Abstract
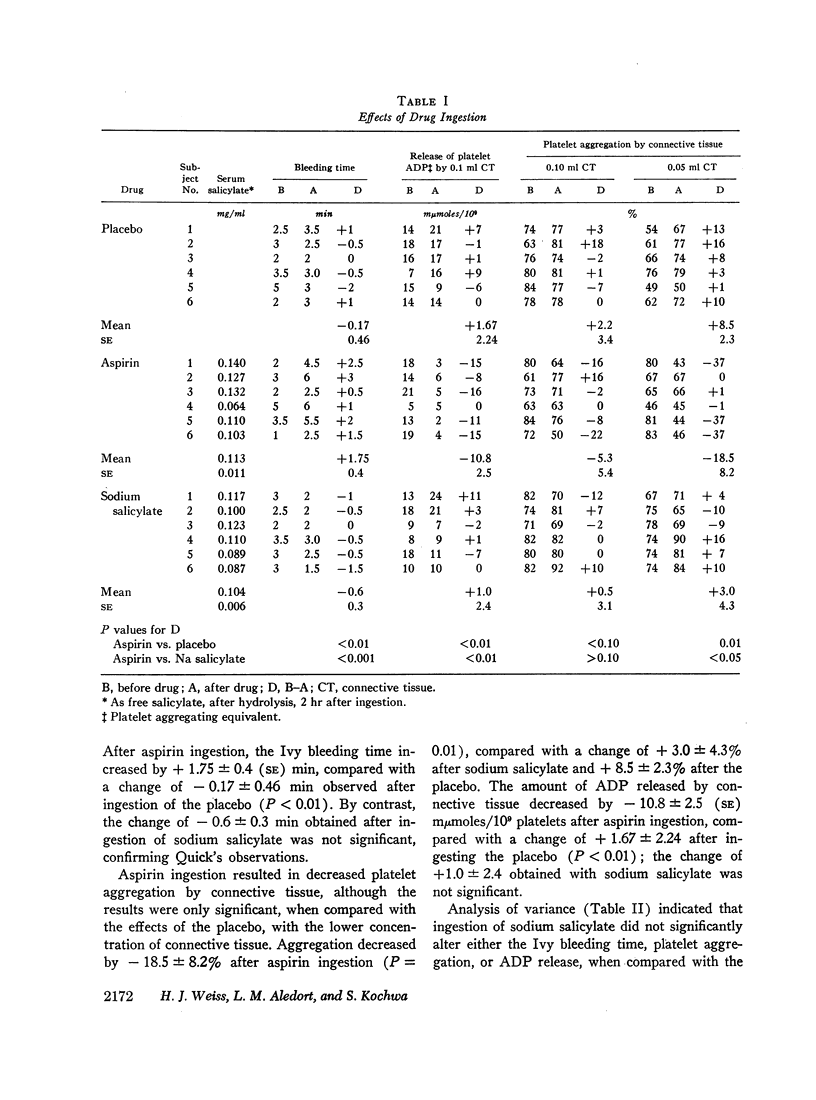
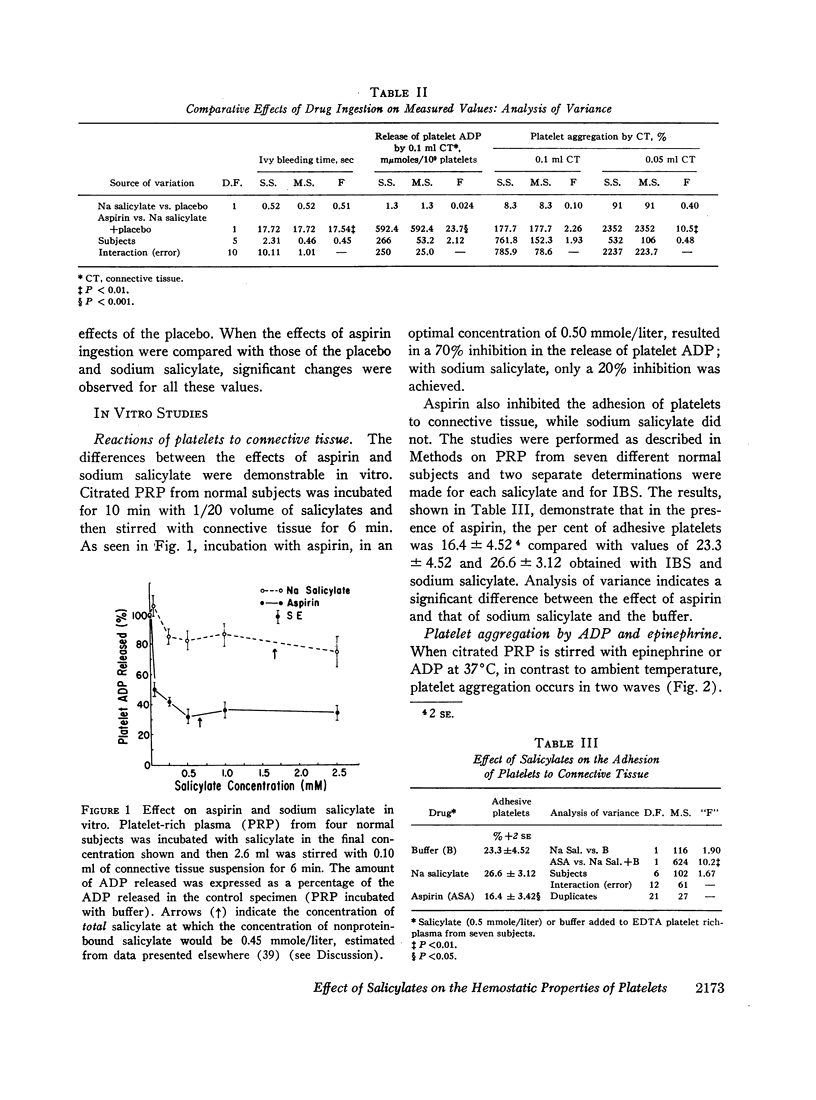
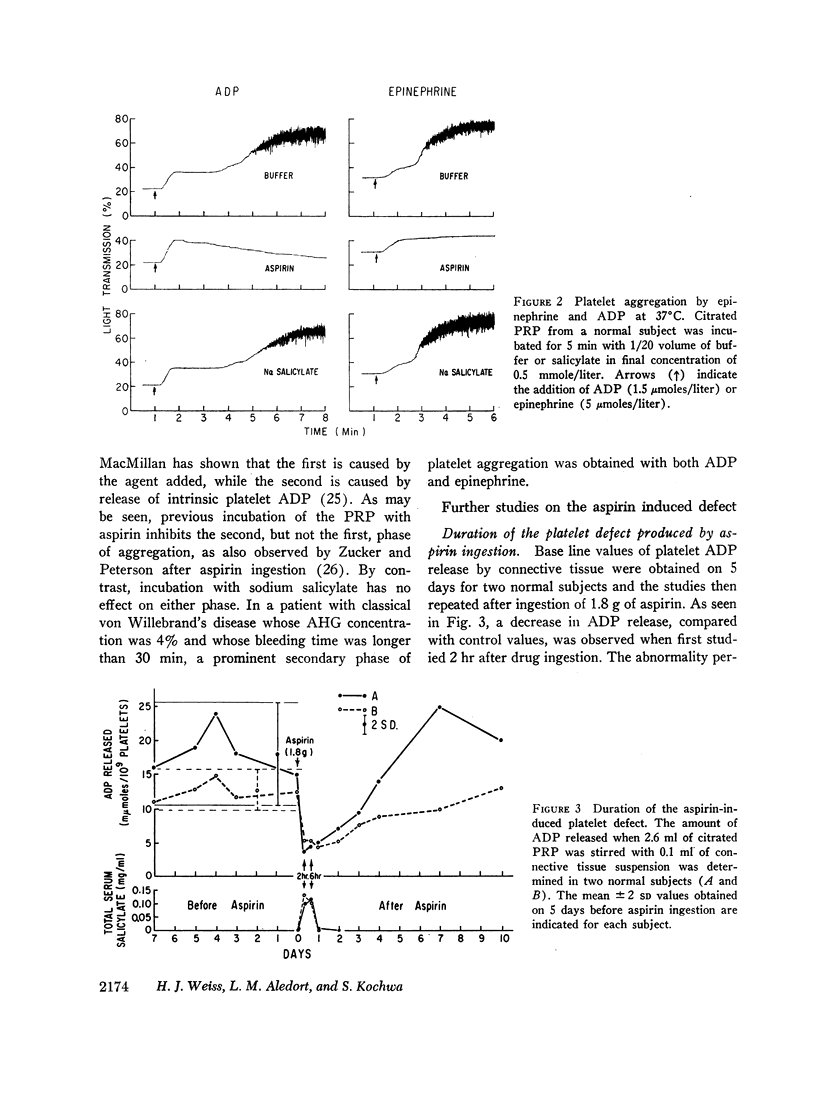
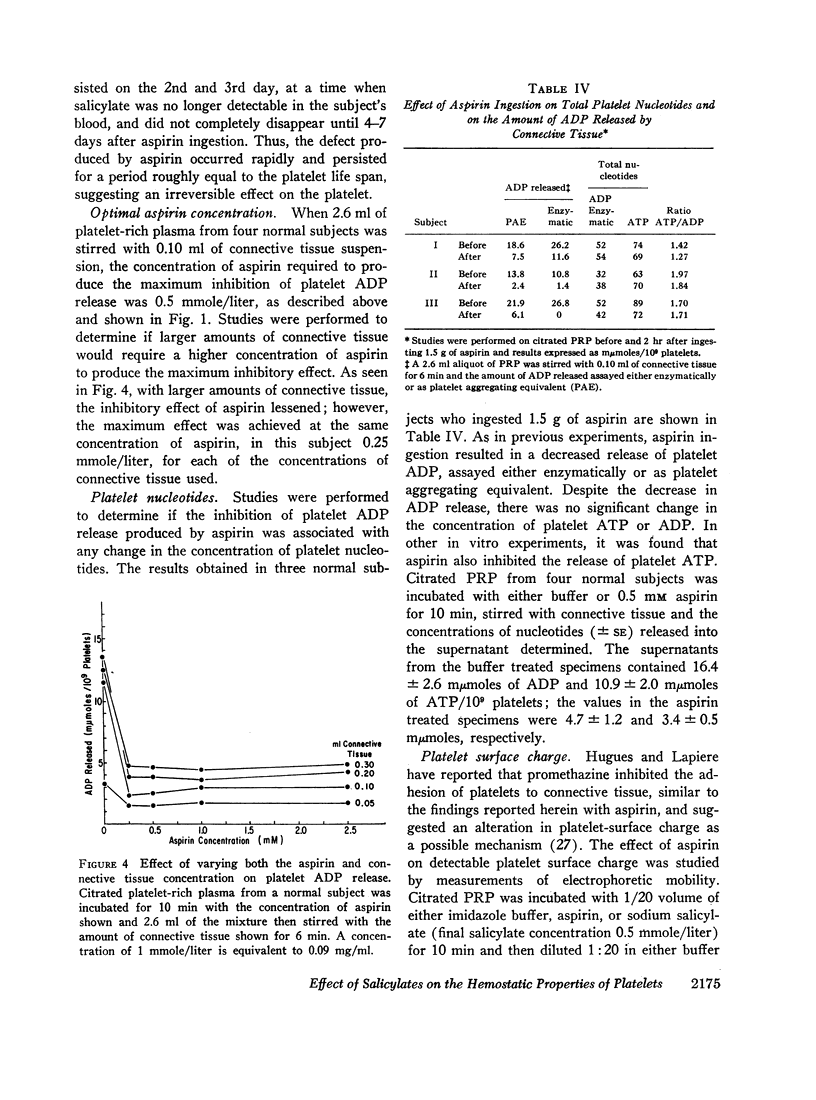
Ingestion of 1.5 g of aspirin, but not of sodium salicylate, produced a significant prolongation of the bleeding time in six normal male subjects when compared with the effects of a placebo. Similar differences in the effect of the two drugs on platelets was also observed. Aspirin ingestion resulted in impaired platelet aggregation by connective tissue and was associated with a decreased release of platelet adenosine diphosphate (ADP); sodium salicylate had no effect on these values. In vitro, incubation of platelet-rich plasma with an optimum aspirin concentration of 0.50 mmole/liter (0.045 mg/ml) inhibited both the adhesion of platelets to connective tissue and the release of ADP as well as the secondary wave of platelet aggregation produced with ADP or epinephrine; sodium salicylate had no effect on these reactions, which were also normal in patients with von Willebrand's disease. The inhibitory effect produced by ingesting a single 1.8 g dose of aspirin was detectable for 4-7 days at which time salicylate was no longer detectable in the blood, which suggested an irreversible effect on the platelet. Aspirin also inhibited the release of platelet adenosine triphosphate (ATP), but had no effect on the platelet surface charge, available platelet ATP or ADP, or the destruction of ADP by plasma ADPase. These studies lend further support to the hypothesis that ingestion of aspirin, in contrast to sodium salicylate, prolongs the bleeding time by inhibiting the release of platelet ADP, perhaps reflecting the findings in other cell systems which suggest that aspirin alters membrane permeability.