Abstract
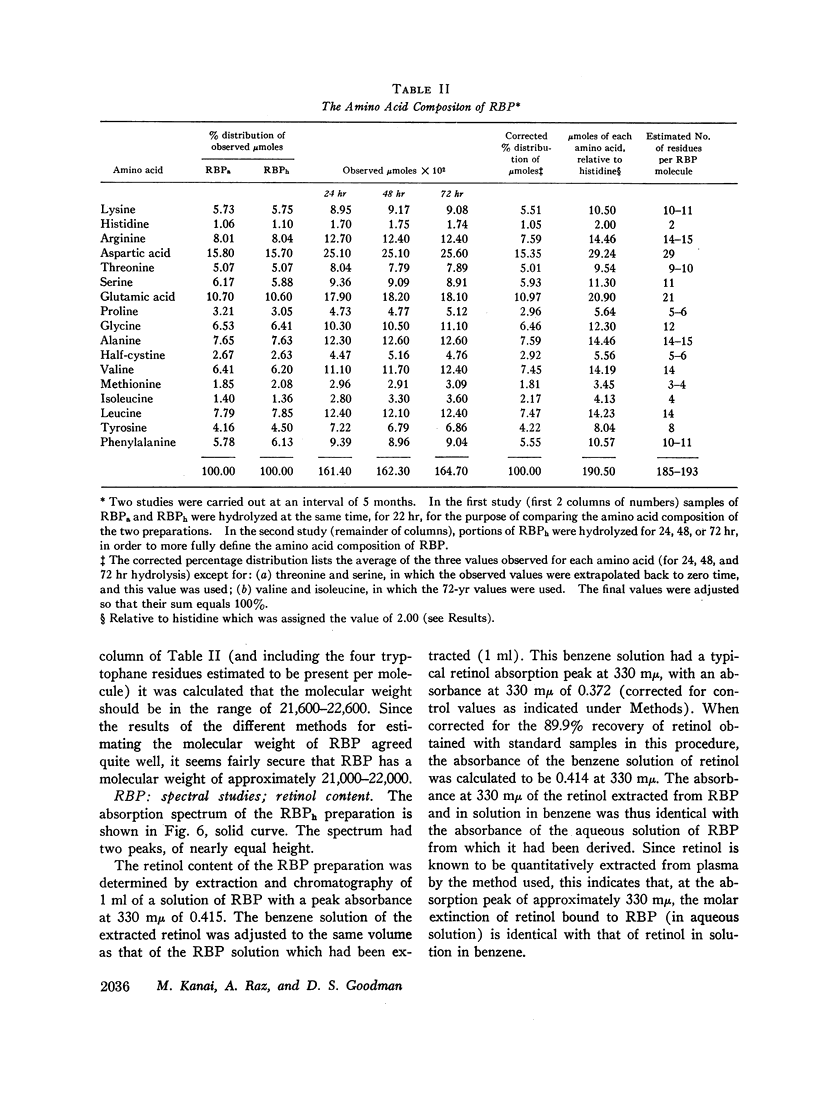
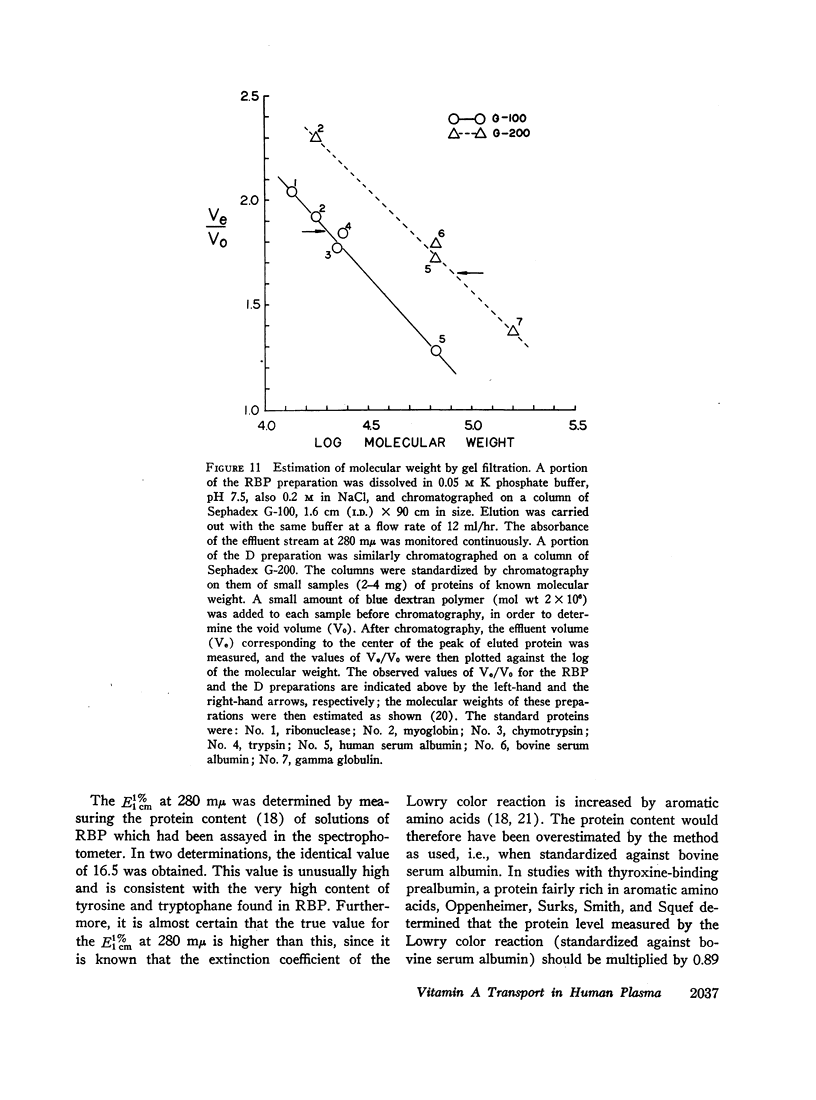
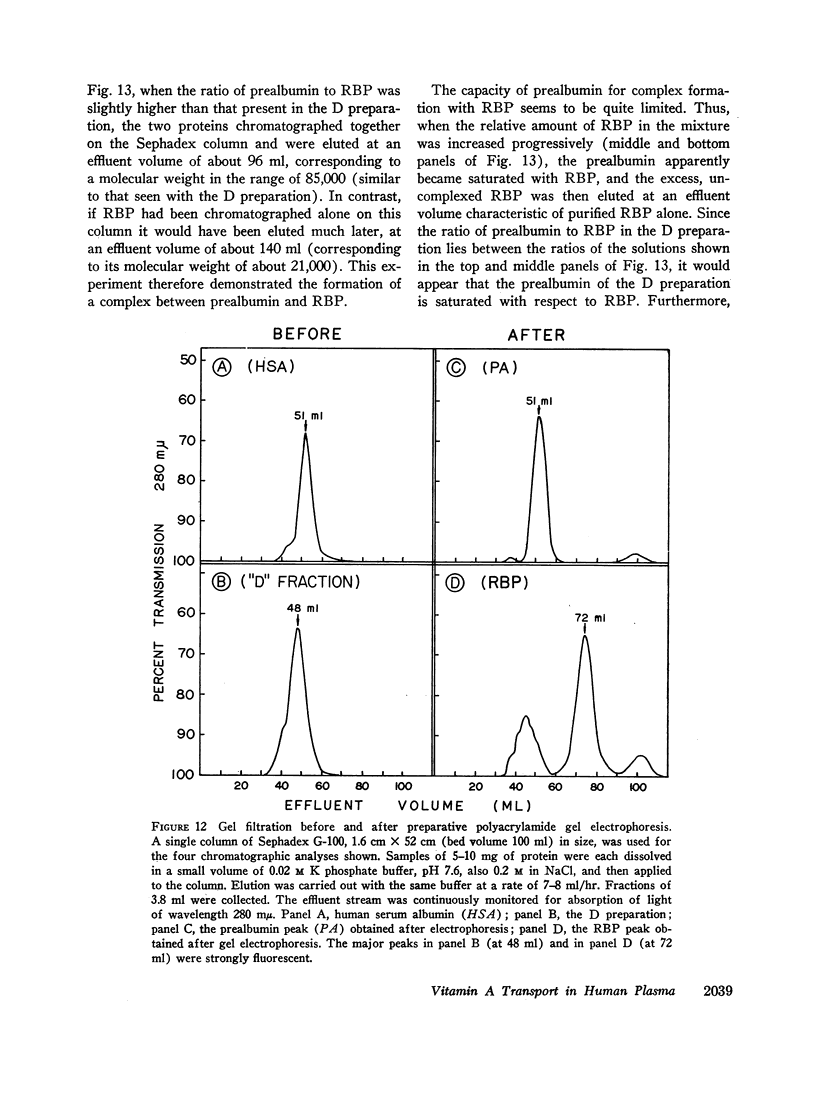
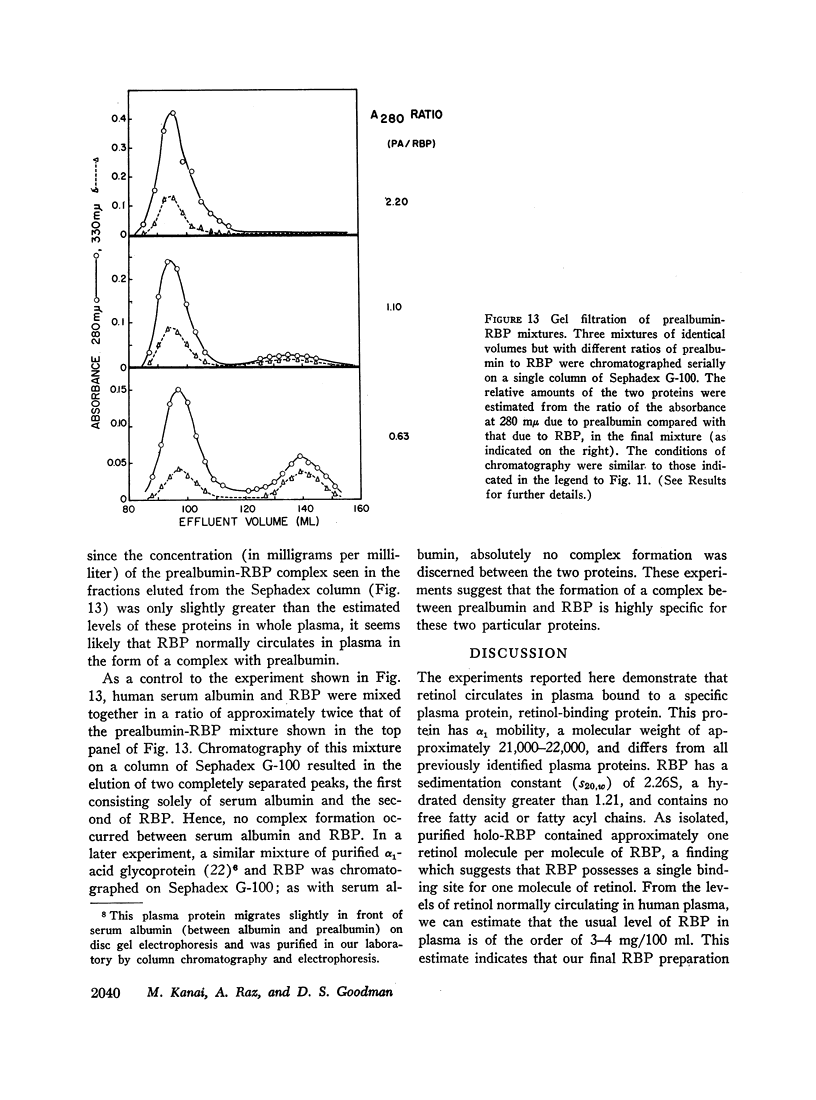
Vitamin A circulates in human plasma as retinol bound to a specific transport protein. This protein differs from the known low and high density plasma lipoproteins and has a hydrated density greater than 1.21. In order to study this protein, volunteers were injected intravenously with retinol-15-14C. Plasma was collected 1-3 days later, and the purification of retinol-binding protein (RBP) was monitored by assaying for 14C and also by following the fluorescence of the protein-bound retinol. Purification of RBP was effected by the sequence: Cohn fractionation, chromatography on columns of Sephadex G-200 and diethylaminoethyl (DEAE)-Sephadex, preparative polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and finally chromatography on Sephadex G-100. These procedures resulted in a preparation of RBP which was at least 98% pure and which had been purified more than 1500-fold. Purified RBP has α1 mobility on