Abstract
Sodium taurolithocholate and sodium taurocholenate were infused intravenously into rats and hamsters. Each bile acid salt was given alone or in combination with varying amounts of a primary bile salt, either sodium taurocholate or sodium taurochenodeoxycholate. Bile flow, total bile acid salt excretion, and the excretion of sodium taurolithocholate were quantitatively determined. In addition, mannitol excretion in bile was determined at various flow rates.
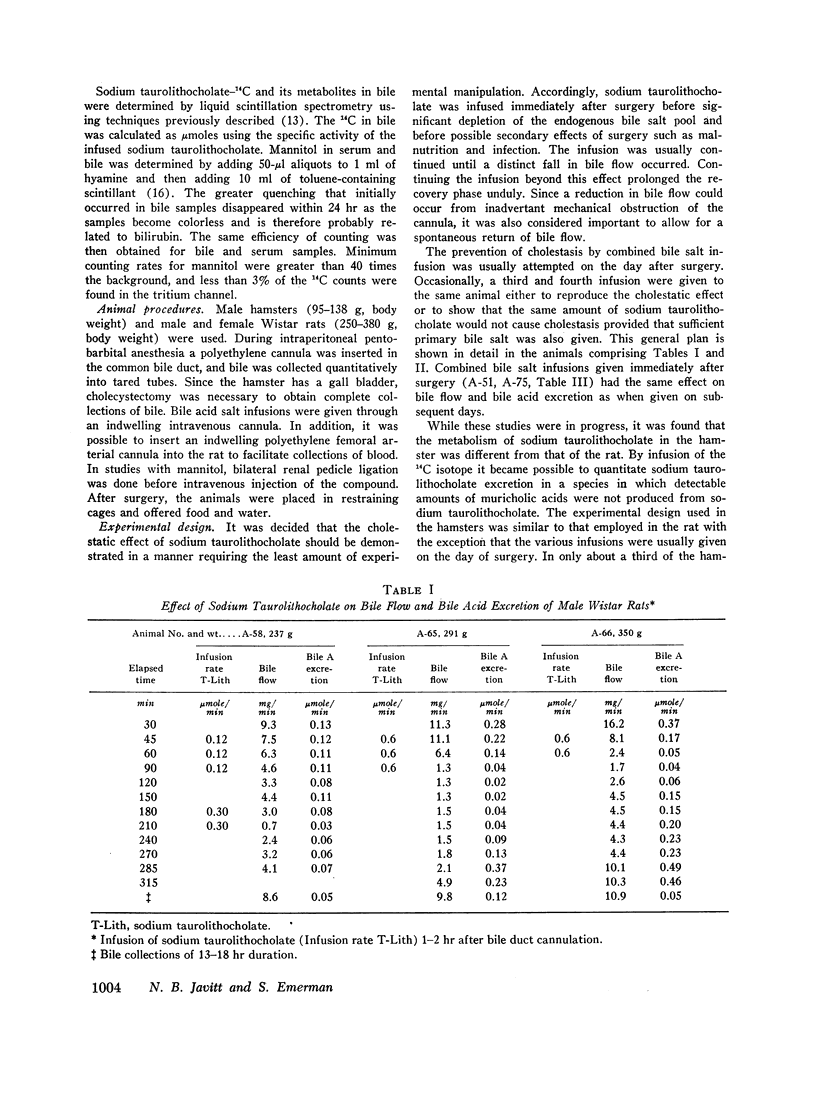
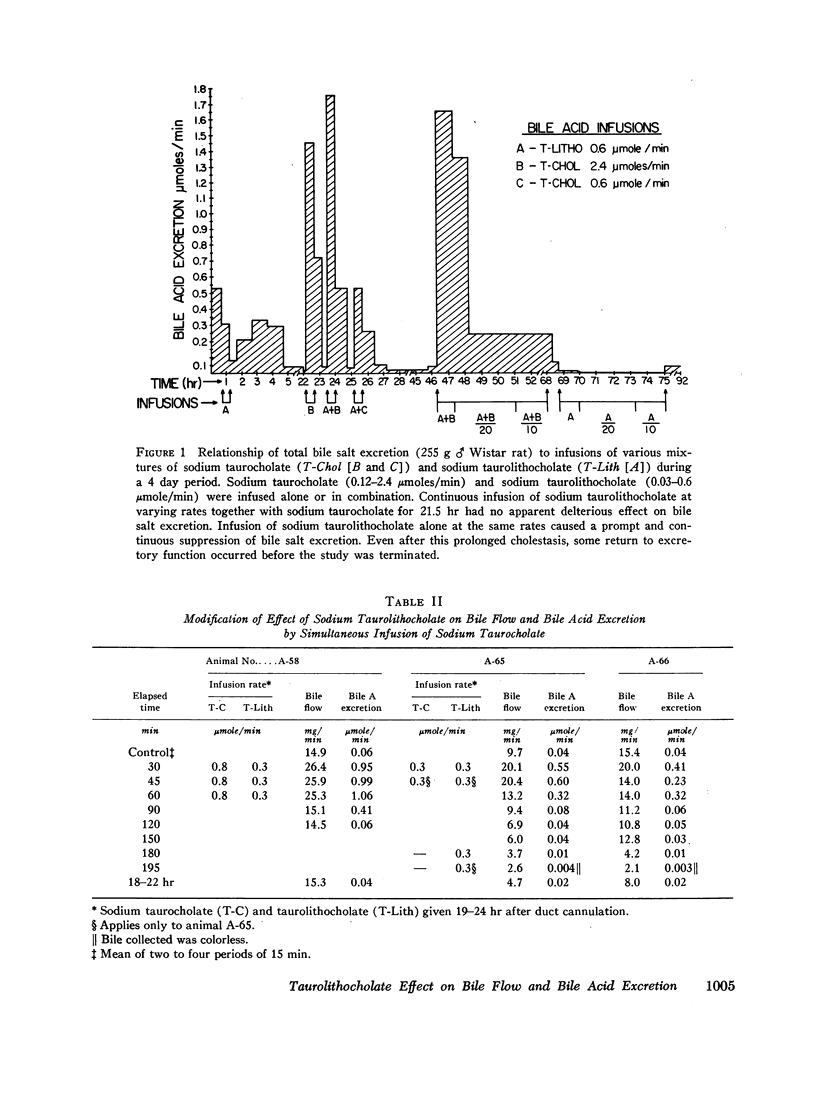
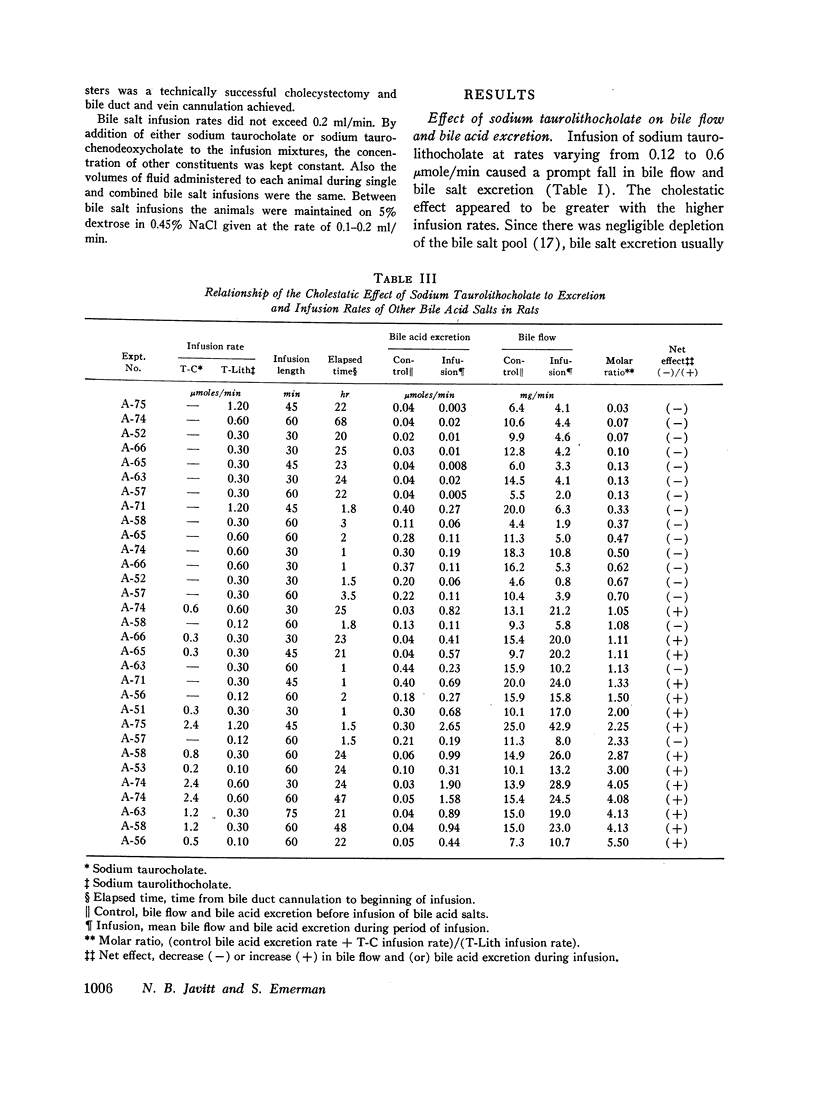
