Abstract
Epigenetic silencing of foreign genes introduced into plants poses an unsolved problem for transgenic technology. Here we have used the simple multicellular green alga Volvox carteri as a model to analyse the relation of DNA methylation to transgenic silencing. Volvox DNA contains on average 1.1% 5-methylcytosine and 0.3% N6-methyladenine, as revealed by electrospray mass spectrometry and phosphoimaging of chromatographically separated 32P-labelled nucleotides. In two nuclear transformants of V.carteri, produced in 1993 by biolistic bombardment with a foreign arylsulphatase gene (C-ars), the transgene is still expressed in one (Hill 181), but not in the other (Hill 183), after an estimated 500–1000 generations. Each transformant clone contains multiple intact copies of C-ars, most of them integrated into the genome as tandem repeats. When the bisulphite genomic sequencing protocol was applied to examine two select regions of transgenic C-ars, we found that the inactivated copies (Hill 183) exhibited a high-level methylation (40%) of CpG dinucleotides, whereas the active copies (Hill 181) displayed low-level (7%) CpG methylation. These are average values from 40 PCR clones sequenced from each DNA strand in the two portions of C-ars. The observed correlation of CpG methylation and transgene inactivation in a green alga will be discussed in the light of transcriptional silencing.
INTRODUCTION
The multicellular green alga Volvox carteri has long been used as an attractive model for studying the molecular genetics and origins of cell differentiation and development (1–5). This work has greatly advanced since the advent of nuclear transformation, facilitating the introduction and propagation of foreign genes in Volvox (6). Random integration of transforming DNA into the nuclear genome occurs generally by non-homologous recombination, and the transgenes are stably transmitted as Mendelian traits. However, the full use of the transformation technology is frequently hampered by variable levels or lack of transgene expression, commonly referred to as ‘transgene silencing’ (7–9).
The molecular mechanisms that govern gene silencing in animals and plants are largely unknown. In an attempt to clarify underlying processes, we have analysed and compared two Volvox transformants, one with active and the other with inactive transgenic Chlamydomonas-derived arylsulphatase genes (C-ars). The results of bisulphite genomic sequencing (10,11) revealed an inverse relationship between transgene expression and CpG methylation, suggesting that the inactivation of transgenic C-ars is associated with DNA methylation in Volvox.
The importance of DNA methylation in eukaryotes for chromatin stability (12), genetic imprinting (11), differential gene control in conjunction with histone deacetylase (13) and gene silencing (7) has been documented. The most common and best-studied DNA targets for methylation are cytosines modified to 5-methylcytosines (5mC). Little is known about N6-methyladenosine (6mA), only found in a few eukaryotic DNAs (14). In vertebrate DNA, 3–6% of the cytosines are methylated, but this value decreases when stepping down the evolutionary scale, so that the DNAs of many insects and single-celled eukaryotes contain no detectable 5mC (15). Higher plant DNAs may have as much as 30% of their cytosines methylated (16), most of which are probably involved in silencing ‘parasitic’ transposable and viral DNAs (9,17). Whereas in animal DNAs, methylation is usually restricted to CpG dinucleotides as the preferential target, in higher plants, cytosine methylation can occur at other symmetric (e.g. CpNpG) or even asymmetric sequences (9).
