Abstract
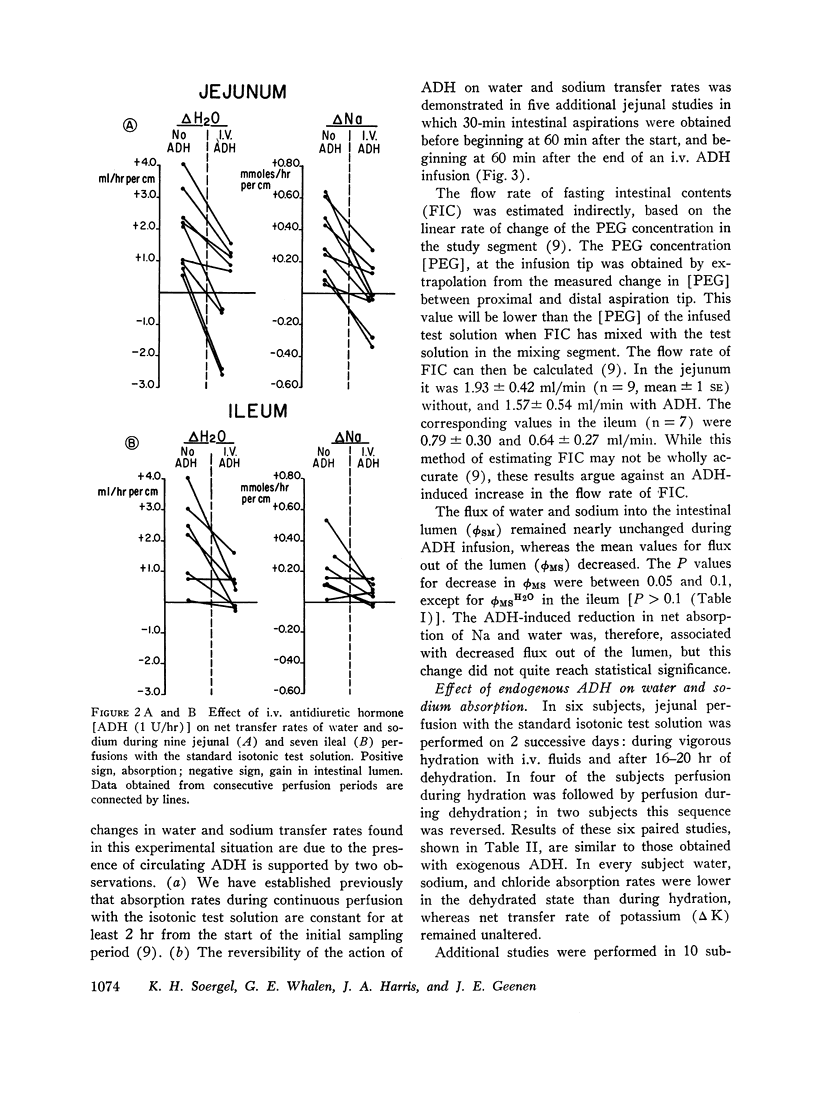
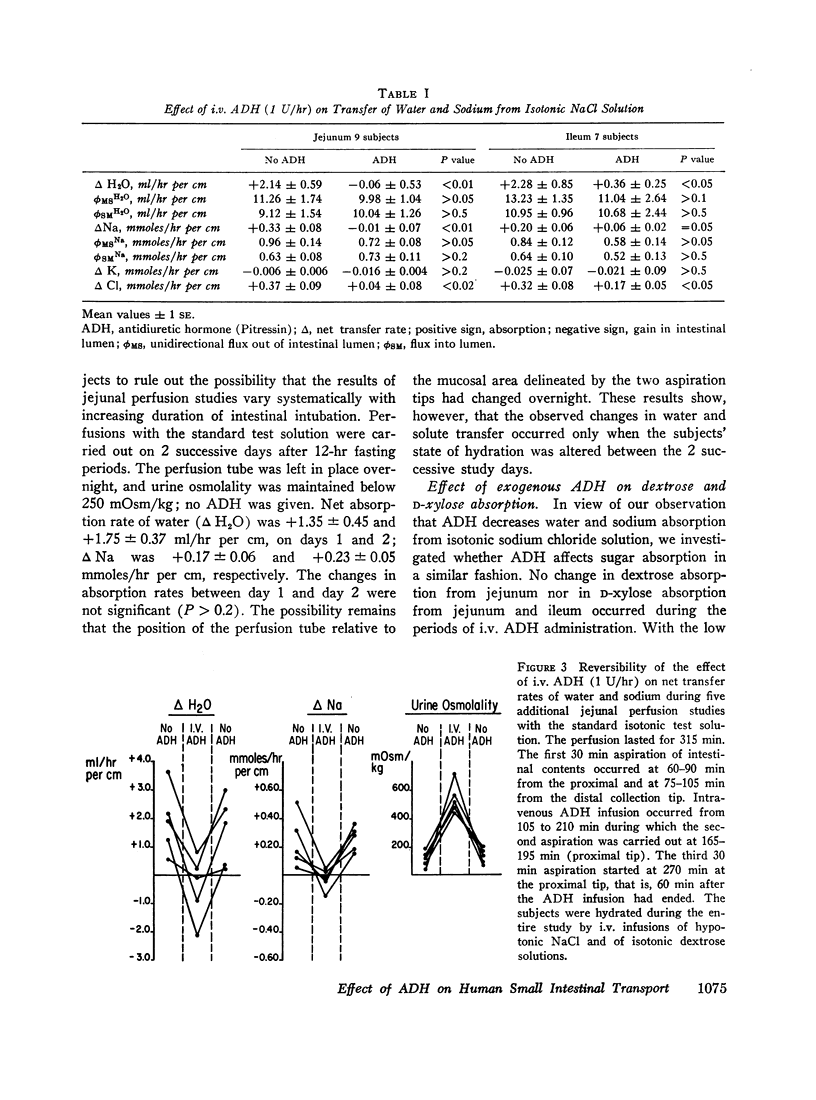
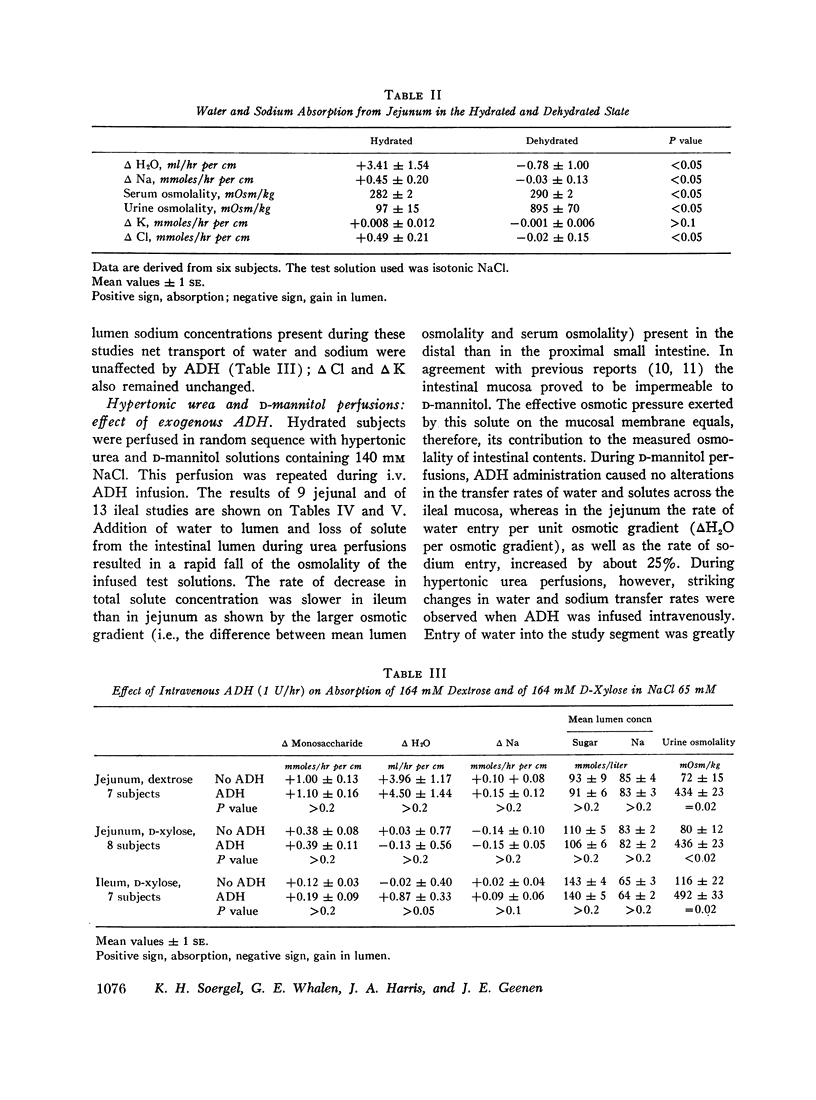
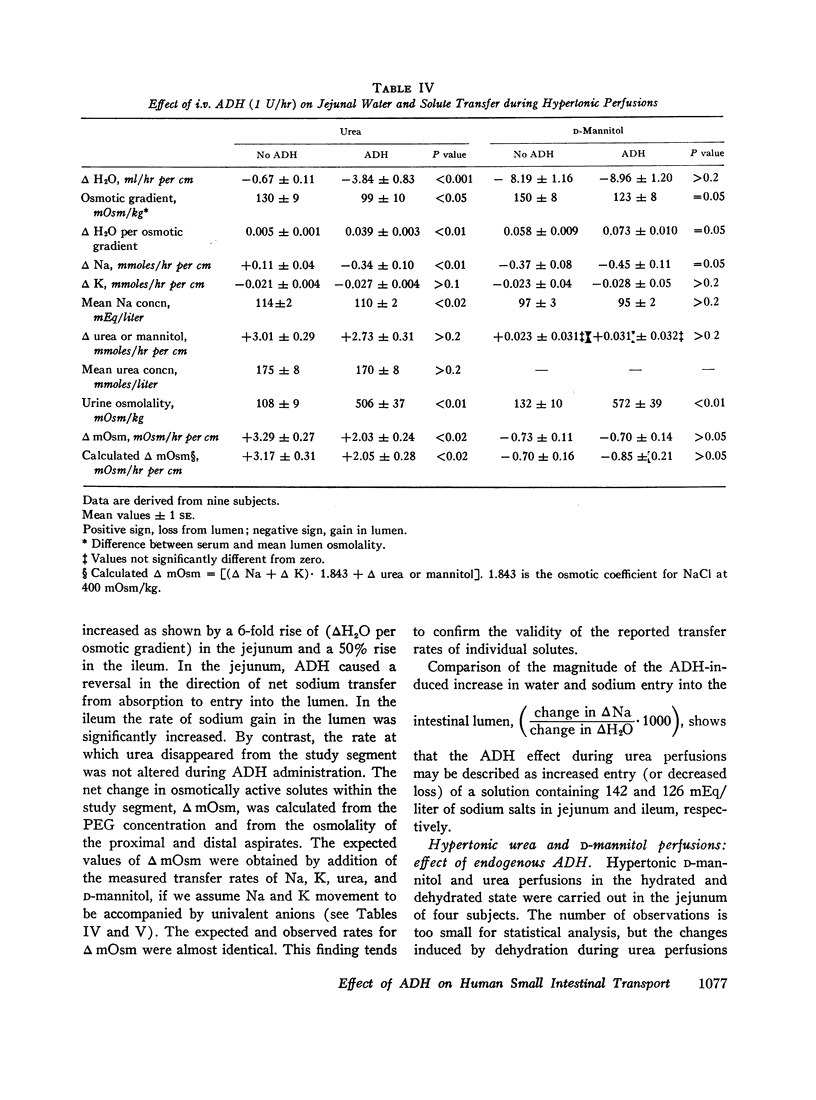
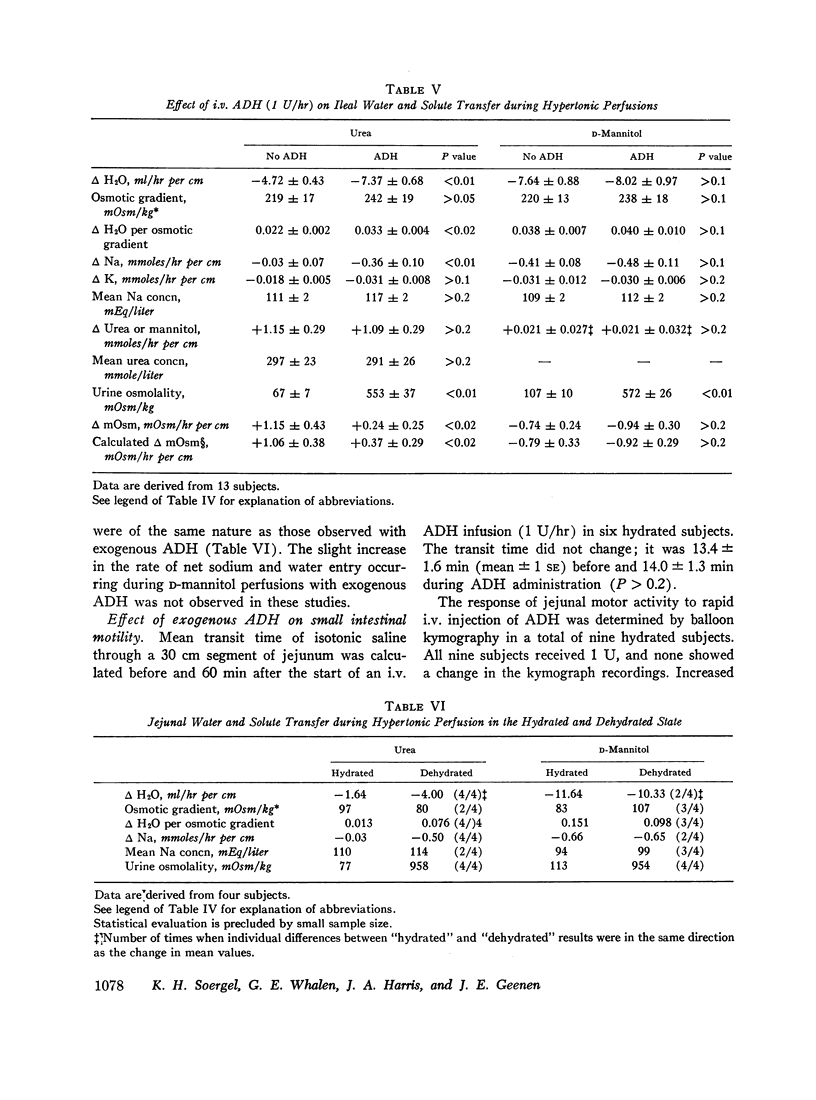
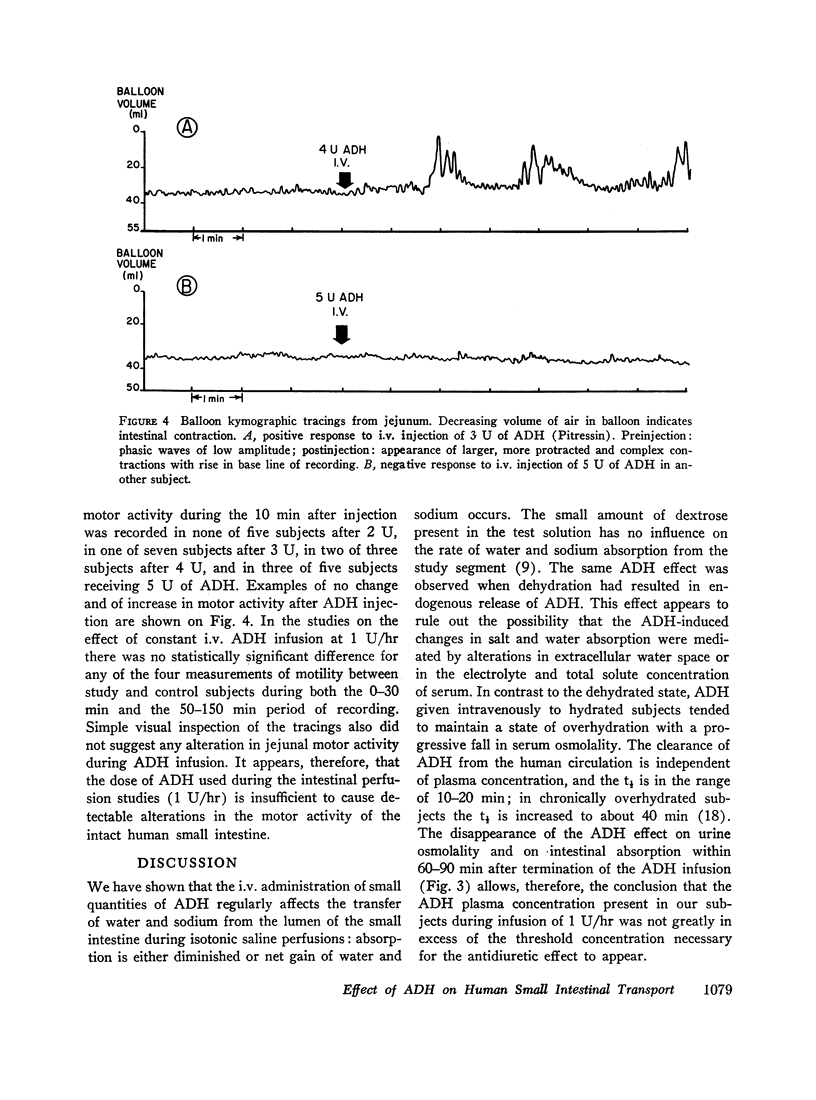
The effect of i.v. Pitressin (ADH) in a dose of 1 U/hr on permeability characteristics and on absorptive capacity of the normal human small intestine was investigated. The method of continuous intestinal perfusion was employed with polyethylene glycol 4000 as a nonabsorbable marker. Unidirectional flux rates of Na and H2O were calculated from the disappearance of 22Na and of 3HOH from isotonic saline solution within the intestinal lumen. Each study consisted of two successive perfusion periods: one while the subject was hydrated, the other during ADH infusion or while the subject was dehydrated. Water and sodium absorption from isotonic NaCl occurred in the hydrated state and was abolished by ADH as well as by dehydration in the jejunum. In some instances, net gain of water and sodium in the lumen occurred. In the ileum, ADH and dehydration caused a decrease in water and sodium absorption