Abstract
Techniques are described in detail for a radioimmunoassay of plasma adrenocorticotropin (ACTH) that is capable of detecting hormone in unextracted normal human plasma at 1:5 dilution under the conditions described. The sensitivity of the assay is at the level of 1 μμg/ml (equivalent to 0.014 mU/100 ml).
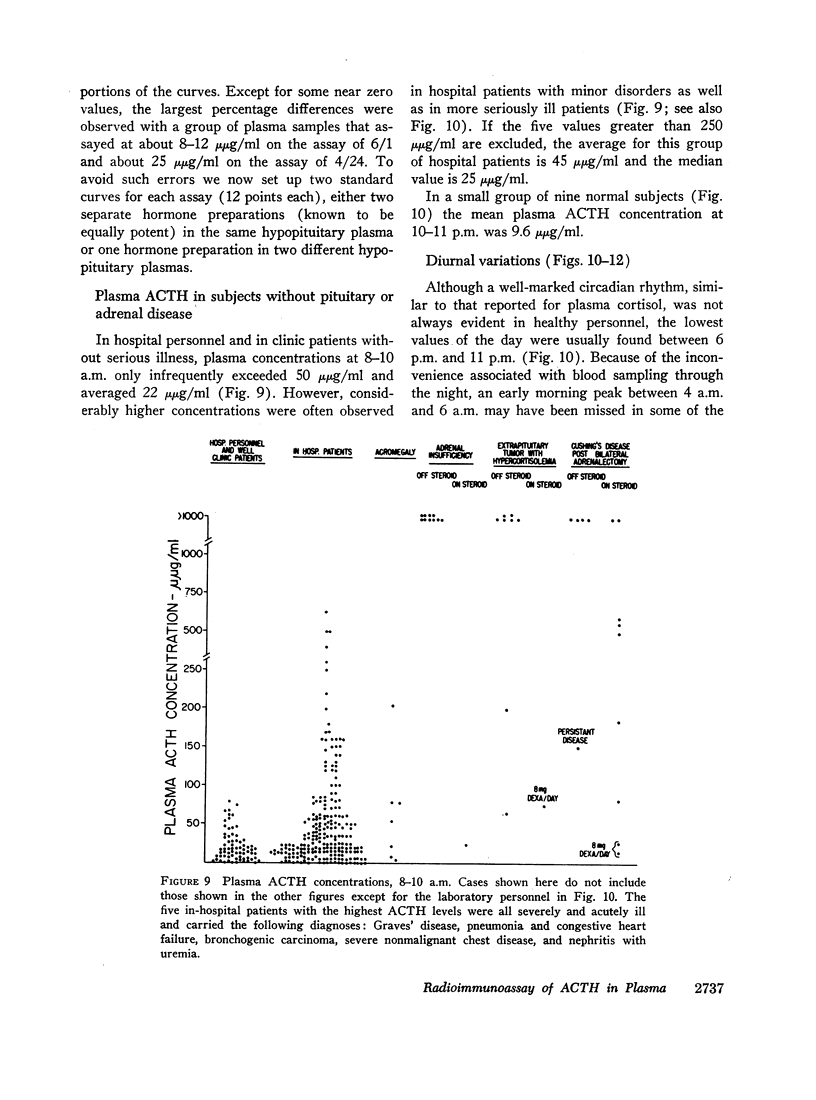
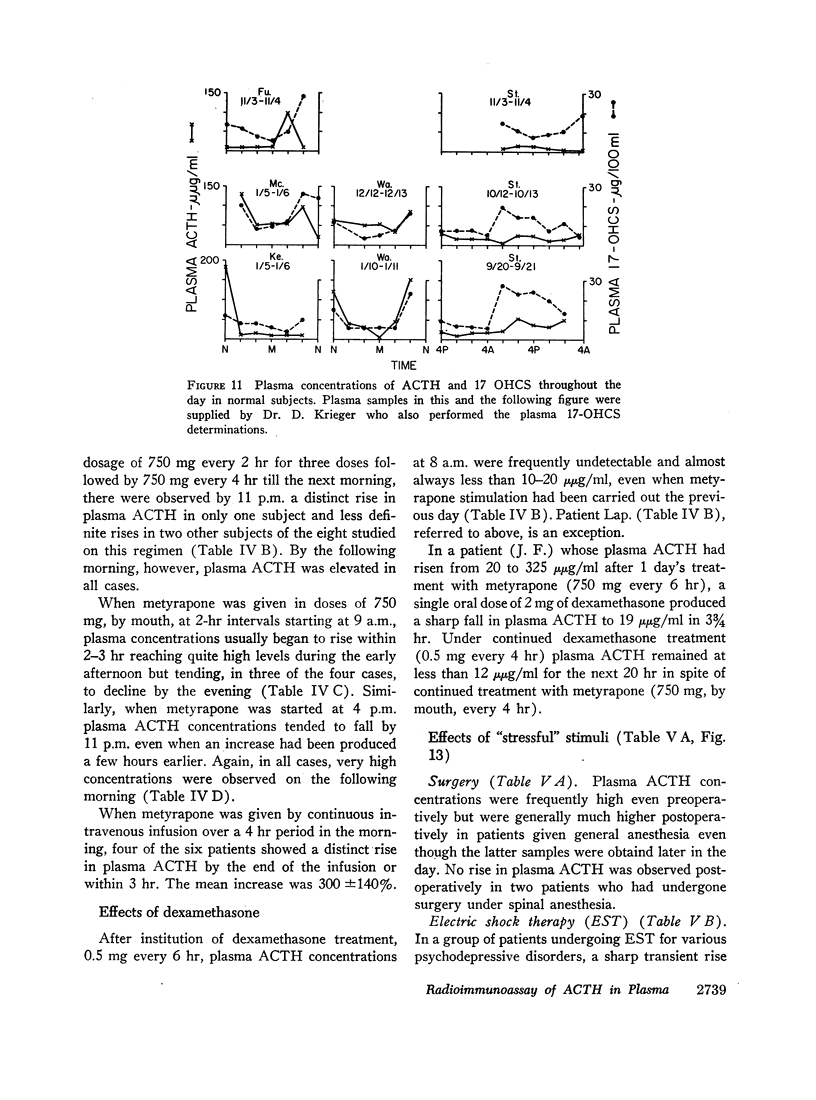
In normal subjects ACTH concentrations averaged 22 μμg/ml (equivalent to 0.308 mU/100 ml) plasma at 8-10 a.m. In a smaller group the concentrations averaged 9.6 μμg/ml (equivalent to 0.134 mU/100 ml) at 10-11 p.m. Although a circadian rhythm in normal subjects was not always well marked throughout the daytime hours, plasma ACTH usually fell to its lowest value in the late evening. In hospital patients who were not acutely ill, concentrations were infrequently above 100 μμg/ml in the morning and usually fell to significantly lower levels in the late evening. Severely ill hospital patients occasionally exhibited a.m. concentrations above 200 μμg/ml.
