Abstract
In the title compound, [Rh(C13H16NO)(C18H15P)(CO)]·0.5C3H6O, the Rh atom exhibits a square-planar coordination geometry, being coordinated by the N and O atoms of the bidentate β-diketonato ligand, a P atom from the triphenylphosphine unit and a C atom from the carbonyl group. The asymmetric unit also contains a disordered half-molecule, lying about an inversion center, of the acetone solvate. Intermolecular C—H⋯O hydrogen bonds are observed between a C—H group of the triphenylphosphine unit and a carbonyl O atom and between the methyl group of the enaminoketonato backbone and the solvent O atom. In addition, an intramolecular interaction is observed between a C—H group of the triphenylphosphine unit and the O atom of the enaminoketonato ligand.
Related literature
For synthetic background, see: Shaheen et al. (2006 ▶); Cornils & Hermann (1996); Bonati & Wilkinson (1964 ▶). For appplications of rhodium(I) dicarbonyl complexes, see: Cornils & Herrmann (1996 ▶); Trzeciak & Ziolkowski (1994 ▶); Van Rooy et al. (1995 ▶). For related structures, see: Damoense et al. (1994 ▶); Varshavsky et al. (2001 ▶); Venter et al. (2009 ▶).
Experimental
Crystal data
[Rh(C13H16NO)(C18H15P)(CO)]·0.5C3H6O
M r = 624.5
Monoclinic,

a = 16.8558 (8) Å
b = 11.4028 (5) Å
c = 16.4059 (8) Å
β = 108.733 (1)°
V = 2986.2 (2) Å3
Z = 4
Mo Kα radiation
μ = 0.66 mm−1
T = 100 K
0.31 × 0.15 × 0.11 mm
Data collection
Bruker X8 APEXII 4K Kappa CCD diffractometer
Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2004 ▶) T min = 0.822, T max = 0.931
23158 measured reflections
7425 independent reflections
6081 reflections with > 2σI)
R int = 0.042
Refinement
R[F 2 > 2σ(F 2)] = 0.038
wR(F 2) = 0.112
S = 1.09
7425 reflections
354 parameters
1 restraint
H-atom parameters constrained
Δρmax = 1.54 e Å−3
Δρmin = −1.32 e Å−3
Data collection: APEX2 (Bruker, 2005 ▶); cell refinement: SAINT-Plus (Bruker, 2004 ▶); data reduction: SAINT-Plus; program(s) used to solve structure: SIR97 (Altomare et al., 1999 ▶); program(s) used to refine structure: SHELXL97 (Sheldrick, 2008 ▶); molecular graphics: DIAMOND (Brandenburg & Putz, 2005 ▶); software used to prepare material for publication: WinGX (Farrugia, 1999 ▶).
Supplementary Material
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680904817X/pv2227sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680904817X/pv2227Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report
Table 1. Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °).
| D—H⋯A | D—H | H⋯A | D⋯A | D—H⋯A |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C332—H332⋯O12 | 0.95 | 2.38 | 3.201 (3) | 144 |
| C334—H334⋯O14i | 0.95 | 2.51 | 3.201 (4) | 130 |
| C1—H1B⋯O01ii | 0.98 | 2.54 | 3.372 (9) | 142 |
Symmetry codes: (i)  ; (ii)
; (ii)  .
.
Table 2. Comparative geometrical parameters (Å, °) for similar [Rh(N,O-bid)(CO)(PPh3)] complexes.
| Parameters | (I)a | (II)b | (III)c | (IV)d |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rh1—N11 | 2.077 (2) | 2.069 (2) | 2.045 (4) | 2.045 (3) |
| Rh1—O12 | 2.027 (2) | 2.028 (2) | 2.044 (3) | 2.045 (2) |
| Rh1—P13 | 2.2704 (7) | 2.2635 (6) | 2.275 (1) | 2.281 (2) |
| Rh1—C14 | 1.812 (3) | 1.807 (2) | 1.784 (5) | 1.804 (3) |
| C14—O14 | 1.147 (3) | 1.152 (3) | 1.142 (7) | 1.148 (4) |
| N11⋯O12 | 2.885 (3) | 2.885 (3) | 2.826 (6) | 2.841 (3) |
| N11—Rh1—O12 | 89.31 (9) | 89.54 (8) | 87.4 (1) | 87.95 (8) |
| O12—Rh1—P13 | 85.95 (6) | 84.97 (5) | 89.7 (1) | 89.91 (5) |
| P13—Rh1—C14 | 91.57 (9) | 91.87 (7) | 90.3 (2) | 89.48 (9) |
| N11—Rh1—C14 | 93.1 (1) | 93.6 (1) | 92.6 (2) | 92.6 (1) |
| N11—C2—C4—O12 | −2.6 (2) | 4.1 (2) | 1.2 (4) | 1.5 (2) |
| θE e | 155.77 (2) | 156.39 (3) | 156.0 (2) | 156.23 (4) |
Acknowledgments
Financial assistance from the University of the Free State is gratefully acknowledged, while Mr Leo Kirsten is thanked for the data collection. We also express our gratitude to SASOL and the South African National Research Foundation (SA-NRF/THRIP) for financial support of this project. Part of this material is based on work supported by the SA-NRF/THRIP under grant No. GUN 2068915. Opinions, findings, conclusions or recommendations expressed in this material are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the SA-NRF.
supplementary crystallographic information
Comment
Rhodium(I) dicarbonyl complexes of the type [Rh(L,L')(CO)2] containing chelating mono-anionic bidentate (L,L') ligands coordinated to rhodium via (O,O) donor atoms have been studied as catalyst precursors (Cornils & Herrmann, 1996; Trzeciak et al., 1994; Van Rooy et al., 1995). The investigation of these complexes is followed by complexes containing bidentate β-enaminoketonato ligands such as 4-(phenylamino)pent-3-en-2-onato (Phony) (Shaheen et al., 2006) coordinated to rhodium via (N,O) donor atoms. It was suggested that only one CO-group in a [Rh(N,O-bid)(CO)2]-type complex will be substituted by triphenyl phosphine, with the product being one of two possible isomers (Bonati & Wilkinson, 1964). Since the N-donor atom has a larger trans-influence than the O-atom, the CO-group trans to the N-atom will be substituted. This is evident in the title compound, (I), where [Rh(2,6-diMe-Phony)(CO)(PPh3)] is formed by the substitution of the carbonyl ligand in the dicarbonyl rhodium(I) complex [Rh(2,6-diMe-Phony)(CO)2] by PPh3.