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ABOOD L. G., KIMIZUKA H., ROGENESS G., BIEL J. H. Some antidepressant drugs and their mechanism of action on excitable membranes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1963 Jul 8;107:1139–1146. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1963.tb13356.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aledort L. M., Weed R. I., Troup S. B. Ionic effects on firefly bioluminescence assay of red blood cell ATP. Anal Biochem. 1966 Nov;17(2):268–277. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90205-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORN G. V., CROSS M. J. THE AGGREGATION OF BLOOD PLATELETS. J Physiol. 1963 Aug;168:178–195. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1963.sp007185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRODY T. M. Action of sodium salicylate and related compounds on tissue metabolism in vitro. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1956 May;117(1):39–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEMAN A. R., SPIRTES M. A. Effects of chlorpromazine on biological membranes-II. Chlorpromazine-induced changes in human erythrocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 1963 Jan;12:47–53. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(63)90008-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAARDER A., JONSEN J., LALAND S., HELLEM A., OWREN P. A. Adenosine diphosphate in red cells as a factor in the adhesiveness of human blood platelets. Nature. 1961 Nov 11;192:531–532. doi: 10.1038/192531a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GROSSMAN M. I., MATSUMOTO K. K., LICHTER R. J. Fecal blood loss produced by oral and intravenous administration of various salicylates. Gastroenterology. 