Abstract
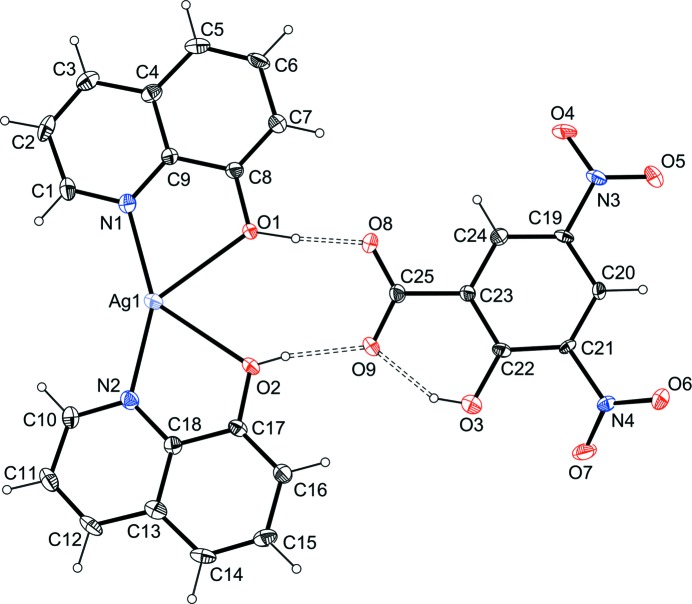
The title compound, [Ag(C9H7NO)2](C7H3N2O7), was prepared from 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS), quinolin-8-ol and AgNO3. The AgI atom is coordinated by two N atoms and two O atoms from two quinolin-8-ols in a roughly planar [maximum deviation = 0.223 (2) Å] environment. The two quinolin-8-ol ligands are bent slightly with respect to each other, making a dihedral angle of 9.55 (9)°. The DNS anion interacts with the silver complex through O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds
Related literature
For related structures, see: Smith & Thomasson (1999 ▶); Smith et al. (2001 ▶); Wu et al. (2006 ▶).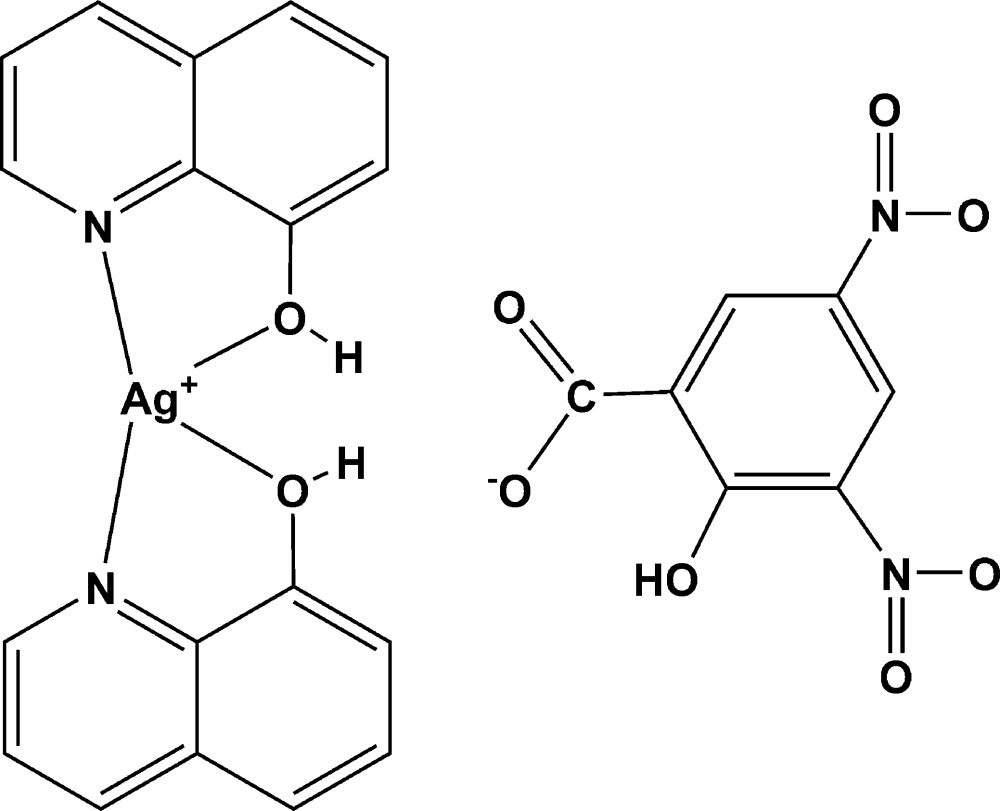
Experimental
Crystal data
[Ag(C9H7NO)2](C7H3N2O7)
M r = 625.30
Monoclinic,
a = 9.0154 (18) Å
b = 7.6122 (15) Å
c = 17.138 (3) Å
β = 104.38 (3)°
V = 1139.3 (4) Å3
Z = 2
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.95 mm−1
T = 293 K
0.20 × 0.15 × 0.11 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer
Absorption correction: none
10841 measured reflections
4602 independent reflections
4356 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.022
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.024
wR(F 2) = 0.057
S = 1.09
4602 reflections
353 parameters
1 restraint
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.70 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.30 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 1770 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: 0.006 (18)
Data collection: SMART (Bruker, 1997 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 1997 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: ORTEPIII (Burnett & Johnson, 1996 ▶) and ORTEP-3 for Windows (Farrugia, 1997 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXL97.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809045905/dn2508sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809045905/dn2508Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O1—H1AA⋯O8 | 1.00 | 1.60 | 2.602 (3) | 175 |
| O2—H2AA⋯O9 | 0.77 | 1.88 | 2.636 (3) | 168 |
| O3—H3B⋯O9 | 0.82 | 1.74 | 2.483 (3) | 150 |
