Abstract
The effect of luminal sodium on intestinal glucose absorption at a variety of glucose concentrations was studied with a segmental perfusion technique in normal subjects.
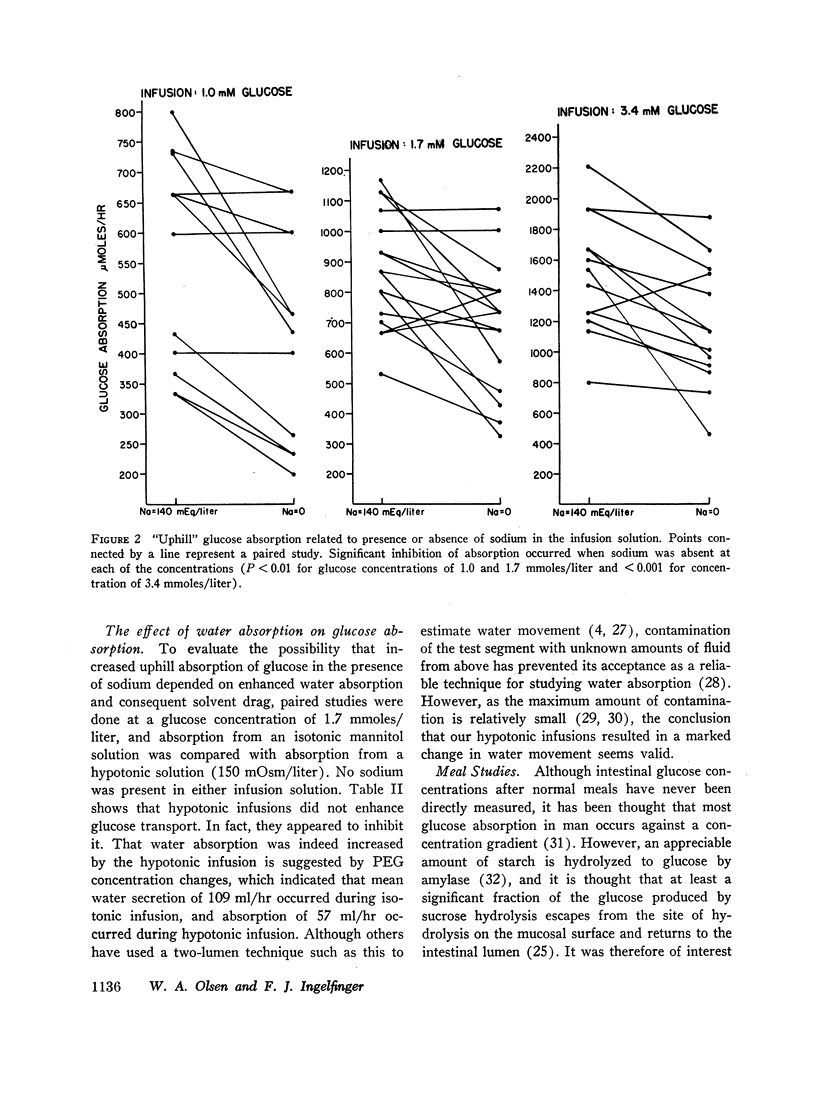
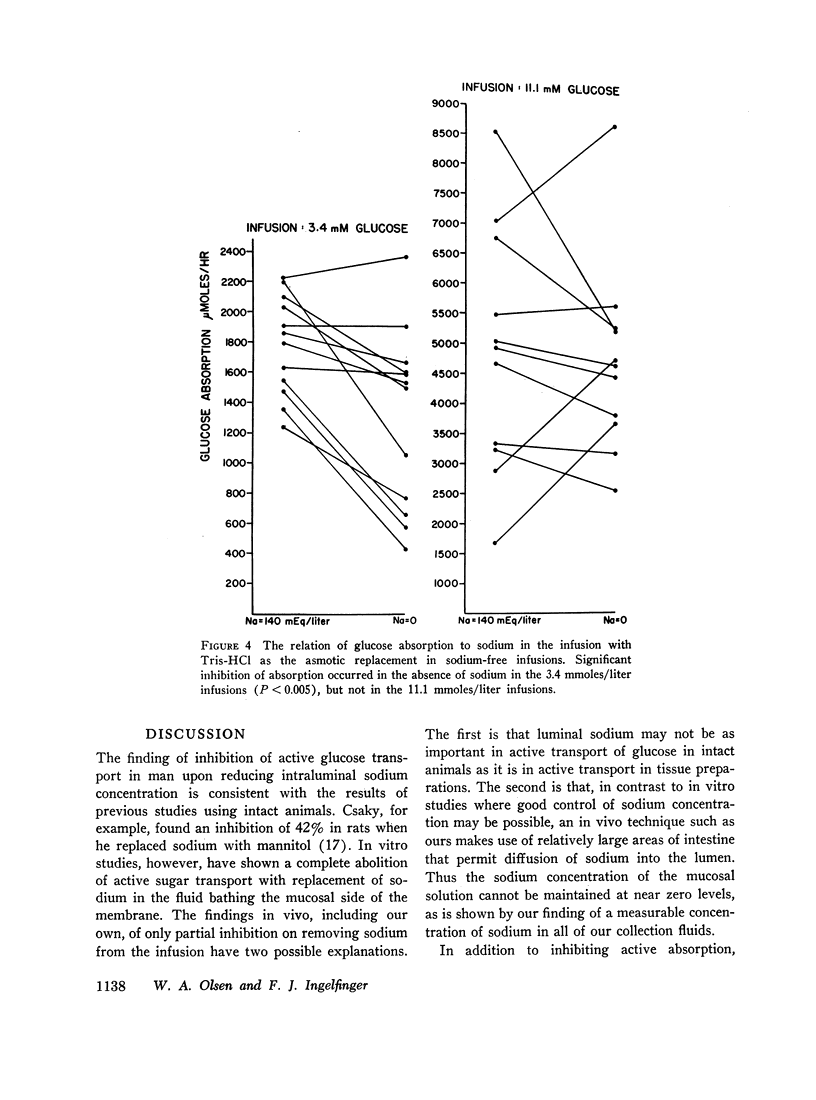
Uphill glucose transport was inhibited with sodium-free perfusions with either mannitol or Tris-HCl as the osmotic replacement of sodium (P < 0.01-P < 0.001). This effect did not appear to be the result of solvent drag, as increasing net water absorption without supplying sodium to the lumen did not increase glucose absorption.
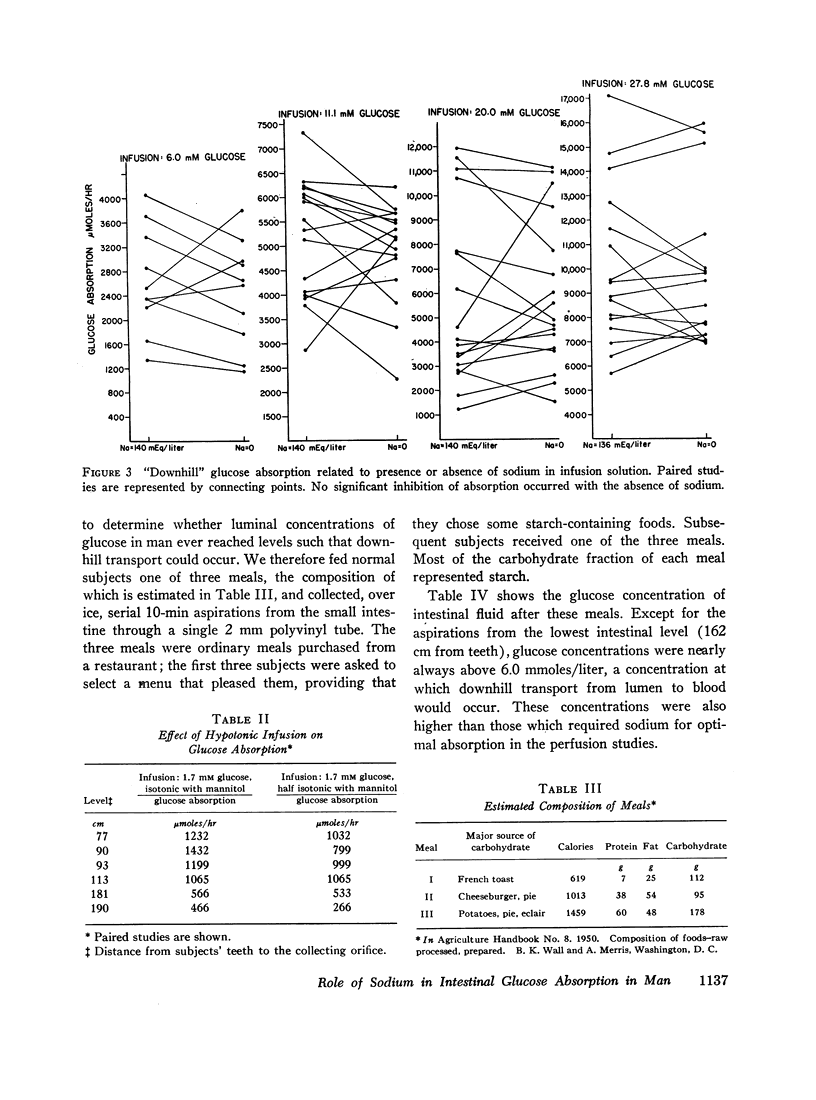
Downhill glucose transport (infusion concentrations of 6.0-27.8 mmoles/liter), on the other hand, was not affected by the absence of sodium in the infusion solution.
