Abstract
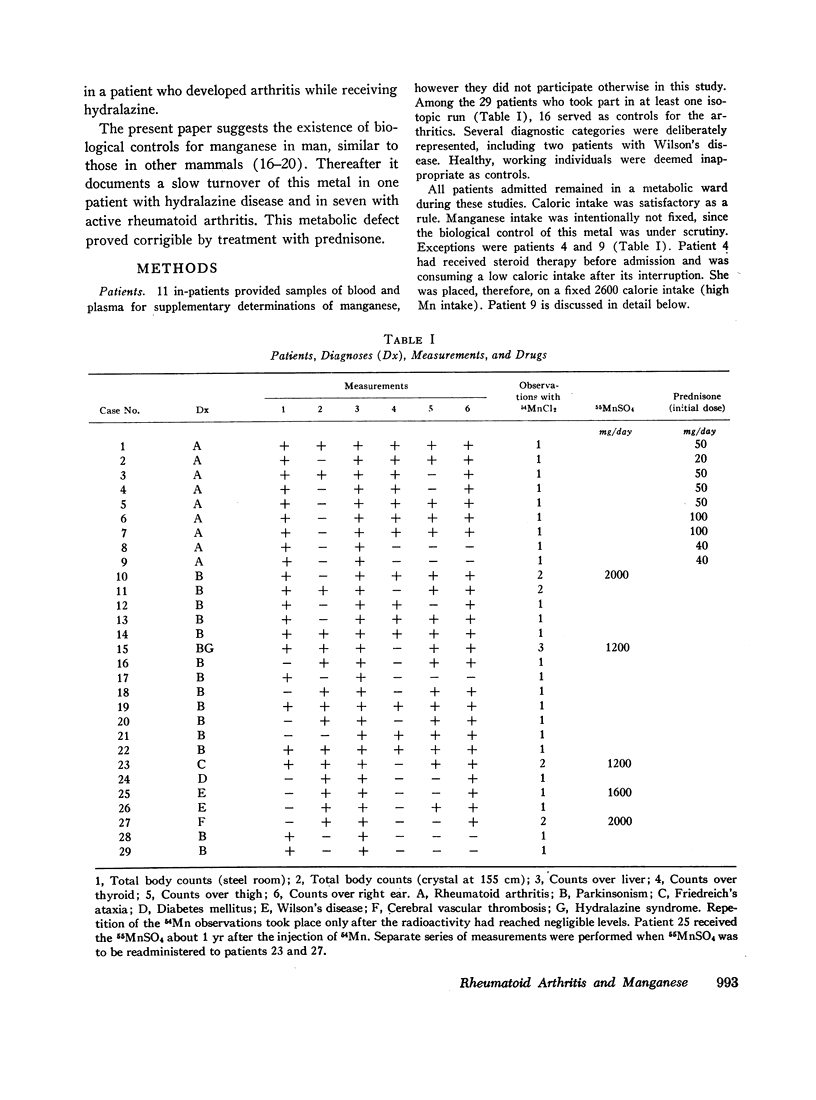
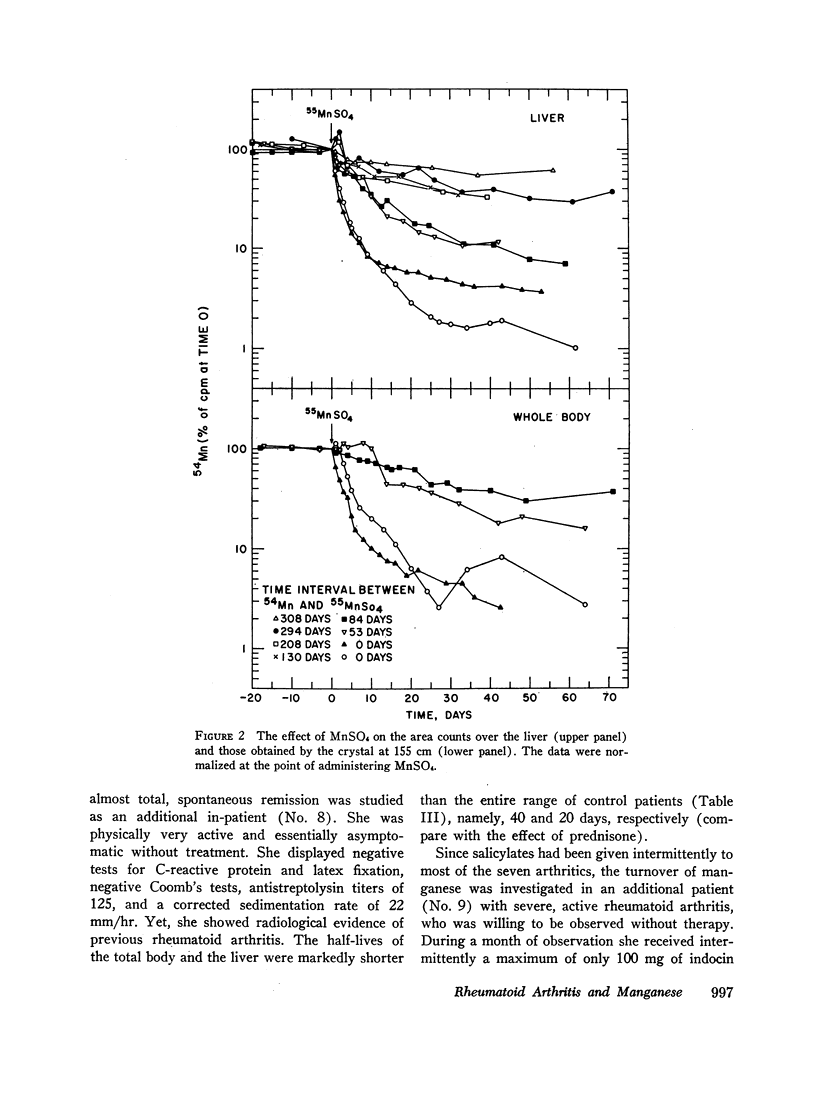
Total body and area counts of intravenously injected 54Mn were measured periodically in 29 in-patients. A heterogeneous group of 19 control patients showed fair reproducibility in the immediate distribution, and