Abstract
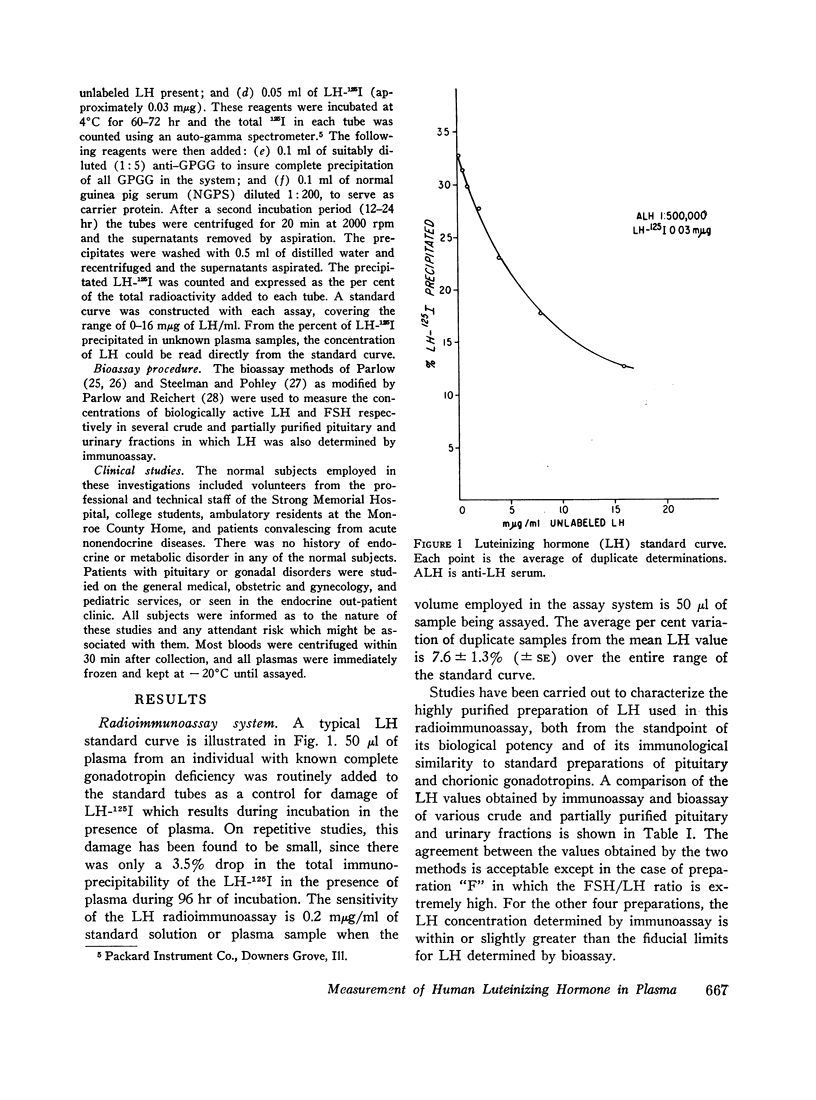
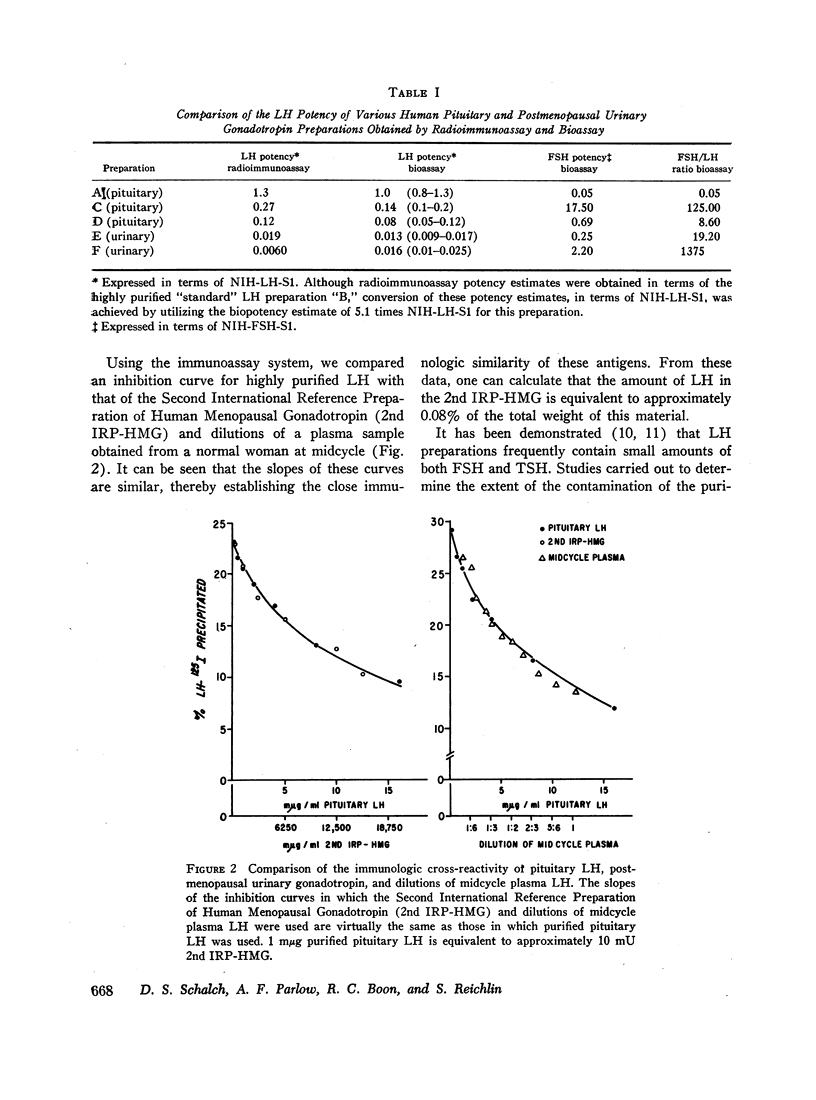
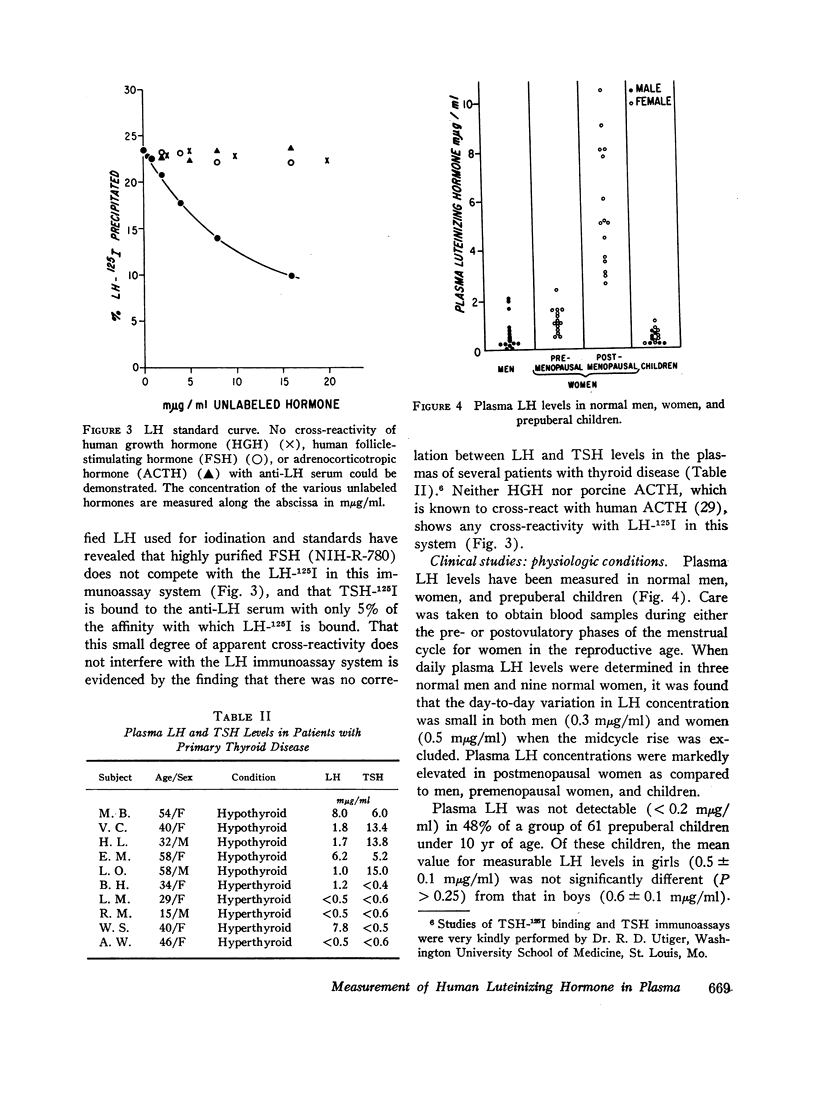
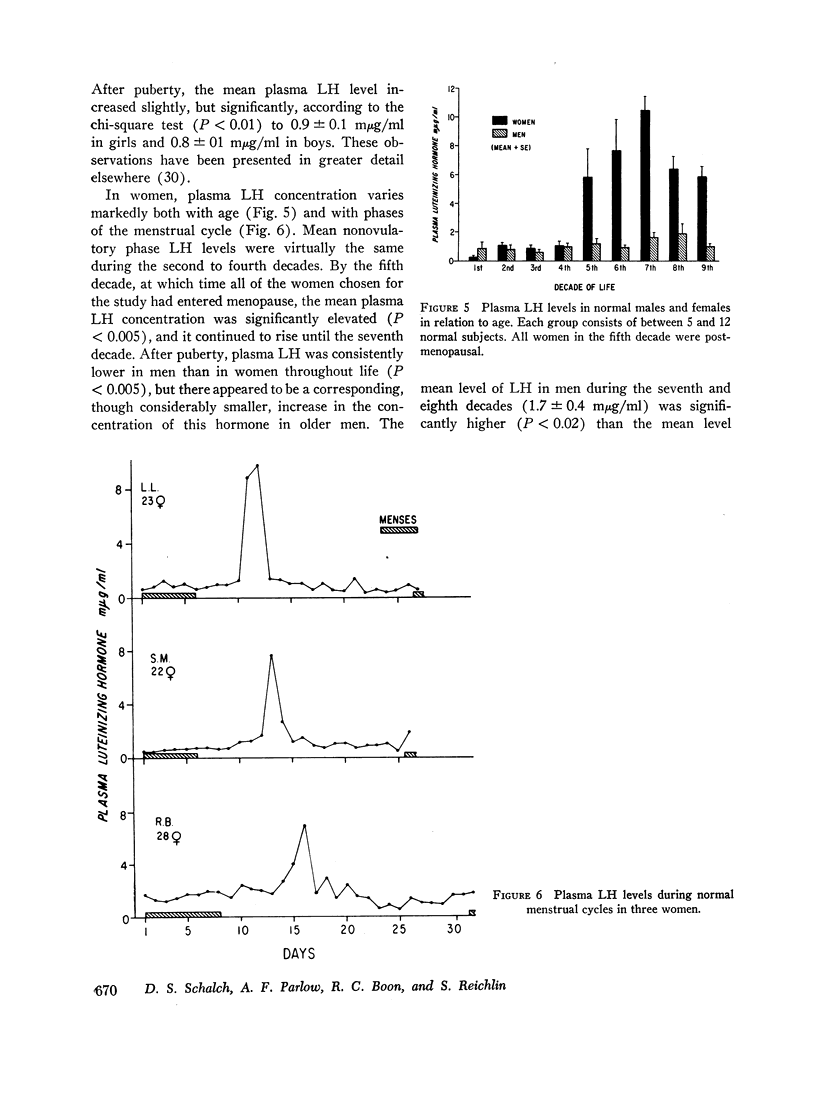
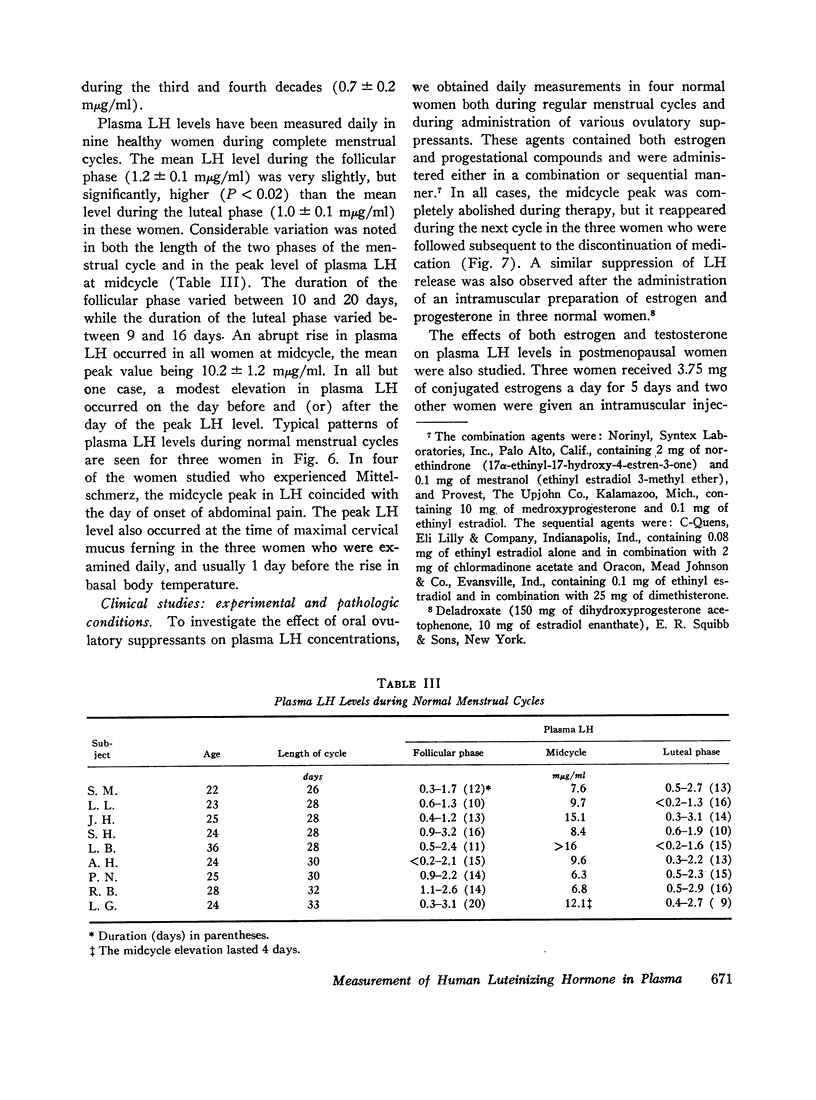
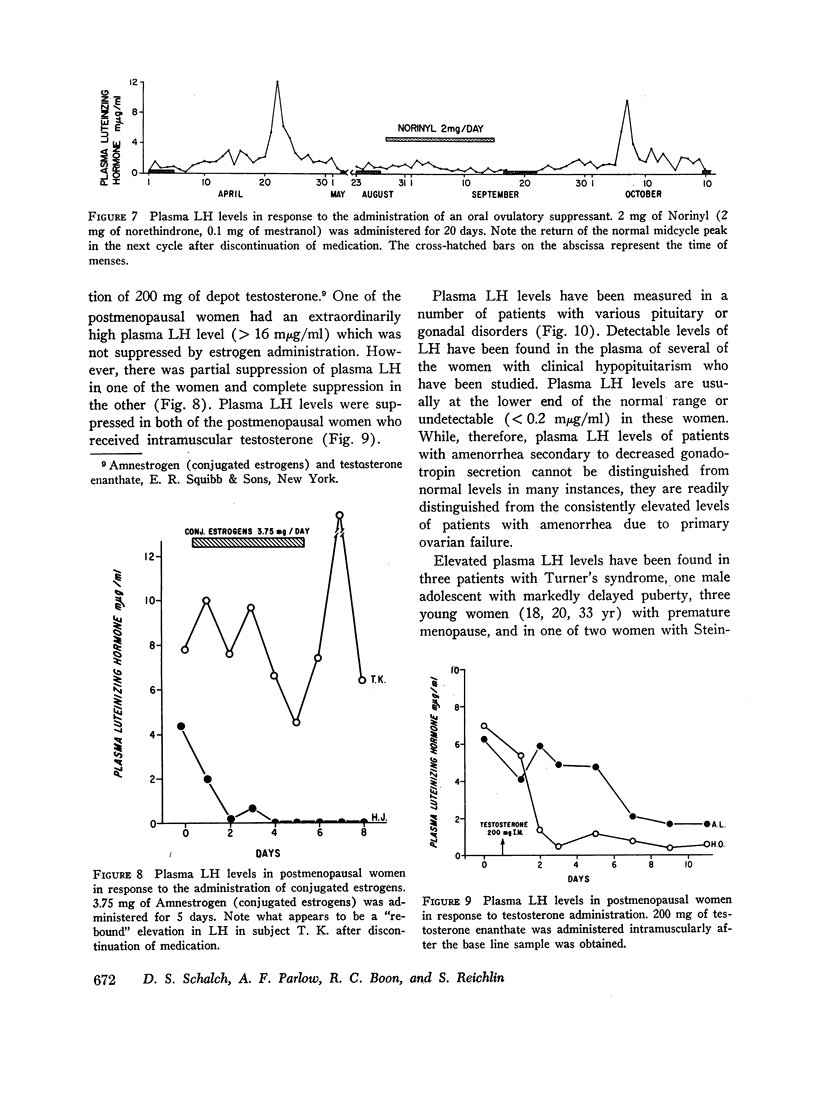
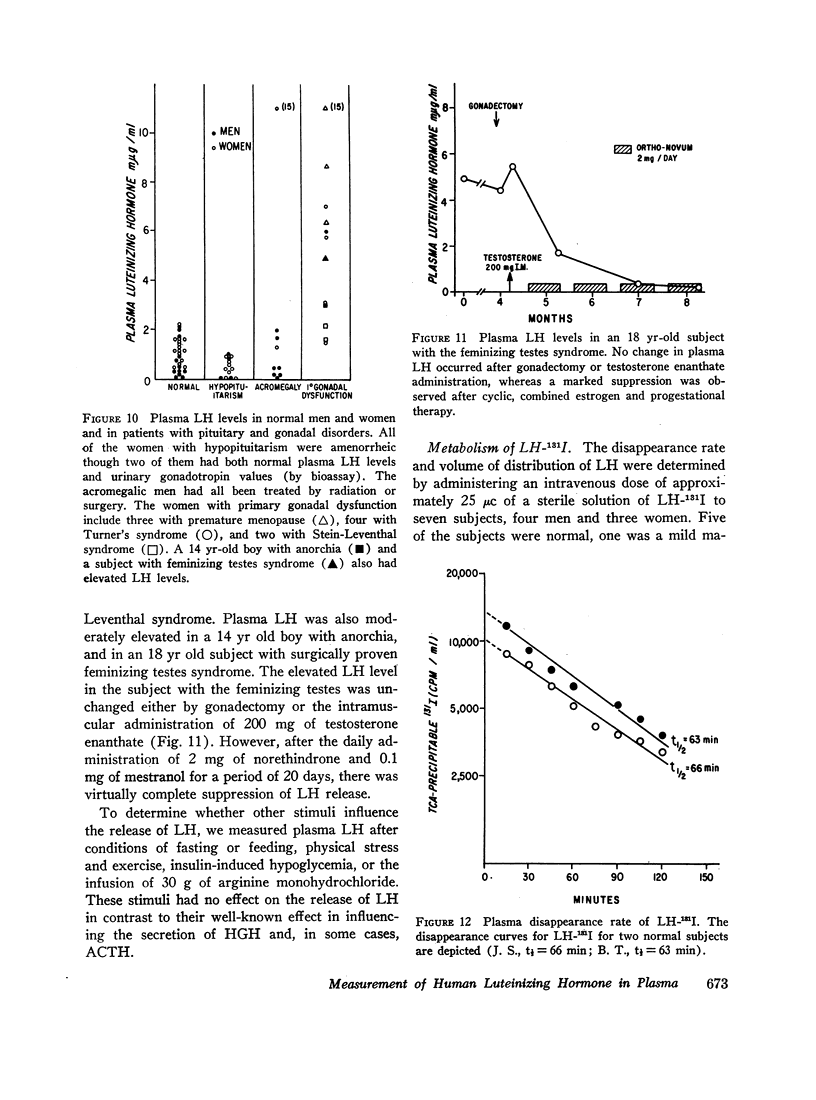
The recent isolation of highly purified human pituitary luteinizing hormone (LH) has permitted the development of a sensitive and specific radioimmunoassay for this hormone in plasma. Results of this immunoassay system employing anti-LH serum agree closely with previous reports for the measurement of plasma LH in which immunoassays employing cross-reactive antisera to human chorionic gonadotropin were used. The immunoassay and bioassay of LH in several crude and partially purified pituitary and urinary extracts show acceptable agreement. The sensitivity of the LH immunoassay (0.2 mμg/ml) is adequate to measure LH levels in almost half of all prepuberal children and in all but a few normal adults. A small, but significant, rise in plasma LH level occurs at pubescence in both boys and girls. In women, plasma LH level varies with both age and the phase of the menstrual cycle. The mean LH concentration in nine normal women during the follicular phase (1.2 mμg/ml was found to be significantly higher than during the luteal phase (1.0 mμg/ml). At midcycle, the mean peak LH level was 10.2 mμg/ml. In a large group of normal women, the mean plasma LH concentration rose significantly