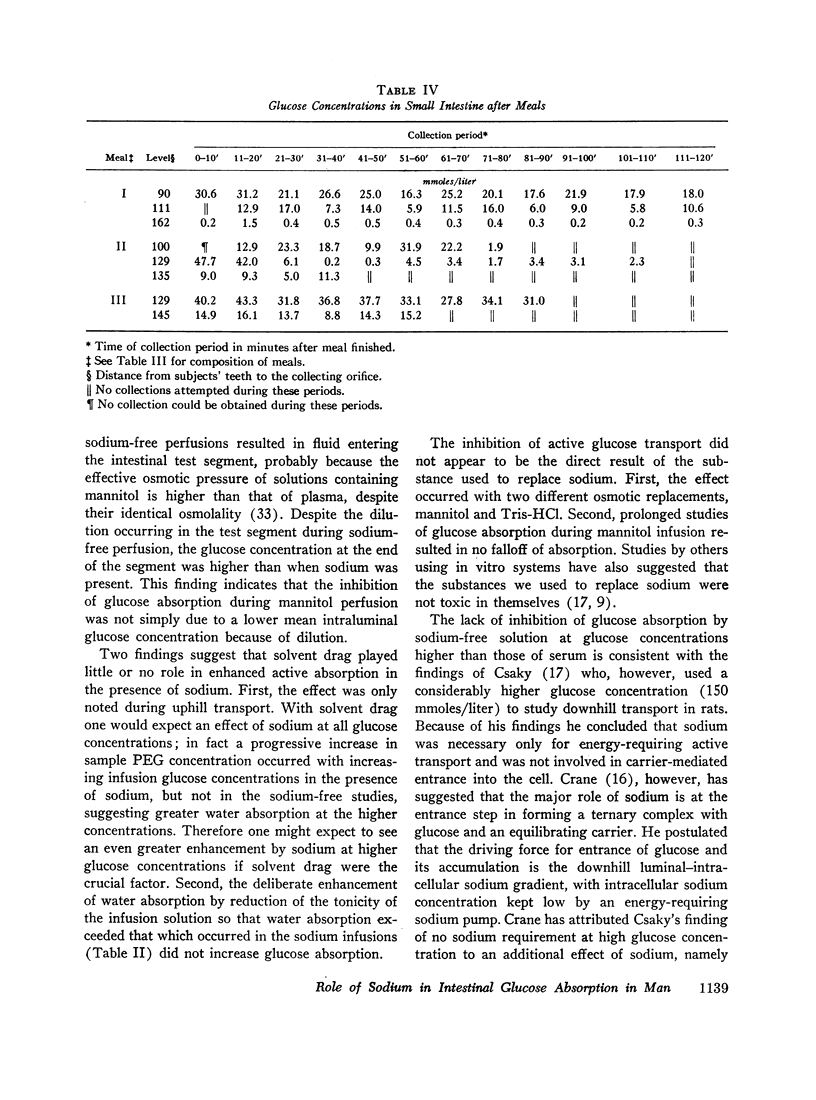
Glucose concentrations of upper intestinal fluid after normal carbohydrate meals were usually found to exceed serum concentrations; thus, downhill glucose absorption, with, at most, a very limited dependence upon intraluminal sodium concentration, may account for a significant part of normal carbohydrate absorption.