considerable individual variance in the subsequent loss of the isotope. Eight studies of the effects of feeding excesses of manganous sulfate to five patients showed acceleration of the rate of loss of the radioisotope from the whole body and the liver. These findings seem compatible with the presence of control mechanisms in man, operating to vary the metal's excretion, while tending to preserve constancy of its concentration in tissues.
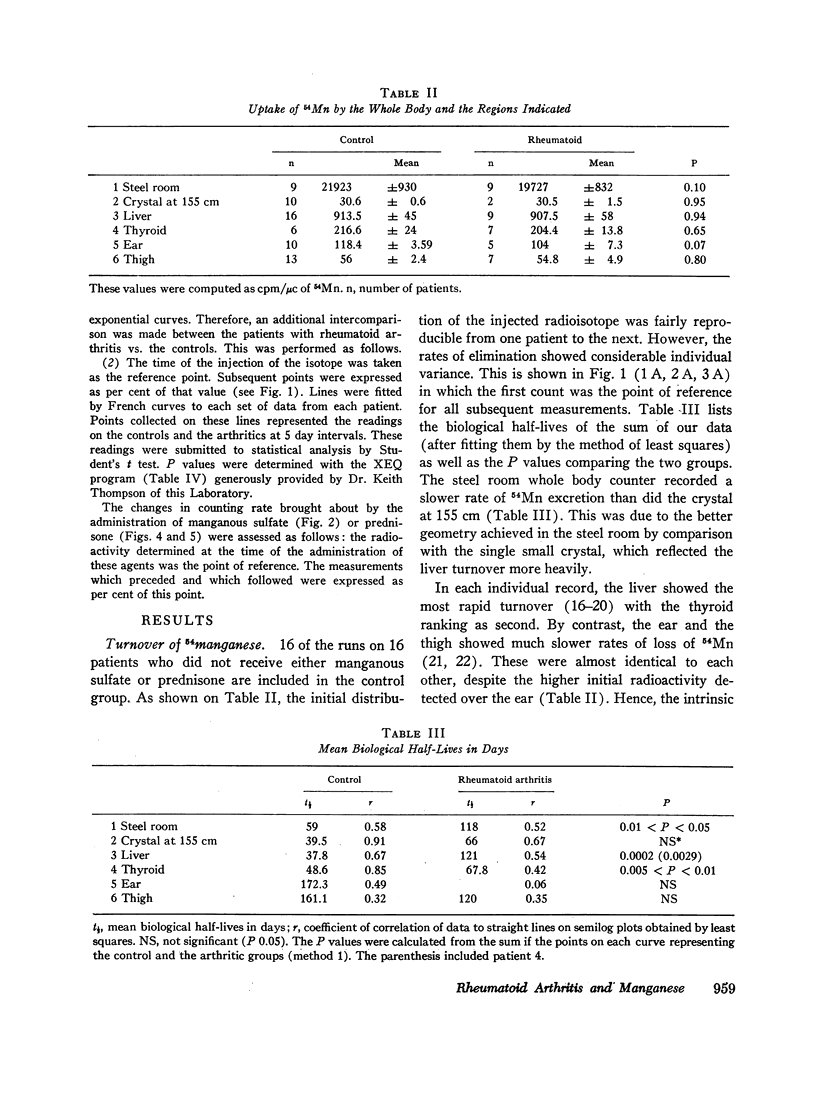
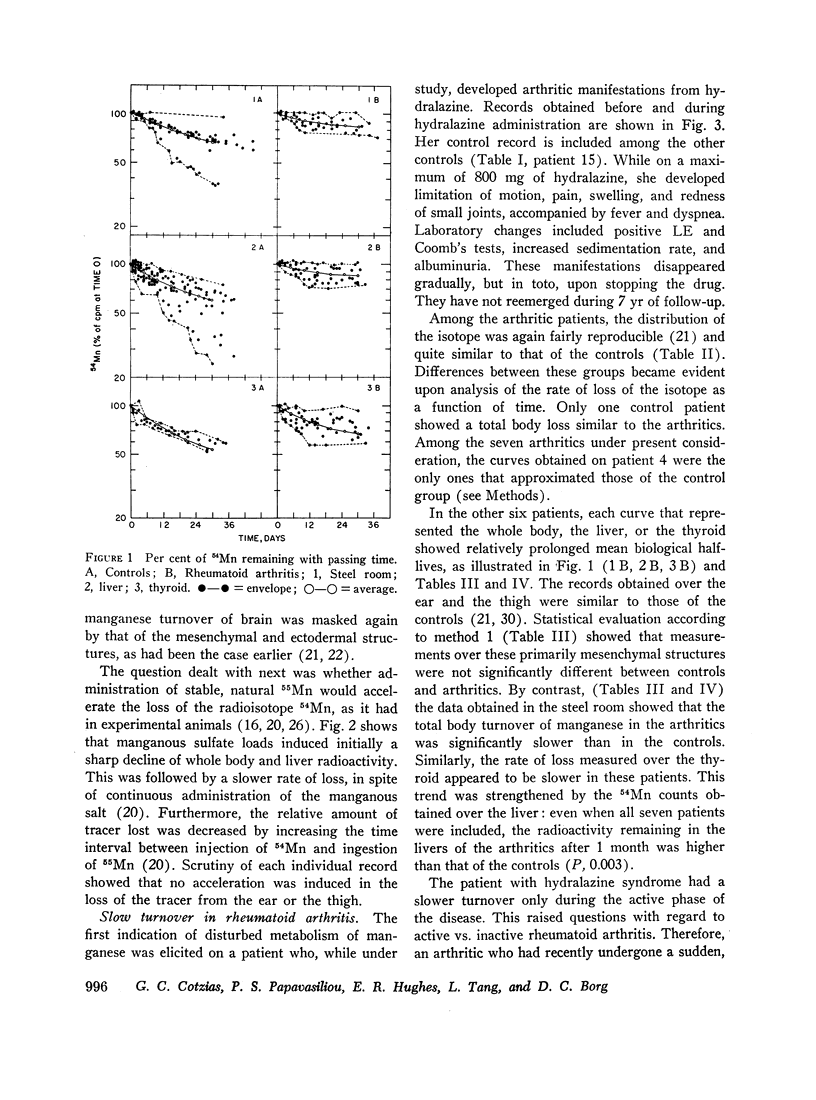
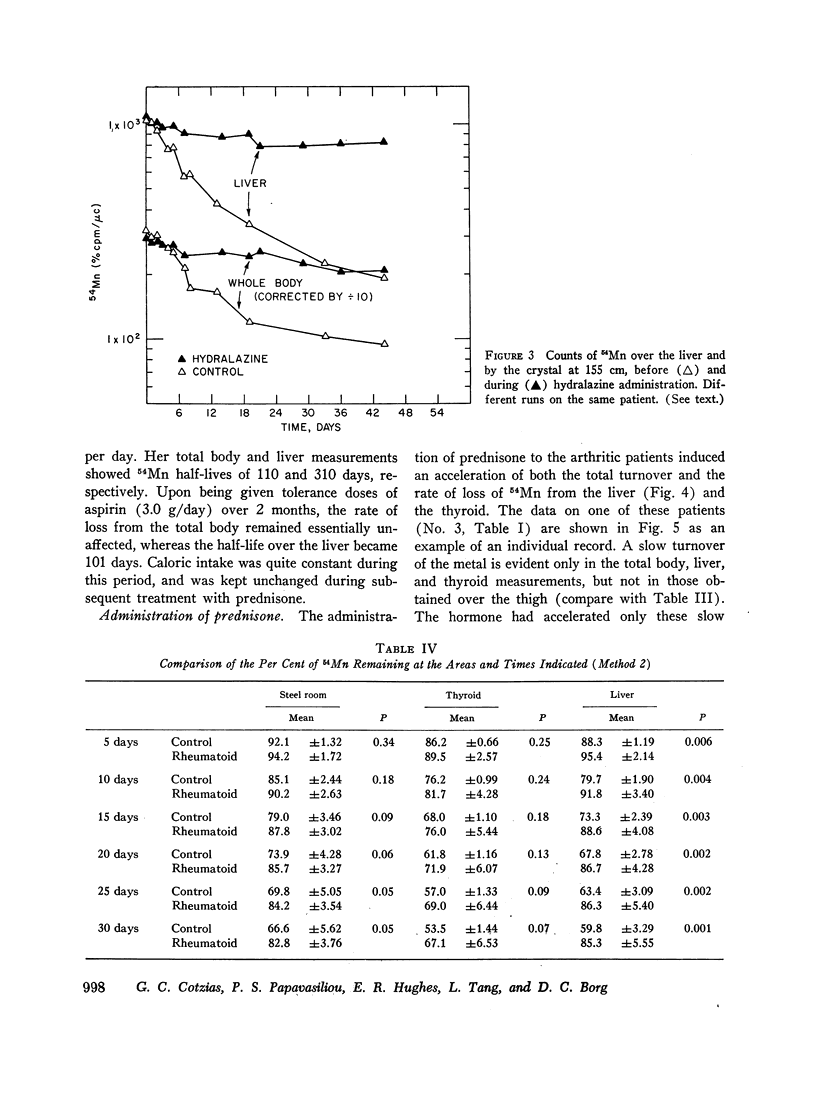
Slow turnover rates of the metal were demonstrated in seven out of eight patients with active rheumatoid arthritis, in one with hydralazine disease, but not in one arthritic undergoing an impressive, spontaneous remission. Statistically significant differences were encountered in the measurements of 54Mn turnover of the total body, the thyroid, and the liver.
