Abstract
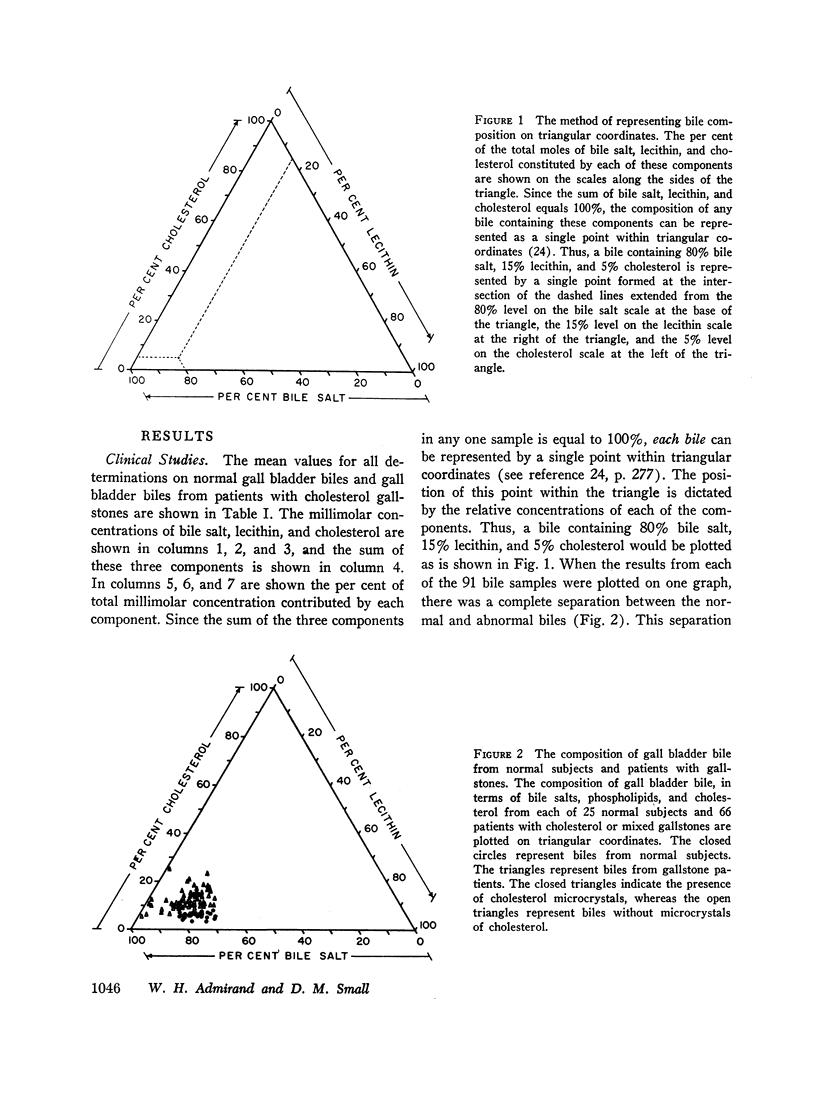
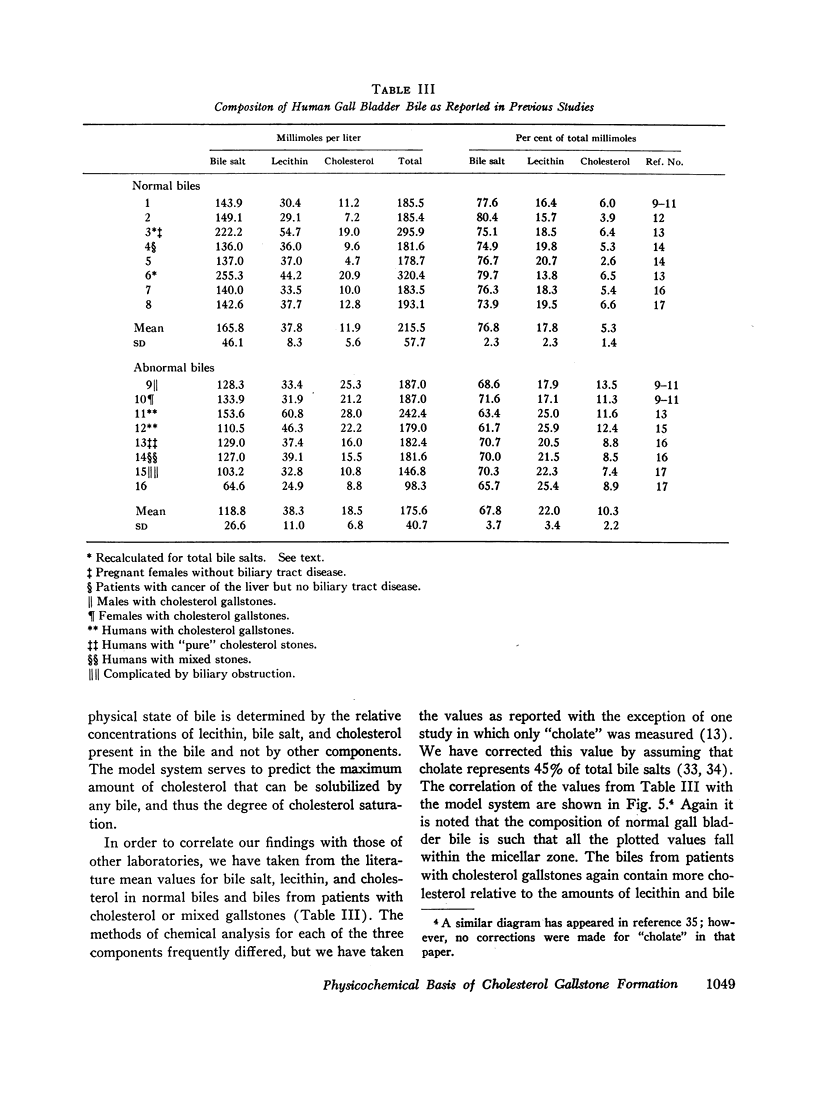
The concentrations of bile salt, lecithin, and cholesterol were determined on each of 66 samples of gall bladder bile from patients with cholesterol gallstones and 25 samples of normal gall bladder bile. When these three constituents