Abstract
In the title compound, [Cu(C11H11NO4)(H2O)]·H2O, each CuII ion is four-coordinated by one N and two O atoms from the tridentate Schiff base ligand, and by one O atom from the coordinated water molecule in a distorted square-planar geometry. Intermolecular O—H⋯O hydrogen bonds link complex molecules and solvent water molecules into flattened columns propagated in [100].
Related literature
For general background to the chemistry of transition metal complexes with Schiff base ligands composed of salicylaldehyde, 2-formylpyridine or their analogues, and α-amino acids, see: Casella & Guillotti (1983 ▶); Vigato & Tamburini (2004 ▶); Ganguly et al. (2008 ▶). For related structures, see: Usman et al. (2003 ▶); Parekh et al. (2006 ▶); Basu Baul et al. (2007 ▶). For details of the synthesis, see: Plesch et al. (1997 ▶).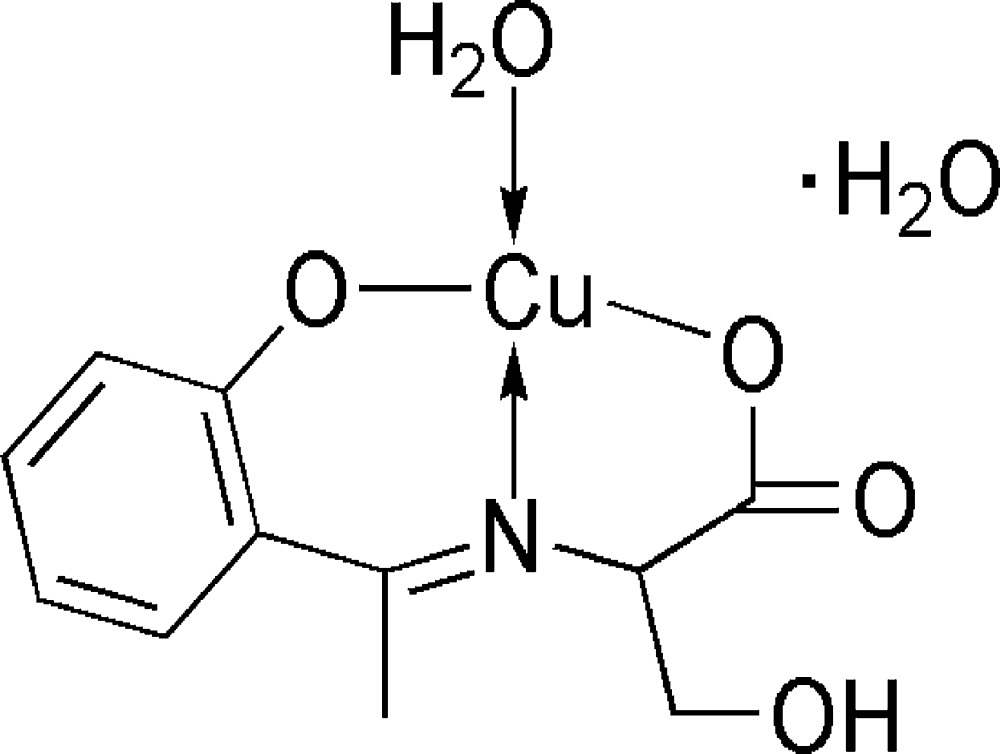
Experimental
Crystal data
[Cu(C11H11NO4)(H2O)]·H2O
M r = 320.78
Orthorhombic,

a = 5.6701 (9) Å
b = 13.788 (2) Å
c = 15.536 (2) Å
V = 1214.6 (3) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 1.82 mm−1
T = 296 K
0.25 × 0.20 × 0.20 mm
Data collection
Bruker SMART APEXII CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996 ▶) T min = 0.659, T max = 0.712
6314 measured reflections
2149 independent reflections
2038 reflections with I > 2σ(I)
R int = 0.027
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.022
wR(F 2) = 0.053
S = 1.09
2149 reflections
176 parameters
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 0.21 e Å−3
Δρmin = −0.24 e Å−3
Absolute structure: Flack (1983 ▶), 869 Friedel pairs
Flack parameter: 0.011 (13)
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2008 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT (Bruker, 2008 ▶); data reduction: SAINT; program(s) used to solve structure: SHELXS97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: SHELXTL (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: SHELXTL.