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Quinolin-8-ol [quinolin-8-ol (oxine)] is well known as a particularly versatile ligand for use in metal complex chemistry (G. Smith, et al.,2001). It is also known that most of AgI in biological systems is not in the form of free AgI ions, but is coordinated by the abundance of biological ligands (Wu, et al.,2006). As part of our search for new biologically active compounds the title compound has been synthesized and we report its crystal structure here.
Scheme I
The AgI atom is coordinated by two N atoms and two O atoms from two quinolin-8-ols in a roughly planar environment with the largest deviation from the mean plane of the non H atoms being 0.223 (2)Å at C14 (Fig. 1). However, the two quinolin-8-ols are slightly bent with respect to each other making a dihedral angle of 9.55 (9)°. In the DNS anion, the NO2 and CO2 groups are twisted with respect to the phenyl ring making dihedral angles of of 29.5 (1)° for C21, N4, O6, O7, 10.7 (2)° for C19, N3, O4, 05 and 10.0 (2)° for C23, C25, O8, O9. All of the bond lengths and bond angles are in normal ranges (Smith, et al.,1999; Smith, et al.,2001; Wu, et al., 2006).
There are O—H···O hydrogen-bond interactions between two quinolin-8-ol and DNS which stabilize the crystal structure (Table 1, Fig. 1).
Experimental
The title compound(I) was prepared by the process as following: A mixture of 3,5-Dinitrosalicylic acid (0.01 mol), salt of quinolin-8-ol and sulfuric acid (0.02 mol) was stirred in distilled water (30 ml) for 3 h to obtain yellow deposit. A mixture of the deposit and AgNO3(0.01 mol) was stirred in ethanol (20 ml) at 353 K for 5 h, then afford the title compound (yield 83%). Single crystals suitable for X-ray measurements were obtailed by recrystallization from ethanol at room temperature.
Refinement
H atoms were included in calculated positions, with C—H distances constrained to 0.93Å (aromatic CH) and O—H distances constrained to 0.86Å and with Uiso=1.2–1.5Ueq.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The molecular structure of the title compound with the atom-labeling scheme. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 30% probability level. H atoms are represented as small spheres of arbitrary radii. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed lines.