at menopause to a level of 5.8 mμg/ml during the fifth decade and 10.5 mμg/ml during the seventh decade. A small, but significant, rise in plasma LH concentration also occurred in men from the third and fourth decades (0.7 mμg/ml to the seventh and eighth decades (1.7 mμg/ml). Both estrogen and testosterone suppress plasma LH levels, but marked variation in response exists. The immunoassay serves as a useful diagnostic tool in evaluating men with gonadal failure, amenorrheic women of reproductive age, and postmenopausal women suspected of hypopituitarism. From the half-time disappearance of LH-131I in plasma (mean 69 min) and the calculated volume of distribution (2.5-2.8 liters) it has been determined that approximately 30 μg of LH is secreted per day in men, and in women except at midcycle, at which time the release of LH is estimated to be 10-15 times this basal rate.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- APOSTOLAKIS M. Detection and estimation of pituitary gonadotrophins in human plasma. J Endocrinol. 1959 Dec;19:377–388. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0190377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECKER K. L., ALBERT A. URINARY EXCRETION OF FOLLICLE-STIMULATING AND LUTEINIZING HORMONES. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Jul;25:962–974. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-7-962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BYRNES W. W., MEYER R. K. The inhibition of gonadotrophic hormone secretion by physiological doses of estrogen. Endocrinology. 