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809045292/cv2643sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809045292/cv2643Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| O4—H4A⋯O3i | 0.82 | 1.84 | 2.651 (3) | 171 |
| O1W—H1WA⋯O2W ii | 0.82 | 1.91 | 2.694 (3) | 161 |
| O1W—H1WB⋯O2iii | 0.85 | 1.92 | 2.740 (3) | 162 |
| O2W—H2WA⋯O4 | 0.85 | 2.04 | 2.837 (3) | 156 |
| O2W—H2WB⋯O1ii | 0.85 | 2.02 | 2.817 (3) | 157 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  ; (iii)
; (iii)  .
.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Sciences Foundation of China (grant No. 20877036) and High-Level Personnel Foundation of Pingdingshan University (grant No. 2009001).
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
In the past decades, significant progress has been achieved in understanding the chemistry of transition metal complexes with Schiff base ligands composed of salicylaldehyde, 2-formylpyridine or their analogues, and α-amino acids (Vigato & Tamburini, 2004; Ganguly et al., 2008; Casella & Guillotti, 1983). A few stuctural studies have been performed on Schiff base complexes derived from 2-Hydroxyacetophenone and animo acids (Usman et al., 2003; Basu Baul et al., 2007; Parekh et al., 2006). We report here the crystal structure of the title compound (I).
The asymmetric unit of (I) contains a monomeric square-planar coordinated CuII complex and one solvate water molecule (Fig. 1). The Cu—N bond length is 1.9335 (19) Å, while Cu—O bond lengths lie in the range 1.8595 (18)-1.9677 (18) Å.
The crystal structure is stabilized by O—H···O type hydrogen bonds (Table 1), which link complex molecules and solvent water molecules into flattened columns propagated in direction [100].
Experimental
The title compound was synthesized as described in the literature (Plesch et al., 1997). To L-serine (1.00 mmol) and potassium hydroxide (1.00 mmol) in 10 ml of methanol was added 2-Hydroxyacetophenone (1.00 mmol in 10 ml of methanol) dropwise. The yellow solution was stirred for 2.0 h at 333 K. The resultant mixture was added dropwise to copper (II) acetate monohydrate (1.00 mmol) in an aqueous methanolic solution (20 ml, 1:1 v/v), and heated with stirring for 2.0 h at 333 K. The dark green solution was filtered and left for several days, dark green crystals had formed that were filtered off, washed with water, and dried under vacuum.
Refinement
All H atoms were positioned geometrically (C—H = 0.93-0.97 Å, O—H = 0.82-0.85 Å) and refined as riding, with Uiso(H) = 1.2-1.5Ueq of the parent atom.
Figures
Fig. 1.
The structure of the title compound, showing 50% probability displacement ellipsoids and the atom-numbering scheme.
Crystal data
| [Cu(C11H11NO4)(H2O)]·H2O | F(000) = 660 |
| Mr = 320.78 | Dx = 1.754 Mg m−3 |
| Orthorhombic, P212121 | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: P 2ac 2ab | Cell parameters from 3823 reflections |
| a = 5.6701 (9) Å | θ = 2.6–27.3° |
| b = 13.788 (2) Å | µ = 1.82 mm−1 |
| c = 15.536 (2) Å | T = 296 K |
| V = 1214.6 (3) Å3 | Block, dark green |
| Z = 4 | 0.25 × 0.20 × 0.20 mm |
Data collection
