Abstract
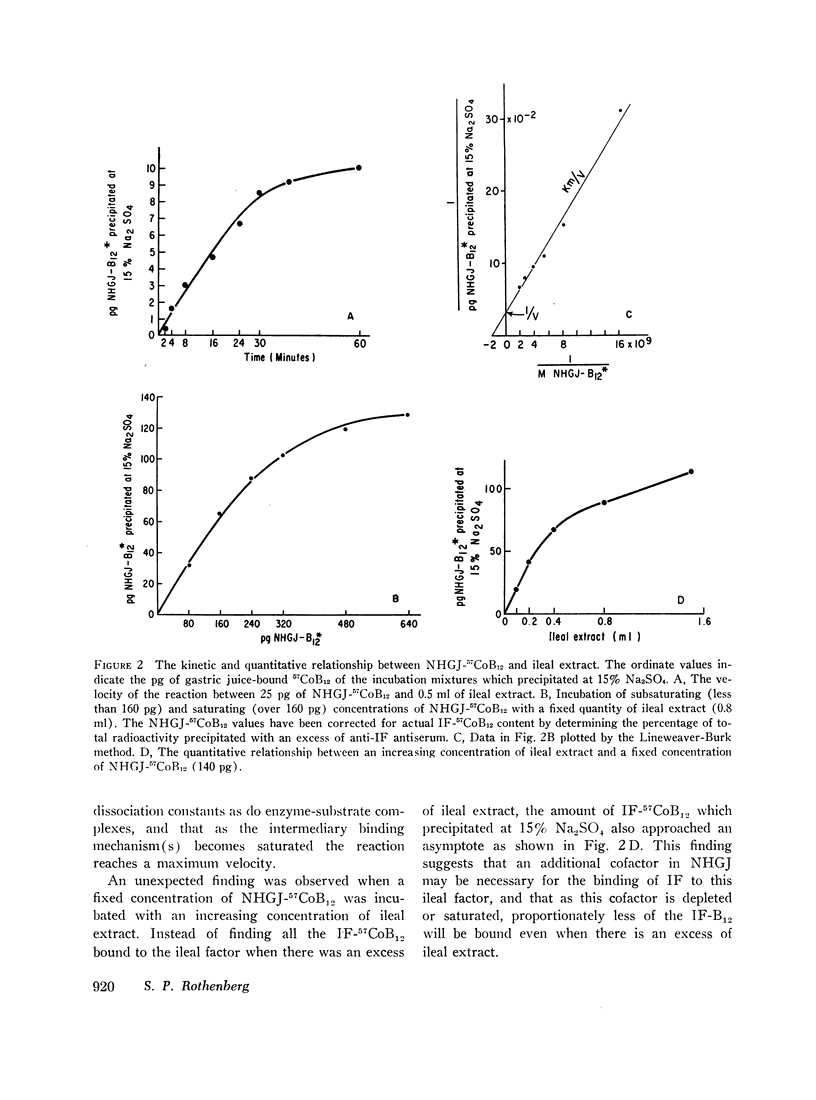
The precipitate which resulted when 57CoB12 bound to normal human gastric juice was subjected to a 15% concentration of Na2SO4 contained virtually no radioactivity. However, after in vivo incubation of the gastric juice-57CoB12 mixture in the distal ileum of the guinea pig, the dialyzed extract of the washed mucosa contained a fraction of 57CoB12 which was precipitated at 15% Na2SO4. In addition, in vitro incubation of gastric juice-57CoB12 with an extract of the ileal mucosa or brush border membranes also resulted in the formation of a 15% Na2SO4-insoluble fraction which contained 57CoB12. The formation of this 57CoB12-containing insoluble fraction did not occur or was diminished by (a) addition of an excess of B12-free normal human gastric juice. (b) reducing the incubation pH to 2, (c) incubating the mixture at 4°C, (d) pretreating the ileal extract at 56°C for 30 min, (e) incubating the reaction in sodium EDTA but not calcium EDTA, (f) incubating gastric juice-57CoB12 with an extract of jejunal mucosa. Sephadex gel filtration was used to demonstrate that the factor in the ileal extract which reacted with the gastric juice-57CoB12 filtered through G-100 and G-200 columns in the excluded volume.