1951 Feb;48(2):133–136. doi: 10.1210/endo-48-2-133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagshawe K. D., Wilde C. E., Orr A. H. Radioimmunoassay for human chorionic gonadotrophin and luteinising hormone. Lancet. 1966 May 21;1(7447):1118–1121. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)91136-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CONDLIFFE P. G. Purification of human thyrotrophin. Endocrinology. 1963 Jun;72:893–896. doi: 10.1210/endo-72-6-893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppage W. S., Jr, Cooner A. E. Testosterone in human plasma. N Engl J Med. 1965 Oct 21;273(17):902–907. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196510212731704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FITSCHEN W., CLAYTON B. E. URINARY EXCRETION OF GONADOTROPHINS WITH PARTICULAR REFERENCE TO CHILDREN. Arch Dis Child. 1965 Feb;40:16–26. doi: 10.1136/adc.40.209.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUKUSHIMA M., STEVENS V. C., GANTT C. L., VORYS N. URINARY FSH AND LH EXCRETION DURING THE NORMAL MENSTRUAL CYCLE. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Feb;24:205–213. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-2-205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faiman C., Ryan R. J. Radioimmunoassay for human follicle stimulating hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Mar;27(3):444–447. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-3-444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENBLATT R. B., BARFIELD W. E., JUNGCK E. C., RAY A. W. Induction of ovulation with MRL/41. Preliminary report. JAMA. 1961 Oct 14;178:101–104. doi: 10.1001/jama.1961.03040410001001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gwinup G., Wieland R. G., Besch P. K., Hamwi G. J. Studies on the mechanism of the production of the testicular feminization syndrome. Am J Med. 1966 Sep;41(3):448–452. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(66)90090-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARTREE A. S., BUTT W. R., KIRKHAM K. E. THE SEPARATION AND PURIFICATION OF HUMAN LUTEINIZING AND THYROTROPHIC HORMONES. J Endocrinol. 1964 Apr;29:61–69. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0290061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KINCL F. A., BIRCH A. J., DORFMAN R. I. PITUITARY GONADOTROPIC INHIBITORY ACTIVITY OF VARIOUS STEROIDS IN OVARIECTOMIZED-INTACT FEMALE RATS IN PARABIOSIS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Nov;117:549–552. doi: 10.3181/00379727-117-29634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller P. J. Studies on pituitary gonadotrophins in human plasma. 1. Normal values in men and women of all ages. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1966 Jul;52(3):341–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kistner R. W. Use of clomiphene citrate, human chorionic gonadotropin, and human menopausal gonadotropin for induction of ovulation in the human female. Fertil Steril. 