Abstract
A sensitive, specific, and relatively simple immunoassay permitting measurement of pharmacological levels of digitoxin in human serum has been developed. The assay involves binding of 125I-labeled tyrosine-digitoxigenin (specific activity > 400 mc/mg) by rabbit antibody to digitoxin. Antibody-bound radioactivity is precipitated by addition of a second antibody (goat anti-rabbit gamma globulin), and precipitate radioactivity is measured. Unlabeled digitoxin can be determined by the extent to which it competes with 125I-labeled digitoxigenin and thus reduces precipitation of radioactivity. Before the assay, unlabeled digitoxin is extracted from serum with chloroform, and the chloroform solution is evaporated to dryness. Quantitation is accomplished by reference to a standard curve in which known amounts of digitoxin are added to normal serum. As little as 1 mμg of digitoxin per ml of serum produces significant reduction in precipitate radioactivity.
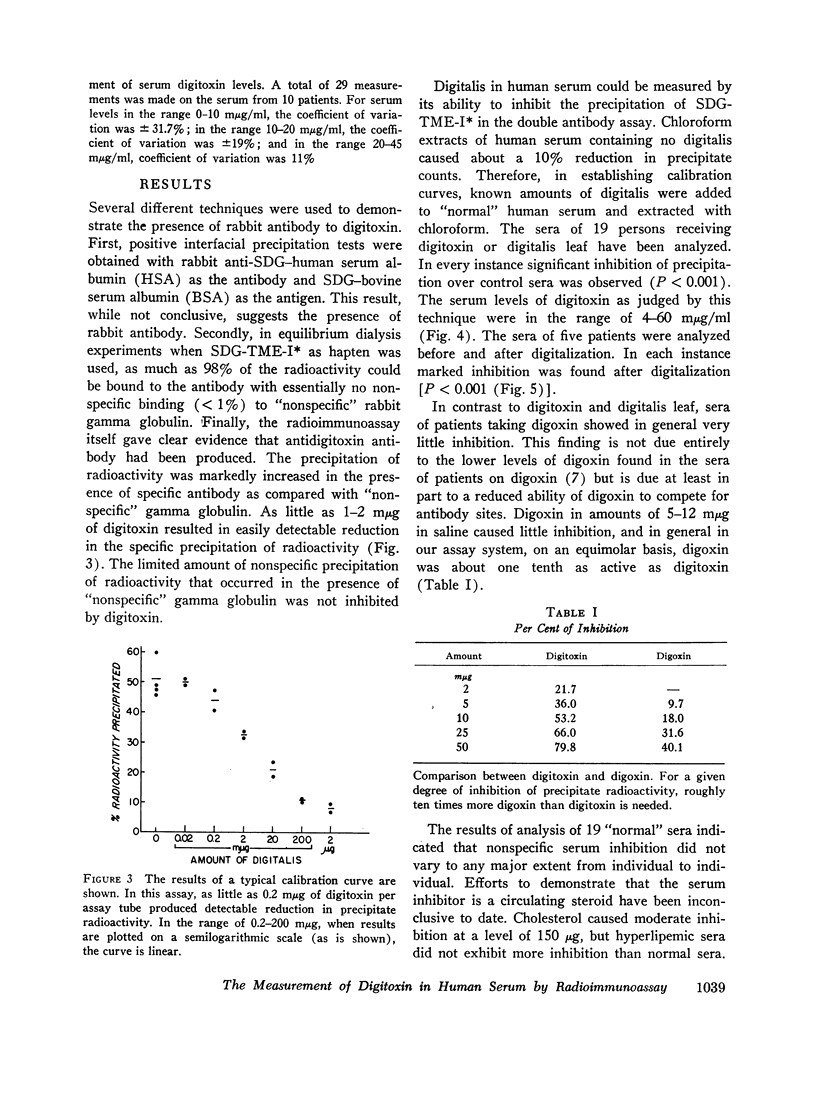
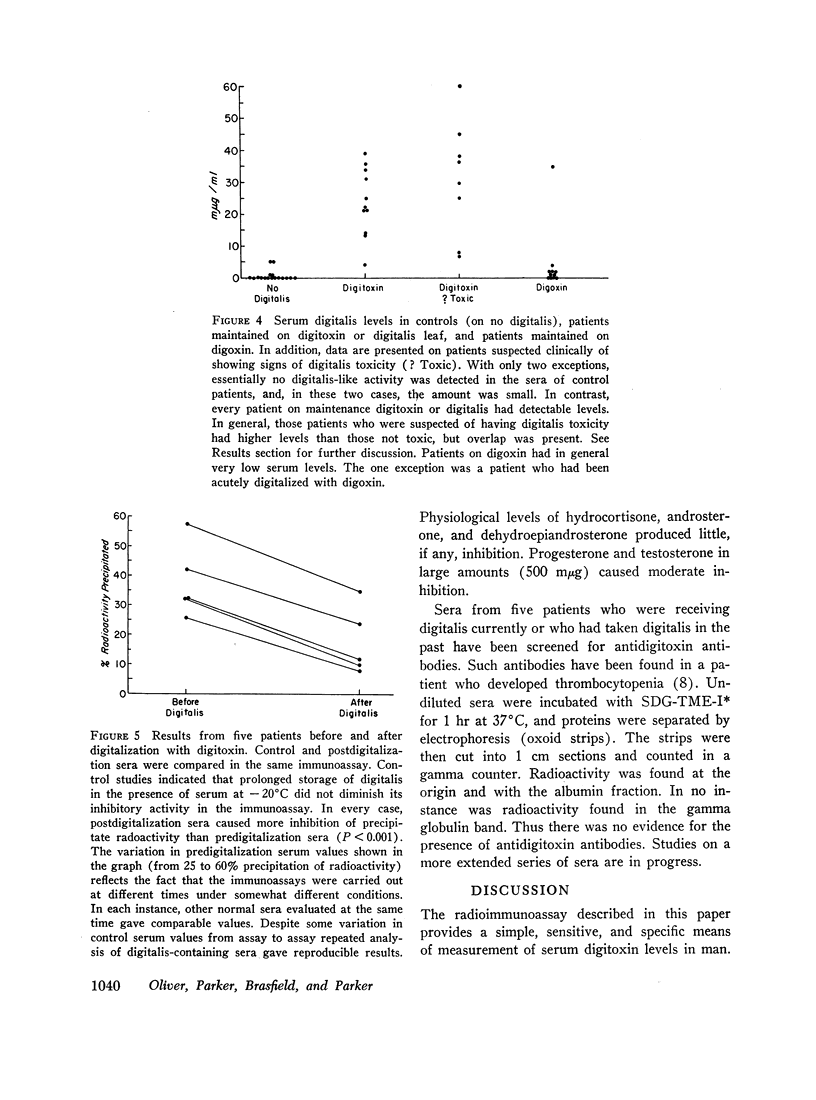
The sera of 5 patients were analyzed before and after digitalization. A highly significant reduction in precipitate counts in the postdigitalization sera was observed (P < 0.001). Serum digitalis levels were measured in 19 patients receiving no digitalis and in 19 patients taking digitoxin or digitalis leaf. Little of no digitalis-like activity was detected in control sera, whereas serum levels averaged 27 mμg/ml in those on digitalis (range 4-60 mμg/ml, P < 0.001). Patients judged clinically to show digitals toxicity in general had higher levels than those without signs of toxicity. Patients receiving digoxin had little or no detectable digitalis in their serum with this method.
In addition to the assay itself, other potential uses of the antidigitalis antibody include treatment of digitalis toxicity and studies on the tissue localization of digitalis.
