Abstract
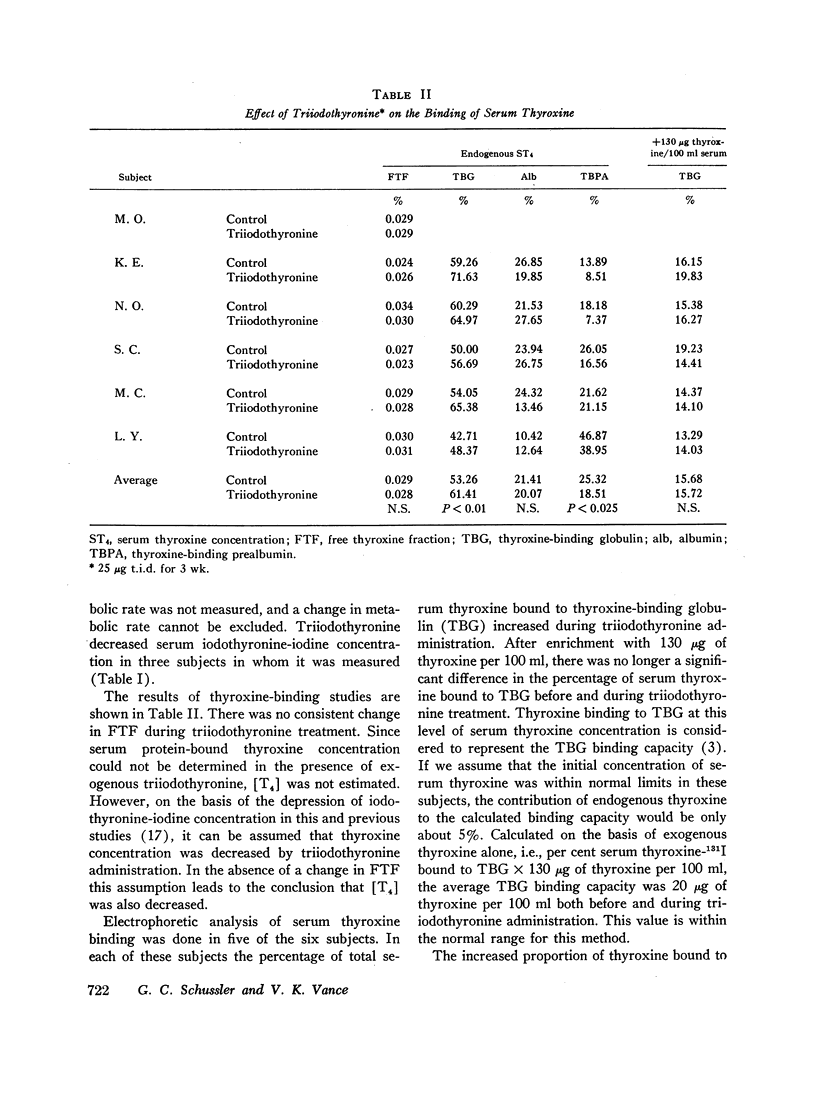
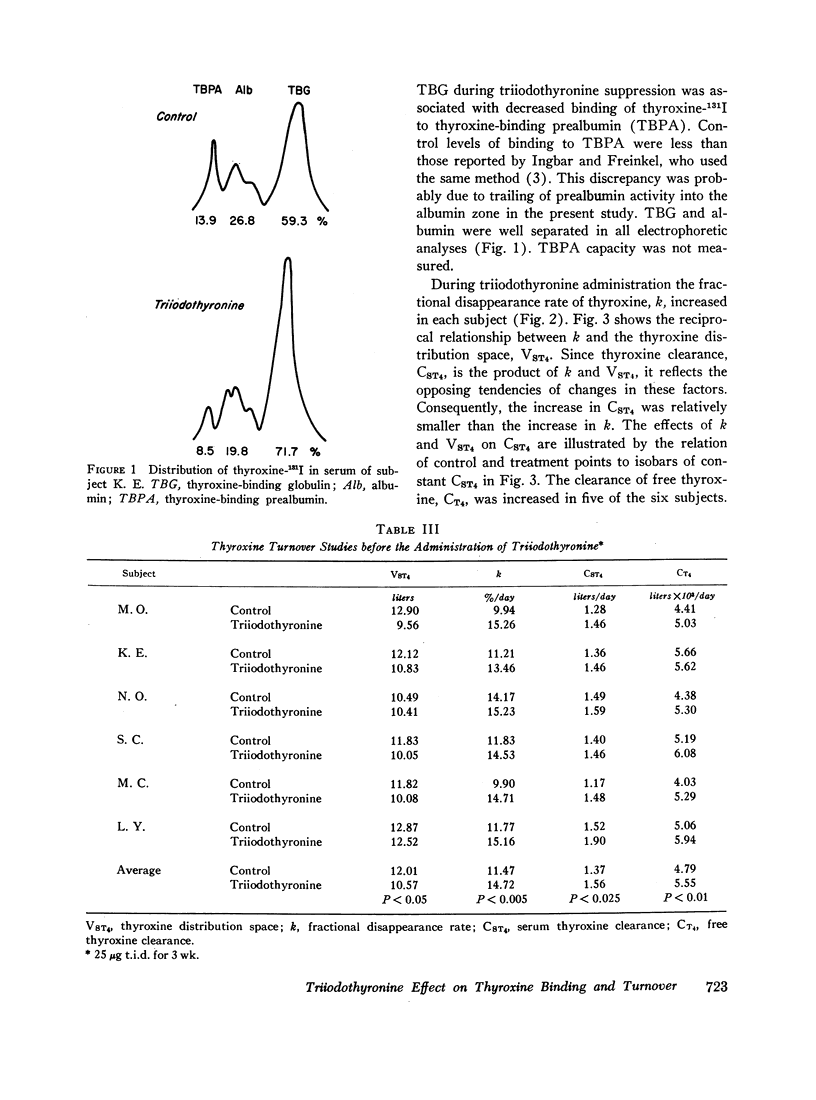
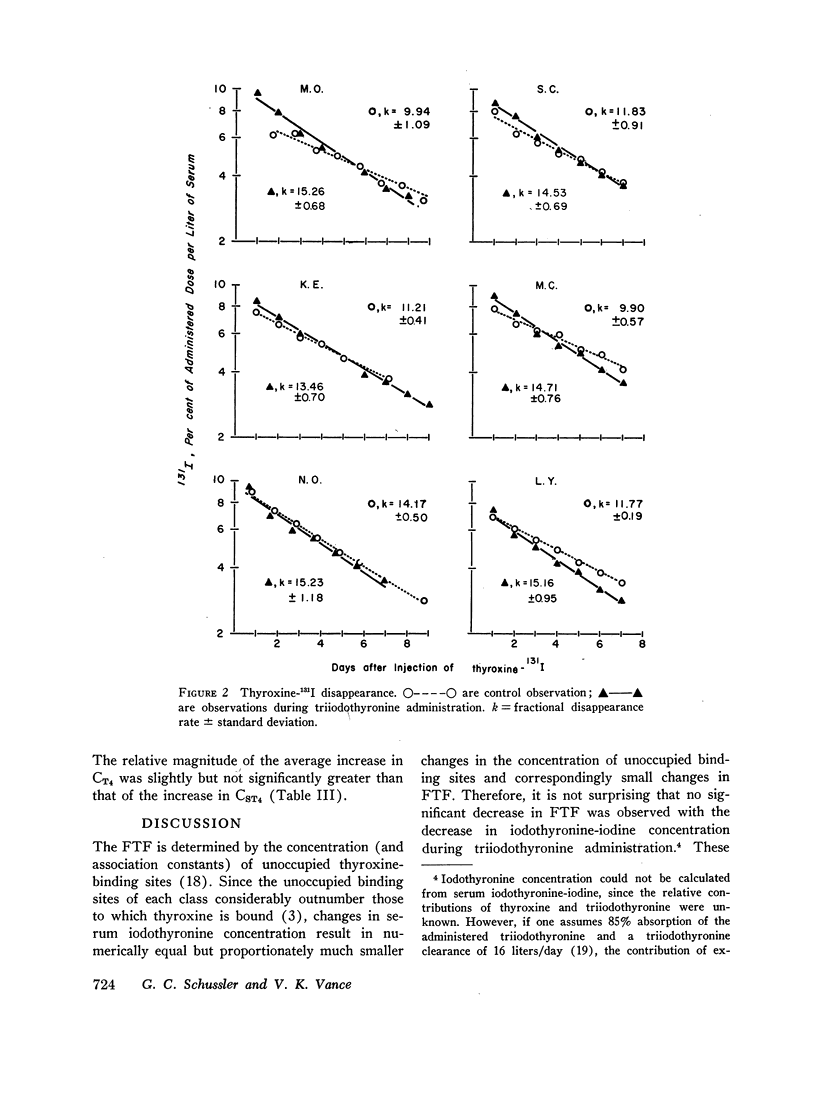
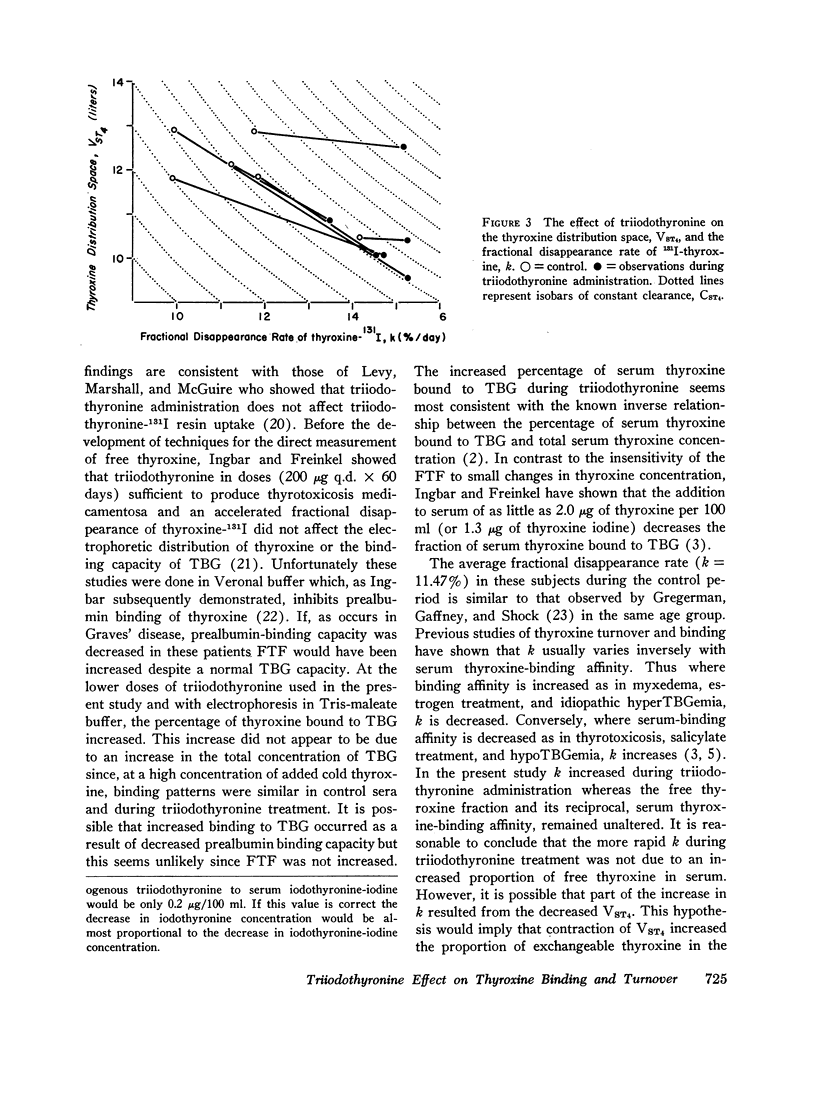
The relationship between free thyroxine concentration and thyroxine turnover was studied during thyroid suppression with triiodothyronine. Although there was some increase in the proportion of serum thyroxine bound to thyroxine-binding globulin, the ratio of ultrafilterable to protein-bound hormone was not significantly affected. The fractional disappearance rate of thyroxine increased from an average control value of 11.47%/day to 14.72%/day. Because of contraction of the thyroxine distribution space the clearance of thyroxine was less markedly affected, increasing from 1.37 to 1.56 liters/day. Since the ratio of thyroxine turnover to free thyroxine concentration, i.e., the free thyroxine clearance, increased proportionately (4.79-5.55 liters × 103/day) we conclude that triiodothyronine stimulates thyroxine clearance by a mechanism that is independent of effects on free thyroxine concentration.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anbar M., Guttmann S., Rodan G., Stein J. A. The determination of the rate of deiodination of thyroxine in human subjects. J Clin Invest. 1965 Dec;44(12):1986–1991. doi: 10.1172/JCI105305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein G., Hasen J., Oppenheimer J. H. Turnover of 131-I-thyroxine in patients subjected to surgical trauma. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 May;27(5):741–744. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-5-741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braverman L. W., Dawber N. A., Ingbar S. H. Observations concerning the binding of thyroid hormones in sera of normal subjects of varying ages. J Clin Invest. 1966 Aug;45(8):1273–1279. doi: 10.1172/JCI105434. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELGEE N. J., WILLIAMS R. H. Effects of thyroid function on insulin-I131 degradation. Am J Physiol. 1955 Jan;180(1):13–15. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.180.1.13. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER D. A., ODDIE T. H. WHOLE-BODY COUNTING OF 131-I-LABELED TRIIODOTHYRONINE. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Aug;24:733–739. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-8-733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREGERMAN R. I., GAFFNEY G. W., SHOCK N. W., CROWDER S. E. Thyroxine turnover in euthyroid man with special reference to changes with age. J Clin Invest. 1962 Nov;41:2065–2074. doi: 10.1172/JCI104664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGBAR S. H., FREINKEL N. Regulation of the peripheral metabolism of the thyroid hormones. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1960;16:353–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGBAR S. H., FREINKEL N. Simultaneous estimation of rates of thyroxine degradation and thyroid hormone synthesis. J Clin Invest. 1955 Jun;34(6):808–819. doi: 10.1172/JCI103136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGBAR S. H., FREINKEL N. Studies of thyroid function and the peripheral metabolism of I 131-labeled thyroxine in patients with treated Graves disease. J Clin Invest. 1958 Nov;37(11):1603–1614. doi: 10.1172/JCI103753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- INGBAR S. H. Observations concerning the binding of thyroid hormones by human serum prealbumin. J Clin Invest. 1963 Feb;42:143–160. doi: 10.1172/JCI104701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingbar S. H. CLINICAL AND PHYSIOLOGICAL OBSERVATIONS IN A PATIENT WITH AN IDIOPATHIC DECREASE IN THE THYROXINE-BINDING GLOBULIN OF PLASMA. J Clin Invest. 1961 Nov;40(11):2053–2063. doi: 10.1172/JCI104431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JABLONSKI J. R., NEILAN B., SUNDER J. H., ZARA C. C., MOSES C. Effects of dextro and levo-thyroxine and triiodothyronine on lipoprotein partition and red cell T3 I-131 uptake. Metabolism. 