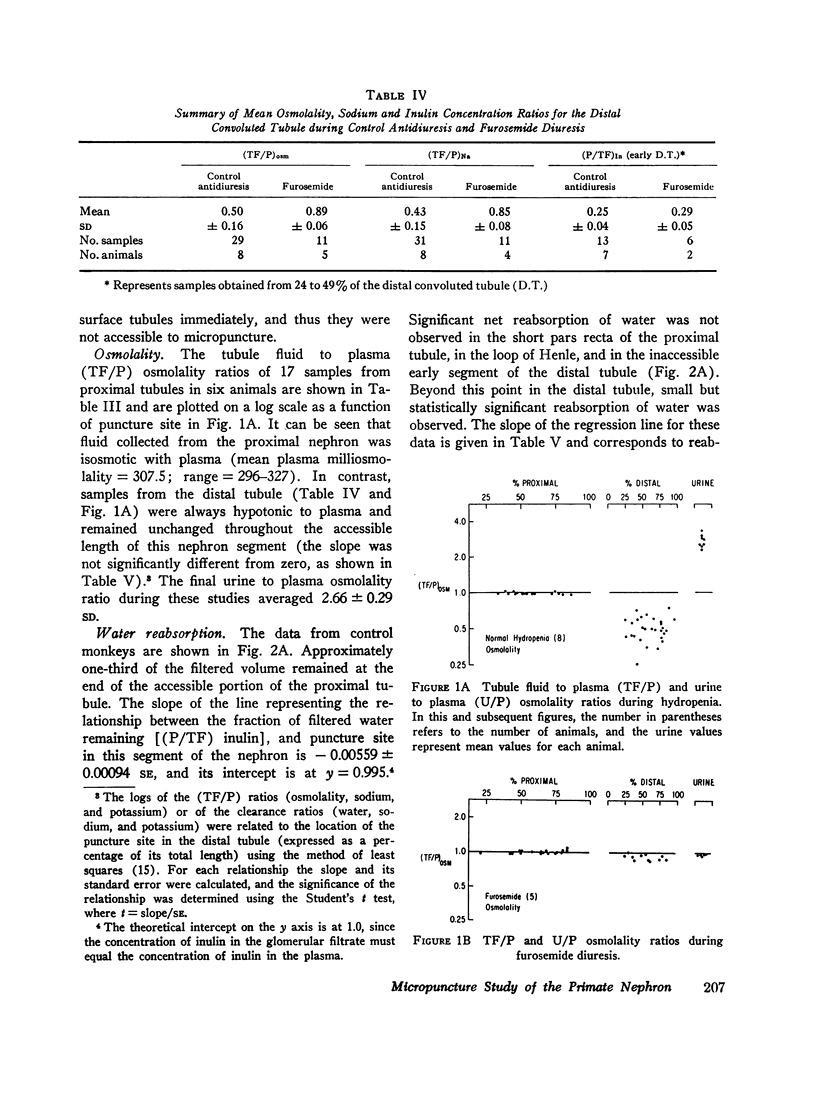
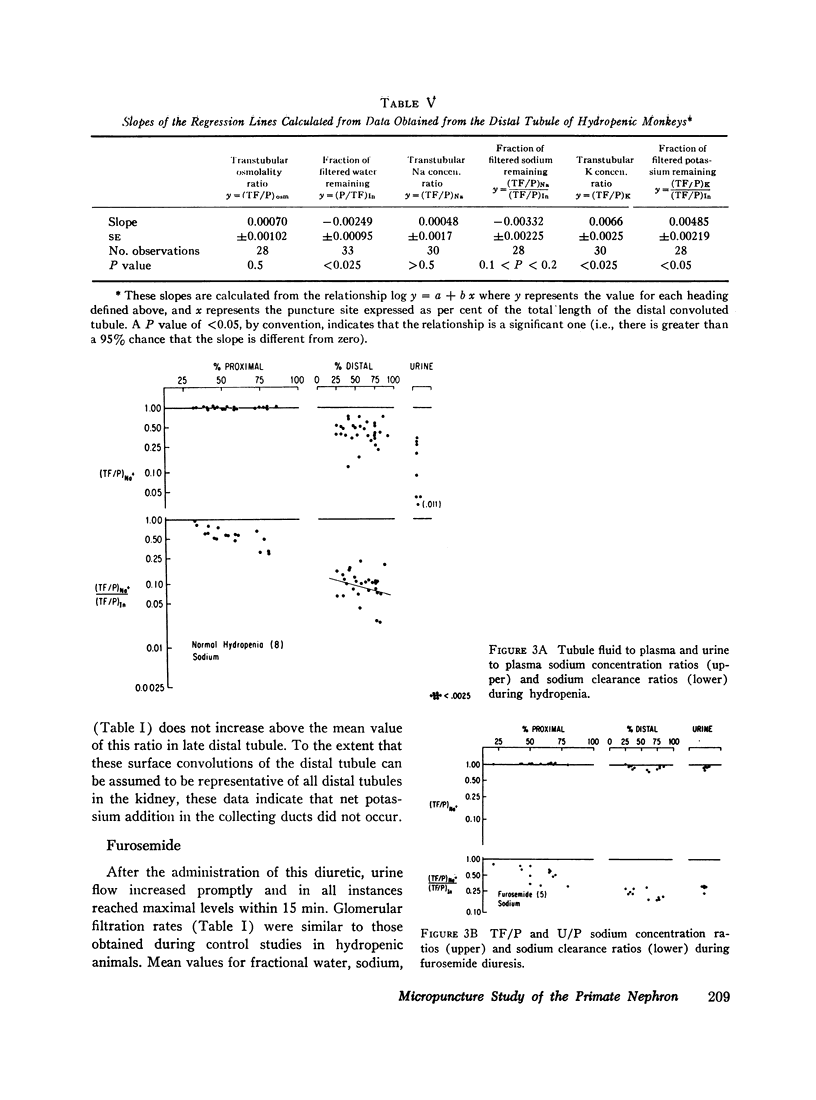
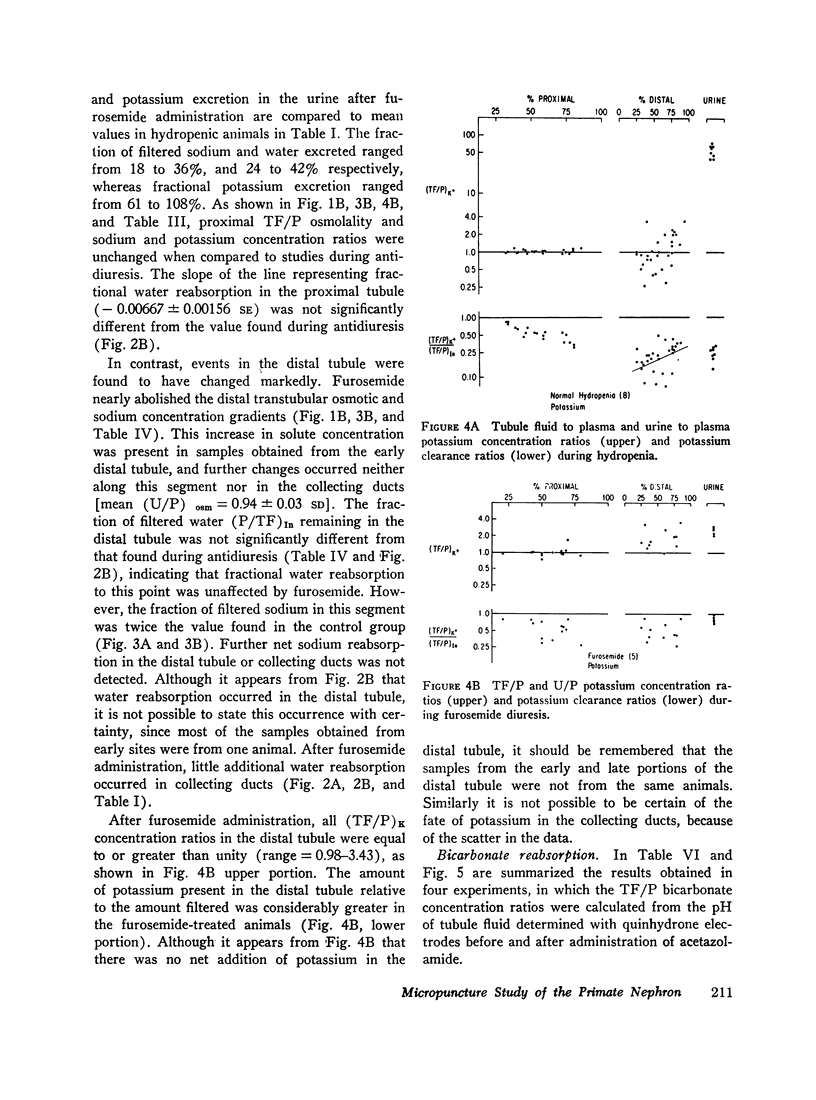
In the proximal tubule, fluid to plasma ratios for sodium, potassium, and osmolality approximated unity. During antidiuresis, about 30% of the filtered water remained at the end of the accessible portion of this segment (92% of length). Fluid was hypotonic to plasma throughout the distal tubule. 25% of the filtered water was present in the early distal tubule. Small but significant water reabsorption (about 8% of filtered) occurred in remainder of this segment. Tubule fluid to plasma potassium concentration ratios tended to increase along the distal tubule, and the amount of potassium, relative to the amount filtered, increased from 13% in the early portion of this segment to 26% in the late portion.
After furosemide was administered animals excreted about one-third of the filtered sodium and water. Despite this diuresis, electrolyte and water reabsorption along the proximal tubule did not differ from values obtained in control animals. Osmolality and sodium concentration of fluid from the distal tubule approached those of plasma. 22% of the filtered sodium (twice the control values) reached the distal tubule, whereas the fraction of filtered water remaining was only slightly increased. These findings indicate that, after the administration of this drug, inhibition of sodium reabsorption occurred in the water-impermeable segment of the nephron, rather than in the proximal tubule. After furosemide administration, all tubule fluid to plasma potassium concentration ratios in the distal tubule were equal to or greater than one, suggesting inhibition of active potassium reabsorption at or prior to this site.