In the title complex (Fig. 1), the bond distances involving rhodium differ significantly from the distances in related complexes, with the exception of [Rh(2,3-diMe-Phony)(CO)(PPh3)] (Venter et al., 2009), wherein all angles and distances are comparable to (I) (Table 2). The distance, Rh—N, in (I) is longer than in similar complexes while the Rh—O bond distance is shorter. This is due to the steric influence of the phenyl group connected to nitrogen in the title compound, as opposed to the hydrogen in the related complexes. The Rh—C and the carbonyl C—O distances are comparable with those distances in the related complexes (Table 2). The N—Rh—O bite angle is slightly larger than that observed in similar complexes found in the literature. The effective cone angle, θE, (Tolman, 1977) of 155.77 (2)° is similar to the angles in the related compounds. The acetone solvate was disordered and was located about an inversion center. Intermolecular and intramolecular hydrogen bonds of the type C—H···O are observed in the structure.
Experimental
To a 5 ml acetone solution of [Rh(2,6-diMe-Phony)(CO)2] (0.0302 g, 83.61 µmol) was added PPh3 (0.0219 g, 83.50 µmol) resulting in an immediate evolution of gas with the formation of the title compound. Crystallization from acetone produced yellow crystals of (I) in quantitative (0.0516 g, 100%) yield. IR (KBr): νCO 1971.1 s cm-1.
Refinement
The methyl and aromatic H atoms were placed in geometrically idealized positions and constrained to ride on their parent atoms, with C—H = 0.95 and 0.98 Å and Uiso(H) = 1.5Ueq(C) and 1.2Ueq(C), respectively. The methyl groups were generated to fit the difference electron density and the groups were then refined as rigid rotors. The acetone solvate was disordered about inversion center. The highest residual electron- density peak in the final difference map was located 0.65Å from H316 and was essentially meaningless.
Figures
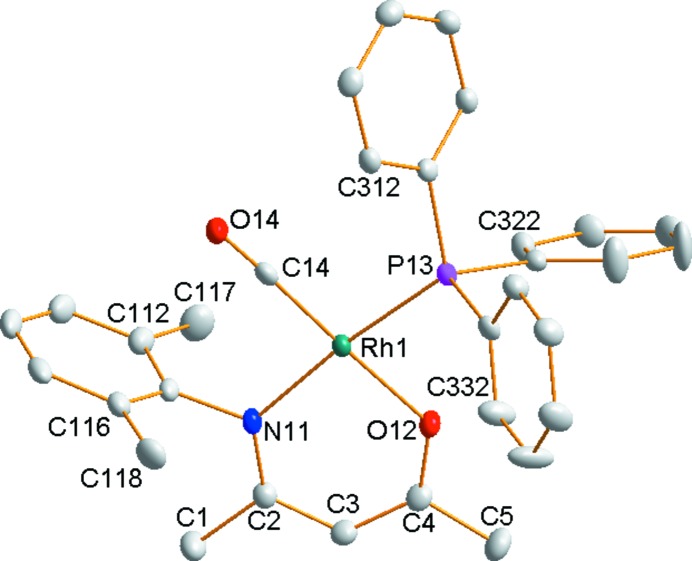
Fig. 1.
Molecular structure of the title compound. Displacement ellipsoids are drawn at the 50% probability displacement level. H atoms and disordered solvate molecule have been omitted for clarity.
Fig. 2.
A view of the unit cell of (I) illustrating the C—H···O interactions; hydrogen atoms have been omitted for clarity.