1966 Sep-Oct;17(5):569–583. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)36060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOUCHART J., TRUFFERT J., DECOURT J. DOSAGE DE L'HORMONE LUTEINISANTE DANS LE PLASMA HUMAIN. RESULTATS CHEZ LES SUJETS NORMAUX DES DEUX SEXES. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1965 Jun;49:293–298. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCARTHUR J. W., ANTONIADES H. N., LARSON L. H., PENNELL R. B., INGERSOLL F. M., ULFELDER H. FOLLICLE-STIMULATING HORMONE AND LUTEINIZING HORMONE CONTENT OF POOLED HUMAN MENOPAUSAL PLASMA AND OF SUBFRACTIONS PREPARED BY COHN METHODS 6 AND 9. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 May;24:425–431. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-5-425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McARTHUR J. W., INGERSOLL F. M., WORCESTER J. The urinary excretion of interstitial-cell and follicle-stimulating hormone activity by women with diseases of the reproductive system. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1958 Nov;18(11):1202–1215. doi: 10.1210/jcem-18-11-1202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McARTHUR J. W., WORCESTER J., INGERSOLL F. M. The urinary excretion of interstitial-cell and follicle-stimulating hormone activity during the normal menstrual cycle. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1958 Nov;18(11):1186–1201. doi: 10.1210/jcem-18-11-1186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midgley A. R., Jr Radioimmunoassay: a method for human chorionic gonadotropin and human luteinizing hormone. Endocrinology. 1966 Jul;79(1):10–18. doi: 10.1210/endo-79-1-10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midgley A. R. Radioimmunoassay for human follicle-stimulating hormone. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Feb;27(2):295–299. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-2-295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odell W. D., Ross G. T., Rayford P. L. Radioimmunoassay for human luteinizing hormone. Metabolism. 1966 Apr;15(4):287–289. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(66)90142-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Odell W. D., Ross G. T., Rayford P. L. Radioimmunoassay for luteinizing hormone in human plasma or serum: physiological studies. J Clin Invest. 1967 Feb;46(2):248–255. doi: 10.1172/JCI105527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARLOW A. F., CONDLIFFE P. G., REICHERT L. E., Jr, WILHELMI A. E. RECOVERY AND PARTIAL PURIFICATION OF FSH AND LH DURING THE PURIFICATION OF TSH FROM HUMAN PITUITARY GLANDS. Endocrinology. 1965 Jan;76:27–34. doi: 10.1210/endo-76-1-27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARLOW A. F., REICHERT L. E., Jr SPECIES DIFFERENCES IN FOLLICLE-STIMULATING HORMONE AS REVEALED BY THE SLOPE IN THE STEELMAN-POHLEY ASSAY. Endocrinology. 