Abstract
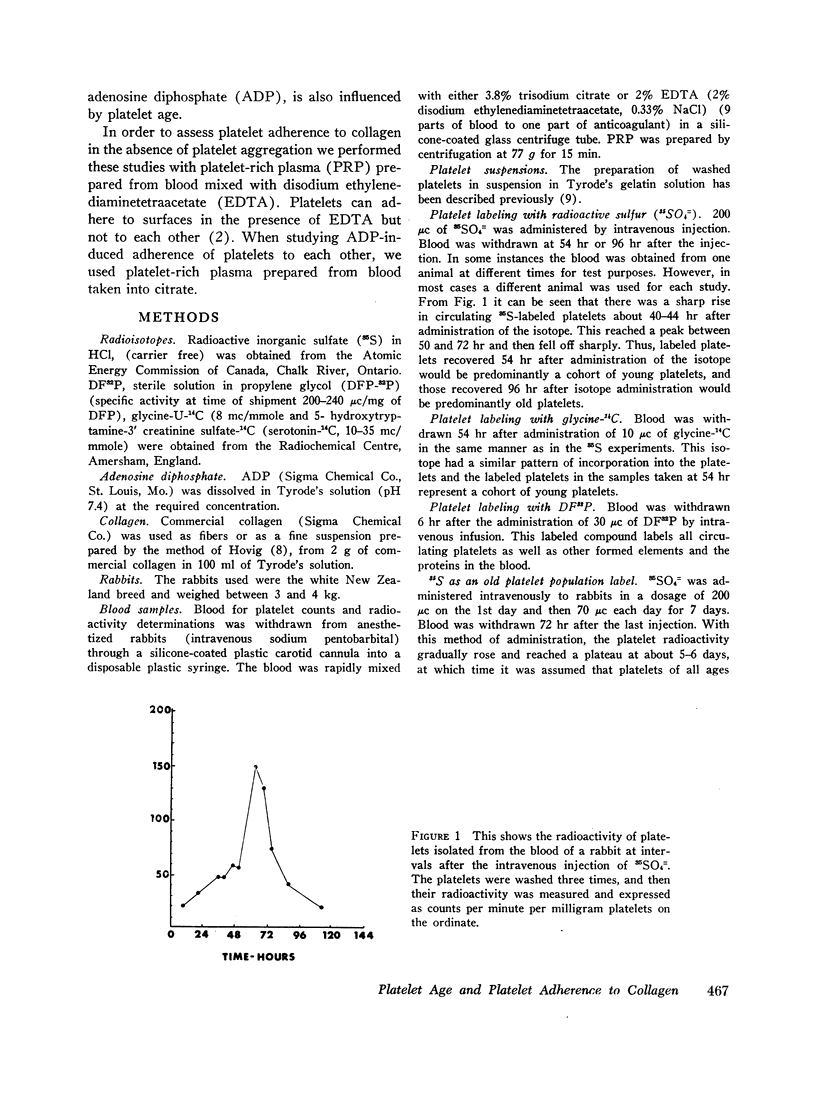
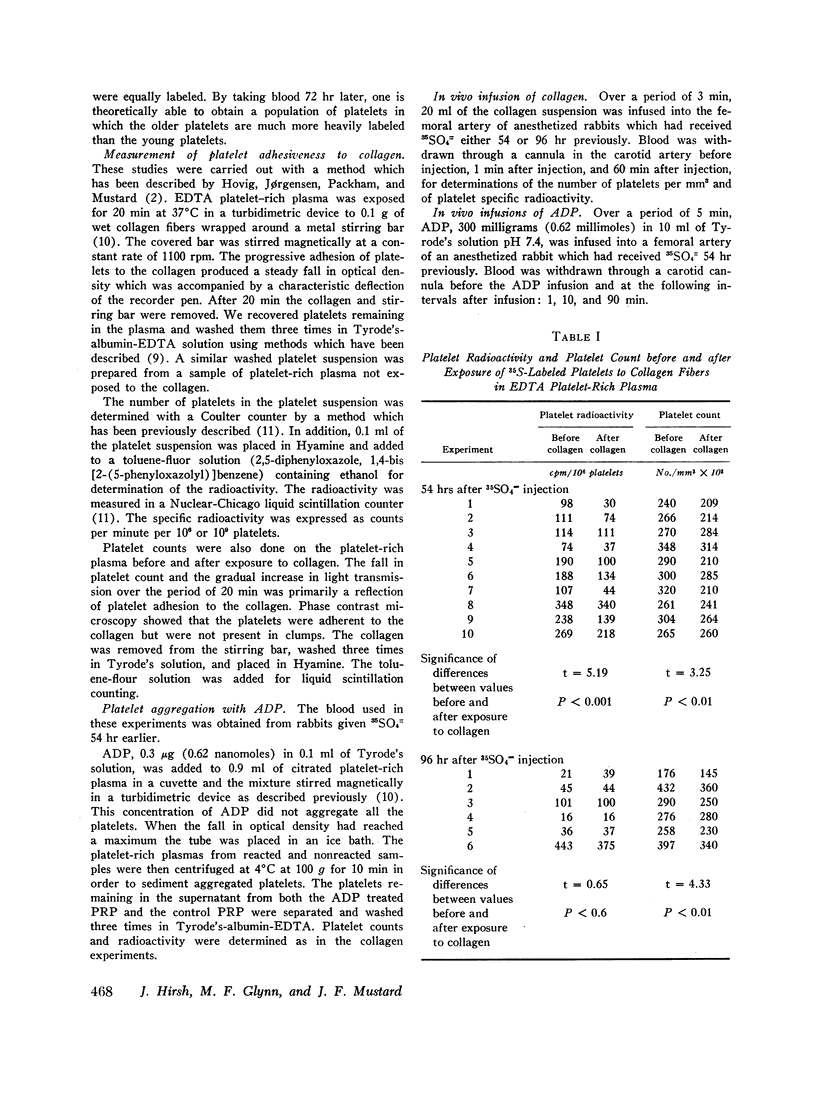
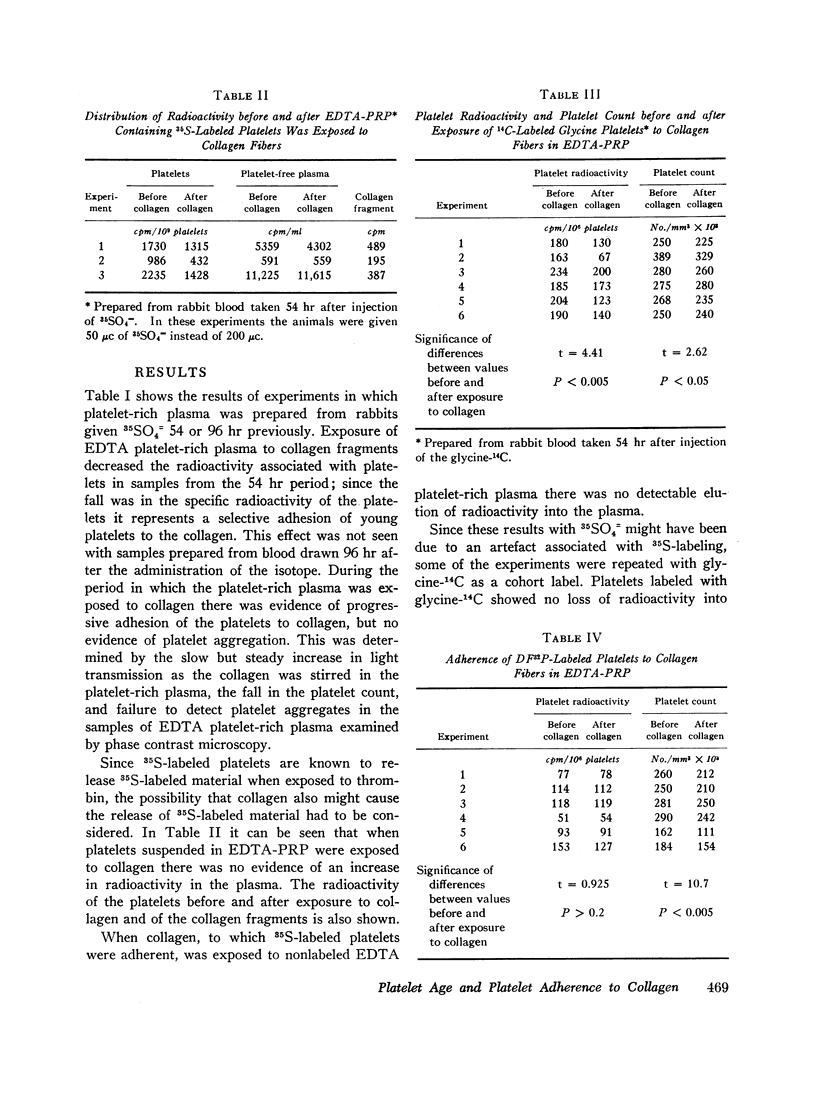
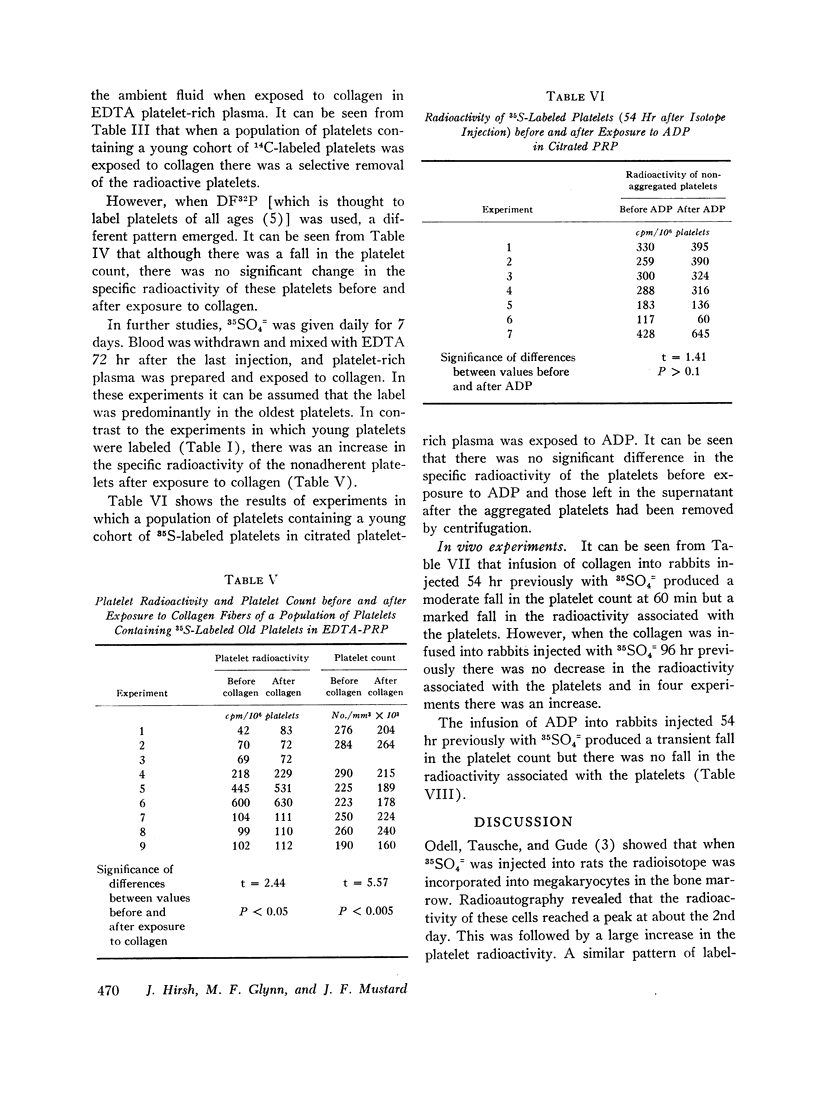
The adherence to collagen of rabbit platelets labeled in vivo with 35SO4= has been studied both in vitro and in vivo. The young platelets are labeled with 35SO4= 2-3 days after administration of the isotope to the animals. We exposed platelet-rich plasma (ethylenediamine-tetraacetate, EDTA, as anticoagulant), prepared from blood taken from rabbits 54 hr after giving the 35SO4=, to collagen in vitro. There was a fall in the specific radioactivity of the nonadherent platelets which indicated a selective adhesion of young platelets to the collagen. In experiments designed to have most of the 35S label in the oldest platelets it was found that exposure of plasma containing these platelets to collagen resulted in an increase in the specific radioactivity of the nonadherent platelets. Similar observations were obtained when glycine-14C was used as a platelet label. However, when DF32P (di-isopropyl