Abstract
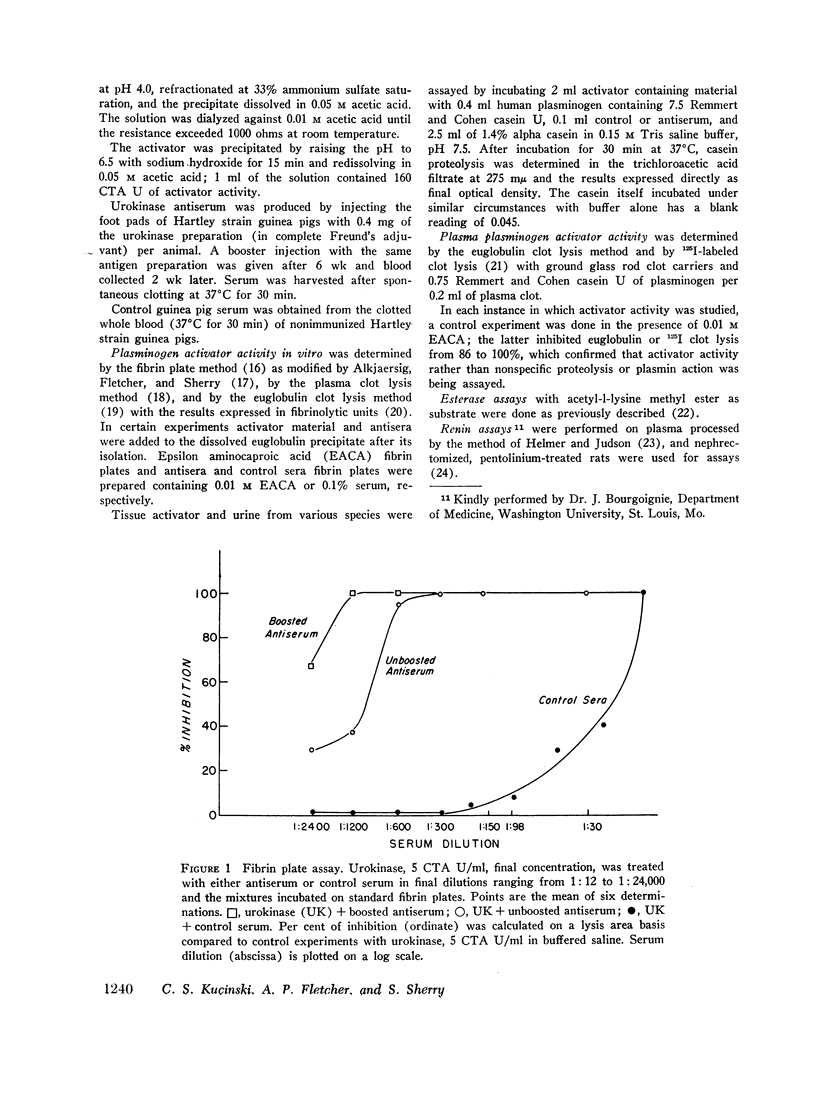
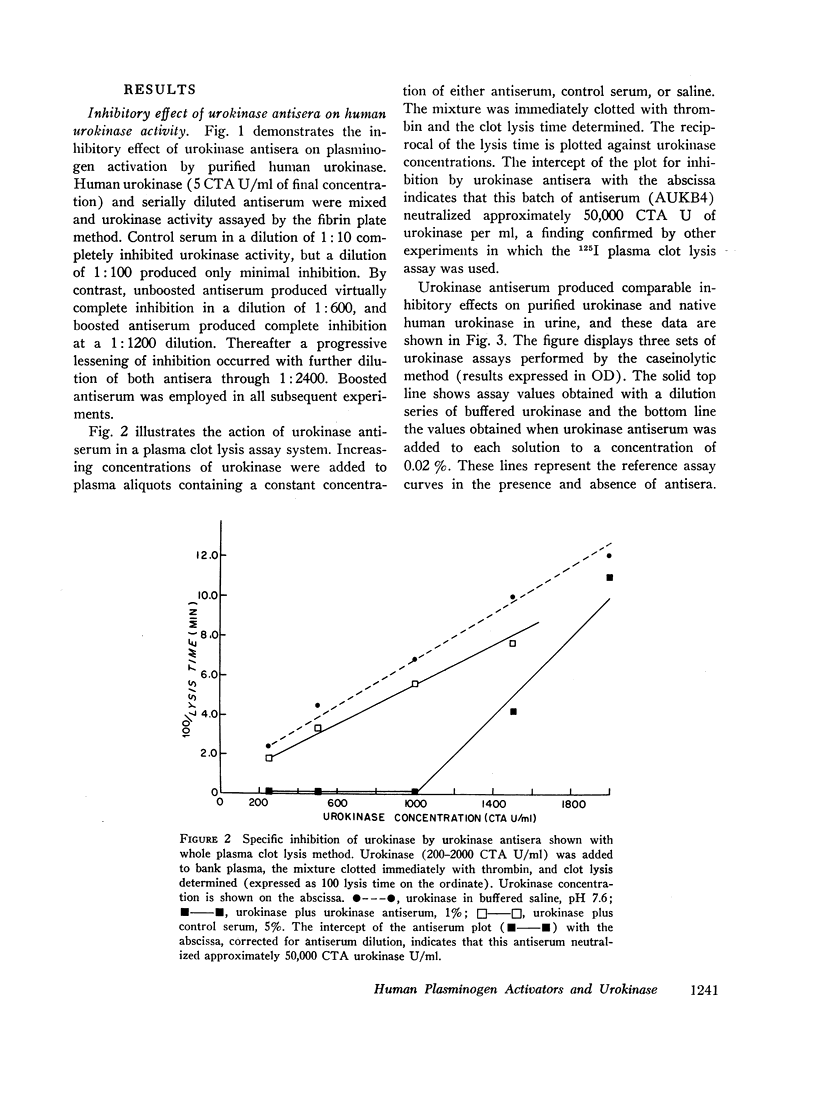
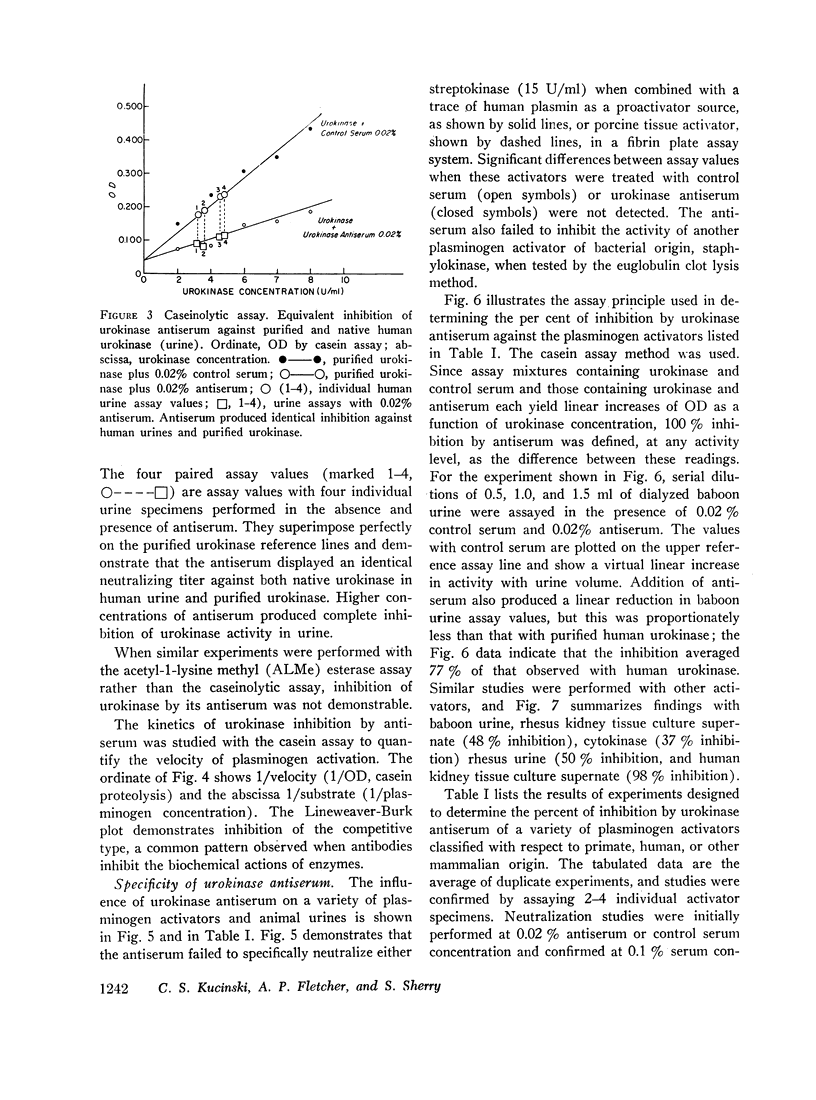
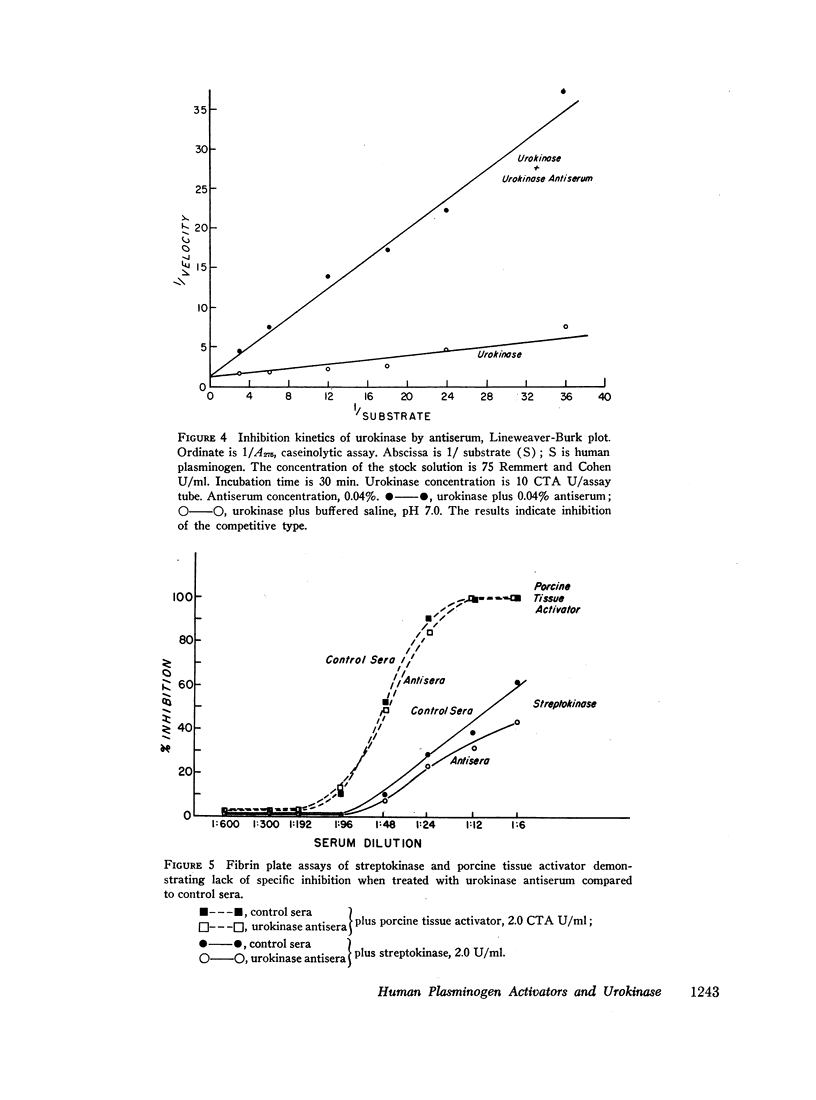
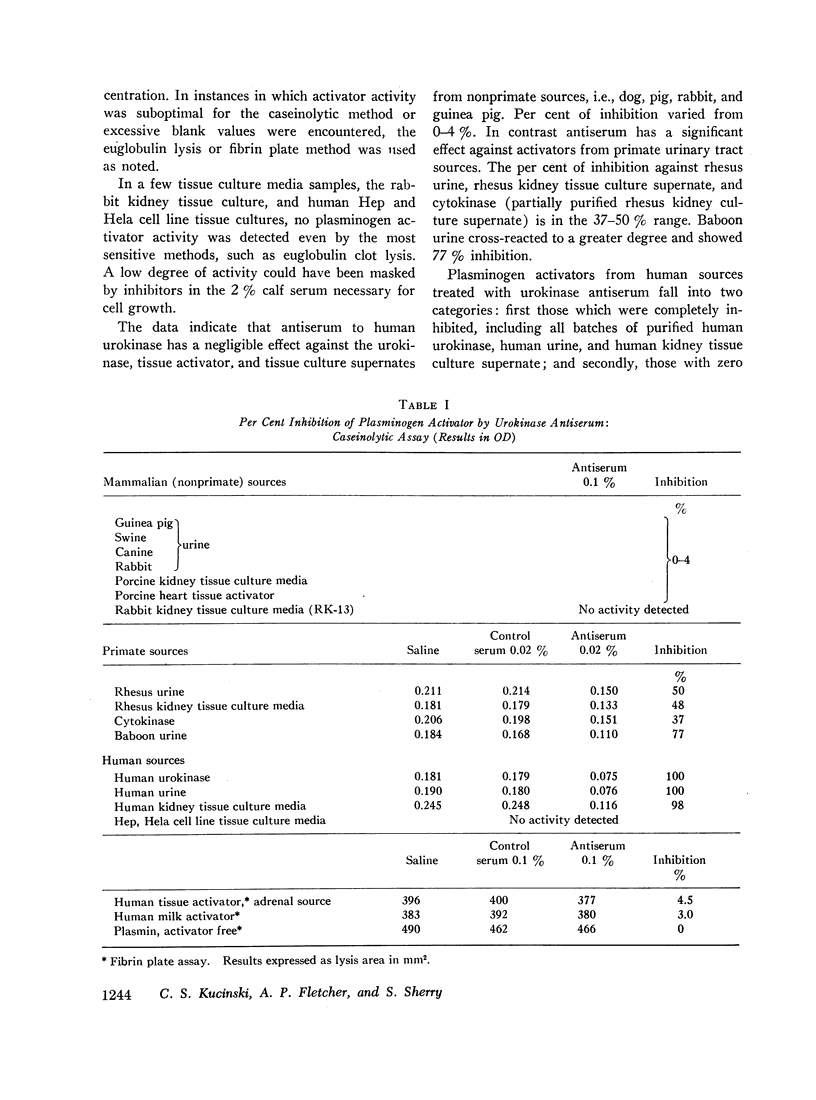
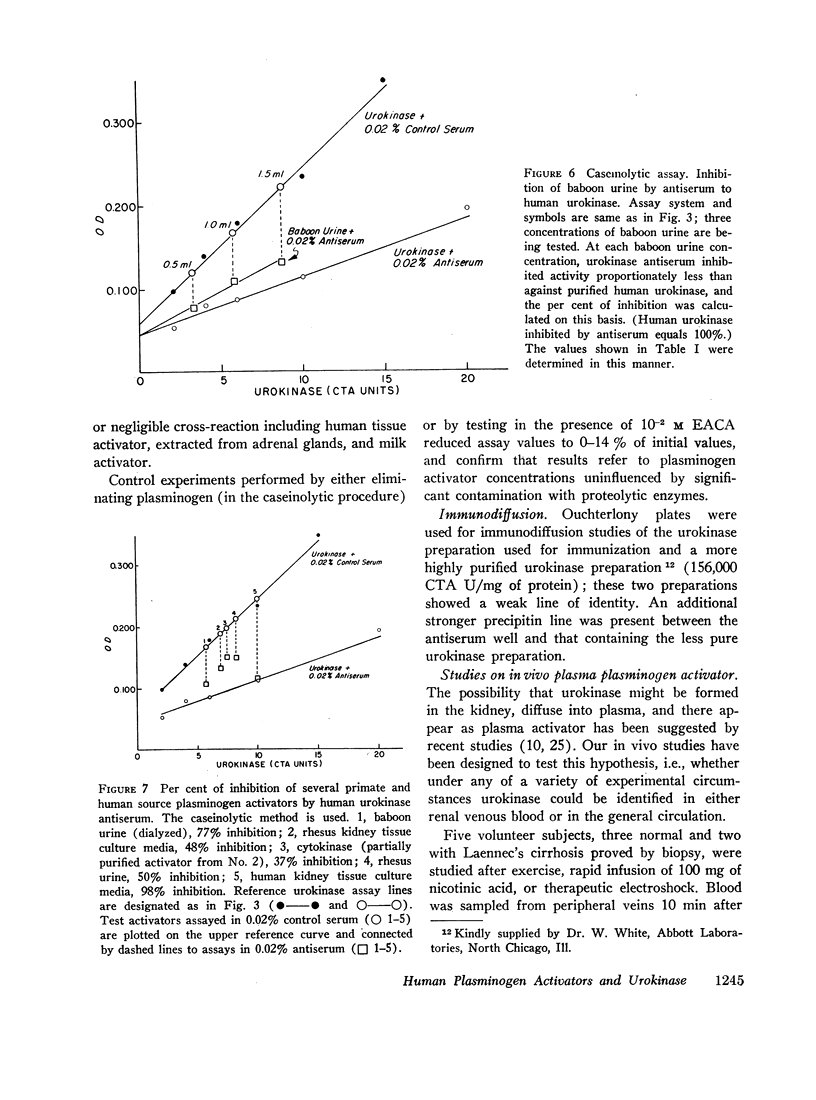
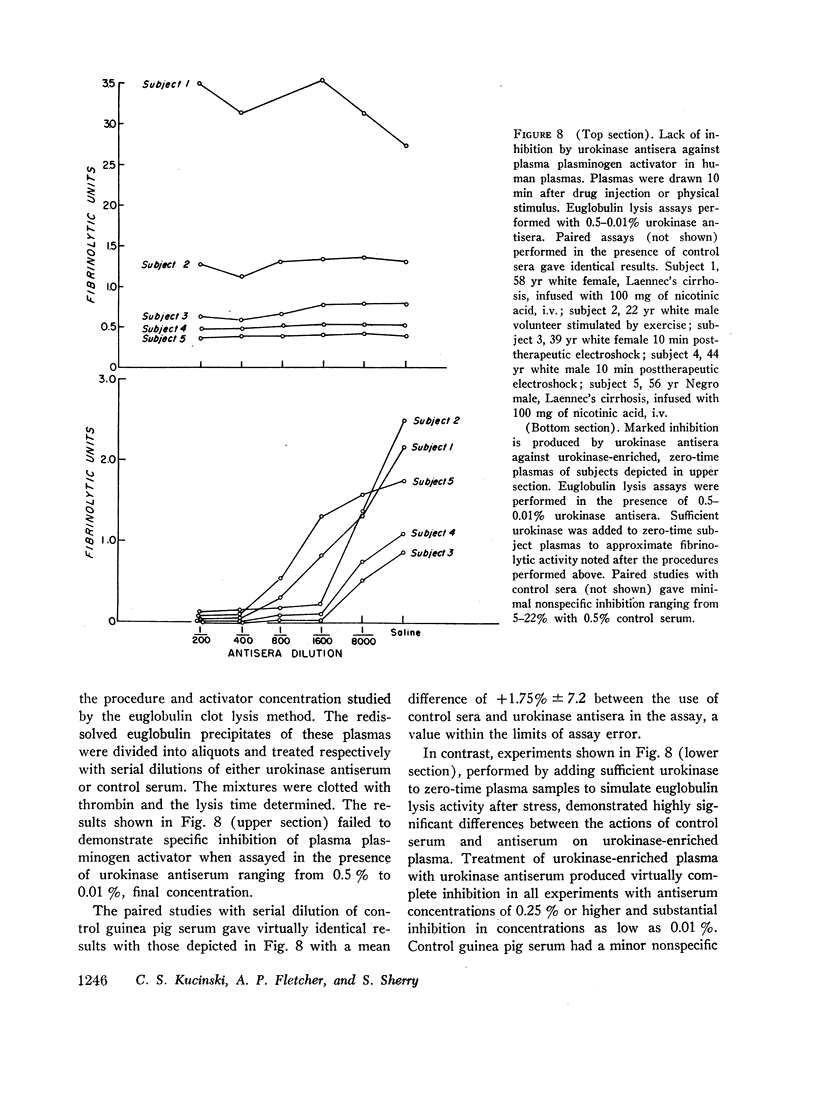
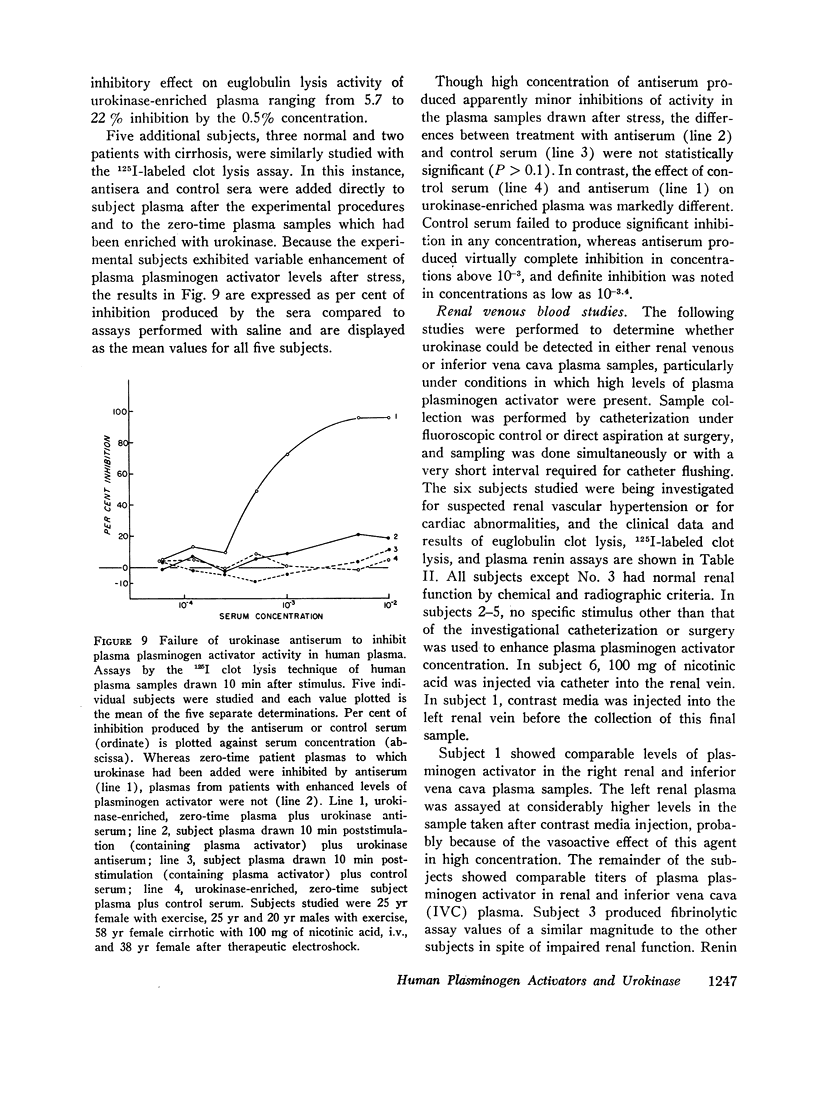
Antiserum against purified human urokinase was produced by immunization of Hartley strain guinea pigs. The antiserum was capable of neutralizing the plasminogen activator activity of the antigen and of native urokinase in human urine. The antiserum did not inhibit plasminogen activators of bacterial origin, i.e., streptokinase and staphylokinase; neither did it inhibit urokinase from nonprimate mammals, i.e., dog, pig, rabbit, guinea pig, nor tissue activator or tissue culture supernatants from porcine sources. Partial cross-reactivity against urokinase from primates, i.e., rhesus monkey and baboon, was noted as well as with supernatant from rhesus kidney tissue culture. In vitro studies showed lack of immunologic identity between human urokinase and human milk activator