1962 Sep;11:935–939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVIN M. E., DAUGHADAY W. H. The influence of the thyroid on adrenocortical function. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1955 Dec;15(12):1499–1511. doi: 10.1210/jcem-15-12-1499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVY R. P., MARSHALL J. S., MCGUIRE W. L. THE EFFECT OF THYROXINE AND TRIIODOTHYRONINE TREATMENT ON THE RESIN UPTAKE OF I-131-THYROXINE AND TRIIODOTHYRONINE. Metabolism. 1964 Jun;13:557–561. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(64)90144-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MISRA S., HAMBURGER J. I. LIOTHYRONINE SUPPRESSION OF PROTEIN-BOUND IODINE: A TEST FOR HYPERTHYROIDISM IN PREGNANCY. Obstet Gynecol. 1965 Aug;26:165–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicoloff J. T., Dowling J. T. Estimation of thyroxine distribution in man. J Clin Invest. 1968 Jan;47(1):26–37. doi: 10.1172/JCI105712. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERSON R. E. The influence of the thyroid on adrenal cortical function. J Clin Invest. 1958 May;37(5):736–743. doi: 10.1172/JCI103659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RECANT L., RIGGS D. S. Thyroid function in nephrosis. J Clin Invest. 1952 Aug;31(8):789–797. doi: 10.1172/JCI102664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIGGS D. S. Quantitative aspects of iodine metabolism in man. Pharmacol Rev. 1952 Sep;4(3):284–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS J., RALL J. E. Proteins associated with the thyroid hormones. Physiol Rev. 1960 Jul;40:415–489. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1960.40.3.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBBINS J., RALL J. E. The interaction of thyroid hormones and protein in biological fluids. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1957;13:161–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHSCHILD M. A., BAUMAN A., YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. The effect of large doses of desiccated thyroid on the distribution and metabolism of albumin-I 131 in euthyroid subjects. J Clin Invest. 