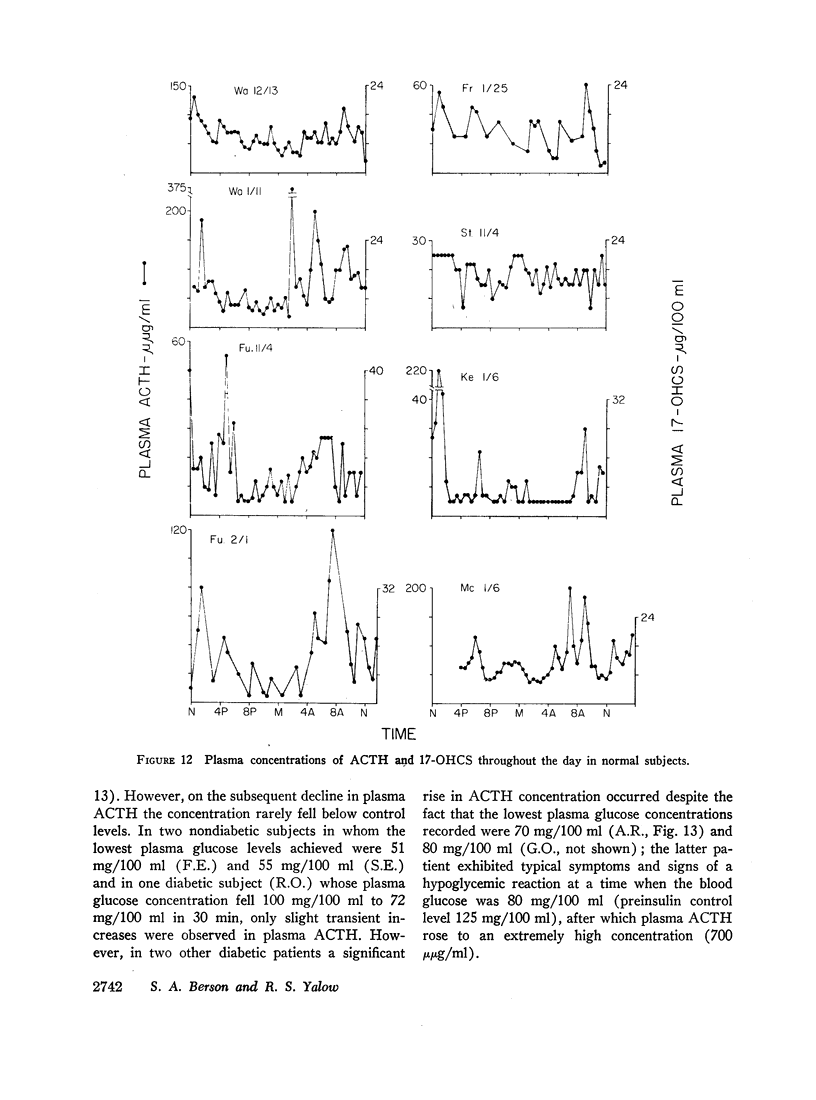
In a group of subjects showing frequent spiking of plasma 17-OHCS concentrations throughout the day parallel spiking of plasma ACTH as well was generally observed.
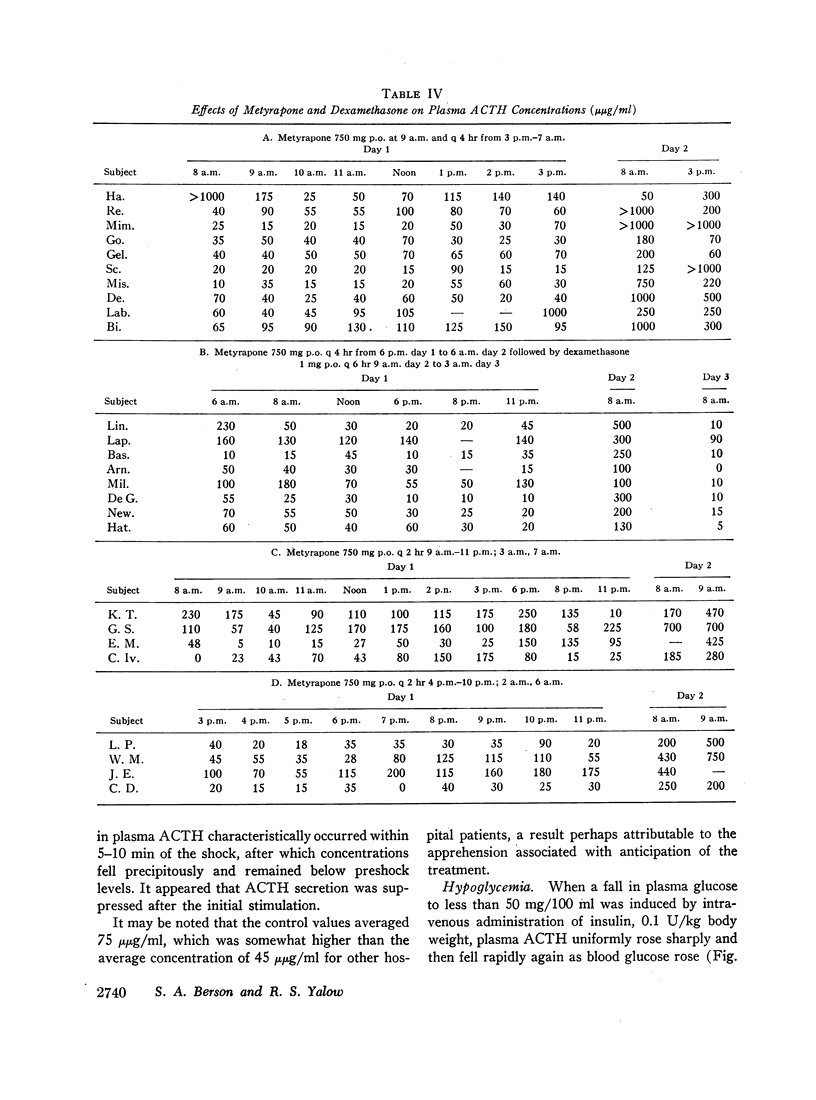
Metyrapone produced marked increases in plasma ACTH within 24 hr in all cases and generally within 3-6 hr except when started late in the day. Dexamethasone brought about a persistent reduction in plasma ACTH in a patient under continued treatment with metyrapone.