rate. By contrast, unidirectional flux into the intestinal lumen of water and sodium, as well as dextrose and D-xylose diffusion, remained unchanged by ADH. During perfusions with hypertonic urea solutions the rates of sodium and water entry into the intestine were greatly increased during i.v. ADH infusion, whereas urea loss from the study segment remained constant. ADH in the dosage used did not affect human intestinal motility. The results suggest that circulating ADH in physiologic concentrations affects the small intestine in one of two ways: increased secretion of water and salt into the lumen or direct interference with the active sodium transport mechanism.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AULSEBROOK K. A. Effect of vasopressin on sodium transfer by rat colon in vitro. Endocrinology. 1961 Jun;68:1063–1065. doi: 10.1210/endo-68-6-1063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BINGHAM J. R., INGELFINGER F. J., SMITHWICK R. H. The effects of sympathectomy on the motility of the human gastrointestinal and biliary tracts. Gastroenterology. 1950 May;15(1 1):6–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLICKENSTAFF D. D. Increase in intestinal absorption of water from isosmotic saline following pitressin administration. Am J Physiol. 1954 Dec;179(3):471–472. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1954.179.3.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CURRAN P. F., SOLOMON A. K. Ion and water fluxes in the ileum of rats. J Gen Physiol. 1957 Sep 20;41(1):143–168. doi: 10.1085/jgp.41.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper H., Levitan R., Fordtran J. S., Ingelfinger F. J. A method for studying absorption of water and solute from the human small intestine. Gastroenterology. 1966 Jan;50(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOMBRADI G. A., KRIZSA F., JANCSO T. [Kinetics of intestinal water absorption in rats under the influence of ADH]. Acta Physiol Acad Sci Hung. 1960;17:301–308. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S., Dietschy J. M. Water and electrolyte movement in the intestine. Gastroenterology. 1966 Feb;50(2):263–285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S., Rector F. C., Jr, Ewton M. F., Soter N., Kinney J. Permeability characteristics of the human small intestine. J Clin Invest. 