Full text
PDF


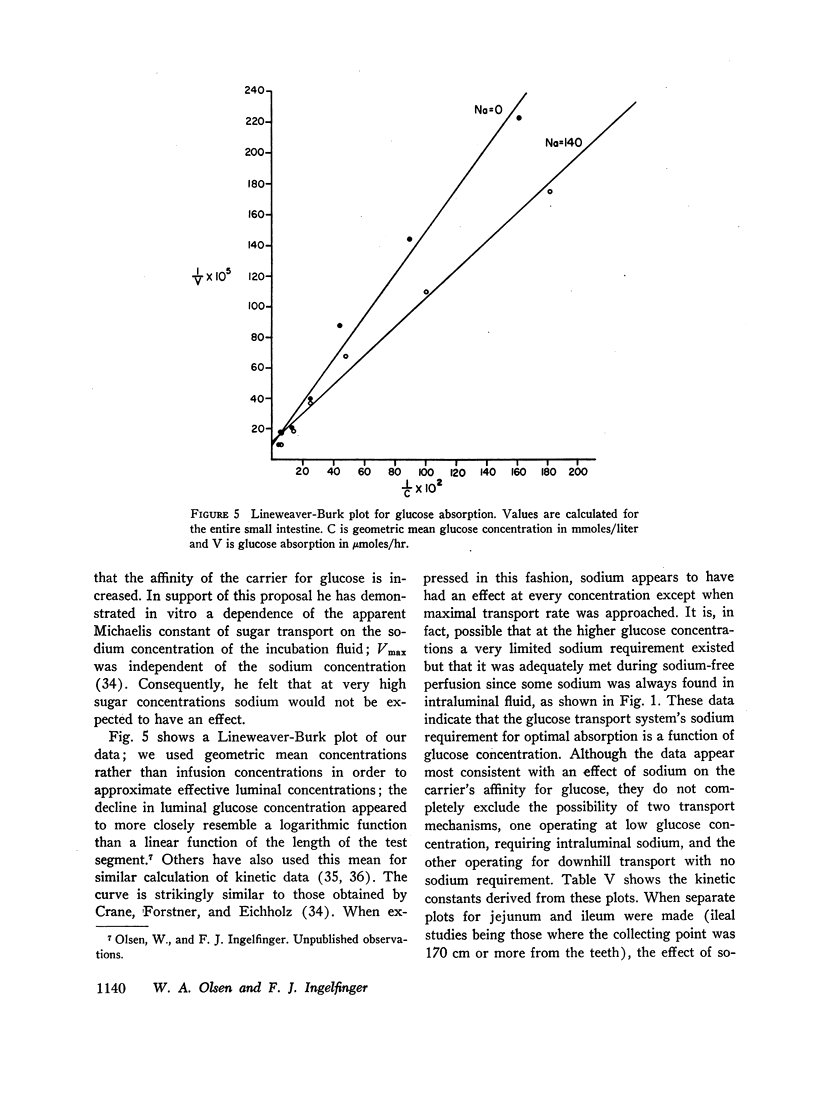


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANNEGERS J. H. SOME EFFECTS OF CATIONS AND OF WATER ABSORPTION ON INTESTINAL HEXOSE, GLYCINE AND CATION ABSORPTION. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Aug-Sep;116:933–937. doi: 10.3181/00379727-116-29413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BIHLER I., CRANE R. K. Studies on the mechanism of intestinal absorption of sugars. V. The influence of several cations and anions on the active transport of sugars, in vitro, by various preparations of hamster small intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 May 7;59:78–93. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(62)90699-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CSAKAY T. Z. A possible link between active transport of electrolytes and nonelectrolyes. Fed Proc. 1963 Jan-Feb;22:3–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CSAKY T. Z. Significance of sodium ions in active intestinal transport of nonelectrolytes. Am J Physiol. 1961 Dec;201:999–1001. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1961.201.6.999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CSAKY T. Z., ZOLLICOFFER L. Ionic effect on intestinal transport of glucose in the rat. Am J Physiol. 1960 May;198:1056–1058. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1960.198.5.1056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper H., Levitan R., Fordtran J. S., Ingelfinger F. J. A method for studying absorption of water and solute from the human small intestine. Gastroenterology. 1966 Jan;50(1):1–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crane R. K., Forstner G., Eichholz A. Studies on the mechanism of the intestinal absorption of sugars. X. An effect of Na+ concentration on the apparent Michaelis constants for intestinal sugar transport, in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Nov 29;109(2):467–477. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(65)90172-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crane R. K. Na+ -dependent transport in the intestine and other animal tissues. Fed Proc. 1965 Sep-Oct;24(5):1000–1006. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csáky T. Z., Ho P. M. The effect of potassium on the intestinal transport of glucose. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Sep;50(1):113–128. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.1.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHLQVIST A., BORGSTROM B. Digestion and absorption of disaccharides in man. Biochem J. 1961 Nov;81:411–418. doi: 10.1042/bj0810411. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FISHER R. B., PARSONS D. S. Glucose movements across the wall of the rat small intestine. J Physiol. 1953 Feb 27;119(2-3):210–223. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FORDTRAN J. S., SOERGEL K. H., INGELFINGER F. J. Intestinal absorption of D-xylose in man. N Engl J Med. 1962 Aug 9;267:274–279. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196208092670602. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleshler B., Butt J. H., Wismar J. D. Absorption of glycine and L-alanine by the human jejunum. J Clin Invest. 1966 Sep;45(9):1433–1441. doi: 10.1172/JCI105451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fordtran J. S. Speculations on the pathogenesis of diarrhea. Fed Proc. 1967 Sep;26(5):1405–1414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY G. M., INGELFINGER F. J. INTESTINAL ABSORPTION OF SUCROSE IN MAN: THE SITE OF HYDROLYSIS AND ABSORPTION. J Clin Invest. 