| Bruker SMART APEXII CCD diffractometer | 2149 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 2038 reflections with I > 2σ(I) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.027 |
| φ and ω scans | θmax = 25.0°, θmin = 2.6° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Sheldrick, 1996) | h = −2→6 |
| Tmin = 0.659, Tmax = 0.712 | k = −16→16 |
| 6314 measured reflections | l = −18→18 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| Least-squares matrix: full | H-atom parameters constrained |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.022 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0174P)2 + 0.2008P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| wR(F2) = 0.053 | (Δ/σ)max = 0.001 |
| S = 1.09 | Δρmax = 0.21 e Å−3 |
| 2149 reflections | Δρmin = −0.24 e Å−3 |
| 176 parameters | Extinction correction: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008), Fc*=kFc[1+0.001xFc2λ3/sin(2θ)]-1/4 |
| 0 restraints | Extinction coefficient: 0.0120 (11) |
| Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods | Absolute structure: Flack (1983), 869 Friedel pairs |
| Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map | Flack parameter: 0.011 (13) |
Special details
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
| Refinement. Refinement of F2 against ALL reflections. The weighted R-factor wR and goodness of fit S are based on F2, conventional R-factors R are based on F, with F set to zero for negative F2. The threshold expression of F2 > σ(F2) is used only for calculating R-factors(gt) etc. and is not relevant to the choice of reflections for refinement. R-factors based on F2 are statistically about twice as large as those based on F, and R- factors based on ALL data will be even larger. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | ||
| Cu1 | 0.18718 (6) | 0.09862 (2) | 0.532935 (19) | 0.02947 (11) | |
| C1 | 0.5839 (5) | −0.02296 (17) | 0.50130 (16) | 0.0286 (6) | |
| C2 | 0.7793 (5) | −0.04620 (19) | 0.44924 (16) | 0.0378 (7) | |
| H2 | 0.8084 | −0.0092 | 0.4003 | 0.045* | |
| C3 | 0.9287 (5) | −0.12205 (18) | 0.46860 (19) | 0.0390 (6) | |
| H3 | 1.0554 | −0.1360 | 0.4326 | 0.047* | |
| C4 | 0.8899 (5) | −0.17732 (19) | 0.54164 (19) | 0.0382 (7) | |
| H4 | 0.9903 | −0.2284 | 0.5553 | 0.046* | |
| C5 | 0.7019 (6) | −0.15591 (18) | 0.59347 (16) | 0.0340 (6) | |
| H5 | 0.6780 | −0.1933 | 0.6425 | 0.041* | |
| C6 | 0.5428 (5) | −0.07988 (16) | 0.57613 (15) | 0.0268 (6) | |
| C7 | 0.3496 (5) | −0.06175 (17) | 0.63784 (15) | 0.0283 (6) | |
| C8 | 0.0332 (5) | 0.03559 (19) | 0.69616 (16) | 0.0304 (6) | |
| H8 | −0.0484 | −0.0238 | 0.7139 | 0.036* | |
| C9 | −0.1447 (4) | 0.10765 (19) | 0.66029 (18) | 0.0354 (6) | |
| C10 | 0.3232 (7) | −0.1327 (2) | 0.71079 (18) | 0.0469 (8) | |
| H10A | 0.4539 | −0.1260 | 0.7496 | 0.070* | |
| H10B | 0.3200 | −0.1976 | 0.6883 | 0.070* | |
| H10C | 0.1788 | −0.1199 | 0.7410 | 0.070* | |
| C11 | 0.1466 (5) | 0.0833 (2) | 0.77456 (16) | 0.0393 (7) | |
| H11A | 0.0281 | 0.0931 | 0.8187 | 0.047* | |
| H11B | 0.2671 | 0.0408 | 0.7978 | 0.047* | |
| N1 | 0.2116 (4) | 0.01209 (14) | 0.63046 (12) | 0.0247 (4) | |
| O1 | 0.4525 (3) | 0.05113 (12) | 0.47659 (11) | 0.0372 (4) | |