electrophoresis and has a molecular weight of approximately 21,000-22,000. There appears to be one binding site for retinol per molecule of RBP. Solutions of RBP are fluorescent (characteristic of retinol) and have ultraviolet absorption spectra with peaks at 330 mμ (resulting from the bound retinol) and at 280 mμ. There are no fatty acid or fatty acyl chains present in purified RBP. The usual concentration of RBP in plasma is of the order of 3-4 mg/100 ml. In plasma, RBP apparently circulates as a complex, together with another, larger protein with prealbumin mobility on electrophoresis. The RBP-prealbumin complex remains intact during Cohn fractionation and during chromatography on Sephadex and on DEAE-Sephadex columns. The complex dissociates during gel electrophoresis, permitting the isolation and subsequent purification of each of the components. The complex is again formed by mixing together solutions of the separated RBP and of prealbumin. Retinol transport in plasma thus appears to involve both a lipid-protein (retinol-RBP) interaction and a protein-protein (RBP-prealbumin) interaction.
Full text
PDF



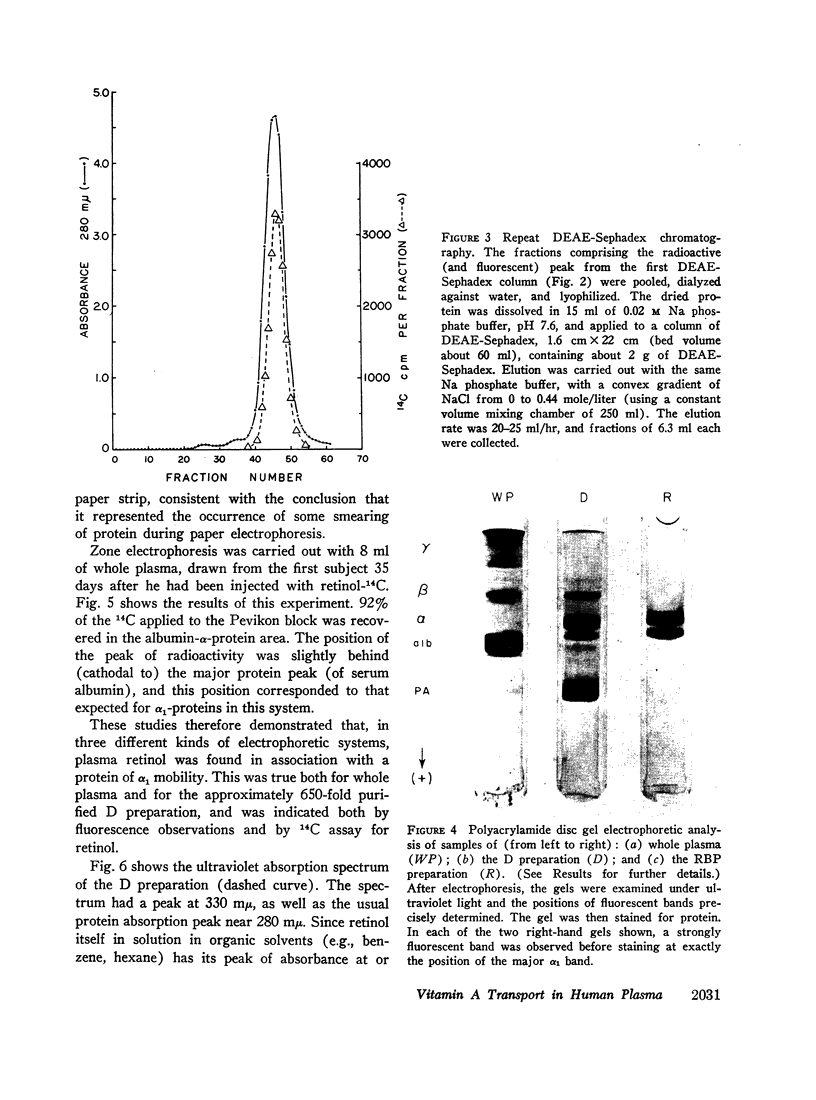
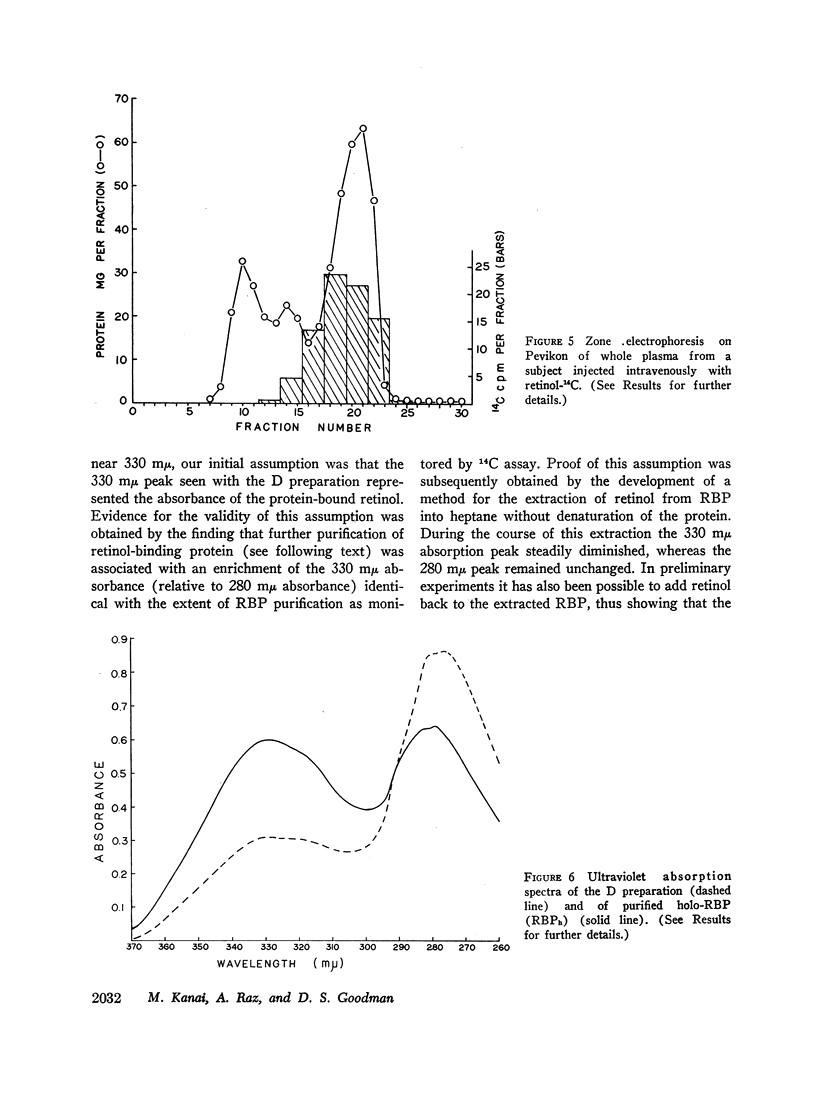
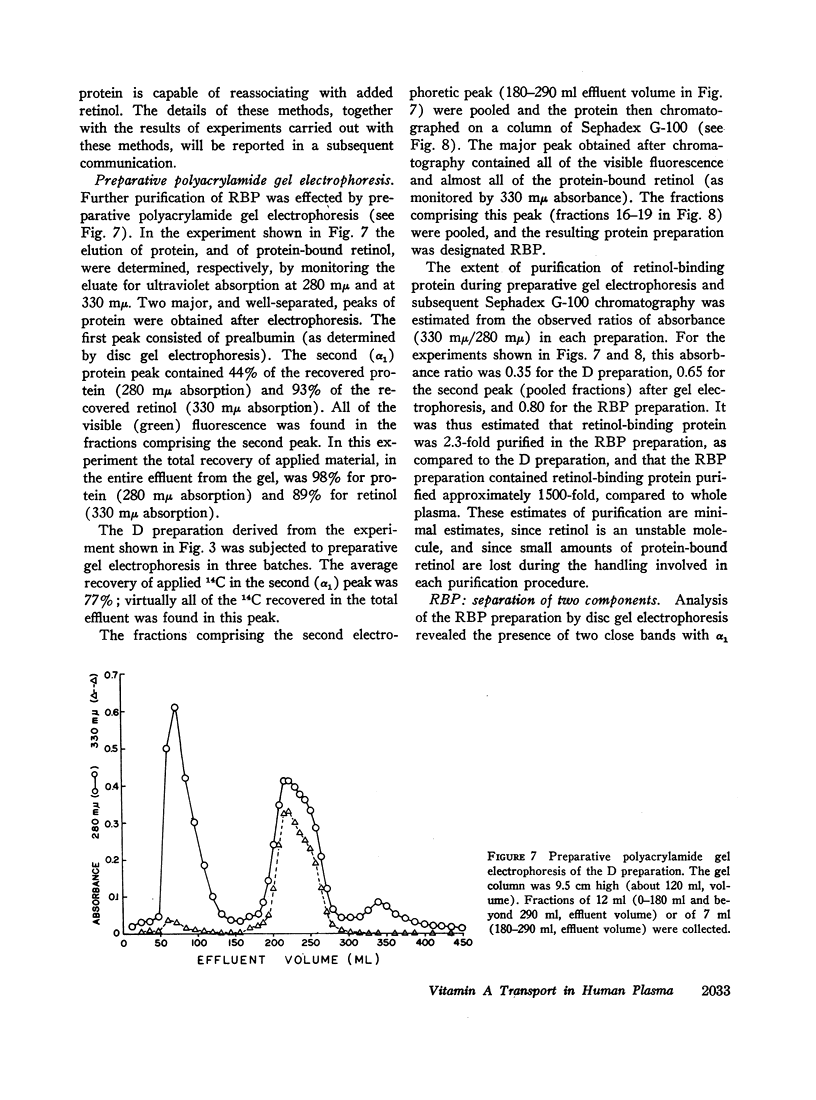
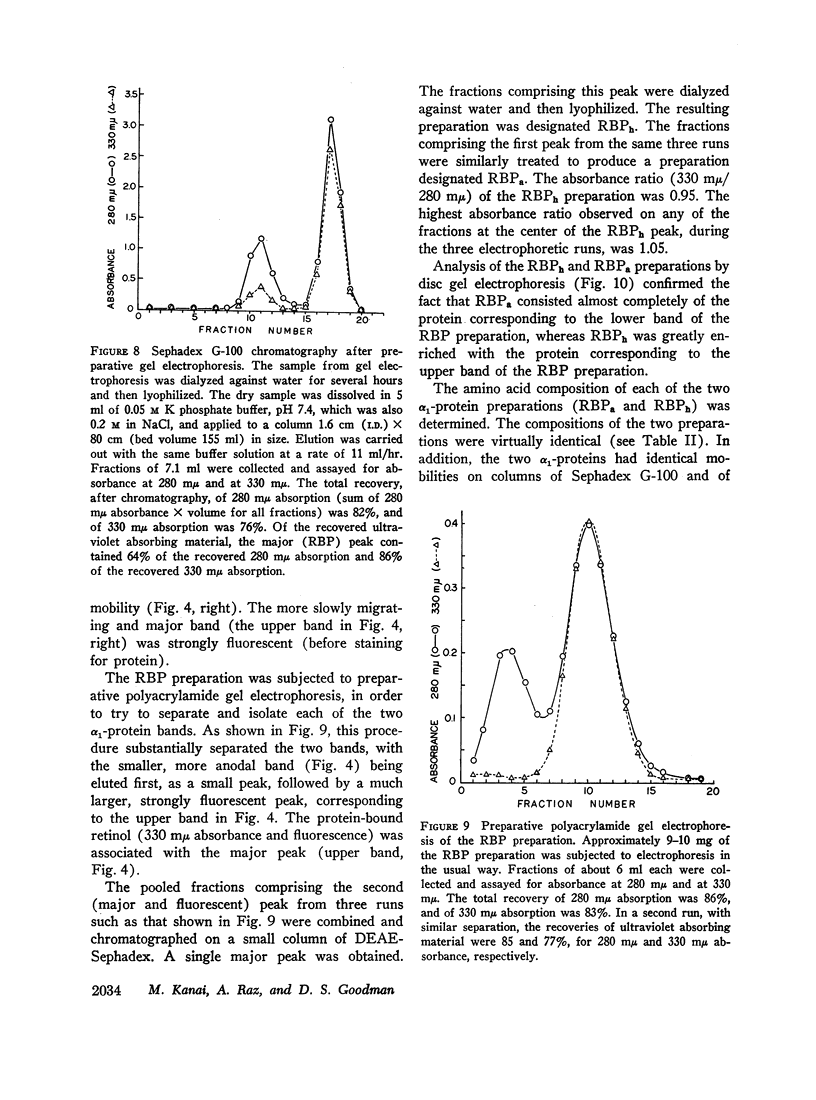






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alvsaker J. O., Haugli F. B., Laland S. G. The presence of vitamin A in human tryptophan-rich prealbumin. Biochem J. 1967 Jan;102(1):362–366. doi: 10.1042/bj1020362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake C. C., Johnson L. N., Mair G. A., North A. C., Phillips D. C., Sarma V. R. Crystallographic studies of the activity of hen egg-white lysozyme. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1967 Apr 18;167(1009):378–388. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1967.0035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREDRICKSON D. S., GORDON R. S., Jr Transport of fatty acids. Physiol Rev. 1958 Oct;38(4):585–630. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1958.38.4.585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredrickson D. S., Levy R. I., Lees R. S. Fat transport in lipoproteins--an integrated approach to mechanisms and disorders. N Engl J Med. 1967 Jan 5;276(1):34–contd. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196701052760107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GARBERS C. F., GILLMAN J., PEISACH M. The transport of vitamin A in rat serum with special reference to the occurrence of unidentified metabolites of vitamin A in the rat. Biochem J. 1960 Apr;75:124–132. doi: 10.1042/bj0750124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GLOVER J., WALKER R. J. ABSORPTION AND TRANSPORT OF VITAMIN A. Exp Eye Res. 1964 Dec;3:374–382. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(64)80048-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOODMAN D. W., HUANG H. S., SHIRATORI T. TISSUE DISTRIBUTION AND METABOLISM OF NEWLY ABSORBED VITAMIN A IN THE RAT. J Lipid Res. 1965 Jul;6:390–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman D. S., Shiratori T. Fatty acid composition of human plasma lipoprotein fractions. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jul;5(3):307–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodwin T. W., Morton R. A. The spectrophotometric determination of tyrosine and tryptophan in proteins. Biochem J. 1946;40(5-6):628–632. doi: 10.1042/bj0400628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granda J. L., Scanu A. Solubilization and properties of the apoproteins of the very low- and low-density lipoproteins of human serum. Biochemistry. 1966 Oct;5(10):3301–3308. doi: 10.1021/bi00874a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUANG H. S., GOODMAN D. S. VITAMIN A AND CAROTENOIDS. I. INTESTINAL ABSORPTION AND METABOLISM OF 14C-LABELLED VITAMIN A ALCOHOL AND BETA-CAROTENE IN THE RAT. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jul;240:2839–2844. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOVIN T., CHRAMBACH A., NAUGHTON M. A. AN APPARATUS FOR PREPARATIVE TEMPERATURE-REGULATED POLYACRYLAMIDE GEL ELECTROPHORESIS. Anal Biochem. 1964 Nov;9:351–369. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90192-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KENDREW J. C. Myoglobin and the structure of proteins. Science. 