Crystal data
| [Rh(C13H16NO)(C18H15P)(CO)]·0.5C3H6O | F(000) = 1288 |
| Mr = 624.5 | Dx = 1.389 Mg m−3 |
| Monoclinic, P21/c | Mo Kα radiation, λ = 0.71073 Å |
| Hall symbol: -P 2ybc | Cell parameters from 6670 reflections |
| a = 16.8558 (8) Å | θ = 2.5–28.2° |
| b = 11.4028 (5) Å | µ = 0.66 mm−1 |
| c = 16.4059 (8) Å | T = 100 K |
| β = 108.733 (1)° | Cuboid, yellow |
| V = 2986.2 (2) Å3 | 0.31 × 0.15 × 0.11 mm |
| Z = 4 |
Data collection
| Bruker X8 APEXII 4K Kappa CCD diffractometer | 7425 independent reflections |
| Radiation source: fine-focus sealed tube | 6081 reflections with > 2σI) |
| graphite | Rint = 0.042 |
| ω and φ scans | θmax = 28.3°, θmin = 1.3° |
| Absorption correction: multi-scan (SADABS; Bruker, 2004) | h = −21→22 |
| Tmin = 0.822, Tmax = 0.931 | k = −15→11 |
| 23158 measured reflections | l = −21→21 |
Refinement
| Refinement on F2 | Primary atom site location: structure-invariant direct methods |
| Least-squares matrix: full | Secondary atom site location: difference Fourier map |
| R[F2 > 2σ(F2)] = 0.038 | Hydrogen site location: inferred from neighbouring sites |
| wR(F2) = 0.112 | H-atom parameters constrained |
| S = 1.09 | w = 1/[σ2(Fo2) + (0.0577P)2 + 1.4787P] where P = (Fo2 + 2Fc2)/3 |
| 7425 reflections | (Δ/σ)max = 0.002 |
| 354 parameters | Δρmax = 1.54 e Å−3 |
| 1 restraint | Δρmin = −1.32 e Å−3 |
Special details
| Experimental. The intensity data was collected on a Bruker X8 ApexII 4 K Kappa CCD diffractometer using an exposure time of 60 s/frame. A total of 688 frames were collected with a frame width of 0.5° covering up to θ = 28.24° with 99.8% completeness accomplished. |
| Geometry. All e.s.d.'s (except the e.s.d. in the dihedral angle between two l.s. planes) are estimated using the full covariance matrix. The cell e.s.d.'s are taken into account individually in the estimation of e.s.d.'s in distances, angles and torsion angles; correlations between e.s.d.'s in cell parameters are only used when they are defined by crystal symmetry. An approximate (isotropic) treatment of cell e.s.d.'s is used for estimating e.s.d.'s involving l.s. planes. |
Fractional atomic coordinates and isotropic or equivalent isotropic displacement parameters (Å2)
| x | y | z | Uiso*/Ueq | Occ. (<1) | |
| C1 | 0.7144 (2) | 0.7625 (3) | 0.4744 (2) | 0.0257 (7) | |
| H1A | 0.7697 | 0.7807 | 0.5152 | 0.039* | |
| H1B | 0.6712 | 0.7804 | 0.5007 | 0.039* | |
| H1C | 0.7048 | 0.8097 | 0.4222 | 0.039* | |
| C2 | 0.71032 (17) | 0.6337 (2) | 0.45128 (18) | 0.0168 (5) | |
| C3 | 0.65757 (17) | 0.5637 (2) | 0.48382 (18) | 0.0183 (6) | |
| H3 | 0.6324 | 0.6017 | 0.5209 | 0.022* | |
| C4 | 0.63880 (17) | 0.4461 (2) | 0.46740 (19) | 0.0180 (6) | |
| C5 | 0.57863 (19) | 0.3856 (3) | 0.5045 (2) | 0.0265 (7) | |
| H5A | 0.5288 | 0.3609 | 0.4577 | 0.04* | |
| H5B | 0.5621 | 0.4399 | 0.5425 | 0.04* | |
| H5C | 0.6058 | 0.3167 | 0.5375 | 0.04* | |
| C14 | 0.84522 (17) | 0.4446 (2) | 0.32802 (17) | 0.0166 (5) | |
| C111 | 0.80357 (17) | 0.6734 (2) | 0.37352 (18) | 0.0164 (5) | |
| C112 | 0.76869 (19) | 0.7250 (2) | 0.2919 (2) | 0.0223 (6) | |
| C113 | 0.8183 (2) | 0.8000 (3) | 0.2624 (2) | 0.0271 (7) | |
| H113 | 0.7952 | 0.8365 | 0.2078 | 0.033* | |
| C114 | 0.9008 (2) | 0.8226 (2) | 0.3109 (2) | 0.0292 (7) | |
| H114 | 0.9338 | 0.8746 | 0.2897 | 0.035* | |
| C115 | 0.93503 (19) | 0.7690 (2) | 0.3902 (2) | 0.0242 (6) | |
| H115 | 0.9919 | 0.7836 | 0.4228 | 0.029* | |
| C116 | 0.88743 (18) | 0.6938 (2) | 0.42310 (19) | 0.0194 (6) | |
| C117 | 0.6798 (2) | 0.6980 (3) | 0.2380 (2) | 0.0318 (7) | |
| H11A | 0.6667 | 0.7385 | 0.1826 | 0.048* | |
| H11B | 0.6414 | 0.7247 | 0.2682 | 0.048* | |