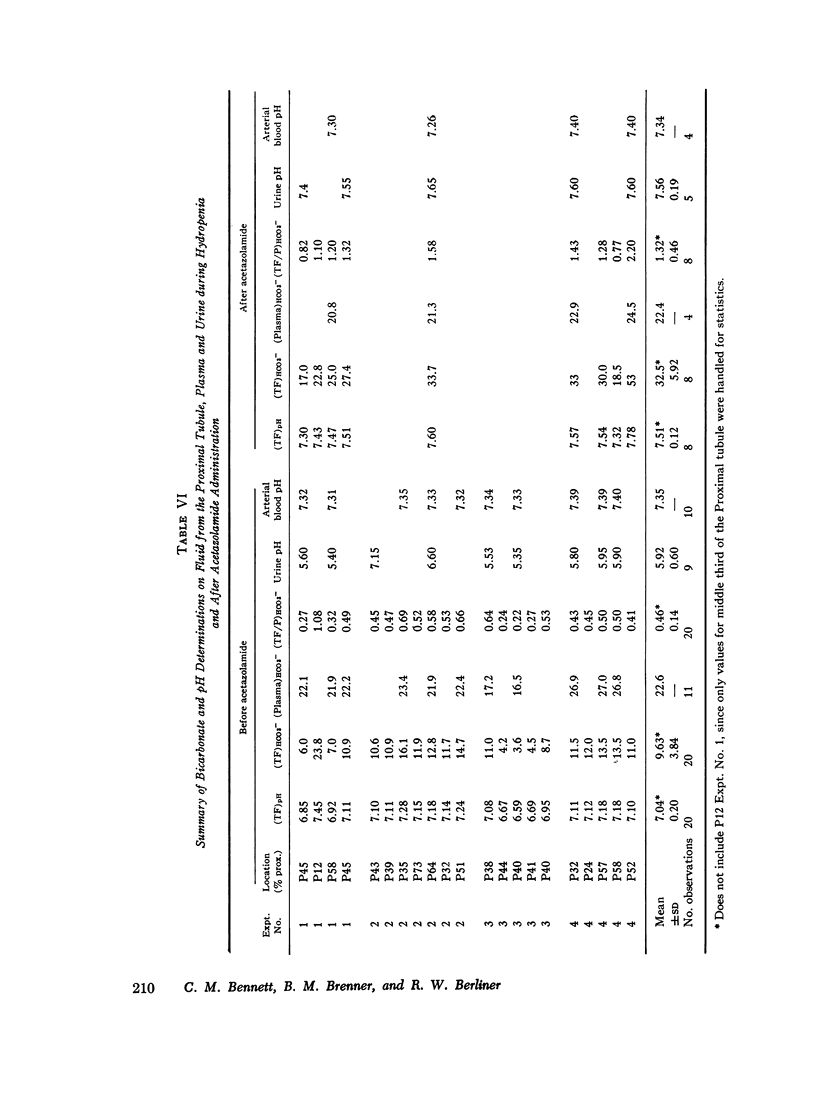
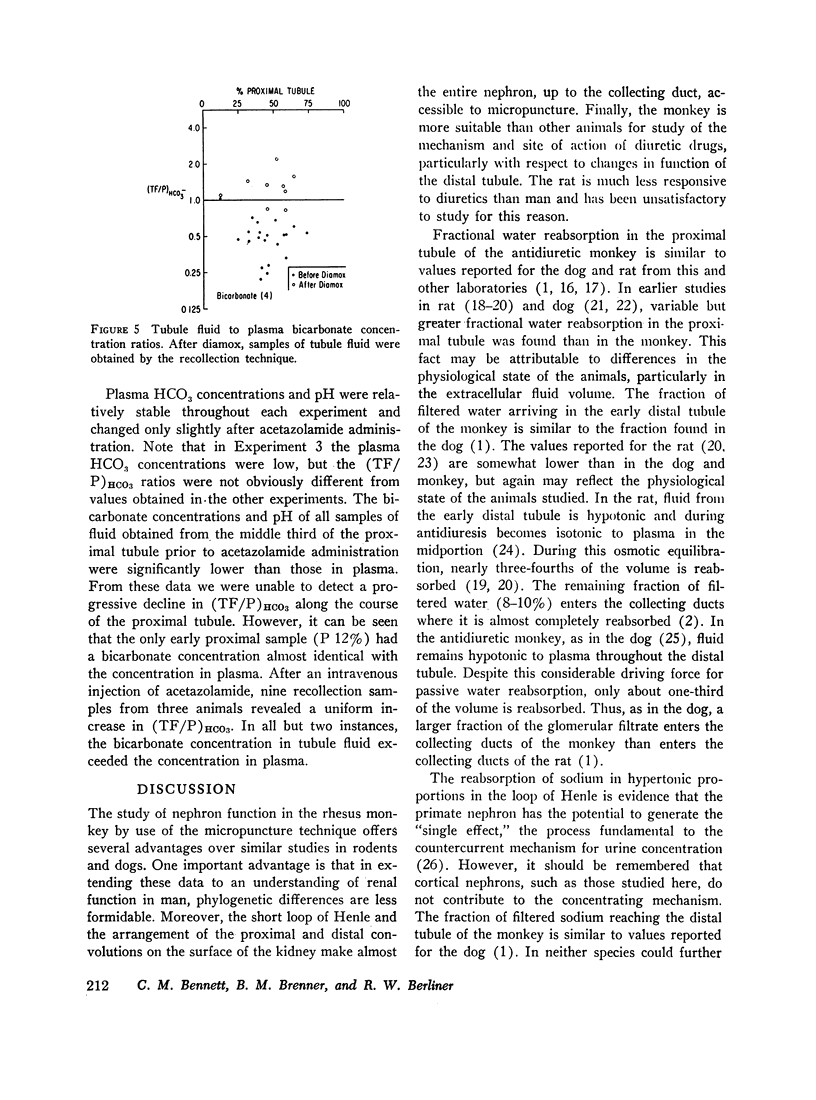
Fluid to plasma bicarbonate concentration ratios from the midportion of the proximal tubule were consistently less than one in normal monkeys. After acetazolamide was administered, the bicarbonate concentration of samples of tubule fluid recollected from these same sites was the same as, or higher than in plasma. This fact demonstrates the inhibition of bicarbonate reabsorption in this portion of the tubule.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLOOMER H. A., RECTOR F. C., Jr, SELDIN D. W. The mechanism of potassium reabsorption in the proximal tubule of the rat. J Clin Invest. 1963 Feb;42:277–285. doi: 10.1172/JCI104714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett C. M., Clapp J. R., Berliner R. W. Micropuncture study of the proximal and distal tubule in the dog. Am J Physiol. 1967 Nov;213(5):1254–1262. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.213.5.1254. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAPP J. R., WATSON J. F., BERLINER R. W. OSMOLALITY, BICARBONATE CONCENTRATION, AND WATER REABSORPTION IN PROXIMAL TUBULE OF THE DOG NEPHRON. Am J Physiol. 1963 Aug;205:273–280. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1963.205.2.