1965 Mar;44:390–398. doi: 10.1172/JCI105152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray G. M., Ingelfinger F. J. Intestinal absorption of sucrose in man: interrelation of hydrolysis and monosaccharide product absorption. J Clin Invest. 1966 Mar;45(3):388–398. doi: 10.1172/JCI105354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOLDSWORTH C. D., DAWSON A. M. THE ABSORPTION OF MONOSACCHARIDES IN MAN. Clin Sci. 1964 Dec;27:371–379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGGETT A. S., NIXON D. A. Use of glucose oxidase, peroxidase, and O-dianisidine in determination of blood and urinary glucose. Lancet. 1957 Aug 24;273(6991):368–370. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)92595-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JACOBSON E. D., BONDY D. C., BROITMAN S. A., FORDTRAN J. S. Validity of polyethylene glycol in estimating intestinal water volume. Gastroenterology. 1963 Jun;44:761–767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson R. A., Schedl H. P. Absorption of sodium, chloride, water, and simple sugars in rat small intestine. Am J Physiol. 1966 Oct;211(4):939–942. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.211.4.939. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PLAYOUST M. R., ISSELBACHER K. J. STUDIES ON THE TRANSPORT AND METABOLISM OF CONJUGATED BILE SALTS BY INTESTINAL MUCOSA. J Clin Invest. 1964 Mar;43:467–476. doi: 10.1172/JCI104932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips S. F., Summerskill W. H. Occlusion of the jejunum for intestinal perfusion in man. Mayo Clin Proc. 1966 Apr;41(4):224–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIKLIS E., QUASTEL J. H. Effects of cations on sugar absorption by isolated surviving guinea pig intestine. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1958 Mar;36(3):347–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rider A. K., Schedl H. P., Nokes G., Shining S. Small intestinal glucose transport. Proximal-distal kinetic gradients. J Gen Physiol. 1967 May;50(5):1173–1182. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.5.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg I. H., Coleman A. L., Rosenberg L. E. The role of sodium ion in the transport of amino acids by the intestine. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 May 25;102(1):161–171. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(65)90210-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEDL H. P., CLIFTON J. A. SOLUTE AND WATER ABSORPTION BY THE HUMAN SMALL INTESTINE. Nature. 1963 Sep 28;199:1264–1267. doi: 10.1038/1991264a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHULTZ S. G., ZALUSKY R. The interaction between active sodium transport and active sugar transport in the isolated rabbit ileum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1963 May 14;71:503–505. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(63)91121-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. G., Fuisz R. E., Curran P. F. Amino acid and sugar transport in rabbit ileum. J Gen Physiol. 1966 May;49(5):849–866. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.5.849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALLEY R. B., SCHEDL H. P., CLIFTON J. A. SMALL INTESTINAL GLUCOSE, ELECTROLYTE, AND WATER ABSORPTION IN CIRRHOSIS. Gastroenterology. 1964 Oct;47:382–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