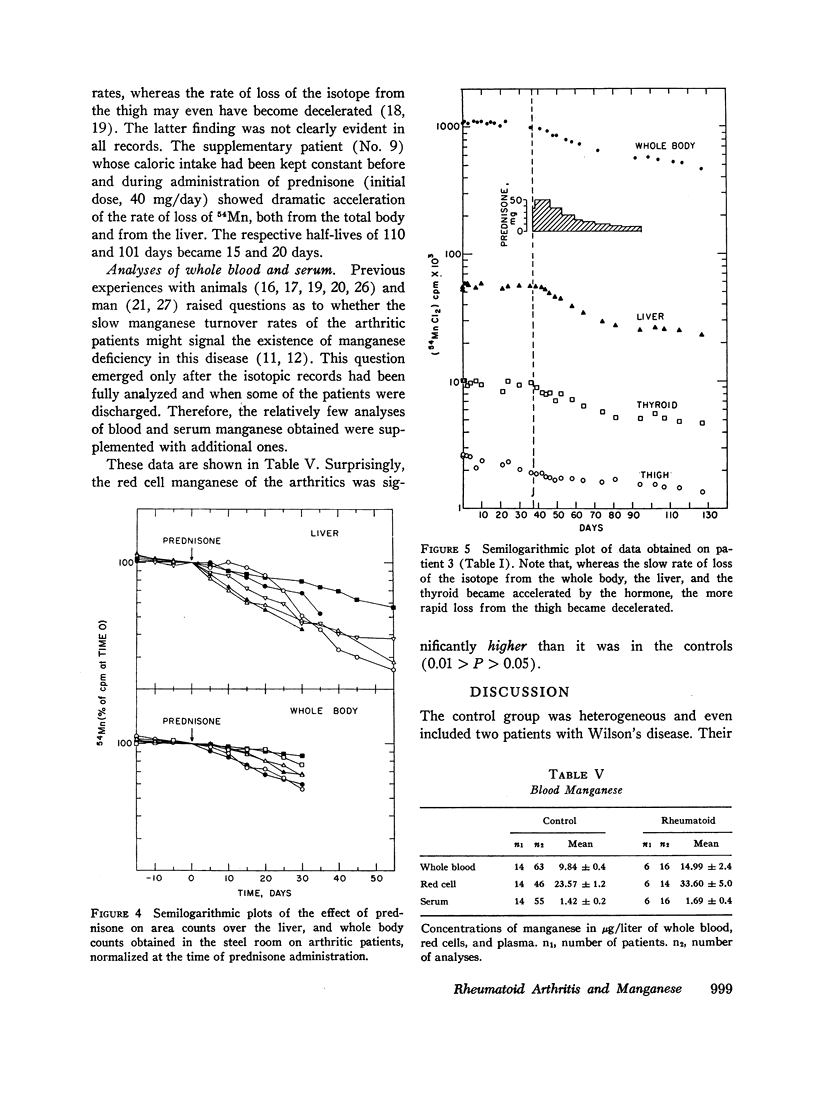
Administration of prednisone induced clinical improvement and significant acceleration of these turnovers. Slow turnovers are characteristic of nutritional manganese deficiency. Therefore, serum and blood manganese determinations were performed by neutron activation analysis on 14 control patients, and on six patients with active rheumatoid arthritis. A statistically significant elevation of the red cell manganese concentration was encountered in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. This argued against the presence of classical tracemetal deficiency and called for an alternative explanation of these findings.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alarcón-Segovia D., Wakim K. G., Worthington J. W., Ward L. E. Clinical and experimental studies on the hydralazine syndrome and its relationship to systemic lupus erythematosus. Medicine (Baltimore) 1967 Jan;46(1):1–33. doi: 10.1097/00005792-196701000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORG D. C., COTZIAS G. C. Manganese metabolism in man: rapid exchange of MN56 with tissue as demonstrated by blood clearance and liver uptake. J Clin Invest. 1958 Sep;37(9):1269–1278. doi: 10.1172/JCI103714. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertinchamps A. J., Miller S. T., Cotzias G. C. Interdependence of routes excreting manganese. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jul;211(1):217–224. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.1.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britton A. A., Cotzias G. C. Dependence of manganese turnover on intake. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jul;211(1):203–206. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.1.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COTZIAS G. C., GREENOUGH J. J. The high specificity of the manganese pathway through the body. J Clin Invest. 1958 Sep;37(9):1298–1305. doi: 10.1172/JCI103718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotzias G. C., Miller S. T., Edwards J. Neutron activation analysis: the stability of manganese concentrations in human blood and serum. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 May;67(5):836–849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DI FERRANTE N. Urinary excretion of acid mucopolysaccharides by patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 1957 Oct;36(10):1516–1520. doi: 10.1172/JCI103548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erway L., Hurley L. S., Fraser A. Neurological defect: manganese in phenocopy and prevention of a genetic abnormality of inner ear. Science. 1966 Jun 24;152(3730):1766–1768. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3730.1766. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grebner E. E., Hall C. W., Neufeld E. F. Glycosylation of serine residues by a uridine diphosphate-xylose: protein xylosyltransferase from mouse mastocytoma. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1966 Sep 26;116(1):391–398. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(66)90045-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grebner E. E., Hall C. W., Neufeld E. F. Incorporation of D-xylose-C14 into glycoprotein by particles from hen oviduct. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Mar 22;22(6):672–677. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90199-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMERMAN D., SANDSON J. UNUSUAL PROPERTIES OF HYALURONATEPROTEIN ISOLATED FROM PATHOLOGICAL SYNOVIAL FLUIDS. J Clin Invest. 1963 Dec;42:1882–1889. doi: 10.1172/JCI104873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGHES E. R., COTZIAS G. C. Adrenocorticosteroid hormones and manganese metabolism. Am J Physiol. 1961 Dec;201:1061–1064. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.201.6.1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes E. R., Miller S. T., Cotzias G. C. Tissue concentrations of manganese and adrenal function. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jul;211(1):207–210. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.1.207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASKIN D. M., ENGEL M. B., JOSEPH N. R., POLLAK V. E. A test of connective tissue state and reactivity in collagen diseases. J Clin Invest. 1961 Dec;40:2153–2161. doi: 10.1172/JCI104441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEACH R. M., Jr, MUENSTER A. M. Studies on the role of manganese in bone formation. I. Effect upon the mucopolysaccharide content of chick bone. J Nutr. 1962 Sep;78:51–56. doi: 10.1093/jn/78.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LYON M. F. Hereditary absence of otoliths in the house mouse. J Physiol. 1951 Jul;114(3):410–418. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1951.sp004632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAYNARD L. S., COTZIAS G. C. The partition of manganese among organs and intracellular organelles of the rat. J Biol Chem. 1955 May;214(1):489–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mena I., Marin O., Fuenzalida S., Cotzias G. C. Chronic manganese poisoning. Clinical picture and manganese turnover. Neurology. 1967 Feb;17(2):128–136. doi: 10.1212/wnl.17.2.128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPAVASILIOU P. S., COTZIAS G. C. Neutron activation analysis: the determination of manganese. J Biol Chem. 1961 Aug;236:2365–2369. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Papavasiliou P. S., Miller S. T., Cotzias G. C. Role of liver in regulating distribution and excretion of manganese. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jul;211(1):211–216. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.1.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson H. C., Telser A., Dorfman A. Studies on biosynthesis of the linkage region of chondroitin sulfate-protein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Dec;56(6):1859–1866. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.6.1859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDSON J., HAMERMAN D. Nondialyzable hexose of human synovial fluid. J Clin Invest. 1960 May;39:782–789. doi: 10.1172/JCI104095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder H. A., Balassa J. J., Tipton I. H. Essential trace metals in man: manganese. A study in homeostasis. J Chronic Dis. 1966 May;19(5):545–571. doi: 10.1016/0021-9681(66)90094-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