At the outset of this study, our knowledge of DNA methylation in Volvox was solely based on data that document 5mC and 6mA in the nuclear DNA and in mt+ gamete chloroplast DNA of the related unicellular Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (18,19). Restriction of DNA with methylation-sensitive endonucleases and observations of epigenetic silencing of foreign genes suggested an involvement of DNA modification in C.reinhardtii (8,20). However, in V.carteri the nature and relative extent of such modifications had not been assessed. We have, therefore, applied reverse-phase high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) combined with electrospray mass spectrometry (ESI-MS) and two-dimensional thin-layer chromatography (2D-TLC) to analyse Volvox DNA. This revealed an average content of 1.1% 5mC and 0.3% 6mA in V.carteri genomic DNA. Further, we present here the first analysis of transgene DNA methylation in a green alga by the bisulphite genomic sequencing technique. This detailed examination was absolutely needed for interpreting transgene methylation patterns and for assessing their role in epigenetic silencing.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Strains, plasmids and nuclear transformation of V.carteri
Escherichia coli strains DH10B (dam+ dcm+) and JM110 (dam– dcm–) (21) were used as hosts for propagating plasmid pSK– (Stratagene). Cells from overnight cultures (30 ml, 37°C) in Luria broth were harvested and plasmid DNA was isolated and purified with a QIAfilter Plasmid Midi Kit (Qiagen). The 11.2 kb plasmid pIK2 is an in vitro recombinant of the complete C-ars gene (22) on a 6.0 kb fragment derived from plasmid pJD54 (23), the Volvox β2-tubulin promoter (P-Vβ2) on a 2.2 kb fragment (24) and pSK+ vector DNA (Stratagene). The pBS+-based 10.8 kb plasmid pVcNR1 contains the V.carteri nitrate reductase gene (nitA; 25) used as a selectable marker for transformation. A 1150 bp BamHI cDNA fragment of the 5.7 kb plasmid pJD27 containing the complete C-ars cDNA was used as a probe for Southern hybridisation.
Volvox carteri f.nagariensis HK10 (Japan) and Poona (India), provided by the UTEX Collection (Austin, TX) and the nitA–, regA–, gls– strain 153-81 (26) used as the recipient in transformation experiments were maintained in standard Volvox medium (SVM) at 30°C under standardised conditions (27). SVM lacking the usual urea or ammonium chloride (N-SVM) was used for its ability to reduce nitrate. Transformant clones, Hill 181 and Hill 183, were isolated in 1993 upon biolistic co-bombardment (6) of V.carteri 153-81 with pIK2 and pVcNR1 and selection on N-SVM as described (3). These transformants have since been subcultivated in N-SVM under a 16:8 light–dark regime for an estimated 500–1000 generations.
Preparation and analysis of DNA by HPLC/MS
Genomic DNA was purified by CsCl ultracentrifugation, phenol extraction and subsequent dialysis as described (28). Residual RNA was removed from purified DNA by RNase A (200 µg/ml) treatment at 37°C for 3 h and protein was removed by precipitation with 2.5 M ammonium acetate and centrifugation at 14 000 r.p.m. for 20 min (29). DNA was ethanol-precipitated, washed and redissolved in water to 0.5 µg/µl. It was denatured by heating for 3 min at 100°C and subsequent chilling in an ice–water slush, then mixed with one-tenth vol of 0.1 M ammonium acetate, pH 5.3. DNA was digested in three steps: (i) incubation with nuclease PI (2 U/25 µg DNA; Roche) at 45°C for 2 h; (ii) addition of one-tenth vol of 1 M ammonium bicarbonate and phosphodiesterase I (0.002 U/25 µg DNA; Roche) and incubation for 2 h at 37°C; (iii) addition of alkaline phosphatase (1 U/50 µg DNA; Roche) and incubation for 1 h at 37°C. Samples were stored at –20°C pending analysis by HPLC/MS.
The separation of deoxynucleosides (dNs) by HPLC in a 40 mM ammonium acetate pH 6.0/40% acetonitrile gradient, their identification by retention times at 254 nm, and analysis of individual fractions by ESI-MS followed established protocols (30). A 2.1 × 250 mm LC-18S column (Supelco, Sigma-Aldrich) was used for HPLC, peak fractions were sampled, lyophilised and redissolved each in 20 µl of 50% methanol/0.5% acetic acid. Samples of 2–5 µl were injected into a Finnigan MAT SSQ 7000 ESI mass spectrometer equipped with a Finnigan electrospray ion source. The electrospray needle was maintained at 4.5 kV, consistent with positive ion formation. The electron multiplier was set to 1150 V. Spectra were scanned from m/z 200 to m/z 900.