Crystal data
| [Ag(C9H7NO)2](C7H3N2O7) | F(000) = 628 |
| Mr = 625.30 | Dx = 1.823 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2yb | Cell parameters from 4356 reflections |
| a = 9.0154 (18) Å | θ = 3.6–27.6° |
| b = 7.6122 (15) Å | µ = 0.95 mm−1 |
| c = 17.138 (3) Å | T = 293 K |
| β = 104.38 (3)° | Block, yellow |
| V = 1139.3 (4) Å3 | 0.20 × 0.15 × 0.11 mm |
| Z = 2 |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART CCD area-detector diffractometer | 4356 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | Rint = 0.022 |
| graphite | θmax = 27.6°, θmin = 3.6° |
| φ and ω scans | h = −11→11 |
| 10841 measured reflections | k = −9→8 |
| 4602 independent reflections | l = −22→22 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.024 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| wR(F2) = 0.057 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.028P)2 + 0.3633P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| S = 1.09 | (Δ/σ)max < 0.001 |
| 4602 reflections | Δρmax = 0.70 e Å−3 |
| 353 parameters | Δρmin = −0.30 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 1770 Friedel pairs |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Flack parameter: 0.006 (18) |
Special details
| Geometry. All esds (except the esd in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell esds are taken into account individually in the estimation of esds in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between esds in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell esds is used for estimating esds involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Ag1 | 0.062198 (19) | 0.74284 (3) | 0.668865 (11) | 0.01870 (6) | |
| O1 | −0.0991 (2) | 0.4624 (3) | 0.64039 (12) | 0.0199 (4) | |
| H1AA | −0.0950 | 0.3450 | 0.6670 | 0.030* | |
| O2 | 0.1744 (2) | 0.5065 (3) | 0.77201 (12) | 0.0217 (4) | |
| H2AA | 0.1409 | 0.4170 | 0.7790 | 0.033* | |
| N1 | −0.1155 (2) | 0.7669 (4) | 0.55612 (13) | 0.0174 (5) | |
| N2 | 0.2684 (3) | 0.8371 (3) | 0.75436 (14) | 0.0163 (5) | |
| C1 | −0.1281 (3) | 0.9178 (4) | 0.51463 (19) | 0.0223 (6) | |
| H1A | −0.0613 | 1.0090 | 0.5354 | 0.027* | |
| C2 | −0.2364 (4) | 0.9449 (4) | 0.44186 (18) | 0.0246 (6) | |
| H2A | −0.2410 | 1.0519 | 0.4152 | 0.030* | |
| C3 | −0.3353 (3) | 0.8132 (4) | 0.41024 (19) | 0.0211 (6) | |
| H3A | −0.4080 | 0.8297 | 0.3618 | 0.025* | |
| C4 | −0.3269 (3) | 0.6506 (4) | 0.45167 (18) | 0.0170 (6) | |
| C5 | −0.4267 (3) | 0.5080 (4) | 0.42261 (17) | 0.0209 (6) | |
| H5A | −0.5013 | 0.5186 | 0.3744 | 0.025* | |
| C6 | −0.4132 (3) | 0.3552 (4) | 0.46543 (18) | 0.0214 (6) | |
| H6A | −0.4774 | 0.2614 | 0.4454 | 0.026* | |
| C7 | −0.3036 (3) | 0.3371 (4) | 0.53957 (17) | 0.0187 (6) | |