or human tissue activator from adrenal sources but demonstrated immunologic identity between human urokinase and the supernatant from human kidney tissue culture. In vivo studies in man failed to show detectable levels of urokinase activity in peripheral venous or renal venous blood under a variety of clinical states and when stimuli such as exercise, electroshock therapy, or nicotinic acid were used to enhance plasminogen activator activity in the plasma. The results establish that human plasma activator, milk activator, and tissue activator from the adrenals are immunologically distinct from human urokinase.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ALKJAERSIG N., FLETCHER A. P., SHERRY S. The mechanism of clot dissolution by plasmin. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jul;38(7):1086–1095. doi: 10.1172/JCI103885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ALKJAERSIG N., FLETCHER A. P., SHERRY S. xi-Aminocaproic acid: an inhibitor of plasminogen activation. J Biol Chem. 1959 Apr;234(4):832–837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASTRUP T., MULLERTZ S. The fibrin plate method for estimating fibrinolytic activity. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1952 Oct;40(2):346–351. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(52)90121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASTRUP T., STERNDORFF I. An activator of plasminogen in normal urine. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1952 Dec;81(3):675–678. doi: 10.3181/00379727-81-19983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astrup T. Tissue activators of plasminogen. Fed Proc. 1966 Jan-Feb;25(1):42–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BACHMANN F., FLETCHER A. P., ALKJAERSIG N., SHERRY S. PARTIAL PURIFICATION AND PROPERTIES OF THE PLASMINOGEN ACTIVATOR FROM PIG HEART. Biochemistry. 1964 Oct;3:1578–1585. doi: 10.1021/bi00898a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BJERREHUUS I. Fibrinolytic activity of urine. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1952;4(3):179–182. doi: 10.3109/00365515209060654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULUK K., FURMAN M. On the controlling function of the kidneys in fibrinolysis. Experientia. 