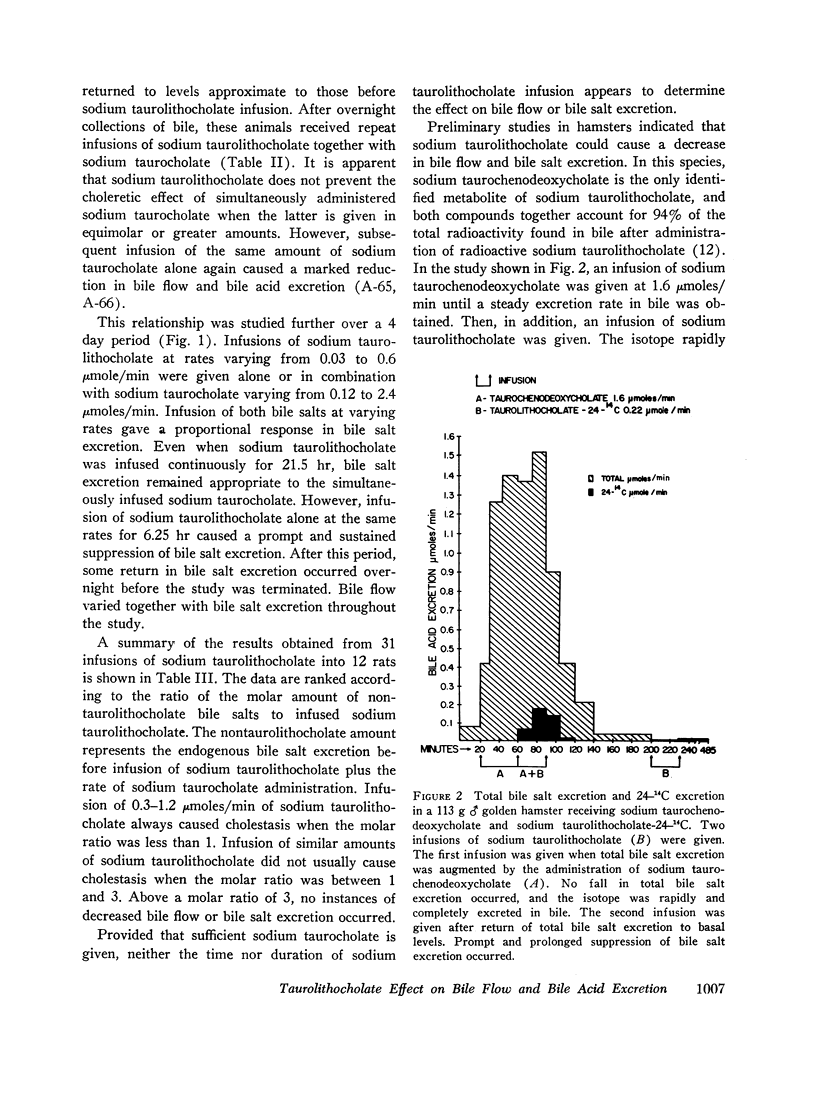
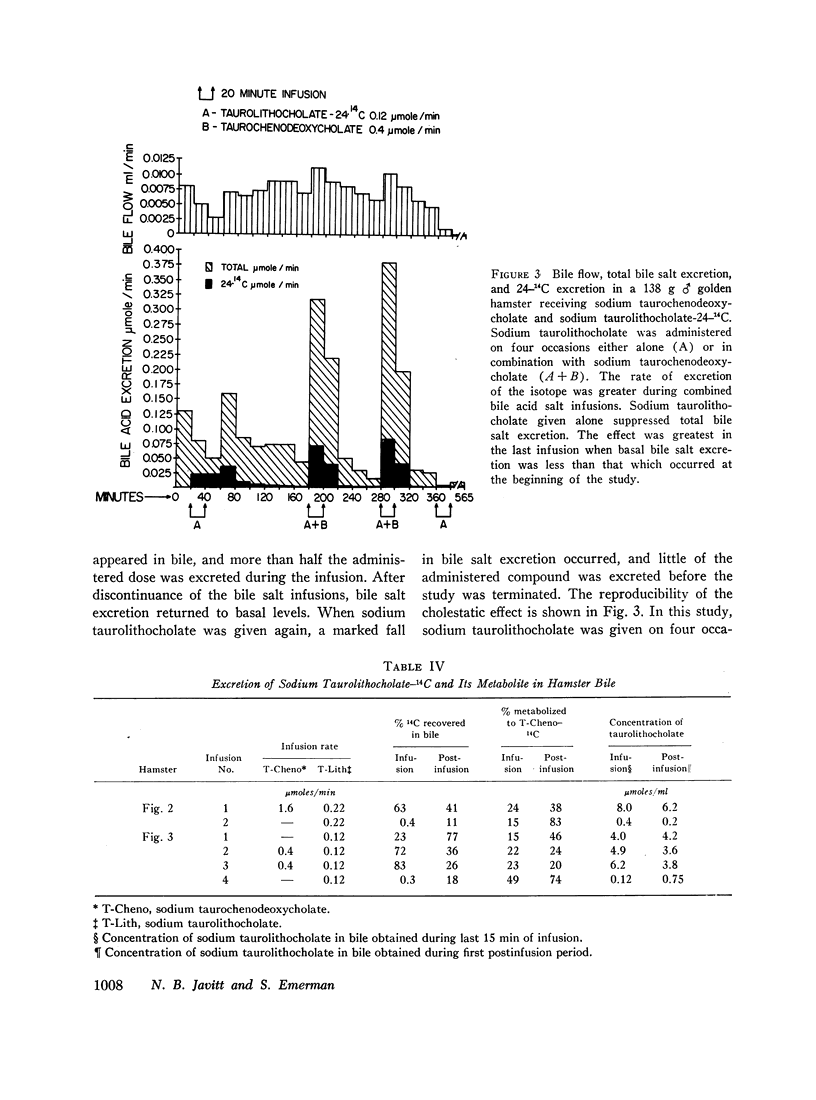
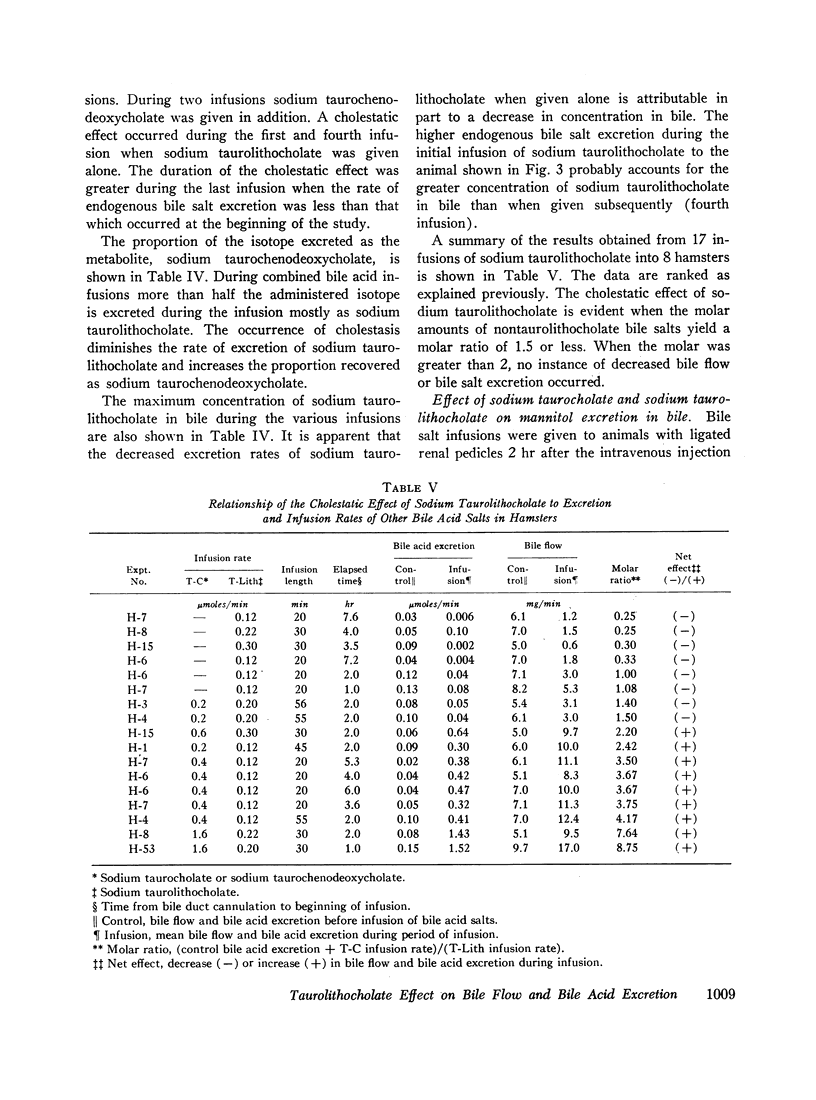
Sodium taurolithocholate was found to be rapidly excreted in bile in concentrations greater than its aqueous solubility. When the endogenous excretion rate of bile salt or the infusion of primary bile salt was less than the molar amount of administered sodium taurolithocholate, cholestasis always occurred. Increasing molar amounts of primary bile salt prevented cholestasis and enhanced the excretion rate of sodium taurolithocholate.