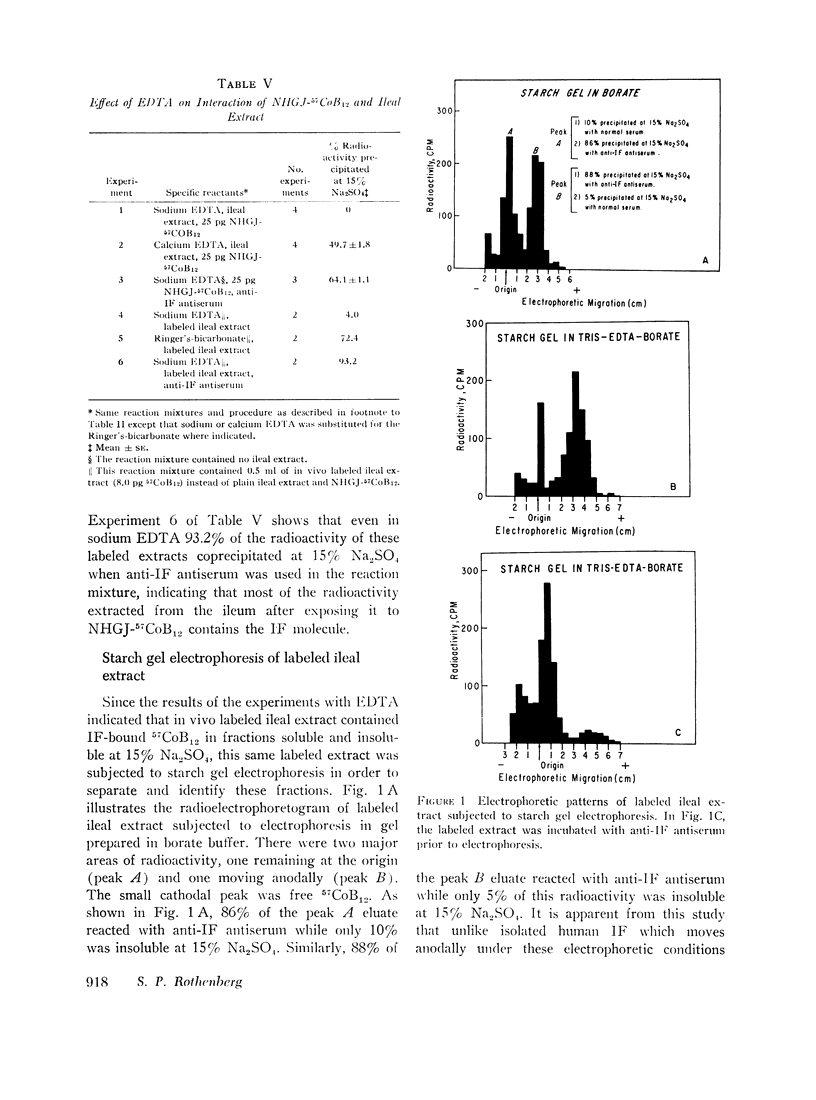
When the ileal extract obtained after in vivo incubation with gastric juice-57CoB12 was subjected to starch gel electrophoresis one peak of radioactivity remained at the origin and another moved anodally. Eluates of each peak reacted with anti-intrinsic factor antibody indicating that at least the immunologically reacting portion of the intrinsic factor molecule was present in two fractions with different electrophoretic mobility.
These studies indicate that immunologically intact intrinsic factor can be extracted from the ileum after in vivo incubation with gastric juice-57CoB12, and that a macromolecular factor is present in the distal ileal mucosa which binds intrinsic factor both in vitro and in vivo, changing its solubility and electrophoretic properties. It is suggested that this ileal binding factor is the previously postulated intestinal receptor for intrinsic factor.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABELS J., VEGTER J. J., WOLDRING M. G., JANS J. H., NIEWEG H. O. The physiologic mechanism of vitamin B12 absorption. Acta Med Scand. 1959 Oct 16;165:105–113. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1959.tb14477.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOASS A., WILSON T. H. INTESTINAL ABSORPTION OF INTRINSIC FACTOR AND B12-INTRINSIC FACTOR COMPLEX. Am J Physiol. 1964 Jul;207:27–32. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.207.1.27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOOTH C. C., CHANARIN I., ANDERSON B. B., MOLLIN D. L. The site of absorption and tissue distribution of orally administered 56Co-labelled vitamin B12 in the rat. Br J Haematol. 1957 Jul;3(3):253–261. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1957.tb05794.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOOTH C. C., MOLLIN D. L. Plasma, tissue and urinary radioactivity after oral administration of 56Co-labelled vitamin B12. Br J Haematol. 1956 Jul;2(3):223–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1956.tb06695.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURGUS R. C., HUFHAM J. B., SCOTT W. M., PFIFFNER J. J. MICROBIAL DEGRADATION OF CORRINOIDS. 3. PIGMENTS DERIVED FROM VITAMIN B12 BY PSEUDOMONAS RUBESCENS. J Bacteriol. 1964 Oct;88:1139–1144. doi: 10.1128/jb.88.4.1139-1144.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CASTLE W. B., NIEWEG H. O., SHEN S. C. Mechanism of intrinsic factor action in the gastrectomized rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Jan;94(1):223–230. doi: 10.3181/00379727-94-22907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER B. A., CASTLE W. B. Sequential mechanisms in the enhanced absorption of vitamin B12 by intrinsic factor in the rat. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jan;39:199–214. doi: 10.1172/JCI104019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER B. A., PARANCHYCH W., LOWENSTEIN L. Studies on the absorption by guinea pig intestine of cyanocobalamin incubated with intrinsic factor. J Clin Invest. 1962 Feb;41:370–377. doi: 10.1172/JCI104491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPER B. A. THE UPTAKE OF CO57-LABELED VITAMIN B12 BY EVERTED SACS OF INTESTINE IN VITRO. Medicine (Baltimore) 1964 Nov;43:689–696. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196411000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donaldson R. M., Jr, Mackenzie I. L., Trier J. S. Intrinsic factor-mediated attachment of vitamin B12 to brush borders and microvillous membranes of hamster intestine. J Clin Invest. 1967 Jul;46(7):1215–1228. doi: 10.1172/JCI105615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRASBECK R., NYBERG W. Inhibition of radiovitamin B12 absorption by ethylenediaminetetraacetate (EDTA) and its reversal by calcium ions. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1958;10(4):448–448. doi: 10.3109/00365515809051257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELGELAND K., JONSEN J., LALAND S., LYGREN T., ROMCKE O. BIOLOGICAL ACTIVITY OF A BROWNISH-YELLOW PIGMENT PRODUCED FROM VITAMIN B 12 BY AEROBACTER AEROGENES. Nature. 1963 Aug 10;199:604–605. doi: 10.1038/199604a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERBERT V. Mechanism of intrinsic factor action in everted sacs of rat small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jan 1;38(1 Pt 1):102–109. doi: 10.1172/JCI103779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JEFFRIES G. H., SLEISENGER M. H. The immunologic identification and quantitation of human intrinsic factor in gastric secretions. J Clin Invest. 1963 Apr;42:442–449. doi: 10.1172/JCI104732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAY A. W. Effect of large doses of histamine on gastric secretion of HCI; an augmented histamine test. Br Med J. 1953 Jul 11;2(4827):77–80. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4827.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAU K. S., GOTTLIEB C., WASSERMAN L. R., HERBERT V. MEASUREMENT OF SERUM VITAMIN B12 LEVEL USING RADIOISOTOPE DILUTION AND COATED CHARCOAL. Blood. 1965 Aug;26:202–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILLER D., CRANE R. K. A procedure for the isolation of the epithelial brush border membrane of hamster small intestine. Anal Biochem. 1961 Jun;2:284–286. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(61)80014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKUDA K. Mucosal adsorption and absorption of vitamin B12 in the intestine of the rat. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1962 Nov;111:320–323. doi: 10.3181/00379727-111-27779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuda K., Sasayama K. Effects of ethylenediaminetetraacetate and metal ions in intestinal absorption of vitamin B 12 in man and rats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1965 Oct;120(1):17–20. doi: 10.3181/00379727-120-30431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROTHENBERG S. P. Assay of serum vitamin B12 concentration using Co57-B12 and intrinsic factor. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1961 Oct;108:45–48. doi: 10.3181/00379727-108-26840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg S. P. A radioimmunoassay for human intrinsic factor. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 May;67(5):879–890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothenberg S. P. Immunologic isolation of human intrinsic factor. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 May;122(1):1–5. doi: 10.3181/00379727-122-31035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITHIES O. Zone electrophoresis in starch gels: group variations in the serum proteins of normal human adults. Biochem J. 1955 Dec;61(4):629–641. doi: 10.1042/bj0610629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STRAUSS E. W., WILSON T. H. Factors controlling B12 uptake by intestinal sacs in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1960 Jan;198:103–107. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.198.1.103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UKYO S., COOPER B. A. INTRINSIC FACTOR-LIKE ACTIVITY IN EXTRACTS OF GUINEA PIG INTESTINE. Am J Physiol. 1965 Jan;208:9–13. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.208.1.9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILSON T. H., STRAUSS E. W. Some species differences in the intrinsic factor stimulation of B12 uptake by small intestine in vitro. Am J Physiol. 1959 Oct;197:926–928. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.197.4.926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