| O2 | −0.0953 (4) | 0.14741 (13) | 0.58792 (13) | 0.0409 (5) | |
| O3 | −0.3178 (4) | 0.12658 (15) | 0.70381 (15) | 0.0552 (6) | |
| O4 | 0.2492 (3) | 0.17369 (14) | 0.75275 (13) | 0.0412 (5) | |
| H4A | 0.3869 | 0.1654 | 0.7383 | 0.062* | |
| O1W | 0.1373 (4) | 0.18950 (14) | 0.43700 (13) | 0.0523 (6) | |
| H1WA | −0.0026 | 0.1897 | 0.4236 | 0.078* | |
| H1WB | 0.1923 | 0.2466 | 0.4318 | 0.078* | |
| O2W | 0.2141 (4) | 0.33399 (16) | 0.63903 (14) | 0.0550 (6) | |
| H2WA | 0.2036 | 0.2776 | 0.6607 | 0.066* | |
| H2WB | 0.1045 | 0.3569 | 0.6077 | 0.066* |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| Cu1 | 0.02747 (17) | 0.02884 (16) | 0.03211 (16) | 0.00077 (15) | −0.00322 (15) | 0.00440 (13) |
| C1 | 0.0274 (14) | 0.0282 (12) | 0.0303 (12) | −0.0033 (11) | −0.0041 (12) | −0.0019 (11) |
| C2 | 0.0400 (17) | 0.0408 (15) | 0.0324 (14) | −0.0022 (13) | 0.0062 (13) | −0.0010 (11) |
| C3 | 0.0339 (15) | 0.0387 (15) | 0.0446 (15) | 0.0005 (12) | 0.0076 (15) | −0.0103 (13) |
| C4 | 0.0327 (15) | 0.0318 (13) | 0.0500 (17) | 0.0059 (12) | −0.0027 (14) | −0.0036 (14) |
| C5 | 0.0379 (15) | 0.0273 (12) | 0.0368 (14) | 0.0001 (14) | −0.0022 (15) | −0.0017 (11) |
| C6 | 0.0254 (13) | 0.0248 (13) | 0.0302 (12) | −0.0027 (11) | −0.0013 (11) | −0.0041 (10) |
| C7 | 0.0267 (15) | 0.0286 (12) | 0.0296 (12) | −0.0029 (11) | −0.0028 (12) | 0.0015 (10) |
| C8 | 0.0228 (14) | 0.0329 (13) | 0.0354 (14) | −0.0055 (12) | 0.0067 (12) | 0.0012 (11) |
| C9 | 0.0238 (15) | 0.0309 (13) | 0.0517 (16) | −0.0047 (13) | −0.0008 (13) | −0.0103 (14) |
| C10 | 0.0446 (19) | 0.0500 (16) | 0.0459 (16) | 0.0087 (16) | 0.0081 (17) | 0.0212 (13) |
| C11 | 0.0340 (17) | 0.0547 (17) | 0.0291 (12) | −0.0025 (14) | 0.0084 (12) | −0.0040 (13) |
| N1 | 0.0224 (11) | 0.0263 (10) | 0.0254 (10) | −0.0043 (10) | −0.0002 (10) | −0.0010 (8) |
| O1 | 0.0353 (10) | 0.0426 (10) | 0.0336 (10) | 0.0061 (9) | 0.0052 (9) | 0.0097 (8) |
| O2 | 0.0347 (11) | 0.0372 (10) | 0.0509 (12) | 0.0099 (9) | −0.0037 (10) | 0.0023 (9) |
| O3 | 0.0287 (12) | 0.0614 (14) | 0.0754 (15) | 0.0059 (11) | 0.0118 (13) | −0.0107 (11) |
| O4 | 0.0291 (13) | 0.0436 (10) | 0.0508 (12) | −0.0034 (8) | 0.0022 (9) | −0.0159 (9) |
| O1W | 0.0461 (15) | 0.0468 (12) | 0.0639 (13) | −0.0085 (10) | −0.0166 (11) | 0.0273 (11) |
| O2W | 0.0374 (12) | 0.0585 (13) | 0.0690 (14) | −0.0080 (12) | −0.0080 (12) | 0.0245 (11) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| Cu1—O1 | 1.8595 (18) | C8—N1 | 1.473 (3) |
| Cu1—N1 | 1.9335 (19) | C8—C9 | 1.522 (4) |
| Cu1—O2 | 1.936 (2) | C8—C11 | 1.527 (4) |
| Cu1—O1W | 1.9677 (18) | C8—H8 | 0.9800 |
| C1—O1 | 1.322 (3) | C9—O3 | 1.220 (3) |
| C1—C2 | 1.408 (4) | C9—O2 | 1.282 (3) |
| C1—C6 | 1.422 (3) | C10—H10A | 0.9600 |
| C2—C3 | 1.379 (4) | C10—H10B | 0.9600 |
| C2—H2 | 0.9300 | C10—H10C | 0.9600 |
| C3—C4 | 1.385 (4) | C11—O4 | 1.416 (3) |
| C3—H3 | 0.9300 | C11—H11A | 0.9700 |
| C4—C5 | 1.368 (4) | C11—H11B | 0.9700 |
| C4—H4 | 0.9300 | O4—H4A | 0.8200 |
| C5—C6 | 1.409 (4) | O1W—H1WA | 0.8200 |
| C5—H5 | 0.9300 | O1W—H1WB | 0.8502 |
| C6—C7 | 1.477 (3) | O2W—H2WA | 0.8500 |
| C7—N1 | 1.289 (3) | O2W—H2WB | 0.8500 |