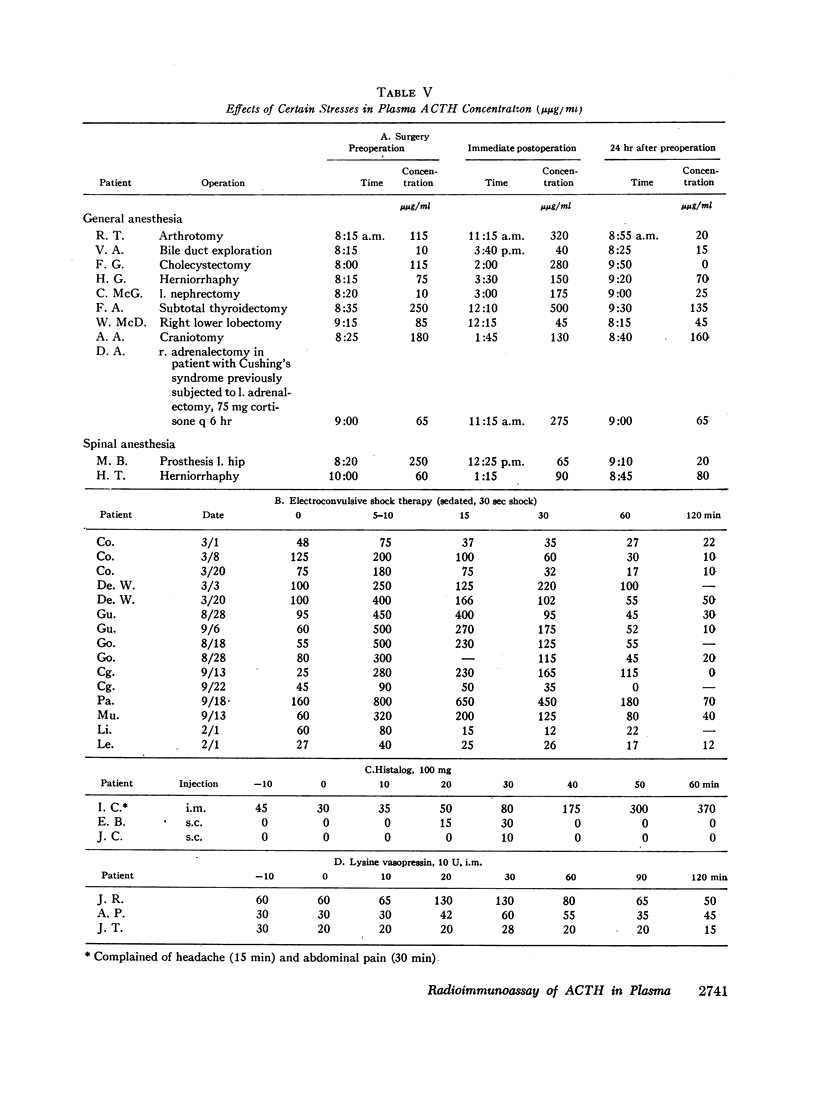
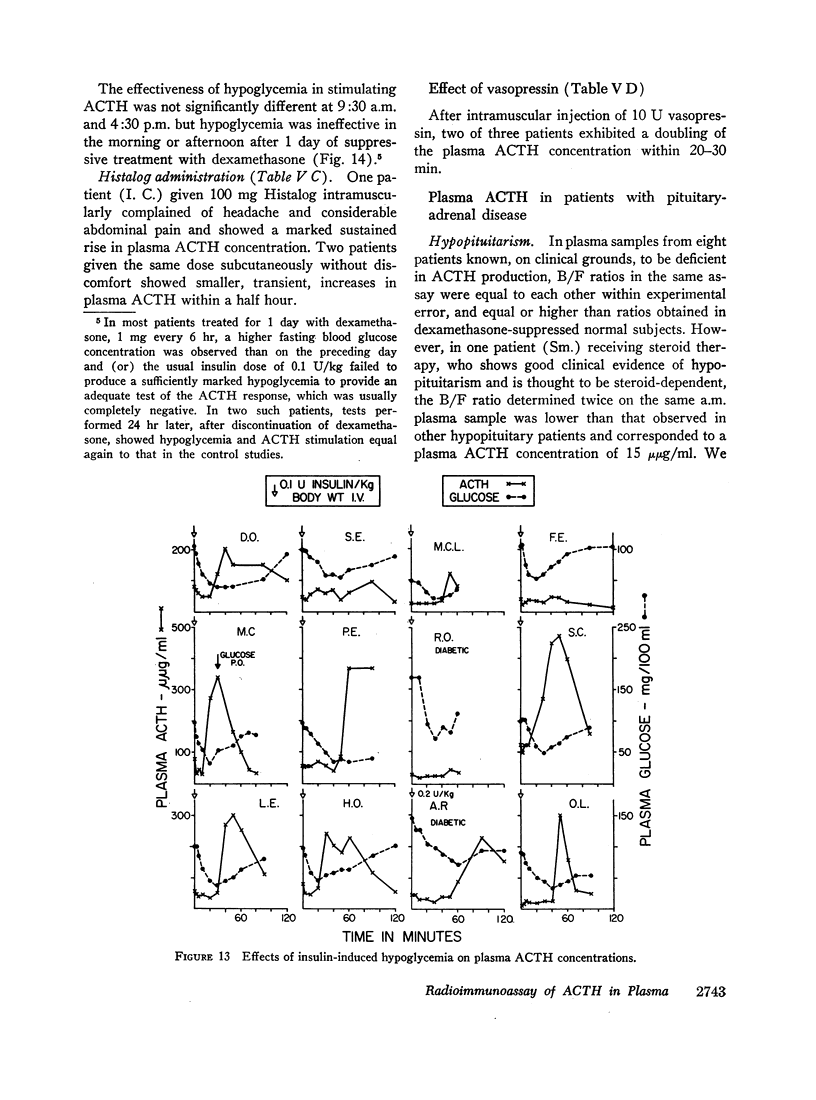
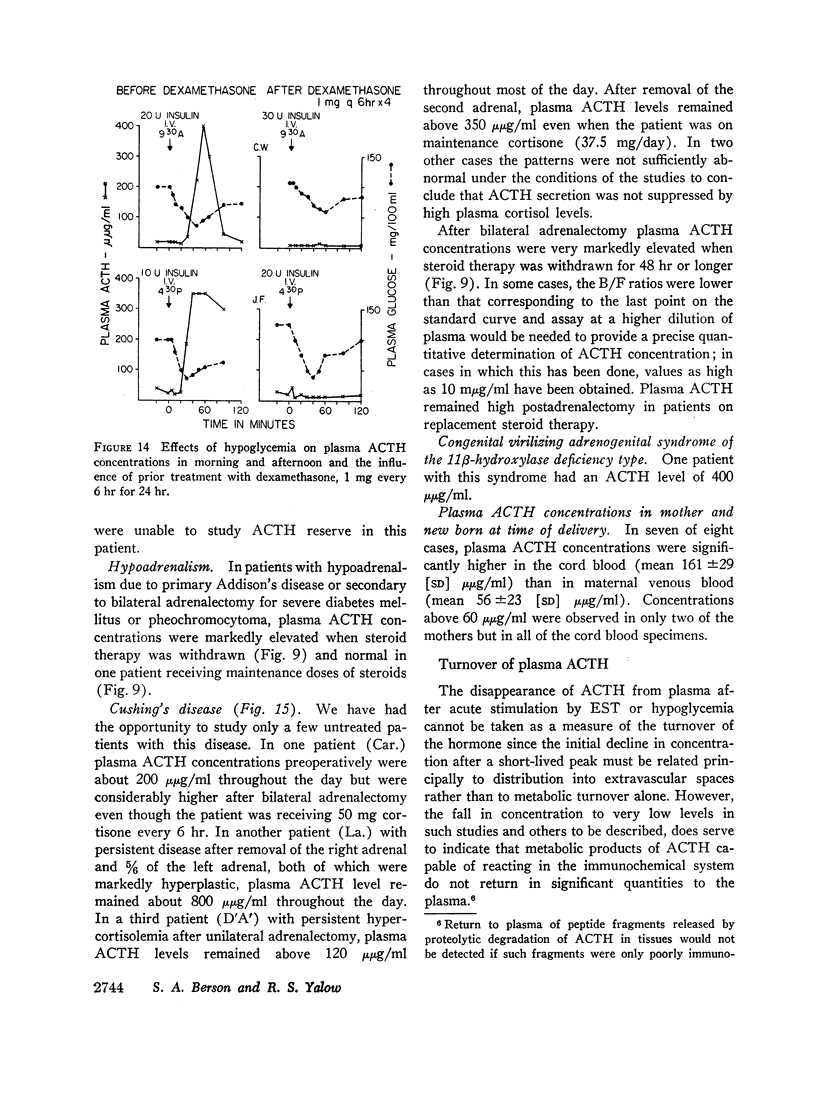
Hypoglycemia, electroshock, surgery under general anesthesia, histalog and vasopressin administration were usually followed by significant increases in plasma ACTH concentration. Prior administration of dexamethasone blocked the response to hypoglycemia.