| H7A | −0.2977 | 0.2327 | 0.5683 | 0.022* | |
| C8 | −0.2059 (3) | 0.4719 (4) | 0.56950 (16) | 0.0149 (5) | |
| C9 | −0.2140 (3) | 0.6332 (4) | 0.52566 (16) | 0.0141 (5) | |
| C10 | 0.3161 (3) | 0.9992 (4) | 0.74638 (17) | 0.0187 (6) | |
| H10A | 0.2572 | 1.0697 | 0.7061 | 0.022* | |
| C11 | 0.4512 (3) | 1.0703 (4) | 0.79573 (19) | 0.0222 (6) | |
| H11A | 0.4807 | 1.1847 | 0.7878 | 0.027* | |
| C12 | 0.5375 (3) | 0.9694 (4) | 0.85498 (18) | 0.0210 (6) | |
| H12A | 0.6277 | 1.0140 | 0.8878 | 0.025* | |
| C13 | 0.4907 (3) | 0.7962 (4) | 0.86706 (17) | 0.0172 (6) | |
| C14 | 0.5745 (3) | 0.6843 (4) | 0.92847 (17) | 0.0199 (6) | |
| H14A | 0.6655 | 0.7235 | 0.9626 | 0.024* | |
| C15 | 0.5225 (3) | 0.5197 (4) | 0.93780 (17) | 0.0206 (6) | |
| H15A | 0.5776 | 0.4479 | 0.9788 | 0.025* | |
| C16 | 0.3864 (3) | 0.4567 (4) | 0.88625 (17) | 0.0177 (6) | |
| H16A | 0.3520 | 0.3443 | 0.8937 | 0.021* | |
| C17 | 0.3044 (3) | 0.5596 (4) | 0.82523 (16) | 0.0144 (5) | |
| C18 | 0.3541 (2) | 0.7342 (6) | 0.81437 (14) | 0.0140 (4) | |
| O3 | 0.1402 (2) | −0.0140 (3) | 0.92529 (13) | 0.0260 (5) | |
| H3B | 0.1405 | 0.0793 | 0.9015 | 0.039* | |
| O4 | −0.4152 (2) | −0.3754 (3) | 0.69128 (14) | 0.0284 (5) | |
| O5 | −0.3271 (2) | −0.5962 (3) | 0.76855 (13) | 0.0273 (5) | |
| O6 | 0.1239 (2) | −0.5246 (3) | 0.98348 (12) | 0.0211 (4) | |
| O7 | 0.1678 (2) | −0.2656 (4) | 1.03550 (11) | 0.0289 (4) | |
| O8 | −0.0981 (2) | 0.1498 (3) | 0.70194 (12) | 0.0242 (5) | |
| O9 | 0.0667 (2) | 0.2136 (3) | 0.81890 (12) | 0.0198 (5) | |
| N3 | −0.3217 (2) | −0.4436 (3) | 0.74770 (14) | 0.0173 (5) | |
| N4 | 0.1088 (2) | −0.3646 (3) | 0.98082 (14) | 0.0151 (5) | |
| C19 | −0.1971 (3) | −0.3338 (4) | 0.79249 (18) | 0.0131 (6) | |
| C20 | −0.1028 (3) | −0.3990 (3) | 0.86303 (16) | 0.0128 (5) | |
| H20A | −0.1152 | −0.5127 | 0.8803 | 0.015* | |
| C21 | 0.0095 (3) | −0.2909 (3) | 0.90660 (15) | 0.0118 (6) | |
| C22 | 0.0328 (3) | −0.1188 (4) | 0.88193 (16) | 0.0131 (5) | |
| C23 | −0.0605 (3) | −0.0602 (3) | 0.80700 (16) | 0.0130 (5) | |
| C24 | −0.1769 (3) | −0.1677 (4) | 0.76339 (18) | 0.0137 (6) | |
| H24A | −0.2405 | −0.1286 | 0.7152 | 0.016* | |
| C25 | −0.0306 (3) | 0.1145 (4) | 0.77252 (16) | 0.0150 (5) |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Ag1 | 0.01624 (8) | 0.01725 (9) | 0.01946 (9) | −0.00342 (12) | −0.00152 (6) | 0.00022 (11) |
| O1 | 0.0213 (10) | 0.0127 (9) | 0.0199 (10) | −0.0063 (8) | −0.0062 (8) | 0.0045 (7) |
| O2 | 0.0185 (9) | 0.0169 (10) | 0.0244 (11) | −0.0079 (8) | −0.0046 (8) | 0.0028 (8) |
| N1 | 0.0194 (9) | 0.0143 (15) | 0.0179 (10) | −0.0003 (11) | 0.0034 (8) | 0.0009 (10) |
| N2 | 0.0138 (10) | 0.0164 (12) | 0.0191 (12) | −0.0018 (9) | 0.0047 (9) | 0.0005 (9) |
| C1 | 0.0256 (14) | 0.0145 (13) | 0.0262 (16) | −0.0040 (13) | 0.0053 (12) | 0.0045 (11) |