1963 Mar 29;139(3561):1259–1266. doi: 10.1126/science.139.3561.1259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRINSKY N. I., CRONWELL D. G., ONCLEY J. L. The transport of vitamin A and carotenoids in human plasma. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1958 Jan;73(1):233–246. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(58)90259-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kartha G., Bello J., Harker D. Tertiary structure of ribonuclease. Nature. 1967 Mar 4;213(5079):862–865. doi: 10.1038/213862a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVY R. I., FREDRICKSON D. S. HETEROGENEITY OF PLASMA HIGH DENSITY LIPOPROTEINS. J Clin Invest. 1965 Mar;44:426–441. doi: 10.1172/JCI105156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MULLER-EBERHARD H. J. A new supporting medium for preparative electrophoresis. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1960;12:33–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis S., Langdon R. G. Studies on human serum beta-1-lipoprotein. I. Amino acid composition. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jan 25;241(2):469–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OPPENHEIMER J. H., SURKS M. I., SMITH J. C., SQUEF R. ISOLATION AND CHARACTERIZATION OF HUMAN THYROXINE-BINDING PREALBUMIN. J Biol Chem. 1965 Jan;240:173–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OPPENHEIMER J. H., TAVERNETTI R. R. Displacement of thyroxine from human thyroxine-binding globulin by analogues of hydantoin. Steric aspects of the thyroxinebinding site. J Clin Invest. 1962 Dec;41:2213–2220. doi: 10.1172/JCI104680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCANU A., HUGHES W. L. Further characterization of the human serum D 1.063-1.21, alpha-lipoprotein. J Clin Invest. 1962 Aug;41:1681–1689. doi: 10.1172/JCI104625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMID K., BINETTE J. P., TOKITA K., MOROZ L., YOSHIZAKI H. THE POLYMORPHIC FORMS OF ALPHA-1-ACID GLYCOPROTEIN OF NORMAL CAUCASIAN INDIVIDUALS. J Clin Invest. 1964 Dec;43:2347–2352. doi: 10.1172/JCI105108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHONENBERGER M., SCHULTZE H. E., SCHWICK G. Uber ein Präalbumin des menschlichen Serums. Biochem Z. 1956;328(4):267–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHORE V., SHORE B. The protein subunit of human serum lipoproteins of density 1.125-1.200 gram/ml. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1962 Nov 27;9:455–460. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(62)90034-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanu A., Granda J. L. Effects of ultracentrifugation on the human serum high-density (1.063 less than p less than 1.21 g/ml) lipoprotein. Biochemistry. 1966 Feb;5(2):446–455. doi: 10.1021/bi00866a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore V., Shore B. Some physical and chemical studies on the protein moiety of a high-density (1.126-1.195 g-ml) lipoprotein fraction of human serum. Biochemistry. 1967 Jul;6(7):1962–1969. doi: 10.1021/bi00859a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switzer S., Eder H. A. Transport of lysolecithin by albumin in human and rat plasma. J Lipid Res. 1965 Oct;6(4):506–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]