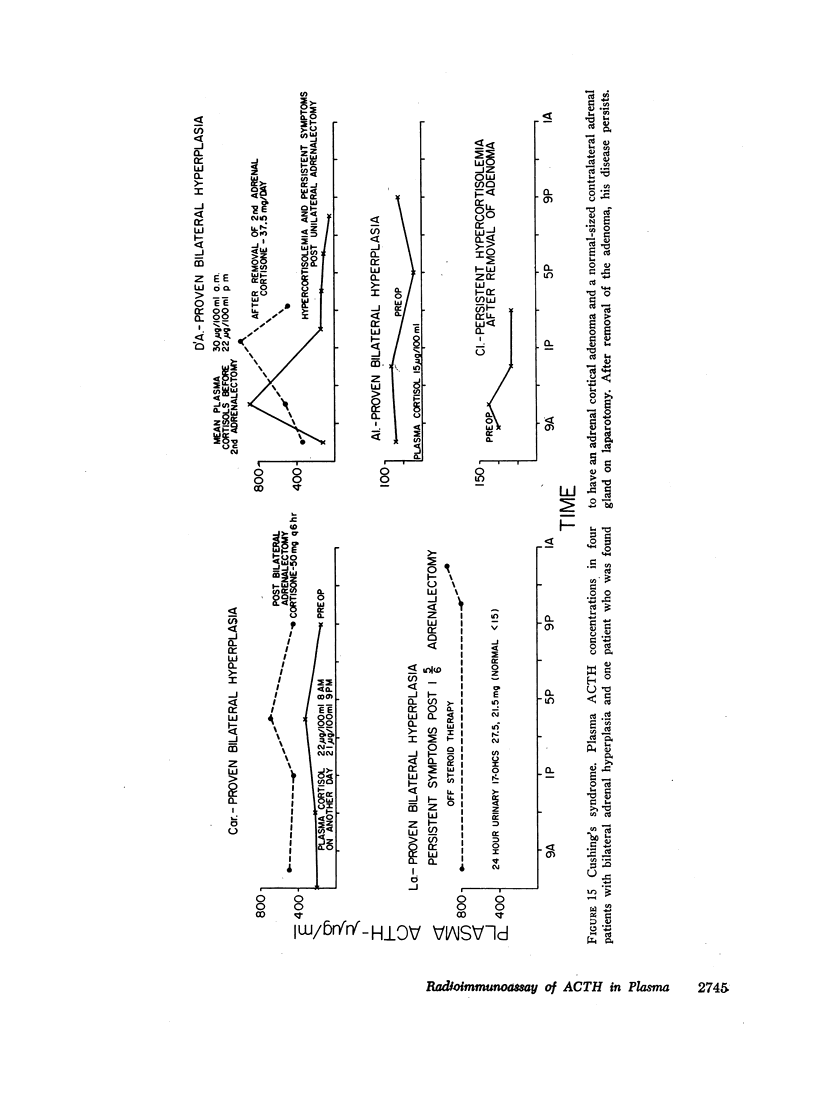
Marked elevations in plasma ACTH were observed in patients with adrenal insufficiency off steroid therapy, in Cushing's disease after adrenalectomy even in the presence of persistent hypercortisolemia, and in some untreated patients with Cushing's disease.
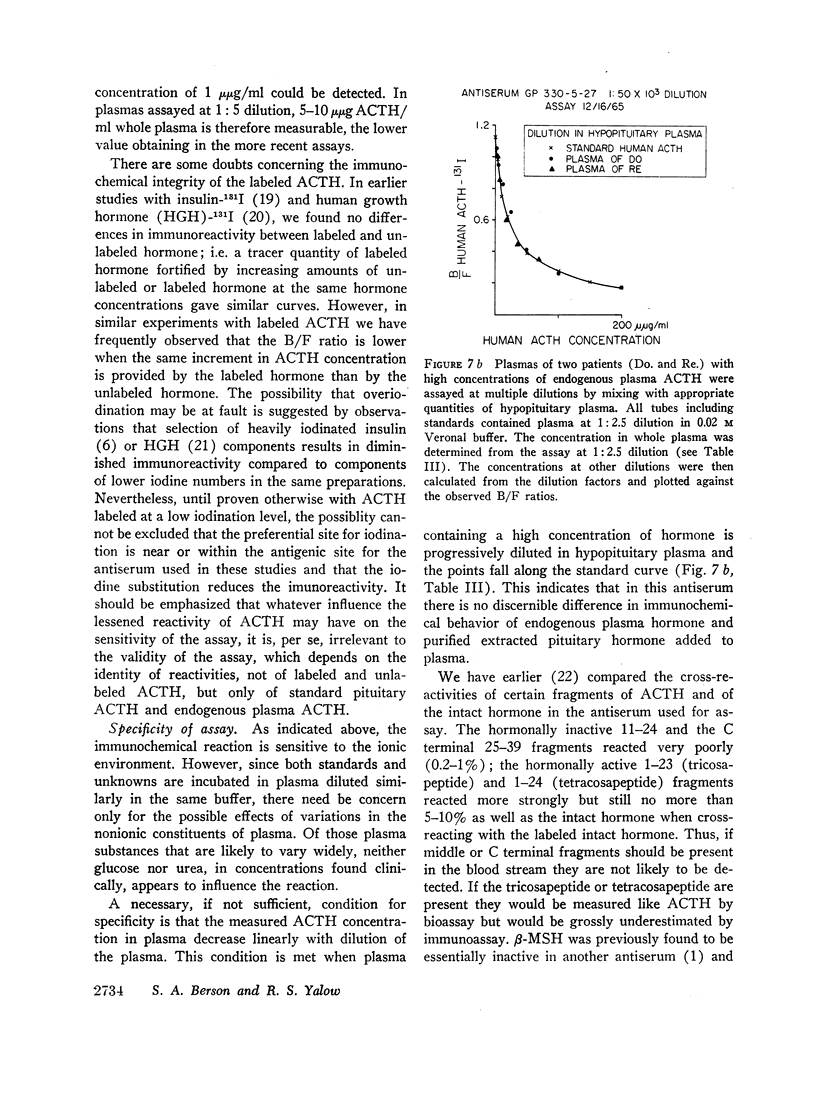
Umbilical cord blood contained higher plasma ACTH concentrations than maternal blood at delivery in seven of eight cases.