| C2 | 0.0331 (16) | 0.0181 (15) | 0.0238 (16) | 0.0071 (14) | 0.0092 (13) | 0.0106 (12) |
| C3 | 0.0216 (13) | 0.0248 (14) | 0.0156 (15) | 0.0061 (12) | 0.0021 (11) | 0.0024 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0139 (12) | 0.0219 (15) | 0.0152 (14) | 0.0027 (11) | 0.0036 (10) | 0.0011 (12) |
| C5 | 0.0161 (13) | 0.0293 (16) | 0.0149 (14) | 0.0008 (13) | −0.0007 (10) | −0.0035 (12) |
| C6 | 0.0154 (13) | 0.0245 (15) | 0.0215 (15) | −0.0088 (12) | −0.0008 (10) | −0.0052 (12) |
| C7 | 0.0181 (13) | 0.0179 (15) | 0.0188 (14) | −0.0042 (11) | 0.0023 (10) | 0.0014 (11) |
| C8 | 0.0142 (12) | 0.0145 (13) | 0.0143 (13) | 0.0003 (11) | 0.0002 (10) | 0.0000 (10) |
| C9 | 0.0142 (12) | 0.0143 (13) | 0.0135 (13) | −0.0007 (11) | 0.0030 (9) | 0.0009 (10) |
| C10 | 0.0208 (13) | 0.0172 (14) | 0.0199 (15) | −0.0023 (12) | 0.0082 (11) | 0.0027 (11) |
| C11 | 0.0261 (14) | 0.0167 (14) | 0.0257 (16) | −0.0085 (13) | 0.0098 (12) | −0.0039 (12) |
| C12 | 0.0182 (13) | 0.0228 (15) | 0.0231 (15) | −0.0110 (12) | 0.0071 (11) | −0.0096 (12) |
| C13 | 0.0141 (11) | 0.0225 (15) | 0.0162 (13) | −0.0030 (10) | 0.0064 (10) | −0.0058 (10) |
| C14 | 0.0112 (11) | 0.0293 (15) | 0.0177 (14) | −0.0033 (11) | 0.0005 (10) | −0.0069 (10) |
| C15 | 0.0138 (12) | 0.0278 (16) | 0.0181 (14) | 0.0033 (12) | 0.0000 (10) | 0.0019 (11) |
| C16 | 0.0162 (12) | 0.0153 (13) | 0.0207 (14) | −0.0018 (11) | 0.0032 (10) | −0.0002 (10) |
| C17 | 0.0111 (11) | 0.0143 (13) | 0.0172 (14) | −0.0019 (11) | 0.0028 (10) | −0.0028 (10) |
| C18 | 0.0113 (9) | 0.0151 (11) | 0.0166 (11) | 0.0013 (17) | 0.0052 (8) | 0.0003 (15) |
| O3 | 0.0224 (10) | 0.0222 (11) | 0.0283 (12) | −0.0065 (9) | −0.0032 (9) | 0.0033 (9) |
| O4 | 0.0209 (10) | 0.0281 (12) | 0.0268 (12) | −0.0043 (9) | −0.0115 (8) | −0.0011 (9) |
| O5 | 0.0294 (11) | 0.0195 (11) | 0.0293 (12) | −0.0131 (10) | 0.0006 (9) | 0.0017 (9) |
| O6 | 0.0213 (10) | 0.0160 (10) | 0.0235 (11) | 0.0028 (8) | 0.0008 (8) | 0.0058 (8) |
| O7 | 0.0344 (9) | 0.0225 (10) | 0.0200 (9) | 0.0054 (15) | −0.0118 (7) | −0.0024 (13) |
| O8 | 0.0317 (11) | 0.0166 (11) | 0.0195 (11) | −0.0060 (9) | −0.0027 (8) | 0.0065 (8) |
| O9 | 0.0211 (8) | 0.0132 (14) | 0.0224 (9) | −0.0063 (9) | 0.0004 (7) | 0.0004 (8) |
| N3 | 0.0140 (10) | 0.0190 (12) | 0.0169 (12) | −0.0061 (10) | 0.0004 (9) | −0.0041 (9) |
| N4 | 0.0115 (10) | 0.0166 (12) | 0.0153 (11) | 0.0017 (9) | −0.0004 (8) | 0.0023 (9) |
| C19 | 0.0078 (11) | 0.0166 (13) | 0.0139 (14) | −0.0039 (10) | 0.0007 (10) | −0.0040 (11) |
| C20 | 0.0160 (12) | 0.0084 (12) | 0.0140 (13) | −0.0004 (10) | 0.0034 (9) | 0.0006 (9) |
| C21 | 0.0095 (9) | 0.0131 (18) | 0.0109 (11) | 0.0044 (10) | −0.0009 (8) | 0.0026 (9) |