1957 Mar;36(3):422–428. doi: 10.1172/JCI103438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERLING K., CHODOS R. B. Radiothyroxine turnover studies in myxedema, thyrotoxicosis, and hypermetabolism without endocrine disease. J Clin Invest. 1956 Jul;35(7):806–813. doi: 10.1172/JCI103333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERLING K., LASHOF J. C., MAN E. B. Disappearance from serum of I131-labeled l-thyroxine and l-triiodothyronine in euthyroid subjects. J Clin Invest. 1954 Jul;33(7):1031–1035. doi: 10.1172/JCI102970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STERLING K. Radiothyroxine turnover studies in thyroid disease after therapy. J Clin Invest. 1958 Oct;37(10):1348–1356. doi: 10.1172/JCI103724. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schussler G. C., Plager J. E. Effect of preliminary purification of 131-I-thyroxine on the determination of free thyroxine in serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Feb;27(2):242–250. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-2-242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterling K., Brenner M. A. Free thyroxine in human serum: simplified measurement with the aid of magnesium precipitation. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jan;45(1):153–163. doi: 10.1172/JCI105320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpert E. M., Martinez M., Oppenheimer J. H. Radioiodinated impurities in commercial preparations of 131-I-thyroxine and their effect on the measurement of free thyroxine in human serum by equilibrium dialysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1967 Mar;27(3):421–428. doi: 10.1210/jcem-27-3-421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WERNER S. C., SPOONER M. A new and simple test for hyperthyroidism employing L-triiodothyronine and the twenty-four hour I-131 uptake method. Bull N Y Acad Med. 1955 Feb;31(2):137–145. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