phosphorofluoridate-32P), which is thought to label platelets of all ages equally, was used, the adherence of platelets to collagen did not result in any changes in the specific activity of the nonadherent platelets. In in vivo studies in which we infused a collagen suspension into rabbits 54 hr after giving 35SO4= we found that the specific radioactivity of the platelets remaining in the circulation fell. This did not occur when we infused the collagen 96 hr after giving the 35SO4=. The results from these studies indicate that young platelets adhere to collagen more readily than older platelets.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- COHEN J. A., LEEKSMA C. H. Determination of the life span of human blood platelets using labelled diisopropylfluorophosphonate. J Clin Invest. 1956 Sep;35(9):964–969. doi: 10.1172/JCI103356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLYNN M. F., MOVAT H. Z., MURPHY E. A., MUSTARD J. F. STUDY OF PLATELET ADHESIVENESS AND AGGREGATION, WITH LATEX PARTICLES. J Lab Clin Med. 1965 Feb;65:179–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOVIG T. AGGREGATION OF RABBIT BLOOD PLATELETS PRODUCED IN VITRO BY SALINE "EXTRACT" OF TENDONS. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1963 Jul 15;143:248–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURPHY E. A., MUSTARD J. F. Coagulation tests and platelet economy in atherosclerotic and control subjects. Circulation. 1962 Jan;25:114–125. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.25.1.114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURPHY E. A., MUSTARD J. F. Dicumarol therapy and platelet turnover. Circ Res. 1961 Mar;9:402–406. doi: 10.1161/01.res.9.2.402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUSTARD J. F., HEGARDT B., ROWSELL H. C., MACMILLAN R. L. EFFECT OF ADENOSINE NUCLEOTIDES ON PLATELET AGGREGATION AND CLOTTING TIME. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Oct;64:548–559. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDONALD L. Coagulability of the blood in ischaemic heart-disease. Lancet. 1957 Sep 7;273(6993):457–460. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)90768-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustard J. F., Rowsell H. C., Murphy E. A. Platelet economy (platelet survival and turnover). Br J Haematol. 1966 Jan;12(1):1–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1966.tb00121.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NESTEL P. J. A note on platelet adhesiveness in ischaemic heart disease. J Clin Pathol. 1961 Mar;14:150–151. doi: 10.1136/jcp.14.2.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ODELL T. T., Jr, TAUSCHE F. G., GUDE W. D. Uptake of radioactive sulfate by elements of the blood and the bone marrow of rats. Am J Physiol. 1955 Mar;180(3):491–494. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1955.180.3.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packham M. A., Warrior E. S., Glynn M. F., Senyi A. S., Mustard J. F. Alteration of the response of platelets to surface stimuli by pyrazole compounds. J Exp Med. 1967 Jul 1;126(1):171–188. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.1.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