| H11C | 0.6734 | 0.6132 | 0.2283 | 0.048* | |
| C118 | 0.92484 (19) | 0.6332 (3) | 0.5082 (2) | 0.0257 (7) | |
| H11D | 0.9859 | 0.6413 | 0.5269 | 0.039* | |
| H11E | 0.9099 | 0.5499 | 0.5021 | 0.039* | |
| H11F | 0.9031 | 0.6689 | 0.551 | 0.039* | |
| C311 | 0.82259 (17) | 0.1691 (2) | 0.27715 (17) | 0.0149 (5) | |
| C312 | 0.90839 (17) | 0.1910 (2) | 0.30147 (18) | 0.0168 (5) | |
| H312 | 0.9352 | 0.2308 | 0.354 | 0.02* | |
| C313 | 0.95533 (17) | 0.1553 (2) | 0.24967 (19) | 0.0193 (6) | |
| H313 | 1.0138 | 0.1707 | 0.267 | 0.023* | |
| C314 | 0.91660 (18) | 0.0976 (2) | 0.17315 (19) | 0.0212 (6) | |
| H314 | 0.9483 | 0.0736 | 0.1375 | 0.025* | |
| C315 | 0.83113 (18) | 0.0749 (2) | 0.14845 (19) | 0.0190 (6) | |
| H315 | 0.8045 | 0.035 | 0.0959 | 0.023* | |
| C316 | 0.78449 (17) | 0.1103 (2) | 0.20019 (18) | 0.0168 (5) | |
| H316 | 0.7261 | 0.0943 | 0.1829 | 0.02* | |
| C321 | 0.66208 (17) | 0.1553 (2) | 0.30122 (17) | 0.0153 (5) | |
| C322 | 0.59944 (17) | 0.2176 (2) | 0.24164 (19) | 0.0202 (6) | |
| H322 | 0.6093 | 0.296 | 0.2279 | 0.024* | |
| C323 | 0.52197 (18) | 0.1657 (3) | 0.2017 (2) | 0.0243 (6) | |
| H323 | 0.4799 | 0.208 | 0.1594 | 0.029* | |
| C324 | 0.50573 (19) | 0.0534 (3) | 0.2231 (2) | 0.0260 (7) | |
| H324 | 0.4523 | 0.019 | 0.1966 | 0.031* | |
| C325 | 0.5676 (2) | −0.0085 (3) | 0.2829 (2) | 0.0386 (9) | |
| H325 | 0.557 | −0.086 | 0.2979 | 0.046* | |
| C326 | 0.6459 (2) | 0.0424 (3) | 0.3217 (2) | 0.0335 (8) | |
| H326 | 0.6884 | −0.001 | 0.3627 | 0.04* | |
| C331 | 0.81170 (17) | 0.1399 (2) | 0.44688 (17) | 0.0156 (5) | |
| C332 | 0.7927 (2) | 0.1752 (3) | 0.51929 (19) | 0.0266 (7) | |
| H332 | 0.7579 | 0.2416 | 0.5163 | 0.032* | |
| C333 | 0.8240 (2) | 0.1144 (3) | 0.5959 (2) | 0.0334 (8) | |
| H333 | 0.8091 | 0.1378 | 0.6447 | 0.04* | |
| C334 | 0.8770 (2) | 0.0196 (3) | 0.60188 (19) | 0.0263 (7) | |
| H334 | 0.8999 | −0.0205 | 0.655 | 0.032* | |
| C335 | 0.89635 (18) | −0.0163 (2) | 0.53013 (19) | 0.0222 (6) | |
| H335 | 0.932 | −0.082 | 0.5339 | 0.027* | |
| C336 | 0.86407 (18) | 0.0429 (2) | 0.45242 (19) | 0.0196 (6) | |
| H336 | 0.8775 | 0.0176 | 0.4032 | 0.024* | |
| N11 | 0.75420 (14) | 0.59212 (18) | 0.40401 (15) | 0.0148 (5) | |
| O12 | 0.66821 (11) | 0.37910 (16) | 0.42069 (13) | 0.0174 (4) | |
| O14 | 0.90058 (13) | 0.46375 (18) | 0.30306 (13) | 0.0225 (4) | |
| P13 | 0.76530 (4) | 0.22182 (6) | 0.34722 (4) | 0.01315 (15) | |
| Rh1 | 0.761010 (12) | 0.417429 (17) | 0.371227 (13) | 0.01263 (8) | |
| O01 | 0.4759 (6) | 0.3631 (7) | 0.0331 (6) | 0.0963 (16) | 0.5 |
| C01 | 0.4182 (4) | 0.5252 (5) | −0.0389 (4) | 0.0963 (16) | |
| H01A | 0.366 | 0.4813 | −0.0482 | 0.144* | |
| H01B | 0.4236 | 0.5472 | −0.0946 | 0.144* | |
| H01C | 0.4173 | 0.5961 | −0.0055 | 0.144* | |
| C02 | 0.4899 (9) | 0.4513 (10) | 0.0086 (9) | 0.0963 (16) | 0.5 |
Atomic displacement parameters (Å2)
| U11 | U22 | U33 | U12 | U13 | U23 | |
| C1 | 0.0290 (16) | 0.0158 (14) | 0.0378 (18) | 0.0010 (12) | 0.0183 (14) | −0.0024 (13) |
| C2 | 0.0145 (13) | 0.0149 (13) | 0.0204 (14) | 0.0019 (10) | 0.0049 (11) | 0.0014 (10) |
| C3 | 0.0165 (13) | 0.0185 (13) | 0.0215 (14) | 0.0041 (11) | 0.0082 (11) | 0.0009 (11) |
| C4 | 0.0127 (13) | 0.0192 (13) | 0.0220 (14) | 0.0039 (10) | 0.0056 (11) | 0.0037 (11) |
| C5 | 0.0233 (15) | 0.0239 (15) | 0.0378 (18) | −0.0002 (12) | 0.0176 (14) | 0.0045 (13) |
| C14 | 0.0190 (14) | 0.0134 (12) | 0.0157 (13) | −0.0017 (10) | 0.0032 (11) | −0.0036 (10) |
| C111 | 0.0206 (14) | 0.0097 (12) | 0.0224 (14) | −0.0009 (10) | 0.0118 (12) | −0.0016 (10) |
| C112 | 0.0273 (15) | 0.0152 (13) | 0.0279 (16) | 0.0027 (11) | 0.0137 (13) | 0.0022 (11) |
| C113 | 0.0408 (19) | 0.0149 (13) | 0.0312 (17) | 0.0020 (13) | 0.0193 (15) | 0.0041 (12) |