1963 Dec;73:740–743. doi: 10.1210/endo-73-6-740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABEN M. S. Preparation of growth hormone from pituitaries of man and monkey. Science. 1957 May 3;125(3253):883–884. doi: 10.1126/science.125.3253.883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMIREZ D. V., McCANN S. M. Comparison of the regulation of luteinizing hormone (LH) secretion in immature and adult rats. Endocrinology. 1963 Mar;72:452–464. doi: 10.1210/endo-72-3-452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosemberg E., Keller P. J. Studies on the urinary excretion of follicle-stimulating and luteinizing hormone activity during the menstrual cycle. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Sep;25(9):1262–1274. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-9-1262. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan G. M., Jr, Goss D. A., Reid D. E. Pituitary gonadotropins during long-term Enovid therapy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1966 Feb 15;94(4):515–517. doi: 10.1016/0002-9378(66)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SATO T., GREENBLATT R. B., MAHESH V. B. LEVELS OF LUTEINIZING HORMONE DURING THE MENSTRUAL CYCLE DETERMINED BY IMMUNOLOGIC TECHNICS. Fertil Steril. 1965 Mar-Apr;16:223–228. doi: 10.1016/s0015-0282(16)35529-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHALCH D. S., PARKER M. L. A SENSITIVE DOUBLE ANTIBODY IMMUNOASSAY FOR HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE IN PLASMA. Nature. 1964 Sep 12;203:1141–1142. doi: 10.1038/2031141a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEELMAN S. L., POHLEY F. M. Assay of the follicle stimulating hormone based on the augmentation with human chorionic gonadotropin. Endocrinology. 1953 Dec;53(6):604–616. doi: 10.1210/endo-53-6-604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalch D. S. Use of I125-labeling in radioimmunoassays. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Apr;121(4):1279–1280. doi: 10.3181/00379727-121-31027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYMOR M. L. EFFECT OF SYNTHETIC PROGESTINS ON PITUITARY GONADOTROPHIN EXCRETION. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Aug;24:803–807. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-8-803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIDE L., GEMZELL C. Immunological determination of pituitary luteinizing hormone in the urine of fertile and post-menopausal women and adult men. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1962 Apr;39:539–546. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0390539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., GLICK S. M., ROTH J., BERSON S. A. RADIOIMMUNOASSAY OF HUMAN PLASMA ACTH. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Nov;24:1219–1225. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-11-1219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



