Abstract
Human serum albumin and human γG globulin were labeled with 131I, and the labeled proteins were then mixed with different amounts of the respective unlabeled protein. These mixtures were injected intravenously into pregnant mice near term, and the amounts of protein-bound radioactivity present in the fetuses and in maternal serum 24 hr later were determined.
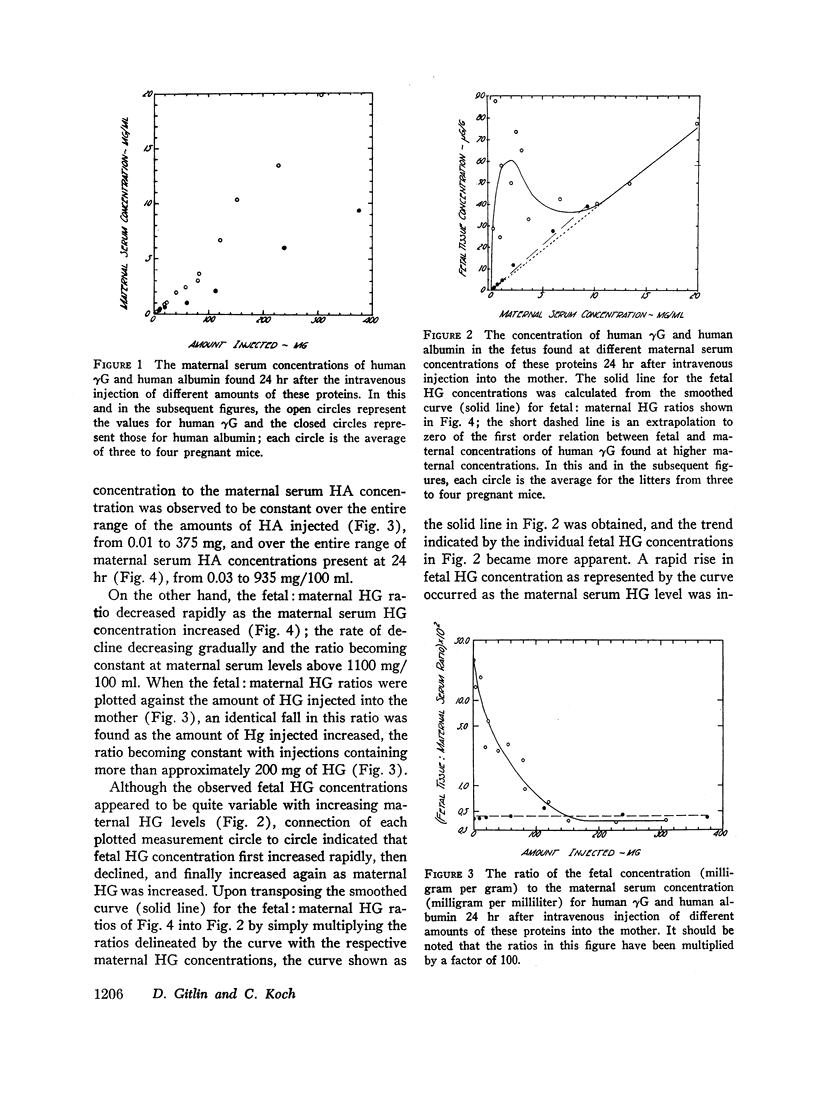
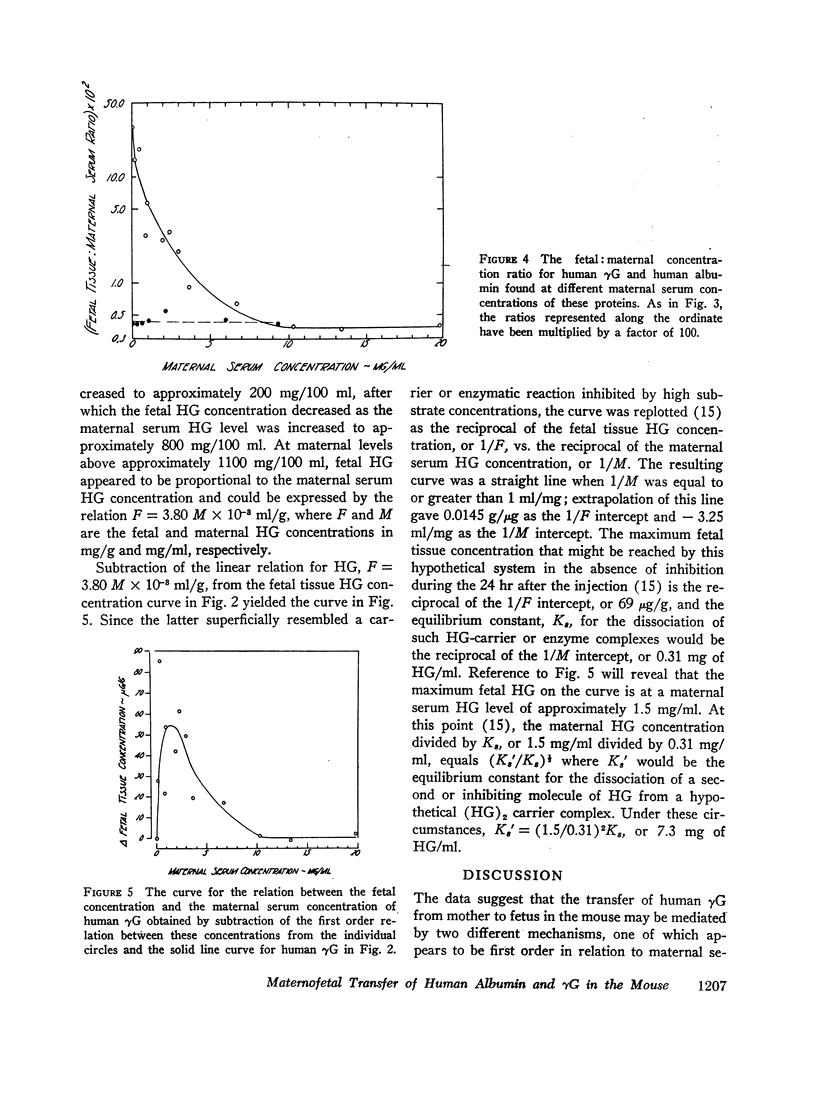
The concentration of human albumin found in the fetus was proportional to the maternal serum concentration of this protein over the maternal range studied, from 0.03 to 935 mg/100 ml. On the other hand, the fetal concentration of human γG first increased rapidly as the maternal concentration increased to approximately 200 mg/100 ml and then decreased as the maternal concentration continued to increase above this level; however, as the maternal human γG level increased above approximately 1100 mg/100 ml, the fetal concentration again increased and became proportional to the maternal concentration. The data suggest that maternofetal transfer of human γG in the mouse may be mediated by two processess; one of these, as with the transfer of human albumin, appears to be first order in relation to the maternal serum concentration, and the other appears to be consistent with a carrier or enzymatic process that is directly or indirectly inhibited at high maternal serum levels.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BANGHAM D. R., HOBBS K. R., TERRY R. J. Selective placental transfer of serum-proteins in the rhesus. Lancet. 1958 Aug 16;2(7042):351–354. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(58)90264-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brambell F. W. The transmission of immunity from mother to young and the catabolism of immunoglobulins. Lancet. 1966 Nov 19;2(7473):1087–1093. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(66)92190-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL R. M., CUTHBERTSON D. P., MATTHEWS C. M., MCFARLANE A. S. Behaviour of 14C- and 131I-labelled plasma proteins in the rat. Int J Appl Radiat Isot. 1956 Jul;1(1-2):66–84. doi: 10.1016/0020-708x(56)90020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANCIS J., LIND J., ORATZ M., SMOLENS J., VARA P. Placental transfer of proteins in human gestation. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1961 Jul;82:167–171. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9378(16)36111-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAHEY J. L., SELL S. THE IMMUNOGLOBULINS OF MICE. V. THE METABOLIC (CATABOLIC) PROPERTIES OF FIVE IMMUNOGLOBULIN CLASSES. J Exp Med. 1965 Jul 1;122:41–58. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GITLIN D., JANEWAY C. A. An immunochemical study of the albumins of serum, urine, ascitic fluid and edema fluid in the nephrotic syndrome. J Clin Invest. 1952 Feb;31(2):223–230. doi: 10.1172/JCI102596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GITLIN D., JANEWAY C. A. Some isotopic studies on the distribution and metabolism of plasma proteins. Adv Biol Med Phys. 1960;7:249–293. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4832-3113-6.50009-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GITLIN D., KUMATE J., URRUSTI J., MORALES C. THE SELECTIVITY OF THE HUMAN PLACENTA IN THE TRANSFER OF PLASMA PROTEINS FROM MOTHER TO FETUS. J Clin Invest. 1964 Oct;43:1938–1951. doi: 10.1172/JCI105068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gitlin D., Kumate J., Morales C. Metabolism and maternofetal transfer of human growth hormone in the pregnant woman at term. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Dec;25(12):1599–1608. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-12-1599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch C., Boesman M., Gitlin D. Maternofoetal transfer of gamma G immunoglobulins. Nature. 1967 Dec 16;216(5120):1116–1117. doi: 10.1038/2161116a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini G., Carbonara A. O., Heremans J. F. Immunochemical quantitation of antigens by single radial immunodiffusion. Immunochemistry. 1965 Sep;2(3):235–254. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(65)90004-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFARLANE A. S. The behavior of I 131-labeled plasma proteins in vivo. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1957 Aug 30;70(1):19–25. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1957.tb35374.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarlane A. S. IN VIVO BEHAVIOR OF I-FIBRINOGEN. J Clin Invest. 1963 Mar;42(3):346–361. doi: 10.1172/JCI104721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRESSMAN D., EISEN H. N. The zone of localization of antibodies. V. An attempt to saturate antibody-binding sites in mouse kidney. J Immunol. 1950 Apr;64(4):273–279. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