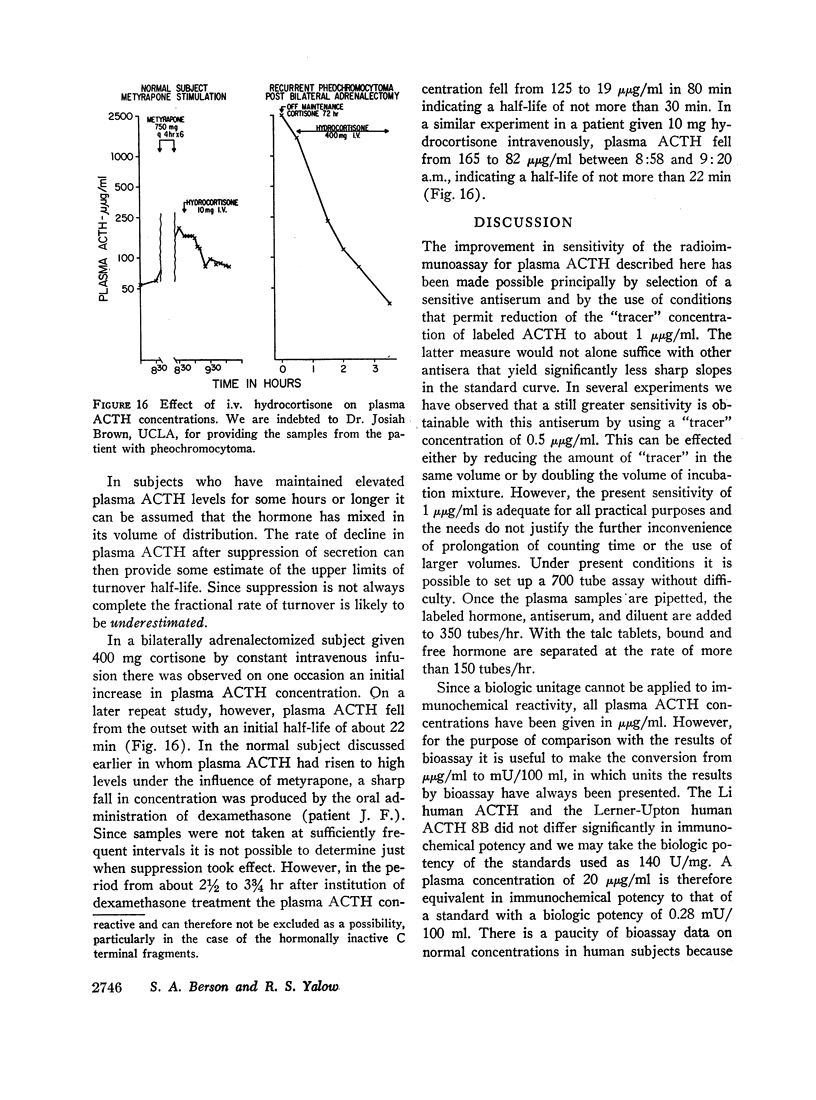
After suppression of ACTH secretion by dexamethasone or cortisol. ACTH disappeared from plasma with half-times ranging from 22 min to 30 min in three cases studied.
Full text
PDF

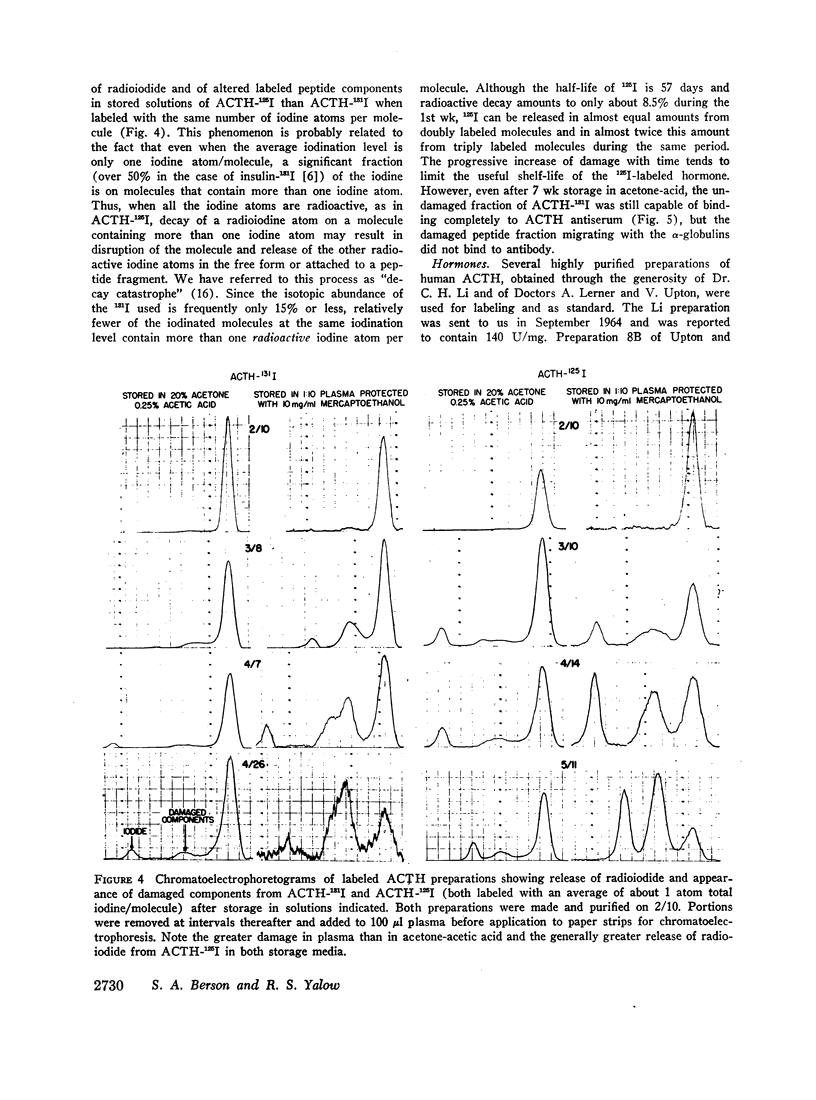
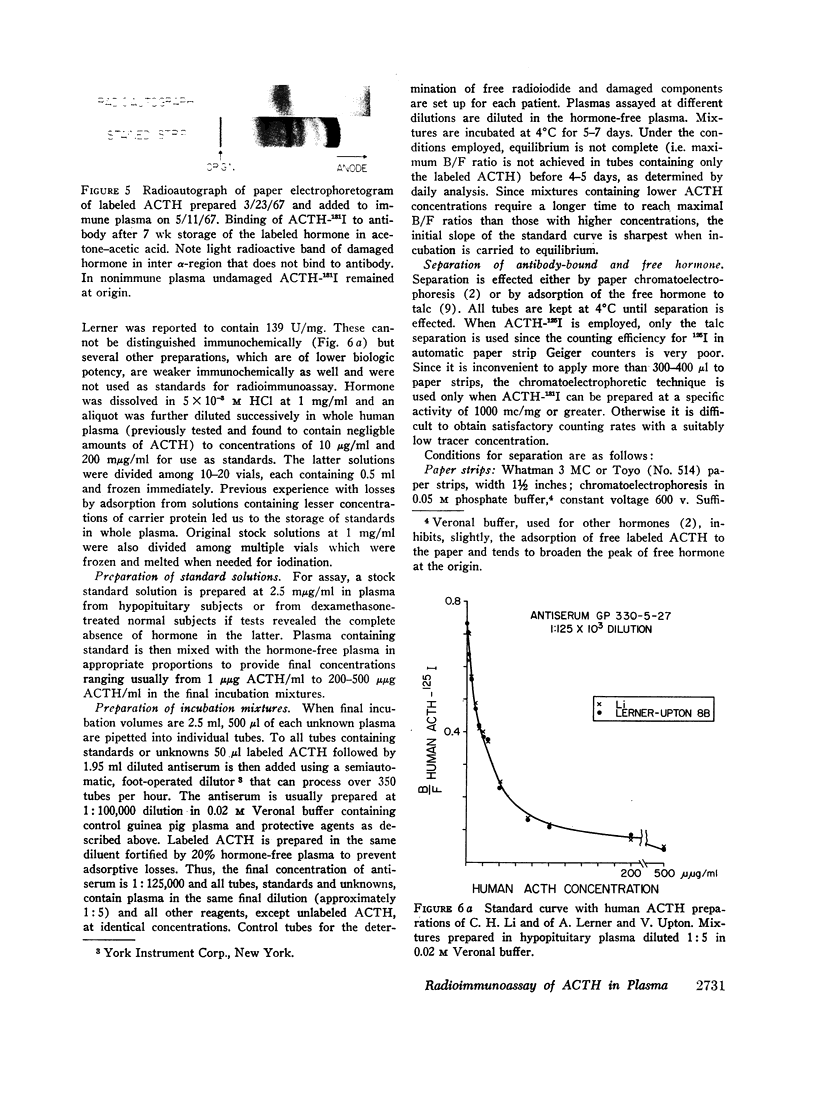
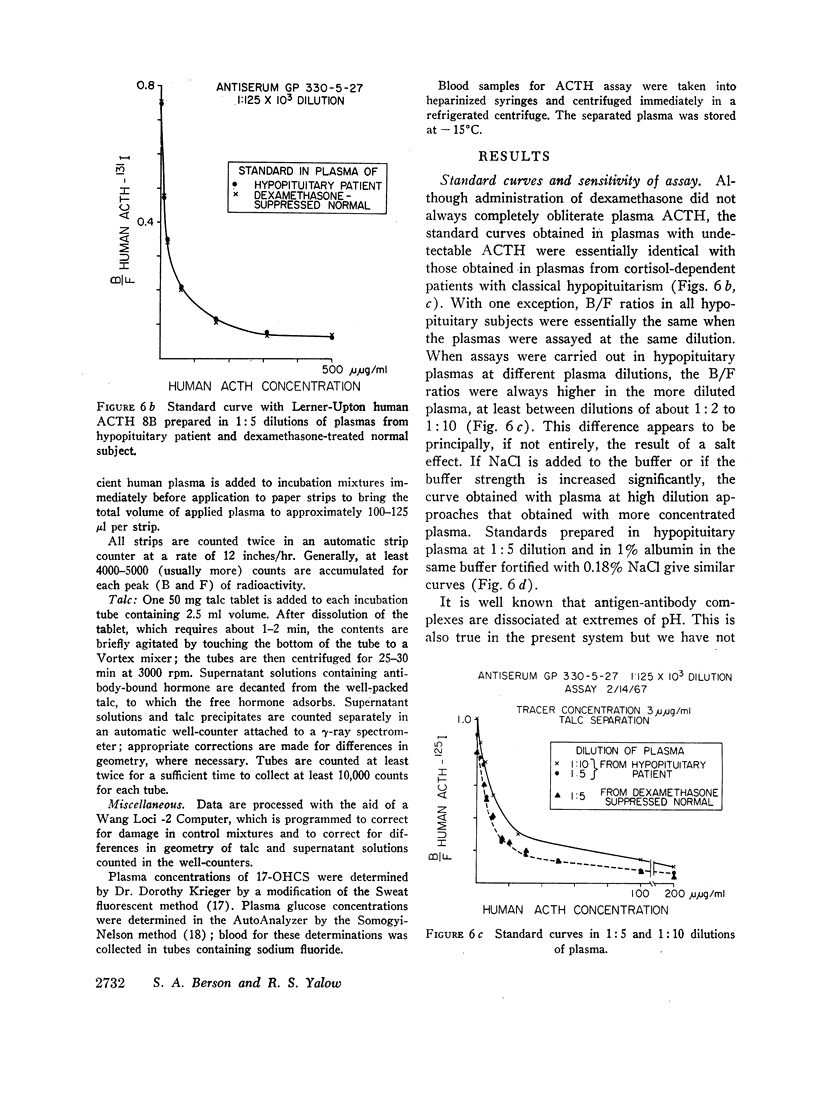
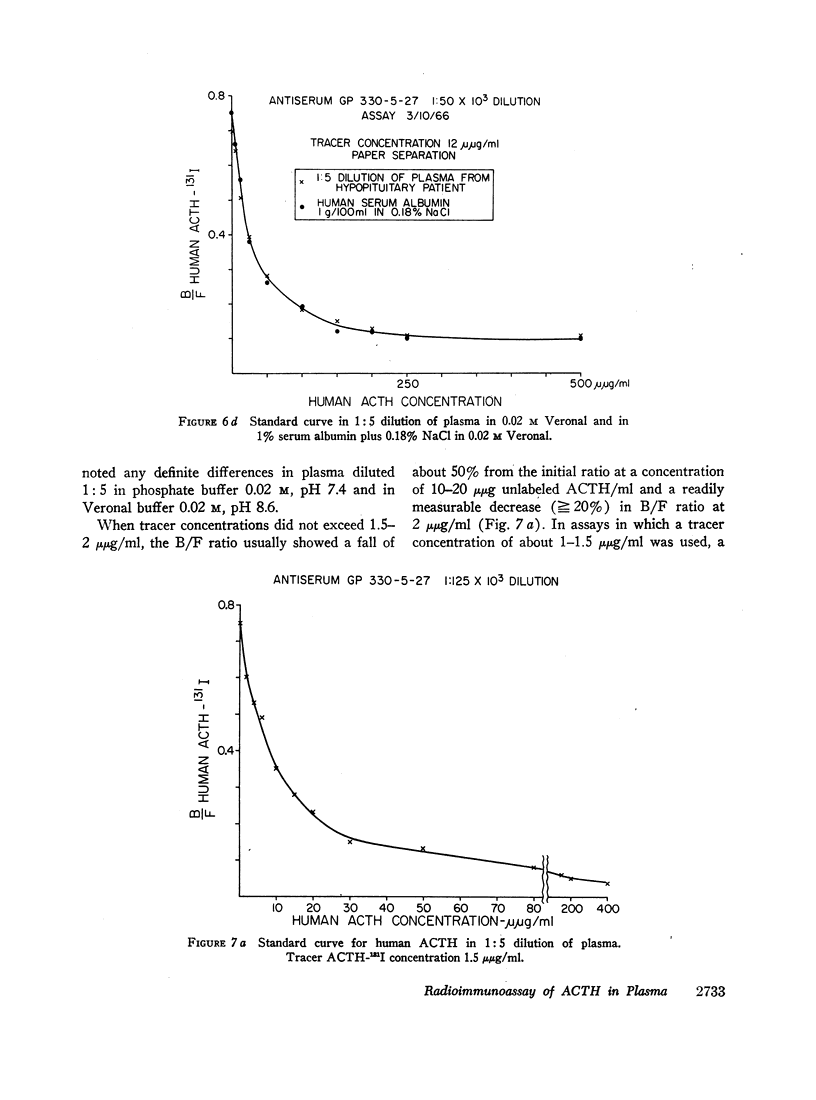
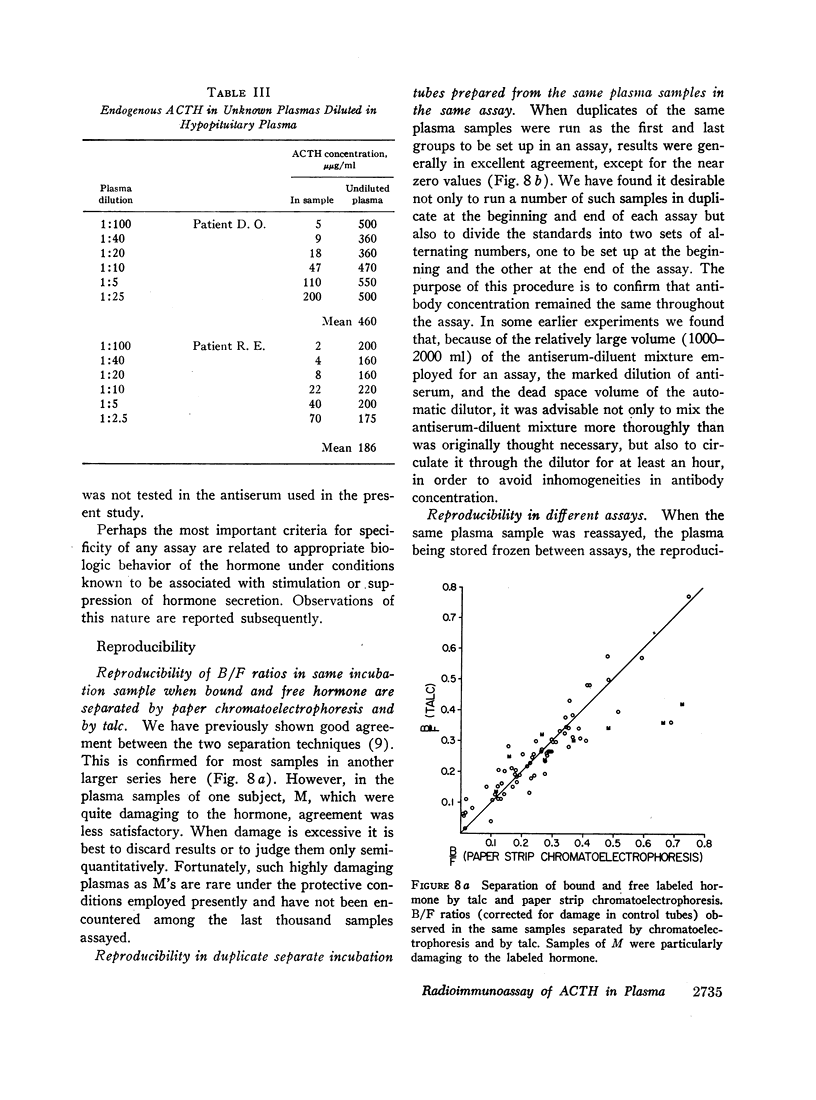






Images in this article
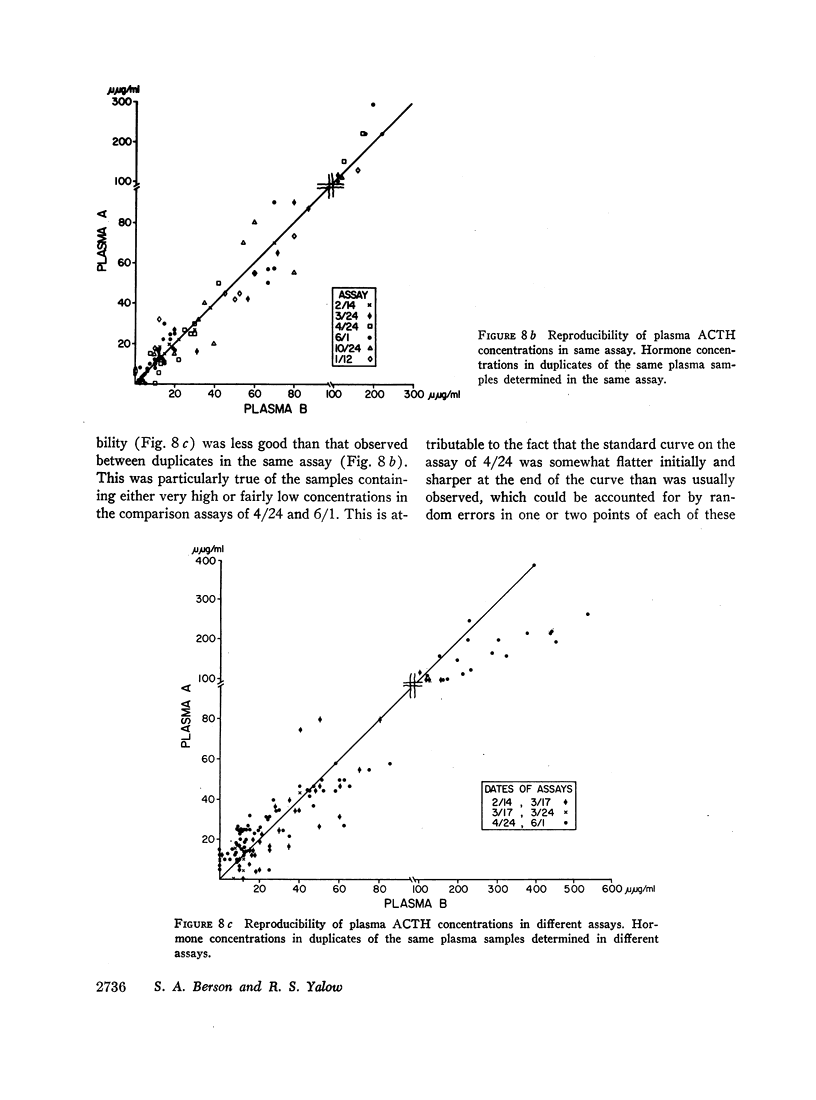
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARTTER F. C., ALBRIGHT F., FORBES A. P., LEAF A., DEMPSEY E., CARROLL E. The effects of adrenocorticotropic hormone and cortisone in the adrenogenital syndrome associated with congenital adrenal hyperplasia: an attempt to explain and correct its disordered hormonal pattern. J Clin Invest. 1951 Mar;30(3):237–251. doi: 10.1172/JCI102438. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERSON S. A., YALOW R. S., BAUMAN A., ROTHSCHILD M. A., NEWERLY K. Insulin-I131 metabolism in human subjects: demonstration of insulin binding globulin in the circulation of insulin treated subjects. J Clin Invest. 1956 Feb;35(2):170–190. doi: 10.1172/JCI103262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERSON S. A., YALOW R. S., GLICK S. M., ROTH J. IMMUNOASSAY OF PROTEIN AND PEPTIDE HORMONES. Metabolism. 1964 Oct;13:SUPPL–SUPPL:1153. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(64)80031-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERSON S. A., YALOW R. S. Isotopic tracers in the study of diabetes. Adv Biol Med Phys. 1958;6:349–430. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4832-3112-9.50013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERSON S. A., YALOW R. S. Quantitative aspects of the reaction between insulin and insulin-binding antibody. J Clin Invest. 1959 Nov;38:1996–2016. doi: 10.1172/JCI103979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BETHUNE J. E., NELSON D. H., THORN G. W. Plasma adrenocorticotrophic hormone in Addison's disease and its modification by the administration of adrenal steroids. J Clin Invest. 1957 Dec;36(12):1701–1707. doi: 10.1172/JCI103571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berson S. A., Yalow R. S. Iodoinsulin used to determine specific activity of iodine-131. Science. 1966 Apr 8;152(3719):205–207. doi: 10.1126/science.152.3719.