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapp J. R., Robinson R. R. Osmolality of distal tubular fluid in the dog. J Clin Invest. 1966 Dec;45(12):1847–1853. doi: 10.1172/JCI105488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortney M. A., Mylle M., Lassiter W. E., Gottschalk C. W. Renal tubular transport of water, solute, and PAH in rats loaded with isotonic saline. Am J Physiol. 1965 Dec;209(6):1199–1205. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.6.1199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEETJEN P. MIKROPUNKTIONSUNTERSUCHUNGEN ZUR WIRKUNG VON FUROSEMID. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1965 Jun 2;284:184–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dirks J. H., Cirksena W. J., Berliner R. W. Micropuncture study of the effect of various diuretics on sodium reabsorption by the proximal tubules of the dog. J Clin Invest. 1966 Dec;45(12):1875–1885. doi: 10.1172/JCI105492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frömter E., Hegel U. Transtubuläre Potentialdifferenzen an proximalen und distalen Tubuli der Rattenniere. Pflugers Arch Gesamte Physiol Menschen Tiere. 1966;291(1):107–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIEBISCH G., KLOSE R. M., WINDHAGER E. E. MICROPUNCTURE STUDY OF HYPERTONIC SODIUM CHLORIDE LOADING IN THE RAT. Am J Physiol. 1964 Apr;206:687–693. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.206.4.687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLABMAN S., AYNEDJIAN H. S., BANK N. MICROPUNCTURE STUDY OF THE EFFECT OF ACUTE REDUCTIONS IN GLOMERULAR FILTRATION RATE ON SODIUM AND WATER REABSORPTION BY THE PROXIMAL TUBULES OF THE RAT. J Clin Invest. 