| C114 | 0.0410 (19) | 0.0138 (14) | 0.043 (2) | −0.0063 (13) | 0.0286 (16) | −0.0043 (13) |
| C115 | 0.0243 (15) | 0.0173 (14) | 0.0375 (18) | −0.0055 (11) | 0.0189 (14) | −0.0117 (12) |
| C116 | 0.0220 (14) | 0.0136 (12) | 0.0242 (15) | −0.0014 (11) | 0.0099 (12) | −0.0038 (11) |
| C117 | 0.0293 (17) | 0.0335 (17) | 0.0289 (17) | 0.0046 (14) | 0.0043 (14) | 0.0104 (14) |
| C118 | 0.0217 (15) | 0.0267 (16) | 0.0243 (16) | −0.0035 (12) | 0.0013 (13) | −0.0047 (12) |
| C311 | 0.0186 (13) | 0.0098 (12) | 0.0171 (13) | 0.0012 (10) | 0.0066 (11) | 0.0014 (10) |
| C312 | 0.0165 (13) | 0.0147 (12) | 0.0180 (13) | −0.0017 (10) | 0.0037 (11) | −0.0003 (10) |
| C313 | 0.0138 (13) | 0.0189 (13) | 0.0249 (15) | 0.0030 (11) | 0.0059 (11) | 0.0037 (11) |
| C314 | 0.0225 (15) | 0.0196 (14) | 0.0242 (15) | 0.0043 (11) | 0.0112 (13) | 0.0025 (11) |
| C315 | 0.0211 (14) | 0.0176 (13) | 0.0180 (14) | −0.0002 (11) | 0.0060 (12) | −0.0023 (10) |
| C316 | 0.0165 (13) | 0.0143 (12) | 0.0187 (14) | −0.0012 (10) | 0.0041 (11) | −0.0001 (10) |
| C321 | 0.0159 (13) | 0.0149 (12) | 0.0163 (13) | −0.0011 (10) | 0.0067 (11) | −0.0025 (10) |
| C322 | 0.0173 (14) | 0.0168 (13) | 0.0251 (15) | −0.0012 (11) | 0.0049 (12) | −0.0008 (11) |
| C323 | 0.0155 (14) | 0.0265 (16) | 0.0261 (16) | 0.0030 (12) | 0.0001 (12) | 0.0001 (12) |
| C324 | 0.0166 (14) | 0.0312 (16) | 0.0283 (16) | −0.0067 (12) | 0.0045 (13) | −0.0052 (13) |
| C325 | 0.0317 (18) | 0.0261 (17) | 0.048 (2) | −0.0167 (14) | −0.0006 (16) | 0.0098 (15) |
| C326 | 0.0249 (16) | 0.0237 (16) | 0.041 (2) | −0.0047 (13) | −0.0047 (15) | 0.0129 (14) |
| C331 | 0.0162 (13) | 0.0134 (12) | 0.0147 (13) | −0.0016 (10) | 0.0014 (11) | −0.0017 (10) |
| C332 | 0.0368 (18) | 0.0224 (15) | 0.0195 (15) | 0.0132 (13) | 0.0077 (13) | 0.0011 (12) |
| C333 | 0.054 (2) | 0.0313 (17) | 0.0153 (15) | 0.0234 (16) | 0.0113 (15) | 0.0034 (13) |
| C334 | 0.0340 (17) | 0.0214 (15) | 0.0188 (15) | 0.0074 (13) | 0.0022 (13) | 0.0031 (12) |
| C335 | 0.0246 (15) | 0.0168 (14) | 0.0233 (15) | 0.0049 (11) | 0.0052 (12) | 0.0005 (11) |
| C336 | 0.0220 (14) | 0.0160 (13) | 0.0213 (14) | 0.0013 (11) | 0.0075 (12) | −0.0017 (11) |
| N11 | 0.0142 (11) | 0.0107 (10) | 0.0191 (12) | −0.0009 (8) | 0.0049 (9) | 0.0012 (8) |
| O12 | 0.0152 (9) | 0.0148 (9) | 0.0242 (10) | −0.0008 (8) | 0.0091 (8) | 0.0014 (8) |
| O14 | 0.0261 (11) | 0.0180 (10) | 0.0280 (11) | −0.0059 (8) | 0.0152 (9) | −0.0034 (8) |
| P13 | 0.0123 (3) | 0.0117 (3) | 0.0142 (3) | −0.0008 (2) | 0.0027 (3) | −0.0002 (2) |
| Rh1 | 0.01250 (12) | 0.01060 (11) | 0.01490 (12) | −0.00047 (7) | 0.00457 (8) | 0.00021 (7) |
| O01 | 0.139 (5) | 0.057 (3) | 0.104 (4) | −0.010 (3) | 0.054 (4) | 0.007 (2) |
| C01 | 0.139 (5) | 0.057 (3) | 0.104 (4) | −0.010 (3) | 0.054 (4) | 0.007 (2) |
| C02 | 0.139 (5) | 0.057 (3) | 0.104 (4) | −0.010 (3) | 0.054 (4) | 0.007 (2) |
Geometric parameters (Å, °)
| C1—C2 | 1.513 (4) | C313—H313 | 0.95 |
| C1—H1A | 0.98 | C314—C315 | 1.390 (4) |
| C1—H1B | 0.98 | C314—H314 | 0.95 |
| C1—H1C | 0.98 | C315—C316 | 1.389 (4) |
| C2—N11 | 1.320 (4) | C315—H315 | 0.95 |
| C2—C3 | 1.420 (4) | C316—H316 | 0.95 |
| C3—C4 | 1.384 (4) | C321—C326 | 1.380 (4) |
| C3—H3 | 0.95 | C321—C322 | 1.383 (4) |
| C4—O12 | 1.289 (3) | C321—P13 | 1.824 (3) |
| C4—C5 | 1.507 (4) | C322—C323 | 1.391 (4) |
| C5—H5A | 0.98 | C322—H322 | 0.95 |
| C5—H5B | 0.98 | C323—C324 | 1.378 (4) |
| C5—H5C | 0.98 | C323—H323 | 0.95 |
| C14—O14 | 1.154 (3) | C324—C325 | 1.375 (4) |
| C14—Rh1 | 1.805 (3) | C324—H324 | 0.95 |
| C111—C116 | 1.405 (4) | C325—C326 | 1.394 (4) |
| C111—C112 | 1.406 (4) | C325—H325 | 0.95 |