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CLAYTON G. W., LIBRIK L., GARDNER R. L., GUILLEMIN R. STUDIES ON THE CIRCADIAN RHYTHM OF PITUITARY ADRENOCORTICOTROPIC RELEASE IN MAN. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1963 Oct;23:975–980. doi: 10.1210/jcem-23-10-975. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES B. M., CURRIE A. R., SYMINGTON T. Blood corticotrophin in Cushing's syndrome. Nature. 1960 Dec 31;188:1203–1204. doi: 10.1038/1881203b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEDMAN M. L., FARMER T. H., MORRIS C. J. Oxidation-reduction properties of adrenocorticotrophic hormone. Biochem J. 1954 Dec 17;59(335TH):xii–xii. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEDMAN M. L., FARMER T. H., MORRIS C. J. Studies on pituitary adrenocorticotrophin. 3. Identification of the oxidation-reduction centre. Biochem J. 1961 Feb;78:348–352. doi: 10.1042/bj0780348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOE R. P., VENNES J. A., FLINK E. B. Diurnal variation of 17-hydroxycorticosteroids, sodium, potassium, magnesium and creatinine in normal subjects and in cases of treated adrenal insufficiency and Cushing's syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1960 Feb;20:253–265. doi: 10.1210/jcem-20-2-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demura H., West C. D., Nugent C. A., Nakagawa K., Tyler F. H. A sensitive radioimmunoassay for plasma ACTH levels. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1966 Dec;26(12):1297–1302. doi: 10.1210/jcem-26-12-1297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FERREBEE J. W., JOHNSON B. B., MITHOEFER J. C., GARDELLA J. W. Insulin and adrenocorticotropin labelled with radio-iodine. Endocrinology. 1951 Mar;48(3):277–283. doi: 10.1210/endo-48-3-277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUJITA T. Determination of corticotropin (ACTH) in human blood and urine by a modified oxycellulose method. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1957 Apr;17(4):512–518. doi: 10.1210/jcem-17-4-512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIDDLE G. W. Tests of pituitary-adrenal suppressibility in the diagnosis of Cushing's syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1960 Dec;20:1539–1560. doi: 10.1210/jcem-20-12-1539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIPSCOMB H. S., NELSON D. H. Dynamic changes in ascorbic acid and corticosteroids in adrenal vein blood after ACTH. Endocrinology. 