1961 Mar;40:383–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gander G. W., Chaffee J., Goodale F. Studies on the antipyretic action of salicylates. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Oct;126(1):205–209. doi: 10.3181/00379727-126-32402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOGBEN C. A., TOCCO D. J., BRODIE B. B., SCHANKER L. S. On the mechanism of intestinal absorption of drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1959 Apr;125(4):275–282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOVIG T. RELEASE OF A PLATELET-AGGREGATING SUBSTANCE (ADENOSINE DIPHOSPHATE) FROM RABBIT BLOOD PLATELETS INDUCED BY SALINE "EXTRACT" OF TENDONS. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1963 Jul 15;143:264–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGUES J., LAPIERE M. NOUVELLES RECHERCHES SUR L'ACCOLEMENT DES PLAQUETTES AUX FIBRES DE COLLAG'ENE. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1964 Jul 31;11:327–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardisty R. M., Hutton R. A. Bleeding tendency associated with "new" abnormality of platelet behaviour. Lancet. 1967 May 6;1(7497):983–985. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)92363-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy G. Aspirin, absorption rate and analgesic effect. Anesth Analg. 1965 Nov-Dec;44(6):837–841. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macmillan D. C. Secondary clumping effect in human citrated platelet-rich plasma produced by adenosine diphosphate and adrenaline. Nature. 1966 Jul 9;211(5045):140–144. doi: 10.1038/211140a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller W. S., Smith J. G., Jr Effect of acetylsalicylic acid on lysosomes. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Jul;122(3):634–636. doi: 10.3181/00379727-122-31212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustard J. F., Glynn M. F., Nishizawa E. E., Packham M. A. Platelet-surface interactions: relationship to thrombosis and hemostasis. Fed Proc. 1967 Jan-Feb;26(1):106–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien J. R. Effects of salicylates on human platelets. Lancet. 1968 Apr 13;1(7546):779–783. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(68)92228-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packham M. A., Warrior E. S., Glynn M. F., Senyi A. S., Mustard J. F. Alteration of the response of platelets to surface stimuli by pyrazole compounds. J Exp Med. 1967 Jul 1;126(1):171–188. doi: 10.1084/jem.126.1.171. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QUICK A. J., CLESCERI L. Influence of acetylsalicylic acid and salicylaide on the coagulation of blood. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1960 Jan;128:95–98. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quick A. J. Salicylates and bleeding: the aspirin tolerance test. Am J Med Sci. 1966 Sep;252(3):265–269. doi: 10.1097/00000441-196609000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quick A. J. The Minot-von Willebrand syndrome. Am J Med Sci. 1967 May;253(5):520–530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOTT J. T., PORTER I. H., LEWIS S. M., DIXON A. S. Studies of gastrointestinal bleeding caused by corticosteroids, salicylates, and other analgesics. Q J Med. 1961 Apr;30:167–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SEED J. C. A CLINICAL COMPARISON OF THE ANTIPYRETIC POTENCY OF ASPIRIN AND SODIUM SALICYLATE. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1965 May-Jun;6:354–358. doi: 10.1002/cpt196563354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPAET T. H., ZUCKER M. B. MECHANISM OF PLATELET PLUG FORMATION AND ROLE OF ADENOSINE DIPHOSPHATE. Am J Physiol. 1964 Jun;206:1267–1274. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.206.6.1267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STUBBE L. T. Occult blood in faeces after administration of aspirin. Br Med J. 1958 Nov 1;2(5104):1062–1066. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5104.1062. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzman E. W., Chambers D. A., Neri L. L. Incorporation of labelled nucleotides and aggregation of human blood platelets. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1966 Jan 31;15(1):52–68. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J., Aledort L. M. Impaired platelet-connective-tissue reaction in man after aspirin ingestion. Lancet. 1967 Sep 2;2(7514):495–497. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91658-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J. Platelet aggregation, adhesion and adenosine diphosphate release in thrombopathia (platelet factor 3 deficiency). A comparison with Glanzmann's thrombasthenia and von Willebrand's disease. Am J Med. 1967 Oct;43(4):570–578. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(67)90180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss H. J. The effect of clinical dextran on platelet aggregation, adhesion, and ADP release in man: in vivo and in vitro studies. J Lab Clin Med. 1967 Jan;69(1):37–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker M. B., Peterson J. Inhibition of adenosine diphosphate-induced secondary aggregation and other platelet functions by acetylsalicylic acid ingestion. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968 Feb;127(2):547–551. doi: 10.3181/00379727-127-32737. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