1965 Dec;44(12):1935–1944. doi: 10.1172/JCI105299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson E. D., Swan K. G., Grossman M. I. Blood flow and secretion in the stomach. Gastroenterology. 1967 Feb;52(2):414–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lauson H. D. Metabolism of antidiuretic hormones. Am J Med. 1967 May;42(5):713–744. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90091-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leaf A. Membrane effects of antidiuretic hormone. Am J Med. 1967 May;42(5):745–756. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90092-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenstein N. S., Leaf A. Evidence for a double series permeability barrier at the mucosal surface of the toad bladder. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jul 14;137(2):556–565. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb50181.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANDERSON P. H. Potentiometric determination of chloride in biological fluids. Biochem J. 1952 Nov;52(3):502–505. doi: 10.1042/bj0520502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer W. H. Evolution of antidiuretic hormones and their functions. Am J Med. 1967 May;42(5):678–686. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90088-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schapiro H., Storer E. H., Britt L. G. Action of antidiuretic hormone on gastric secretion. Arch Surg. 1966 May;92(5):699–703. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1966.01320230047008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soergel K. H., Whalen G. E., Harris J. A. Passive movement of water and sodium across the human small intestinal mucosa. J Appl Physiol. 1968 Jan;24(1):40–48. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1968.24.1.40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEXTER E. C., Jr Small intestinal blood flow. Am J Dig Dis. 1963 Jul;8:587–613. doi: 10.1007/BF02239457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whalen G. E., Harris J. A., Geenen J. E., Soergel K. H. Sodium and water absorption from the human small intestine. The accuracy of the perfusion method. Gastroenterology. 1966 Dec;51(6):975–984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