| C22 | 0.0084 (11) | 0.0151 (14) | 0.0147 (13) | −0.0009 (10) | 0.0011 (9) | −0.0027 (10) |
| C23 | 0.0130 (11) | 0.0110 (13) | 0.0139 (12) | −0.0003 (11) | 0.0013 (9) | −0.0003 (10) |
| C24 | 0.0122 (12) | 0.0145 (14) | 0.0142 (14) | 0.0023 (11) | 0.0028 (10) | 0.0010 (11) |
| C25 | 0.0151 (12) | 0.0110 (12) | 0.0182 (14) | 0.0005 (11) | 0.0030 (10) | 0.0009 (10) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Ag1—N2 | 2.183 (2) | C12—C13 | 1.415 (4) |
| Ag1—N1 | 2.190 (2) | C12—H12A | 0.9300 |
| Ag1—O2 | 2.549 (2) | C13—C18 | 1.415 (4) |
| Ag1—O1 | 2.561 (2) | C13—C14 | 1.417 (4) |
| O1—C8 | 1.352 (3) | C14—C15 | 1.361 (4) |
| O1—H1AA | 0.9999 | C14—H14A | 0.9300 |
| O2—C17 | 1.355 (3) | C15—C16 | 1.406 (4) |
| O2—H2AA | 0.7666 | C15—H15A | 0.9300 |
| N1—C1 | 1.341 (4) | C16—C17 | 1.367 (4) |
| N1—C9 | 1.366 (4) | C16—H16A | 0.9300 |
| N2—C10 | 1.325 (4) | C17—C18 | 1.430 (5) |
| N2—C18 | 1.368 (4) | O3—C22 | 1.330 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.395 (4) | O3—H3B | 0.8193 |
| C1—H1A | 0.9300 | O4—N3 | 1.229 (3) |
| C2—C3 | 1.361 (5) | O5—N3 | 1.220 (3) |
| C2—H2A | 0.9300 | O6—N4 | 1.225 (3) |
| C3—C4 | 1.420 (4) | O7—N4 | 1.217 (3) |
| C3—H3A | 0.9300 | O8—C25 | 1.241 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.419 (4) | O9—C25 | 1.274 (3) |
| C4—C9 | 1.422 (4) | N3—C19 | 1.457 (3) |
| C5—C6 | 1.364 (4) | N4—C21 | 1.472 (3) |
| C5—H5A | 0.9300 | C19—C20 | 1.386 (4) |
| C6—C7 | 1.409 (4) | C19—C24 | 1.387 (4) |
| C6—H6A | 0.9300 | C20—C21 | 1.373 (4) |
| C7—C8 | 1.366 (4) | C20—H20A | 0.9300 |
| C7—H7A | 0.9300 | C21—C22 | 1.409 (4) |
| C8—C9 | 1.432 (4) | C22—C23 | 1.421 (4) |
| C10—C11 | 1.407 (4) | C23—C24 | 1.393 (4) |
| C10—H10A | 0.9300 | C23—C25 | 1.507 (4) |
| C11—C12 | 1.354 (4) | C24—H24A | 0.9300 |
| C11—H11A | 0.9300 | ||
| N2—Ag1—N1 | 151.54 (9) | C10—C11—H11A | 120.6 |
| N2—Ag1—O2 | 68.97 (8) | C11—C12—C13 | 120.1 (3) |
| N1—Ag1—O2 | 138.45 (9) | C11—C12—H12A | 119.9 |
| N2—Ag1—O1 | 138.63 (8) | C13—C12—H12A | 119.9 |
| N1—Ag1—O1 | 69.23 (8) | C18—C13—C12 | 117.5 (3) |
| O2—Ag1—O1 | 69.67 (6) | C18—C13—C14 | 119.5 (3) |
| C8—O1—Ag1 | 111.74 (16) | C12—C13—C14 | 123.0 (3) |
| C8—O1—H1AA | 113.3 | C15—C14—C13 | 120.3 (2) |
| Ag1—O1—H1AA | 134.7 | C15—C14—H14A | 119.8 |
| C17—O2—Ag1 | 112.59 (16) | C13—C14—H14A | 119.8 |
| C17—O2—H2AA | 117.9 | C14—C15—C16 | 120.8 (3) |
| Ag1—O2—H2AA | 129.2 | C14—C15—H15A | 119.6 |
| C1—N1—C9 | 118.3 (2) | C16—C15—H15A | 119.6 |
| C1—N1—Ag1 | 119.1 (2) | C17—C16—C15 | 120.5 (3) |
| C9—N1—Ag1 | 122.58 (19) | C17—C16—H16A | 119.7 |
| C10—N2—C18 | 118.3 (3) | C15—C16—H16A | 119.7 |
| C10—N2—Ag1 | 118.73 (19) | O2—C17—C16 | 123.9 (3) |
| C18—N2—Ag1 | 123.0 (2) | O2—C17—C18 | 115.9 (2) |
| N1—C1—C2 | 123.3 (3) | C16—C17—C18 | 120.3 (2) |