Full text
PDF

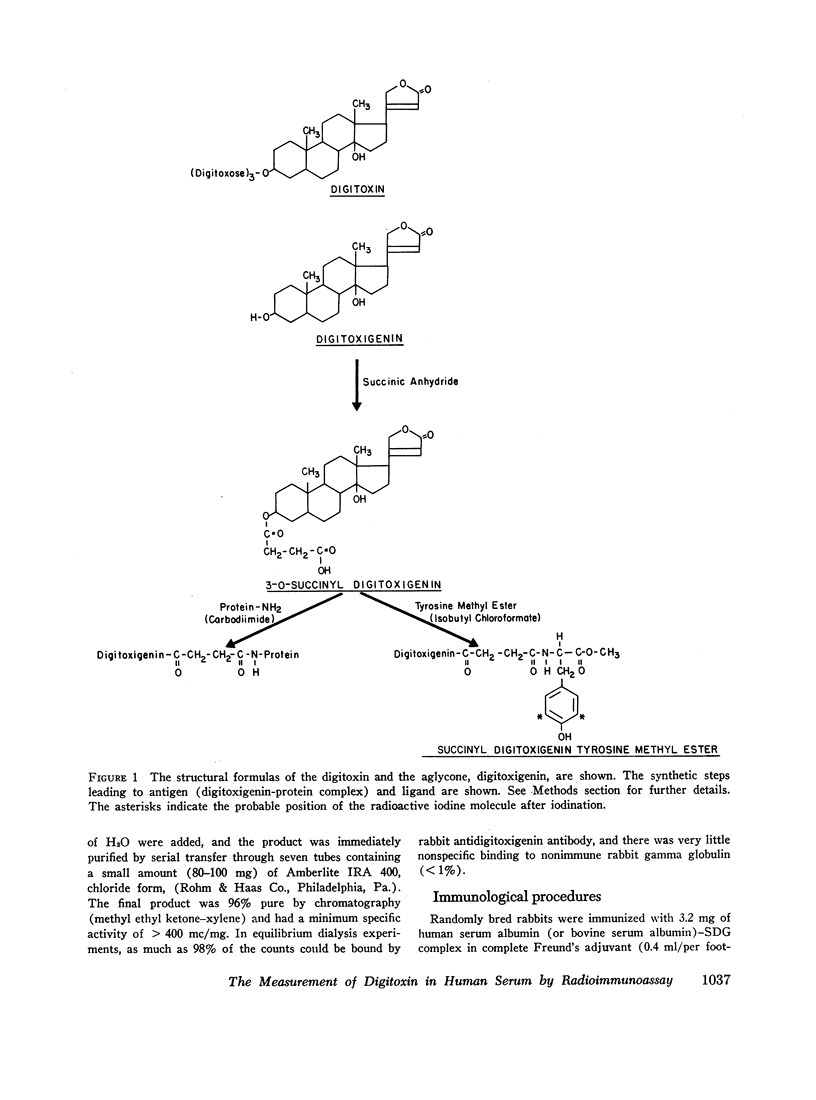



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Butler V. P., Jr, Chen J. P. Digoxin-specific antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jan;57(1):71–78. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOHERTY J. E., PERKINS W. H. Studies with tritiated digoxin in human subjects after intravenous administration. Am Heart J. 1962 Apr;63:528–536. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(62)90310-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty J. E., Perkins W. H. Tissue concentration and turnover of tritiated digoxin in dogs. Am J Cardiol. 1966 Jan;17(1):47–52. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(66)90259-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERLANGER B. F., BOREK F., BEISER S. M., LIEBERMAN S. Steroid-protein conjugates. I. Preparation and characterization of conjugates of bovine serum albumin with testosterone and with cortisone. J Biol Chem. 1957 Oct;228(2):713–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWENSTEIN J. M. A METHOD FOR MEASURING PLASMA LEVELS OF DIGITALIS GLYCOSIDES. Circulation. 1965 Feb;31:228–233. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.31.2.228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowenstein J. M., Corrill E. M. An improved method for measuring plasma and tissue concentrations of digitalis glycosides. J Lab Clin Med. 1966 Jun;67(6):1048–1052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lukas D. A., Peterson R. E. Double isotope dilution derivative assay of digitoxin in plasma, urine, and stool of patients maintained on the drug. J Clin Invest. 1966 May;45(5):782–795. doi: 10.1172/JCI105393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKITA G. T., TALSO P. J., CURRY J. H., Jr, SMITH F. D., Jr, GEILING E. M. Metabolic fate of radioactive digitoxin in human subjects. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1955 Dec;115(4):371–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. C., Nachman R. L., Horowitz H. I. Thrombocytopenia due to digitoxin. Demonstration of antibody and mechanisms of action. Am J Med. 1966 Oct;41(4):605–614. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(66)90222-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