| C111—N11 | 1.439 (3) | C326—H326 | 0.95 |
| C112—C113 | 1.387 (4) | C331—C332 | 1.385 (4) |
| C112—C117 | 1.507 (4) | C331—C336 | 1.400 (4) |
| C113—C114 | 1.388 (5) | C331—P13 | 1.827 (3) |
| C113—H113 | 0.95 | C332—C333 | 1.383 (4) |
| C114—C115 | 1.385 (5) | C332—H332 | 0.95 |
| C114—H114 | 0.95 | C333—C334 | 1.386 (4) |
| C115—C116 | 1.396 (4) | C333—H333 | 0.95 |
| C115—H115 | 0.95 | C334—C335 | 1.380 (4) |
| C116—C118 | 1.503 (4) | C334—H334 | 0.95 |
| C117—H11A | 0.98 | C335—C336 | 1.390 (4) |
| C117—H11B | 0.98 | C335—H335 | 0.95 |
| C117—H11C | 0.98 | C336—H336 | 0.95 |
| C118—H11D | 0.98 | N11—Rh1 | 2.076 (2) |
| C118—H11E | 0.98 | O12—Rh1 | 2.0277 (19) |
| C118—H11F | 0.98 | P13—Rh1 | 2.2701 (7) |
| C311—C316 | 1.391 (4) | O01—C02 | 1.135 (12) |
| C311—C312 | 1.394 (4) | C01—C02 | 1.474 (13) |
| C311—P13 | 1.825 (3) | C01—H01A | 0.98 |
| C312—C313 | 1.395 (4) | C01—H01B | 0.98 |
| C312—H312 | 0.95 | C01—H01C | 0.98 |
| C313—C314 | 1.382 (4) | C02—C01i | 1.492 (16) |
| C2—C1—H1A | 109.5 | C314—C315—H315 | 119.8 |
| C2—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C315—C316—C311 | 120.5 (3) |
| H1A—C1—H1B | 109.5 | C315—C316—H316 | 119.7 |
| C2—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C311—C316—H316 | 119.7 |
| H1A—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C326—C321—C322 | 119.0 (3) |
| H1B—C1—H1C | 109.5 | C326—C321—P13 | 121.6 (2) |
| N11—C2—C3 | 123.8 (2) | C322—C321—P13 | 119.3 (2) |
| N11—C2—C1 | 120.5 (2) | C321—C322—C323 | 120.2 (3) |
| C3—C2—C1 | 115.8 (2) | C321—C322—H322 | 119.9 |
| C4—C3—C2 | 127.1 (3) | C323—C322—H322 | 119.9 |
| C4—C3—H3 | 116.5 | C324—C323—C322 | 120.6 (3) |
| C2—C3—H3 | 116.5 | C324—C323—H323 | 119.7 |
| O12—C4—C3 | 125.6 (3) | C322—C323—H323 | 119.7 |
| O12—C4—C5 | 113.9 (2) | C325—C324—C323 | 119.4 (3) |
| C3—C4—C5 | 120.4 (3) | C325—C324—H324 | 120.3 |
| C4—C5—H5A | 109.5 | C323—C324—H324 | 120.3 |
| C4—C5—H5B | 109.5 | C324—C325—C326 | 120.1 (3) |
| H5A—C5—H5B | 109.5 | C324—C325—H325 | 119.9 |
| C4—C5—H5C | 109.5 | C326—C325—H325 | 119.9 |
| H5A—C5—H5C | 109.5 | C321—C326—C325 | 120.6 (3) |
| H5B—C5—H5C | 109.5 | C321—C326—H326 | 119.7 |
| O14—C14—Rh1 | 177.7 (2) | C325—C326—H326 | 119.7 |
| C116—C111—C112 | 121.1 (3) | C332—C331—C336 | 119.2 (3) |
| C116—C111—N11 | 119.5 (2) | C332—C331—P13 | 117.9 (2) |
| C112—C111—N11 | 119.3 (2) | C336—C331—P13 | 122.8 (2) |
| C113—C112—C111 | 118.4 (3) | C333—C332—C331 | 120.5 (3) |
| C113—C112—C117 | 121.2 (3) | C333—C332—H332 | 119.7 |
| C111—C112—C117 | 120.4 (3) | C331—C332—H332 | 119.7 |
| C112—C113—C114 | 121.3 (3) | C332—C333—C334 | 120.3 (3) |
| C112—C113—H113 | 119.3 | C332—C333—H333 | 119.9 |
| C114—C113—H113 | 119.3 | C334—C333—H333 | 119.9 |
| C115—C114—C113 | 119.6 (3) | C335—C334—C333 | 119.6 (3) |
| C115—C114—H114 | 120.2 | C335—C334—H334 | 120.2 |
| C113—C114—H114 | 120.2 | C333—C334—H334 | 120.2 |
| C114—C115—C116 | 121.2 (3) | C334—C335—C336 | 120.5 (3) |
| C114—C115—H115 | 119.4 | C334—C335—H335 | 119.7 |
| C116—C115—H115 | 119.4 | C336—C335—H335 | 119.7 |
| C115—C116—C111 | 118.3 (3) | C335—C336—C331 | 119.8 (3) |
| C115—C116—C118 | 121.3 (3) | C335—C336—H336 | 120.1 |
| C111—C116—C118 | 120.4 (3) | C331—C336—H336 | 120.1 |
| C112—C117—H11A | 109.5 | C2—N11—C111 | 118.0 (2) |
| C112—C117—H11B | 109.5 | C2—N11—Rh1 | 125.79 (18) |
| H11A—C117—H11B | 109.5 | C111—N11—Rh1 | 116.24 (17) |
| C112—C117—H11C | 109.5 | C4—O12—Rh1 | 127.13 (18) |
| H11A—C117—H11C | 109.5 | C311—P13—C321 | 103.27 (12) |
| H11B—C117—H11C | 109.5 | C311—P13—C331 | 103.55 (12) |
| C116—C118—H11D | 109.5 | C321—P13—C331 | 103.59 (12) |
| C116—C118—H11E | 109.5 | C311—P13—Rh1 | 119.08 (9) |