were plotted simultaneously on triangular coordinates, a complete separation of the normal and “abnormal” bile was achieved. This separation was the result of an increase in the quantity of cholesterol relative to the amounts of bile salts and lecithin contained in the bile from patients with cholesterol gallstones.
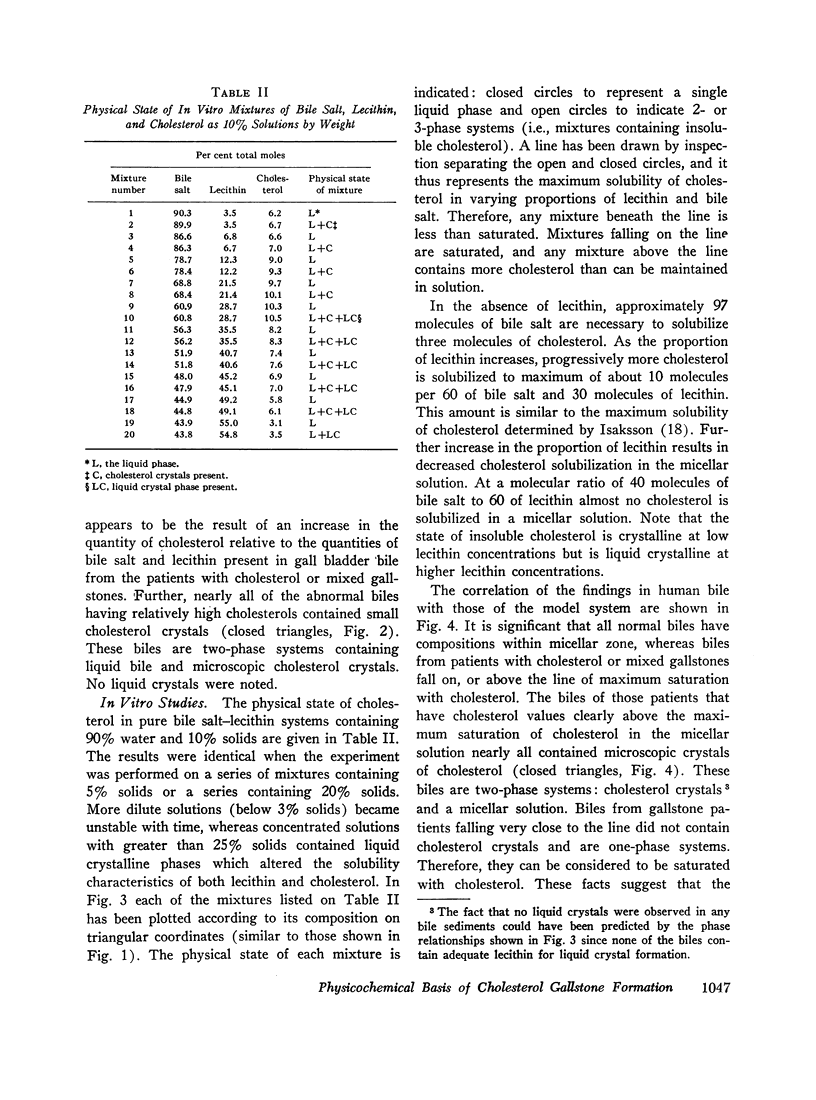
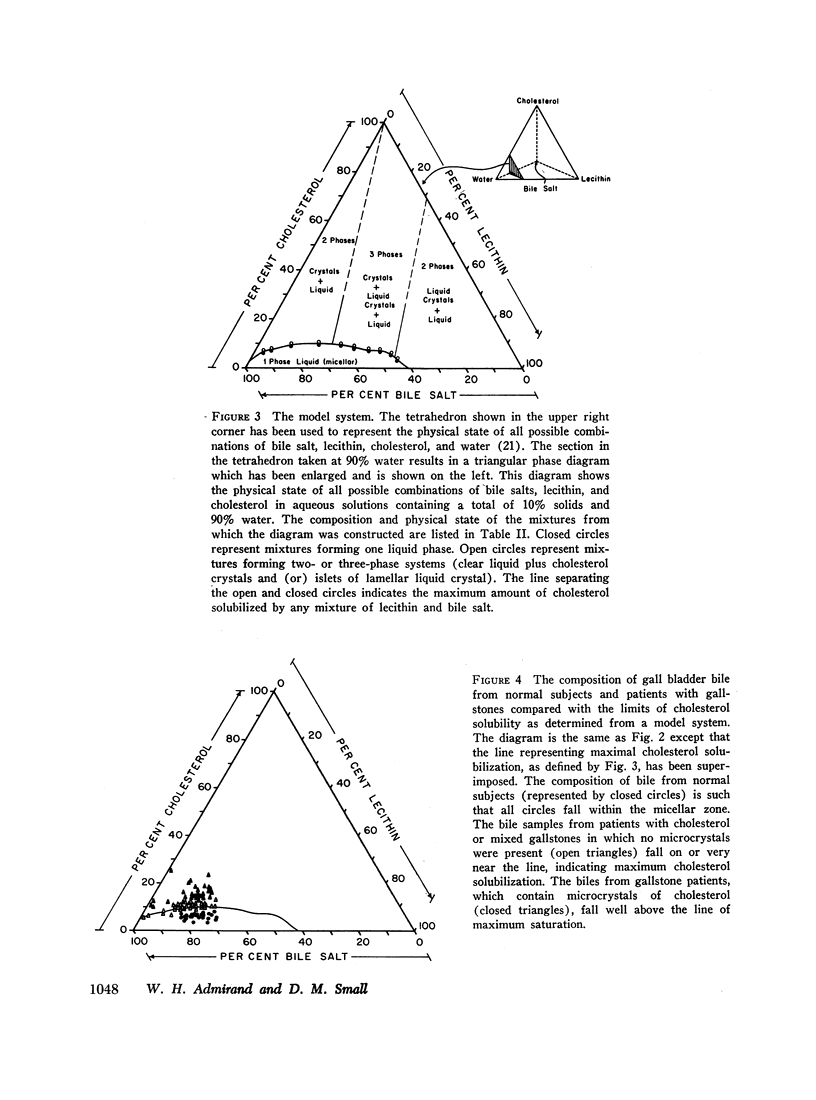
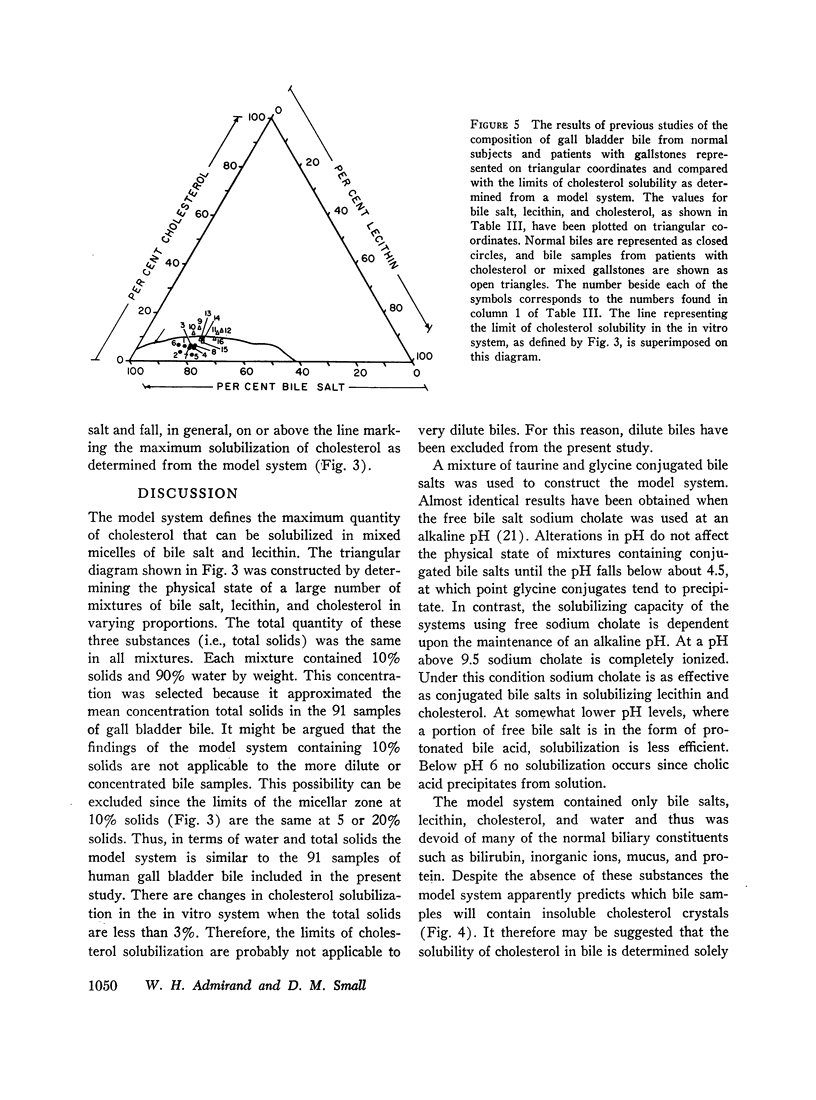
An in vitro model system was constructed (on triangular coordinates) that allows prediction of the maximum amount of cholesterol that can be solubilized in solutions containing varying proportions of bile salt and lecithin. When the bile data were compared with the solubility of cholesterol derived from the model system, normal biles were found to be less than saturated with cholesterol, whereas biles from patients with cholesterol gallstones were saturated and in some cases contained insoluble cholesterol in the form of microcrystals.