| C7—C10 | 1.505 (3) | ||
| O1—Cu1—N1 | 95.37 (8) | C9—C8—C11 | 106.9 (2) |
| O1—Cu1—O2 | 177.99 (9) | N1—C8—H8 | 109.6 |
| N1—Cu1—O2 | 85.87 (9) | C9—C8—H8 | 109.6 |
| O1—Cu1—O1W | 89.08 (9) | C11—C8—H8 | 109.6 |
| N1—Cu1—O1W | 175.46 (9) | O3—C9—O2 | 124.8 (3) |
| O2—Cu1—O1W | 89.66 (9) | O3—C9—C8 | 118.0 (3) |
| O1—C1—C2 | 116.9 (2) | O2—C9—C8 | 117.1 (2) |
| O1—C1—C6 | 124.9 (2) | C7—C10—H10A | 109.5 |
| C2—C1—C6 | 118.2 (2) | C7—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—C1 | 122.0 (2) | H10A—C10—H10B | 109.5 |
| C3—C2—H2 | 119.0 | C7—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C1—C2—H2 | 119.0 | H10A—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—C4 | 119.9 (3) | H10B—C10—H10C | 109.5 |
| C2—C3—H3 | 120.1 | O4—C11—C8 | 111.2 (2) |
| C4—C3—H3 | 120.1 | O4—C11—H11A | 109.4 |
| C5—C4—C3 | 119.2 (2) | C8—C11—H11A | 109.4 |
| C5—C4—H4 | 120.4 | O4—C11—H11B | 109.4 |
| C3—C4—H4 | 120.4 | C8—C11—H11B | 109.4 |
| C4—C5—C6 | 123.1 (2) | H11A—C11—H11B | 108.0 |
| C4—C5—H5 | 118.4 | C7—N1—C8 | 121.9 (2) |
| C6—C5—H5 | 118.4 | C7—N1—Cu1 | 126.91 (17) |
| C5—C6—C1 | 117.5 (2) | C8—N1—Cu1 | 110.98 (15) |
| C5—C6—C7 | 118.5 (2) | C1—O1—Cu1 | 126.28 (16) |
| C1—C6—C7 | 124.0 (2) | C9—O2—Cu1 | 114.80 (17) |
| N1—C7—C6 | 121.7 (2) | C11—O4—H4A | 109.5 |
| N1—C7—C10 | 121.3 (2) | Cu1—O1W—H1WA | 109.5 |
| C6—C7—C10 | 116.9 (2) | Cu1—O1W—H1WB | 127.5 |
| N1—C8—C9 | 110.2 (2) | H1WA—O1W—H1WB | 109.1 |
| N1—C8—C11 | 111.0 (2) | H2WA—O2W—H2WB | 121.1 |
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| O4—H4A···O3i | 0.82 | 1.84 | 2.651 (3) | 171 |
| O1W—H1WA···O2Wii | 0.82 | 1.91 | 2.694 (3) | 161 |
| O1W—H1WB···O2iii | 0.85 | 1.92 | 2.740 (3) | 162 |
| O2W—H2WA···O4 | 0.85 | 2.04 | 2.837 (3) | 156 |
| O2W—H2WB···O1ii | 0.85 | 2.02 | 2.817 (3) | 157 |
Symmetry codes: (i) x+1, y, z; (ii) x−1/2, −y+1/2, −z+1; (iii) x+1/2, −y+1/2, −z+1.
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: CV2643).
References
- Basu Baul, T. S., Masharing, C., Ruisi, G., Jir ásko, R., HolǍpek, M., de Vos, D., Wolstenholme, D. & Linden, A. (2007). J. Organomet. Chem. 692, 4849–4862.
- Bruker (2008). APEX2 and SAINT. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Casella, L. & Guillotti, M. (1983). Inorg. Chem. 22, 2259–2266.
- Flack, H. D. (1983). Acta Cryst. A39, 876–881.
- Ganguly, R., Sreenivasulu, B. & Vittal, J. J. (2008). Coord. Chem. Rev. 252, 1027–1050.
- Parekh, H. M., Mehta, S. R. & Patel, M. N. (2006). Russ. J. Inorg. Chem. 35, 67–72.
- Plesch, G., Friebel, C., Warda, S. A., Sivý, J. & Švajlenová, O. (1997). Transition Met. Chem. 22, 433–440.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (1996). SADABS. University of Göttingen, Germany.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Usman, A., Fun, H.-K., Basu Baul, T. S. & Paul, P. C. (2003). Acta Cryst. E59, m438–m440.
- Vigato, P. A. & Tamburini, S. (2004). Coord. Chem. Rev. 248, 1717–2128.
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809045292/cv2643sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S1600536809045292/cv2643Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report