| H11D—C118—H11E | 109.5 | C321—P13—Rh1 | 113.64 (9) |
| C116—C118—H11F | 109.5 | C331—P13—Rh1 | 112.06 (9) |
| H11D—C118—H11F | 109.5 | C14—Rh1—O12 | 177.36 (10) |
| H11E—C118—H11F | 109.5 | C14—Rh1—N11 | 93.02 (11) |
| C316—C311—C312 | 118.7 (3) | O12—Rh1—N11 | 89.38 (8) |
| C316—C311—P13 | 123.2 (2) | C14—Rh1—P13 | 91.59 (9) |
| C312—C311—P13 | 118.1 (2) | O12—Rh1—P13 | 85.95 (6) |
| C311—C312—C313 | 120.8 (3) | N11—Rh1—P13 | 174.36 (7) |
| C311—C312—H312 | 119.6 | C02—C01—H01A | 109.5 |
| C313—C312—H312 | 119.6 | C02—C01—H01B | 109.5 |
| C314—C313—C312 | 119.8 (3) | H01A—C01—H01B | 109.5 |
| C314—C313—H313 | 120.1 | C02—C01—H01C | 109.5 |
| C312—C313—H313 | 120.1 | H01A—C01—H01C | 109.5 |
| C313—C314—C315 | 119.8 (3) | H01B—C01—H01C | 109.5 |
| C313—C314—H314 | 120.1 | O01—C02—C01 | 117.7 (13) |
| C315—C314—H314 | 120.1 | O01—C02—C01i | 110.6 (12) |
| C316—C315—C314 | 120.3 (3) | C01—C02—C01i | 131.4 (9) |
| C316—C315—H315 | 119.8 | ||
| N11—C2—C3—C4 | −4.8 (5) | P13—C331—C336—C335 | −179.2 (2) |
| C1—C2—C3—C4 | 175.4 (3) | C3—C2—N11—C111 | 178.5 (3) |
| C2—C3—C4—O12 | 1.8 (5) | C1—C2—N11—C111 | −1.7 (4) |
| C2—C3—C4—C5 | −177.6 (3) | C3—C2—N11—Rh1 | −3.0 (4) |
| C116—C111—C112—C113 | −2.1 (4) | C1—C2—N11—Rh1 | 176.8 (2) |
| N11—C111—C112—C113 | −177.7 (3) | C116—C111—N11—C2 | 91.5 (3) |
| C116—C111—C112—C117 | 177.3 (3) | C112—C111—N11—C2 | −92.9 (3) |
| N11—C111—C112—C117 | 1.7 (4) | C116—C111—N11—Rh1 | −87.2 (3) |
| C111—C112—C113—C114 | 1.2 (4) | C112—C111—N11—Rh1 | 88.5 (3) |
| C117—C112—C113—C114 | −178.3 (3) | C3—C4—O12—Rh1 | 9.0 (4) |
| C112—C113—C114—C115 | 0.4 (5) | C5—C4—O12—Rh1 | −171.64 (18) |
| C113—C114—C115—C116 | −1.1 (4) | C316—C311—P13—C321 | 9.9 (3) |
| C114—C115—C116—C111 | 0.1 (4) | C312—C311—P13—C321 | −171.4 (2) |
| C114—C115—C116—C118 | 178.5 (3) | C316—C311—P13—C331 | 117.7 (2) |
| C112—C111—C116—C115 | 1.5 (4) | C312—C311—P13—C331 | −63.6 (2) |
| N11—C111—C116—C115 | 177.1 (2) | C316—C311—P13—Rh1 | −117.1 (2) |
| C112—C111—C116—C118 | −176.9 (3) | C312—C311—P13—Rh1 | 61.6 (2) |
| N11—C111—C116—C118 | −1.3 (4) | C326—C321—P13—C311 | 83.9 (3) |
| C316—C311—C312—C313 | 0.3 (4) | C322—C321—P13—C311 | −93.4 (2) |
| P13—C311—C312—C313 | −178.5 (2) | C326—C321—P13—C331 | −23.8 (3) |
| C311—C312—C313—C314 | 0.1 (4) | C322—C321—P13—C331 | 158.9 (2) |
| C312—C313—C314—C315 | −0.3 (4) | C326—C321—P13—Rh1 | −145.7 (2) |
| C313—C314—C315—C316 | 0.2 (4) | C322—C321—P13—Rh1 | 37.0 (2) |
| C314—C315—C316—C311 | 0.1 (4) | C332—C331—P13—C311 | 168.3 (2) |
| C312—C311—C316—C315 | −0.4 (4) | C336—C331—P13—C311 | −12.7 (3) |
| P13—C311—C316—C315 | 178.3 (2) | C332—C331—P13—C321 | −84.2 (2) |
| C326—C321—C322—C323 | −1.5 (4) | C336—C331—P13—C321 | 94.8 (3) |
| P13—C321—C322—C323 | 175.9 (2) | C332—C331—P13—Rh1 | 38.7 (3) |
| C321—C322—C323—C324 | 2.2 (5) | C336—C331—P13—Rh1 | −142.3 (2) |
| C322—C323—C324—C325 | −1.5 (5) | C4—O12—Rh1—N11 | −11.8 (2) |
| C323—C324—C325—C326 | 0.2 (6) | C4—O12—Rh1—P13 | 165.0 (2) |
| C322—C321—C326—C325 | 0.2 (5) | C2—N11—Rh1—C14 | −170.1 (2) |
| P13—C321—C326—C325 | −177.2 (3) | C111—N11—Rh1—C14 | 8.5 (2) |
| C324—C325—C326—C321 | 0.5 (6) | C2—N11—Rh1—O12 | 8.8 (2) |
| C336—C331—C332—C333 | −0.9 (5) | C111—N11—Rh1—O12 | −172.62 (19) |
| P13—C331—C332—C333 | 178.1 (3) | C311—P13—Rh1—C14 | −14.40 (13) |
| C331—C332—C333—C334 | 2.0 (5) | C321—P13—Rh1—C14 | −136.42 (13) |
| C332—C333—C334—C335 | −2.0 (5) | C331—P13—Rh1—C14 | 106.57 (13) |
| C333—C334—C335—C336 | 0.9 (5) | C311—P13—Rh1—O12 | 166.55 (12) |
| C334—C335—C336—C331 | 0.2 (4) | C321—P13—Rh1—O12 | 44.53 (11) |
| C332—C331—C336—C335 | −0.2 (4) | C331—P13—Rh1—O12 | −72.48 (11) |
Symmetry codes: (i) −x+1, −y+1, −z.
