Abstract
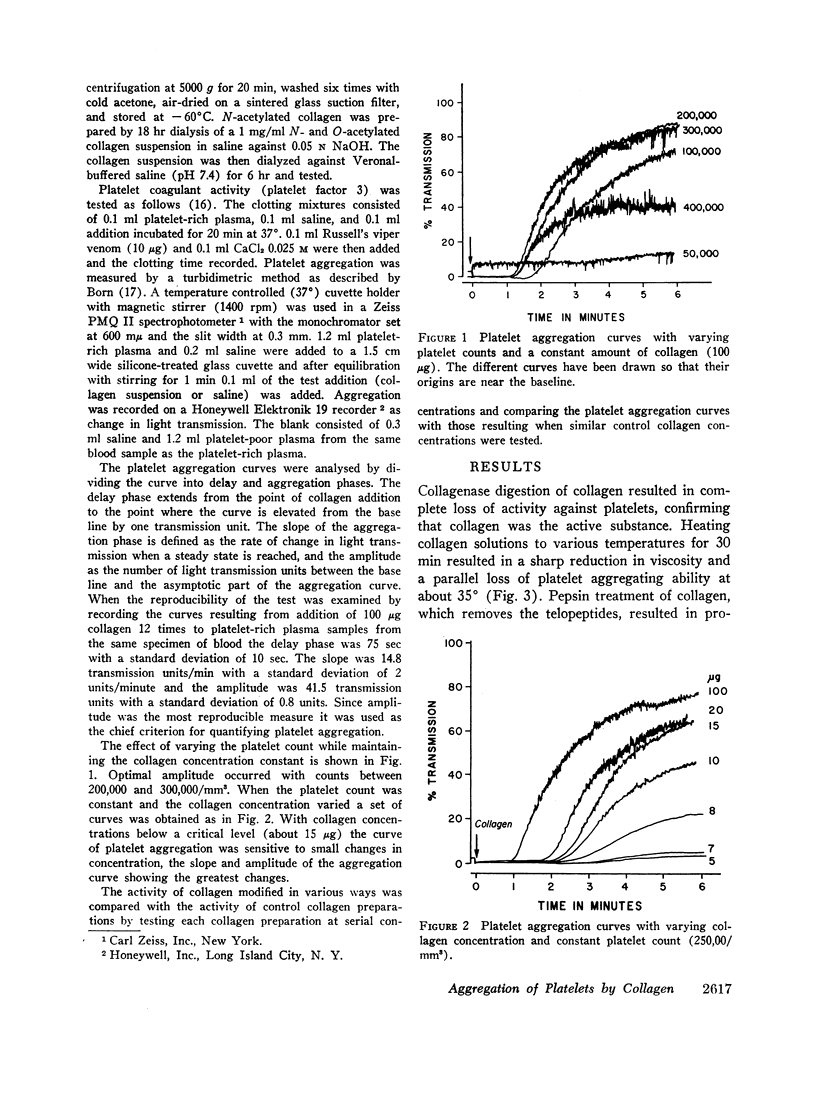
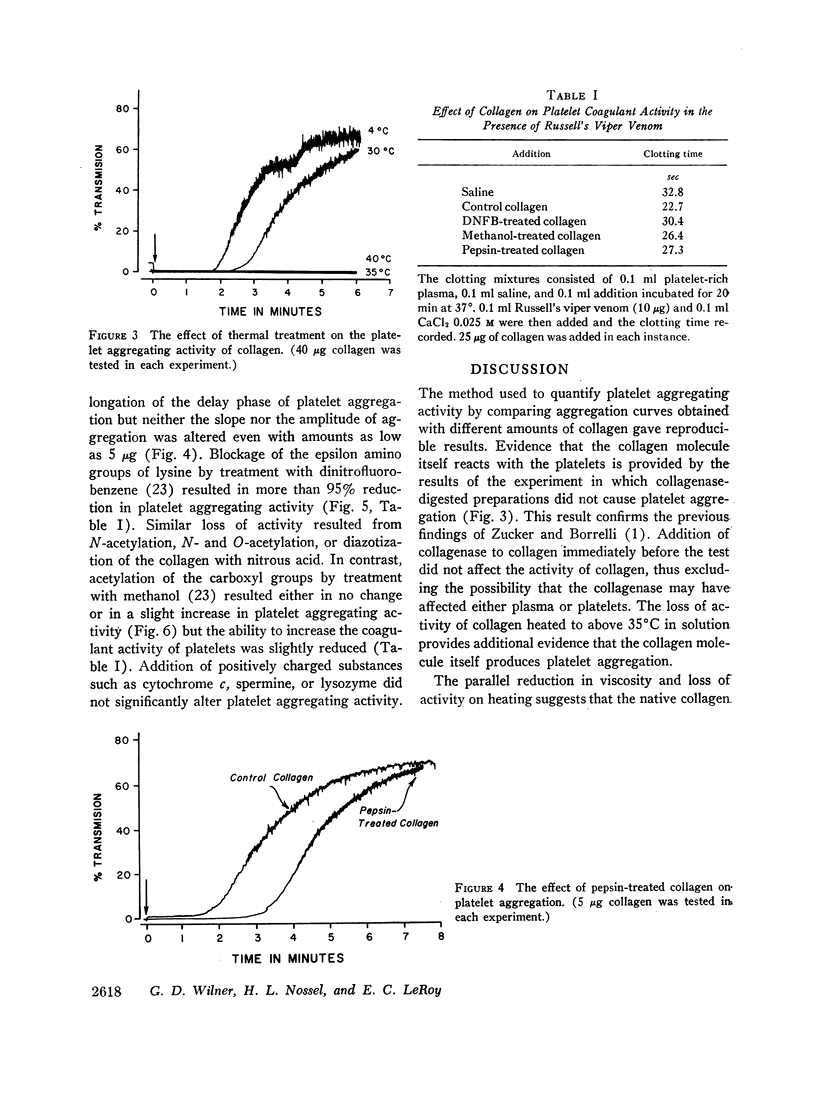
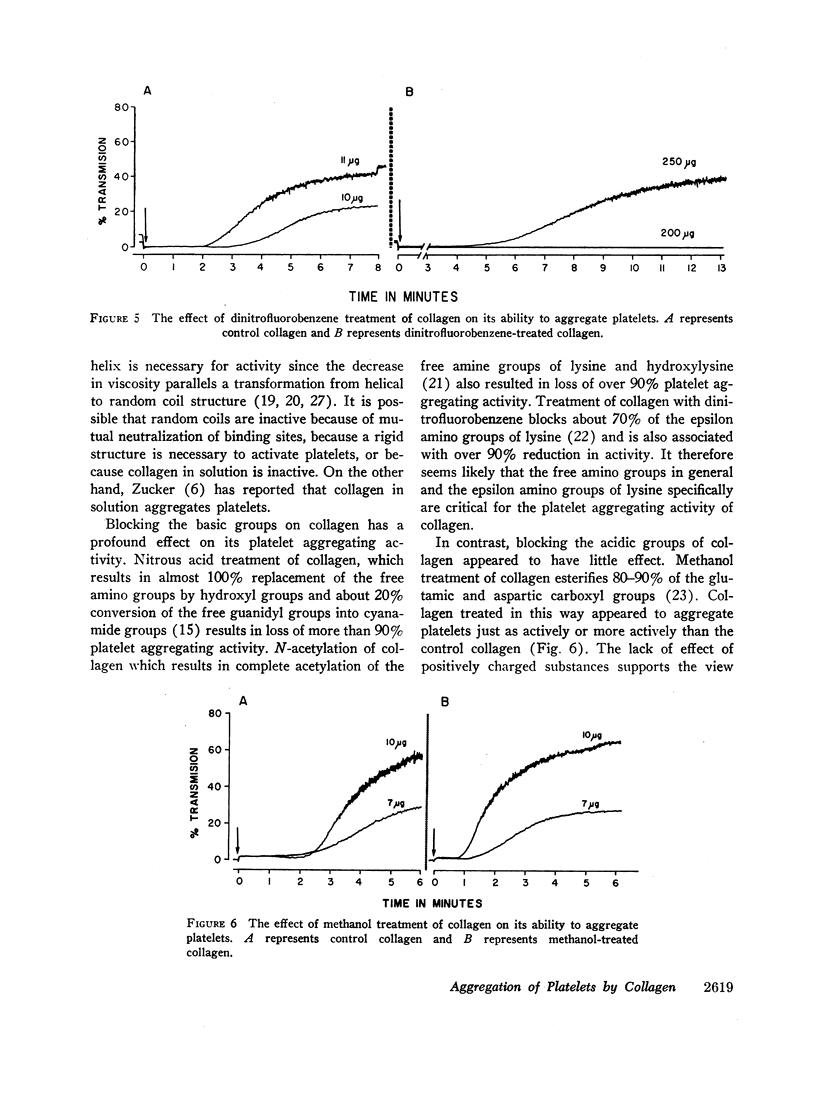
In studying some of the properties of collagen responsible for the ability to aggregate platelets it was found that thermal treatment at pH 2.5 of acid-soluble human collagen resulted in a sharp reduction in relative viscosity and platelet aggregating activity at about 35°C. The reduction in viscosity is known to be associated with structural transition from triple helical to random coil form and it is postulated that the native structure of collagen is essential for its platelet aggregation effect. Blockage of the free amino groups by deamination, N-acetylation, or treatment with dinitrofluorobenzene resulted in over 90% reduction in platelet aggregating activity. Addition of cationic proteins to collagen, removal of the negatively charged telopeptides by treatment with pepsin, or acetylation of the free carboxyl groups did not significantly affect the platelet aggregating activity of collagen. On the basis of these findings it is suggested that the free amino groups and specifically the epsilon amino groups of lysine are critical for the platelet aggregating activity of collagen whereas the carboxyl groups are of relatively little importance.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashford T. P., Frieiman D. G. The role of the endothelium in the initial phases of thrombosis. An electron microscopic study. Am J Pathol. 1967 Feb;50(2):257–273. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BORN G. V. Aggregation of blood platelets by adenosine diphosphate and its reversal. Nature. 1962 Jun 9;194:927–929. doi: 10.1038/194927b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowes J. H., Kenten R. H. The effect of deamination and esterification on the reactivity of collagen. Biochem J. 1949;44(2):142–152. doi: 10.1042/bj0440142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN R. W., ANG K. P., LAM L. C. Acetylation of collagen. Biochem J. 1953 May;54(2):181–187. doi: 10.1042/bj0540181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOVIG T. AGGREGATION OF RABBIT BLOOD PLATELETS PRODUCED IN VITRO BY SALINE "EXTRACT" OF TENDONS. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1963 Jul 15;143:248–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGUES J., LAPIERE M. NOUVELLES RECHERCHES SUR L'ACCOLEMENT DES PLAQUETTES AUX FIBRES DE COLLAG'ENE. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1964 Jul 31;11:327–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hardisty R. M., Hutton R. A. Platelet aggregation and the availability of platelet factor 3. Br J Haematol. 1966 Nov;12(6):764–776. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1966.tb00164.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovig T., Jorgensen L., Packham M. A., Mustard J. F. Platelet adherence to fibrin and collagen. J Lab Clin Med. 1968 Jan;71(1):29–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMITT F. O., LEVINE L., DRAKE M. P., RUBIN A. L., PFAHL D., DAVISON P. F. THE ANTIGENICITY OF TROPOCOLLAGEN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Mar;51:493–497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.3.493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPAET T. H., CINTRON J. STUDIES ON PLATELET FACTOR-3 AVAILABILITY. Br J Haematol. 1965 May;11:269–275. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1965.tb06587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPAET T. H., ZUCKER M. B. MECHANISM OF PLATELET PLUG FORMATION AND ROLE OF ADENOSINE DIPHOSPHATE. Am J Physiol. 1964 Jun;206:1267–1274. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1964.206.6.1267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaet T. H., Erichson R. B. The vascular wall in the pathogenesis of thrombosis. Thromb Diath Haemorrh Suppl. 1966;21:67–86. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ts'ao C. H., Spaet T. H. Ultramicroscopic changes in the rabbit inferior vena cava following partial constriction. Am J Pathol. 1967 Nov;51(5):789–813. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilner G. D., Nossel H. L., LeRoy E. C. Activation of Hageman factor by collagen. J Clin Invest. 1968 Dec;47(12):2608–2615. doi: 10.1172/JCI105943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucker M. B. ADP- and collagen-induced platelet aggregation in vivo and in vitro. Thromb Diath Haemorrh Suppl. 1967;26:175–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