1960 Jan;66:144–146. doi: 10.1210/endo-66-1-144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN M. M., HELLMAN D. E. TEMPORAL VARIATION IN SU-4885 RESPONSIVENESS IN MAN: EVIDENCE IN SUPPORT OF CIRCADIAN VARIATION IN ACTH SECRETION. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Mar;24:253–260. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-3-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MIRSKY I. A., PERISUTTI G., DAVIS N. C. The destruction of glucagon, adrenocorticotropin and somatotropin by human blood plasma. J Clin Invest. 1959 Jan 1;38(1 Pt 1):14–20. doi: 10.1172/JCI103783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NAGAREDA C. S., GAUNT R. Functional relationship between the adrenal cortex and posterior pituitary. Endocrinology. 1951 May;48(5):560–567. doi: 10.1210/endo-48-5-560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NELSON D. H., MEAKIN J. W., THORN G. W. ACTH-producing pituitary tumors following adrenalectomy for Cushing's syndrome. Ann Intern Med. 1960 Mar;52:560–569. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-52-3-560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NEY R. L., SHIMIZU N., NICHOLSON W. E., ISLAND D. P., LIDDLE G. W. CORRELATION OF PLASMA ACTH CONCENTRATION WITH ADRENOCORTICAL RESPONSE IN NORMAL HUMAN SUBJECTS, SURGICAL PATIENTS, AND PATIENTS WITH CUSHING'S DISEASE. J Clin Invest. 1963 Nov;42:1669–1677. doi: 10.1172/JCI104853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARROTT D. M. The assay of adrenocorticotrophic activity in plasma extracts. J Endocrinol. 1955 Mar;12(2):120–129. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.0120120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERKOFF G. T., EIK-NES K., NUGENT C. A., FRED H. L., NIMER R. A., RUSH L., SAMUELS L. T., TYLER F. H. Studies of the diurnal variation of plasma 17-hydroxycorticosteroids in man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1959 Apr;19(4):432–443. doi: 10.1210/jcem-19-4-432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDS J. B., SAYERS G. Fate and excretion of adrenocorticotrophic hormone. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1951 May;77(1):87–93. doi: 10.3181/00379727-77-18687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosselin G., Assan R., Yalow R. S., Berson S. A. Separation of antibody-bound and unbound peptide hormones labelled with iodine-131 by talcum powder and precipitated silica. Nature. 