Hydrogen-bond geometry (Å, °)
| D—H···A | D—H | H···A | D···A | D—H···A |
| C332—H332···O12 | 0.95 | 2.38 | 3.201 (3) | 144 |
| C334—H334···O14ii | 0.95 | 2.51 | 3.201 (4) | 130 |
| C1—H1B···O01iii | 0.98 | 2.54 | 3.372 (9) | 142 |
Symmetry codes: (ii) x, −y+1/2, z+1/2; (iii) −x+1, y+1/2, −z+1/2.
Table 2 Comparative geometrical parameters (Å, °) for similar [Rh(N,O-bid)(CO)(PPh3)] complexes
| Parameters | (I)a | (II)b | (III)c | (IV)d |
| Rh1—N11 | 2.077 (2) | 2.069 (2) | 2.045 (4) | 2.045 (3) |
| Rh1—O12 | 2.027 (2) | 2.028 (2) | 2.044 (3) | 2.045 (2) |
| Rh1—P13 | 2.2704 (7) | 2.2635 (6) | 2.275 (1) | 2.281 (2) |
| Rh1—C14 | 1.812 (3) | 1.807 (2) | 1.784 (5) | 1.804 (3) |
| C14—O14 | 1.147 (3) | 1.152 (3) | 1.142 (7) | 1.148 (4) |
| N11···O12 | 2.885 (3) | 2.885 (3) | 2.826 (6) | 2.841 (3) |
| N11—Rh1—O12 | 89.31 (9) | 89.54 (8) | 87.4 (1) | 87.95 (8) |
| O12—Rh1—P13 | 85.95 (6) | 84.97 (5) | 89.7 (1) | 89.91 (5) |
| P13—Rh1—C14 | 91.57 (9) | 91.87 (7) | 90.3 (2) | 89.48 (9) |
| N11—Rh1—C14 | 93.1 (1) | 93.6 (1) | 92.6 (2) | 92.6 (1) |
| N11—C2—C4—O12 | -2.6 (2) | 4.1 (2) | 1.2 (4) | 1.5 (2) |
| θEe | 155.77 (2) | 156.39 (3) | 156.0 (2) | 156.23 (4) |
Notes: (a) This work; (b) N,O-bid = 4-(2,3-dimethyl phenylamino)pent-3-en-2-onato (Venter et al., 2009); (c) N,O-bid = 4-amino-pent-3-en-2-onato (Damoense et al., 1994); (d) N,O-bid = 4-amino-1,1,1-trifluoro-pent-3-en-2-onato (Varshavsky et al., 2001); (e) Tolman (1977).
Footnotes
Supplementary data and figures for this paper are available from the IUCr electronic archives (Reference: PV2227).
References
- Altomare, A., Burla, M. C., Camalli, M., Cascarano, G. L., Giacovazzo, C., Guagliardi, A., Moliterni, A. G. G., Polidori, G. & Spagna, R. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 115–119.
- Bonati, F. & Wilkinson, G. (1964). J. Chem. Soc. pp. 3156–3160.
- Brandenburg, K. & Putz, H. (2005). DIAMOND. Crystal Impact GbR, Bonn, Germany.
- Bruker (2004). SAINT-Plus and SADABS. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Bruker (2005). APEX2. Bruker AXS Inc., Madison, Wisconsin, USA.
- Cornils, B. & Herrmann, W. A. (1996). Applied Homogeneous Catalysis with Organometallic Compounds. A Comprehensive Handbook, pp. 412–413. Weinheim: VCH.
- Damoense, L. J., Purcell, W., Roodt, A. & Leipoldt, J. G. (1994). Rhodium Express, 5, 10–13.
- Farrugia, L. J. (1999). J. Appl. Cryst. 32, 837–838.
- Shaheen, F., Marchio, L., Badshah, A. & Khosa, M. K. (2006). Acta Cryst. E62, o873–o874.
- Sheldrick, G. M. (2008). Acta Cryst. A64, 112–122. [DOI] [PubMed]
- Tolman, C. A. (1977). Chem. Rev. 77, 313–348.
- Trzeciak, A. M. & Ziolkowski, J. J. (1994). J. Organomet. Chem. 464, 107–111.
- Van Rooy, A., Orji, E. N., Kramer, P. G. J. & Van Leeuwen, P. W. M. N. (1995). Organometallics 14, 34–43.
- Varshavsky, Y. S., Galding, M. R., Cherkasova, T. G., Podkorytov, I. S., Nikol’skii, A. B., Trzeciak, A. M., Olejnik, Z., Lis, T. & Ziolkowski, J. J. (2001). J. Organomet. Chem. 628, 195–210.
- Venter, G. J. S., Steyl, G. & Roodt, A. (2009). Acta Cryst. E65, m1321–m1322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Crystal structure: contains datablocks global, I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680904817X/pv2227sup1.cif
Structure factors: contains datablocks I. DOI: 10.1107/S160053680904817X/pv2227Isup2.hkl
Additional supplementary materials: crystallographic information; 3D view; checkCIF report