It is suggested that the physical state of bile (i.e., the presence or absence of insoluble cholesterol) is determined by the relative concentrations of bile salt, lecithin, and cholesterol, and the other biliary constituents do not appear to significantly effect the solubility of cholesterol in bile.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABEL L. L., LEVY B. B., BRODIE B. B., KENDALL F. E. A simplified method for the estimation of total cholesterol in serum and demonstration of its specificity. J Biol Chem. 1952 Mar;195(1):357–366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgès M., Small D. M., Dervichian D. G. Biophysics of lipid associations. 3. The quaternary systems lecithin-bile salt-cholesterol-water. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Oct 2;144(2):189–201. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgès M., Small D. M., Dervichian D. G. Biophysics of lipidic associations. II. The ternary systems: cholesterol-lecithin-water. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Feb 14;137(1):157–167. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(67)90019-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dam H., Kruse I., Kallehauge H. E., Hartkopp O. E., Jensen M. K. Studies on human bile. I. Composition of bladder bile from cholelithiasis patients and surgical patients with normal bile compared with data for bladder bile of hamsters on different diets. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1966;18(4):385–404. doi: 10.3109/00365516609113159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FURUSAWA T. [Surface-chemical studies on the stability of human bile]. Fukuoka Igaku Zasshi. 1962 Mar;53:124–165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofmann A. F., Small D. M. Detergent properties of bile salts: correlation with physiological function. Annu Rev Med. 1967;18:333–376. doi: 10.1146/annurev.me.18.020167.002001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAKSSON B. On the dissolving power of lecithin and bile salts for cholesterol in human bladder bile. Acta Soc Med Ups. 1954 Sep 30;59(5-6):296–306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAKSSON B. On the lipid constituents of bile from human gallbladder containing cholesterol gallstones; a comparison with normal human bladder bile. Acta Soc Med Ups. 1954 Sep 30;59(5-6):277–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAKSSON B. On the lipid constituents of normal bile. Acta Soc Med Ups. 1951;56(5-6):177–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAKSSON B. On the main cholanic acids of human bile from normal gallbladder and from gallbladder associated with cholesterol stones. Acta Soc Med Ups. 1954 Sep 30;59(5-6):307–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JUNIPER K., Jr, BURSON E. N., Jr Biliary tract studies. II. The significance of biliary crystals. Gastroenterology. 1957 Feb;32(2):175-208; discussion, 208-11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JUNIPER K., Jr PHYSICOCHEMICAL CHARACTERISTICS OF BILE AND THEIR RELATION TO GALLSTONE FORMATION. Am J Med. 1965 Jul;39:98–107. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90249-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LARGE A. M., JOHNSTON C. G., KATSUKI T., FACHNIE H. L. Gallstones and pregnancy: the composition of gallbladder bile in the pregnant woman at term. Am J Med Sci. 1960 Jun;239:713–720. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIRVISH S. S. BILE ACIDS AND OTHER LIPIDS IN THE GALL-BLADDER BILES OF AFRICANS WITH PRIMARY CANCER OF THE LIVER. Br J Cancer. 1964 Sep;13:478–483. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1964.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POLONOVSKI M., BOURRILLON R. Les phospholipides de la bile. Bull Soc Chim Biol (Paris) 1952;34(7-8):712–719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. M., Bourgès M. C., Dervichian D. G. The biophysics of lipidic associations. I. The ternary systems: lecithin-bile salt-water. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Dec 7;125(3):563–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. M., Bourgès M., Dervichian D. G. Ternary and quaternary aqueous systems containing bile salt, lecithin, and cholesterol. Nature. 1966 Aug 20;211(5051):816–818. doi: 10.1038/211816a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Small D. M. Phase equilibria and structure of dry and hydrated egg lecithin. J Lipid Res. 1967 Nov;8(6):551–557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERA H. Sedimentation of bile constituents. Ann Surg. 1963 Mar;157:468–472. doi: 10.1097/00000658-196303000-00019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamesue N., Juniper K., Jr Concentrations of bile salts at the critical micellar concentration of human gall bladder bile. Gastroenterology. 1967 Mar;52(3):473–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VERSCHURE J. C., MIJNLIEFF P. F. The dominating macromolecular complex of human gallbladder bile. Clin Chim Acta. 1956 Mar;1(2):154–166. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(56)90031-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOTTON I. D., WIGGINS H. S. Studies in the bile acids. 2. The non-ketonic acids of human bile. Biochem J. 1953 Sep;55(2):292–294. doi: 10.1042/bj0550292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