| N1—C1—H1A | 118.4 | N2—C18—C13 | 121.9 (3) |
| C2—C1—H1A | 118.4 | N2—C18—C17 | 119.6 (2) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 119.4 (3) | C13—C18—C17 | 118.6 (3) |
| C3—C2—H2A | 120.3 | C22—O3—H3B | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—H2A | 120.3 | O5—N3—O4 | 124.3 (2) |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.6 (3) | O5—N3—C19 | 118.3 (2) |
| C2—C3—H3A | 120.2 | O4—N3—C19 | 117.4 (2) |
| C4—C3—H3A | 120.2 | O7—N4—O6 | 124.3 (2) |
| C5—C4—C3 | 122.8 (3) | O7—N4—C21 | 119.0 (2) |
| C5—C4—C9 | 119.6 (3) | O6—N4—C21 | 116.7 (2) |
| C3—C4—C9 | 117.7 (3) | C20—C19—C24 | 122.2 (3) |
| C6—C5—C4 | 119.9 (3) | C20—C19—N3 | 118.7 (3) |
| C6—C5—H5A | 120.0 | C24—C19—N3 | 119.1 (3) |
| C4—C5—H5A | 120.0 | C21—C20—C19 | 118.0 (2) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 121.2 (3) | C21—C20—H20A | 121.0 |
| C5—C6—H6A | 119.4 | C19—C20—H20A | 121.0 |
| C7—C6—H6A | 119.4 | C20—C21—C22 | 122.6 (2) |
| C8—C7—C6 | 120.5 (3) | C20—C21—N4 | 116.7 (2) |
| C8—C7—H7A | 119.8 | C22—C21—N4 | 120.7 (2) |
| C6—C7—H7A | 119.8 | O3—C22—C21 | 122.2 (2) |
| O1—C8—C7 | 123.1 (2) | O3—C22—C23 | 120.1 (3) |
| O1—C8—C9 | 116.7 (2) | C21—C22—C23 | 117.7 (2) |
| C7—C8—C9 | 120.2 (2) | C24—C23—C22 | 119.9 (3) |
| N1—C9—C4 | 121.7 (2) | C24—C23—C25 | 119.5 (2) |
| N1—C9—C8 | 119.7 (2) | C22—C23—C25 | 120.5 (2) |
| C4—C9—C8 | 118.6 (2) | C19—C24—C23 | 119.4 (3) |
| N2—C10—C11 | 123.4 (3) | C19—C24—H24A | 120.3 |
| N2—C10—H10A | 118.3 | C23—C24—H24A | 120.3 |
| C11—C10—H10A | 118.3 | O8—C25—O9 | 125.1 (3) |
| C12—C11—C10 | 118.9 (3) | O8—C25—C23 | 118.7 (2) |
| C12—C11—H11A | 120.6 | O9—C25—C23 | 116.1 (2) |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O1—H1AA···O8 | 1.00 | 1.60 | 2.602 (3) | 175 |
| O2—H2AA···O9 | 0.77 | 1.88 | 2.636 (3) | 168 |
| O3—H3B···O9 | 0.82 | 1.74 | 2.483 (3) | 150 |
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: DN2508).
References
- Bruker (1997). SMART and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Burnett, M. N. & Johnson, C. K. (1996). ORTEPIII. Report ORNL-6895. Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Tennessee, USA.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1997). J. Appl. Cryst. 30, 565.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Smith, G. & Thomasson, J. H. (1999). Aust. J. Chem. 52, 317–324.
- Smith, G., Wermuth, U. D. & White, J. M. (2001). Aust. J. Chem. 54, 171–175.
- Wu, H., Dong, X.-W., Liu, H.-Y. & Ma, J.-F. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, m281–m282.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809045905/dn2508sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809045905/dn2508Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report