1962 Mar 15;18:146–147. doi: 10.1007/BF02153867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernik M. B., Kwaan H. C. Origin of fibrinolytic activity in cultures of the human kidney. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Oct;70(4):650–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boomgaard J., Vreeken J., Bleyenberg A., Deggeller K. Studies on urokinase. Some physiological considerations concerning normal urokinase excretion. Clin Chim Acta. 1966 Apr;13(4):484–490. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(66)90240-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CELANDER D. R., GUEST M. M. The biochemistry and physiology of urokinase. Am J Cardiol. 1960 Aug;6:409–419. doi: 10.1016/0002-9149(60)90333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE WIT C. D. INVESTIGATIONS ON THE INHIBITORS OF THE FIBRINOLYTIC SYSTEM. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1964 Oct 15;12:105–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLETCHER A. P., BIEDERMAN O., MOORE D., ALKJAERSIG N., SHERRY S. ABNORMAL PLASMINOGEN-PLASMIN SYSTEM ACTIVITY (FIBRINOLYSIS) IN PATIENTS WITH HEPATIC CIRRHOSIS: ITS CAUSE AND CONSEQUENCES. J Clin Invest. 1964 Apr;43:681–695. doi: 10.1172/JCI104953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HELMER O. M., JUDSON W. E. The quantitative determination of renin in the plasma of patients with arterial hypertension. Circulation. 1963 Jun;27:1050–1060. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.27.6.1050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holemans R., McConnell D., Johnston J. G. Urokinase levels in urine after nicotinic acid injection. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1966 Jan 31;15(1):192–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Januszko T., Furman M., Buluk K. The kidneys and the liver as the organs regulating the fibrinolytic system of the circulating blood. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1966 May 15;15(3):554–560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLINE D. L., FISHMAN J. B. Improved procedure for the isolation of human plasminogen. J Biol Chem. 1961 Dec;236:3232–3234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwaan H. C. Tissue fibrinolytic activity studied by a histochemical method. Fed Proc. 1966 Jan-Feb;25(1):52–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LESUK A., TERMINIELLO L., TRAVER J. H. CRYSTALLINE HUMAN UROKINASE: SOME PROPERTIES. Science. 1965 Feb 19;147(3660):880–882. doi: 10.1126/science.147.3660.880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall D. C., Kline D. L. Mechanism of action and some properties of a tissue activator of plasminogen. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1965 Sep 1;14(1-2):116–126. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niewiarowski S., Prokopowicz J., Poplawski A., Worowski K. Inhibition of dog fibrinolytic system in experimental tubular necrosis of kidney. Experientia. 1964 Feb 15;20(2):101–103. doi: 10.1007/BF02151267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEART W. S. A new method of large-scale preparation of hypertensin, with a note on its assay. Biochem J. 1955 Feb;59(2):300–302. doi: 10.1042/bj0590300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHERRY S., ALKJAERSIG N., FLETCHER A. P. ASSAY OF UROKINASE PREPARATIONS WITH THE SYNTHETIC SUBSTRATE ACETYL-L-LYSINE METHYL ESTER. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Jul;64:145–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHERRY S., LINDEMEYER R. I., FLETCHER A. P., ALKJAERSIG N. Studies on enhanced fibrinolytic activity in man. J Clin Invest. 1959 May;38(5):810–822. doi: 10.1172/JCI103863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STARZL T. E., MARCHIORO T. L., VONKAULLA K. N., HERMANN G., BRITTAIN R. S., WADDELL W. R. HOMOTRANSPLANTATION OF THE LIVER IN HUMANS. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1963 Dec;117:659–676. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira E., Arnon R. The mechanism of inhibition of papain by its specific antibodies. Biochemistry. 1967 Dec;6(12):3951–3956. doi: 10.1021/bi00864a042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherry S., Alkjaersig N., Fletcher A. P. Comparative activity of thrombin on substituted arginine and lysine esters. Am J Physiol. 1965 Sep;209(3):577–583. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.3.577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TROLL W., SHERRY S. The activation of human plasminogen by streptokinase. J Biol Chem. 1955 Apr;213(2):881–891. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLIAMS J. R. B. The fibrinolytic activity of urine. Br J Exp Pathol. 1951 Dec;32(6):530–537. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOROWSKI K., NIEWIAROWSKI S., PROKOPOWICZ J. FIBRINOLYSIS AND FIBRINOGEN BREAKDOWN PRODUCTS (ANTITHROMBIN VI) IN RENAL VENOUS BLOOD (RVB) IN DOG. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1964 Oct 15;12:87–104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White W. F., Barlow G. H., Mozen M. M. The isolation and characterization of plasminogen activators (urokinase) from human urine. Biochemistry. 1966 Jul;5(7):2160–2169. doi: 10.1021/bi00871a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von KAULLA K., RIGGENBACH N. Urokinase excretion in man: a method of determination and consideration of its significance. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1960 Dec 15;5:162–178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