Infusion of sodium taurocholenate, a nonhemolytic bile salt, caused an effect on bile flow and bile acid salt excretion qualitatively similar to sodium taurolithocholate.
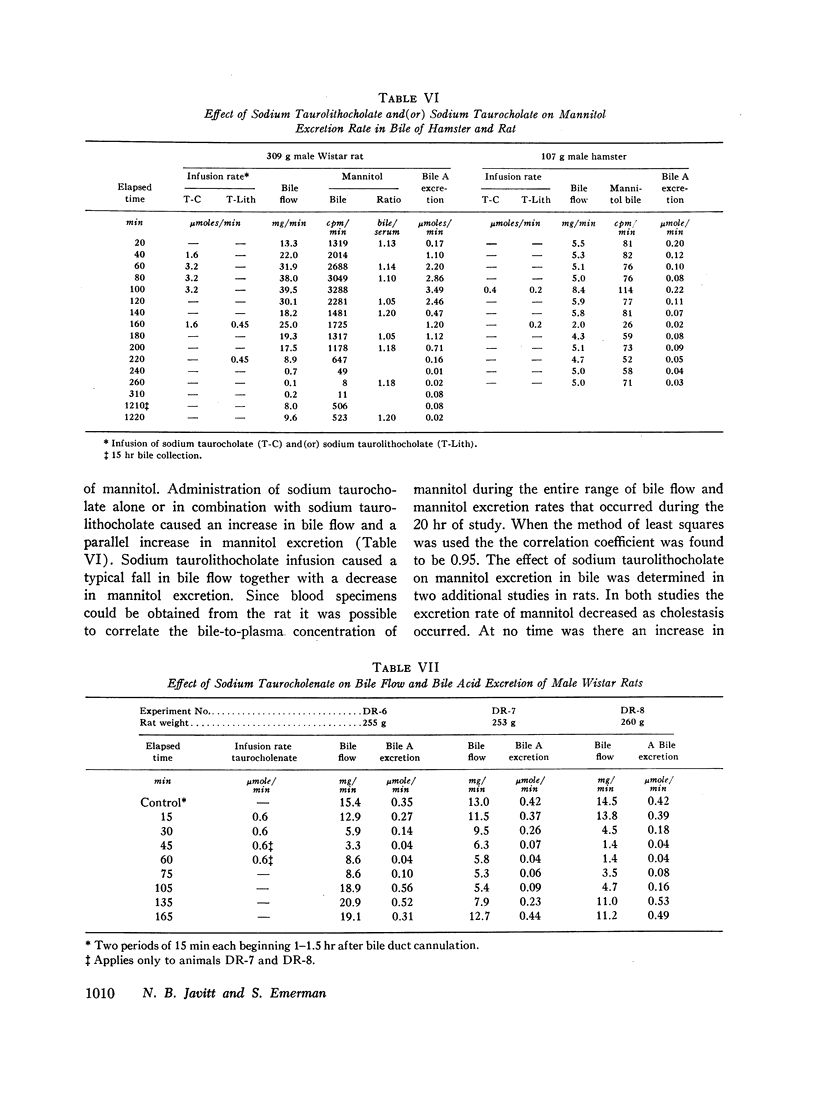
The induction of cholestasis can be attributed to the physical properties of these poorly water soluble bile salts. The reduction in bile flow could not be shown to be related to water reabsorption from the biliary tree since there was no increase in mannitol concentration in bile during cholestasis. Reduction in bile flow may be related to obstruction of segments of the biliary tree by precipitates of sodium taurolithocholate and possibly to a decrease in water entry into the biliary tree during infusion of this bile acid salt.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali S. S., Kuksis A., Beveridge J. M. Excretion of bile acids by three men on a fat-free diet. Can J Biochem. 1966 Jun;44(6):957–969. doi: 10.1139/o66-112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRAUER R. W., PESSOTTI R. L. The effect of choleretic and of hydrocholeretic agents on bile flow and bile solids in the isolated perfused liver. Science. 1952 Feb 8;115(2980):142–143. doi: 10.1126/science.115.2980.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHEN P. S., Jr Liquid scintillation counting of C14 and H3 in plasma and serum. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Jul;98(3):546–547. doi: 10.3181/00379727-98-24102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERIKSSON S. Biliary excretion of bile acids and cholesterol in bile fistula rats; bile acids and steroids. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Mar;94(3):578–582. doi: 10.3181/00379727-94-23018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerman S., Javitt N. B. Metabolism of taurolithocholic acid in the hamster. J Biol Chem. 1967 Feb 25;242(4):661–664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASLEWOOD G. A. THE BIOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE OF CHEMICAL DIFFERENCES IN BILE SALTS. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc. 1964 Nov;39:537–574. doi: 10.1111/j.1469-185x.1964.tb01170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F., Small D. M. Detergent properties of bile salts: correlation with physiological function. Annu Rev Med. 1967;18:333–376. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.18.020167.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAKSSON B. On the dissolving power of lecithin and bile salts for cholesterol in human bladder bile. Acta Soc Med Ups. 1954 Sep 30;59(5-6):296–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IWATA T., YAMASAKI K. ENZYMATIC DETERMINATION AND THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY OF BILE ACIDS IN BLOOD. J Biochem. 