1965 Aug;44:1410–1416. doi: 10.1172/JCI105246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTSCHALK C. W., MYLLE M. Micropuncture study of the mammalian urinary concentrating mechanism: evidence for the countercurrent hypothesis. Am J Physiol. 1959 Apr;196(4):927–936. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.196.4.927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOTTSCHALK C. W. OSMOTIC CONCENTRATION AND DILUTION OF THE URINE. Am J Med. 1964 May;36:670–685. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(64)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASSITER W. E., GOTTSCHALK C. W., MYLLE M. Micropuncture study of net transtubular movement of water and urea in nondiuretic mammalian kidney. Am J Physiol. 1961 Jun;200:1139–1147. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.6.1139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALNIC G., KLOSE R. M., GIEBISCH G. MICROPUNCTURE STUDY OF RENAL POTASSIUM EXCRETION IN THE RAT. Am J Physiol. 1964 Apr;206:674–686. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.206.4.674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malnic G., Klose R. M., Giebisch G. Microperfusion study of distal tubular potassium and sodium transfer in rat kidney. Am J Physiol. 1966 Sep;211(3):548–559. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.3.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malnic G., Klose R. M., Giebisch G. Micropuncture study of distal tubular potassium and sodium transport in rat nephron. Am J Physiol. 1966 Sep;211(3):529–547. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.3.529. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orloff J. Pitfalls in the use of stop-flow for the localization of diuretic action, with special reference to Na reabsorption. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Nov 22;139(2):344–355. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb41208.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pai H. C. Dissection of Nephrons from the Human Kidney. J Anat. 1935 Apr;69(Pt 3):344–349. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RECTOR F. C., Jr, BLOOMER H. A., SELDIN D. W. EFFECT OF POTASSIUM DEFICIENCY ON THE REABSORPTION OF BICARBONATE IN THE PROXIMAL TUBULE OF THE RAT KIDNEY. J Clin Invest. 1964 Oct;43:1976–1982. doi: 10.1172/JCI105071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RECTOR F. C., Jr, BLOOMER H. A., SELDIN D. W. PROXIMAL TUBUAL REABSORPTION OF POTASSIUM DURING MANNITOL DIURESIS IN RATS. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Jan;63:100–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RECTOR F. C., Jr, CARTER N. W., SELDIN D. W. THE MECHANISM OF BICARBONATE REABSORPTION IN THE PROXIMAL AND DISTAL TUBULES OF THE KIDNEY. J Clin Invest. 1965 Feb;44:278–290. doi: 10.1172/JCI105142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rector F. C., Jr, Sellman J. C., Martinez-Maldonado M., Seldin D. W. The mechanism of suppression of proximal tubular reabsorption by saline infusions. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jan;46(1):47–56. doi: 10.1172/JCI105510. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUKI W., RECTOR F. C., Jr, SELDIN D. W. THE SITE OF ACTION OF FUROSEMIDE AND OTHER SULFONAMIDE DIURETICS IN THE DOG. J Clin Invest. 1965 Sep;44:1458–1469. doi: 10.1172/JCI105252. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vurek G. G., Bennett C. M., Jamison R. L., Troy J. L. An air-driven micropipette sharpener. J Appl Physiol. 1967 Jan;22(1):191–192. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1967.22.1.191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vurek G. G., Bowman R. L. Helium-Glow Photometer for Picomole Analysis of Alkali Metals. Science. 1965 Jul 23;149(3682):448–450. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3682.448. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON J. F., CLAPP J. R., BERLINER R. W. MICROPUNCTURE STUDY OF POTASSIUM CONCENTRATION IN PROXIMAL TUBULE OF DOG, RAT, AND NECTURUS. J Clin Invest. 1964 Apr;43:595–605. doi: 10.1172/JCI104944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. F. Effect of saline loading on sodium reabsorption in the dog proximal tubule. Am J Physiol. 1966 Apr;210(4):781–785. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.4.781. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. F. Potassium reabsorption in the proximal tubule of the dog nephron. J Clin Invest. 1966 Aug;45(8):1341–1348. doi: 10.1172/JCI105441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