1966 Oct 22;212(5060):355–357. doi: 10.1038/212355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAYERS G. Blood ACTH. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1955 Jun;15(6):754–759. doi: 10.1210/jcem-15-6-754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SYNDOR K. L., KELLEY V. C., RAILE R. B., ELY R. S., SAYERS G. Blood adrenocorticotrophin in children with congenital adrenal hyperplasia. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Apr;82(4):695–697. doi: 10.3181/00379727-82-20222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takebe K., Setaishi C., Hirama M., Yamamoto M., Horiuchi Y. Effects of a bacterial pyrogen on the pituitary-adrenal axis at various times in the 24 hours. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1966 Apr;26(4):437–442. doi: 10.1210/jcem-26-4-437. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANCE V. K., REDDY W. J., NELSON D. H., THORN G. W. Adrenocorticotropic hormone in human plasma. J Clin Invest. 1962 Jan;41:20–28. doi: 10.1172/JCI104463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vernikos-Danellis J. The regulation of the synthesis and release of ACTH. Vitam Horm. 1965;23:97–152. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60381-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. Assay of plasma insulin in human subjects by immunological methods. Nature. 1959 Nov 21;184(Suppl 21):1648–1649. doi: 10.1038/1841648b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. Immunoassay of endogenous plasma insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jul;39:1157–1175. doi: 10.1172/JCI104130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., GLICK S. M., ROTH J., BERSON S. A. RADIOIMMUNOASSAY OF HUMAN PLASMA ACTH. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1964 Nov;24:1219–1225. doi: 10.1210/jcem-24-11-1219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yalow R. S., Berson S. A. Labeling of proteins--problems and practices. Trans N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jun;28(8):1033–1044. doi: 10.1111/j.2164-0947.1966.tb02406.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yalow R. S., Berson S. A. Purification of 131-I parathyroid hormone with microfine granules of precipitated silica. Nature. 1966 Oct 22;212(5060):357–358. doi: 10.1038/212357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]