1964 Nov;56:424–431. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Javitt N. B. Cholestasis in rats induced by taurolithocholate. Nature. 1966 Jun 18;210(5042):1262–1263. doi: 10.1038/2101262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATSCHINER J. T., MAHOWALD T. A., ELLIOTT W. H., DOISY E. A., Jr, HSIA S. L., DOISY E. A. Bile acids. I. Two new acids from rat bile. J Biol Chem. 1957 Apr;225(2):771–779. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PALMER R. H., GLICKMAN P. B., KAPPAS A. Pyrogenic and inflammatory properties of certain bile acids in man. J Clin Invest. 1962 Aug;41:1573–1577. doi: 10.1172/JCI104614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PREISIG R., COOPER H. L., WHEELER H. O. The relationship between taurocholate secretion rate and bile production in the unanesthetized dog during cholinergic blockade and during secretin administration. J Clin Invest. 1962 May;41:1152–1162. doi: 10.1172/JCI104568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHANKER L. S., HOGBEN C. A. Biliary excretion of inulin, sucrose, and mannitol: analysis of bile formation. Am J Physiol. 1961 May;200:1087–1090. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.200.5.1087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPERBER I. Secretion of organic anions in the formation of urine and bile. Pharmacol Rev. 1959 Mar;11(1):109–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. M., Bourgès M., Dervichian D. G. Ternary and quaternary aqueous systems containing bile salt, lecithin, and cholesterol. Nature. 1966 Aug 20;211(5051):816–818. doi: 10.1038/211816a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALALAY P. Enzymic analysis of steroid hormones. Methods Biochem Anal. 1960;8:119–143. doi: 10.1002/9780470110249.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRUSWELL A. S., MITCHELL W. D. SEPARATION OF CHOLESTEROL FROM ITS COMPANIONS, CHOLESTANOL AND DELTA-7-CHOLESTENOL, BY THIN-LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:438–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOTTON I. D., WIGGINS H. S. Studies in the bile acids. 2. The non-ketonic acids of human bile. Biochem J. 1953 Sep;55(2):292–294. doi: 10.1042/bj0550292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler H. O., Mancusi-Ungaro P. L. Role of bile ducts during secretin choleresis in dogs. Am J Physiol. 1966 May;210(5):1153–1159. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.5.1153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler H. O., Ramos O. L. DETERMINANTS OF THE FLOW AND COMPOSITION OF BILE IN THE UNANESTHETIZED DOG DURING CONSTANT INFUSIONS OF SODIUM TAUROCHOLATE. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jan;39(1):161–170. doi: 10.1172/JCI104015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