32P-post-labelling and 2D-TLC
Individual deoxyribonucleosides were 32P-labelled according to established protocols (31,32) after removal of residual RNA by 1 h hydrolysis in 0.3 M NaOH at 50°C and by extraction using a QUIAEXTM II Gel Extraction Kit (Qiagen). Labelled nucleotides were separated by 2D-TLC on polyethyleneimine (PEI)-impregnated cellulose sheets (Polygram CEL 300PEI/UV254, Macherey Nagel) as described (31). Radioactive spots were recorded by exposure on X-ray film and by a phosphoimager (CycloneTM Storage Phosphor System, Packard Instruments). The percentage of the individual nucleotides was calculated from the data obtained by phosphoimaging using Optiquant software (v. 2.50, Packard Instruments). Plasmid pSK– DNAs (Stratagene) propagated in the C- and A-modifying E.coli strain DH10B (dam+ dcm+) and in the non-modifying mutant strain JM110 (dam– dcm–) were used as a reference for assigning the methylated nucleotides, 5mC and 6mA. The known percentages of methylated bases (2.04% 6mA, 0.67% 5mC) deduced from the numbers of Dam (GATC) and Dcm (CGCG) methylase recognition sites in the pSK– sequence (GenBank accession no. X52324) recommended the plasmid DNA, with and without modifications, as a convenient standard for localising and quantitatively assessing the methylated bases on 2D-TLC.
Genomic sequencing technique
Bisulphite treatment (10) of DNA (2 µg of genomic Volvox DNA mixed with 3 µg of herring sperm DNA) was performed according to Zeschnigk et al. (11). The methylation patterns were determined for each strand in a separate PCR reaction. For PCR, 1 µl of bisulphite-treated DNA (∼250 ng) was used in a 25 µl reaction mixture: 2.5 µl 10× Taq buffer (Eurogentech), 1.7 mM MgCl2, 0.1 mM of each of the dNTPs, 0.5 mM of each primer and 1 U Taq polymerase (Eurogentech). PCR was performed under the following cycle conditions: 95°C for 5 min initial denaturation; subsequently 95°C for 30 s, 50–58°C for 30 s (annealing temperature depending on the primers), and 72°C for 45 s for 35 cycles and 72°C for 5 min. A 1 µl fraction of the PCR products was reamplified by using nested primers.
The PCR products were purified by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis and cloned into pGEM-T (Promega) for transformation of E.coli DH10B. Individual transformant clones were selected by blue/white screening (33). Recombinant plasmid DNA was prepared by standard methods (33), and the nucleotide sequences were determined in an automated Applied Biosystems Sequencer 310 using the SP6 primer.
Southern and dot blot analysis
Endonuclease digestions, electrophoresis of DNA (2 µg per lane) on 0.8% agarose gels and Southern analyses followed standard methods (33). Blots were scanned and quantified by a phosphoimager in combination with Optiquant software v. 2.50 (CycloneTM Storage Phosphor System, Packard Instruments).
Plasmid rescue
Genomic DNA (10 µg) of Volvox transformants containing transgenic ars was digested with 50 U SalI in 200 µl of SalI digestion buffer, phenol-extracted, EtOHx-precipitated, washed and incubated overnight at 14°C in 400 µl ligase buffer containing 6 U T4 DNA ligase to circularise genomic DNA fragments. DNA was EtOH-precipitated, redissolved in 20 µl H2O and used to transform E.coli DH10B. Transformant clones were selected on LB ampicillin plates (33). Plasmids containing the rescued transgene DNA were physically mapped and sequenced.
Arylsulphatase activity test
Arylsulphatase (Ars) activity was determined by hydrolysis of α-naphthylsulphate (23). Approximately 300 Volvox spheroids in 3 ml SVM were sonicated (50 W, 2 × 15 s), sedimented (Sorvall centrifuge, SS34 rotor, 4000 r.p.m. for 5 min), and 500 µl samples of the supernatant were used for enzyme and protein assays (Roti-Nanoquant, Roth). Samples adjusted to equal protein concentration were mixed with 8 µl of 50 mM α-naphthylsulphate to reach a final concentration of 0.8 mM. After a 4 h incubation the reaction was stopped by addition of 500 µl 4% SDS in 0.2 mM Na-acetate, pH 4.8, and mixed with 100 µl of tetrazotised o-dianisidine (10 mg/ml) to yield a purple adduct that was quantified by its absorbance at 540 nm 2 min after mixing. One unit of Ars is defined as the amount that liberates the equivalent of OD540 = 1 per mg of total protein in 4 h.
RESULTS
Detection of 5mC and 6mA in Volvox DNA
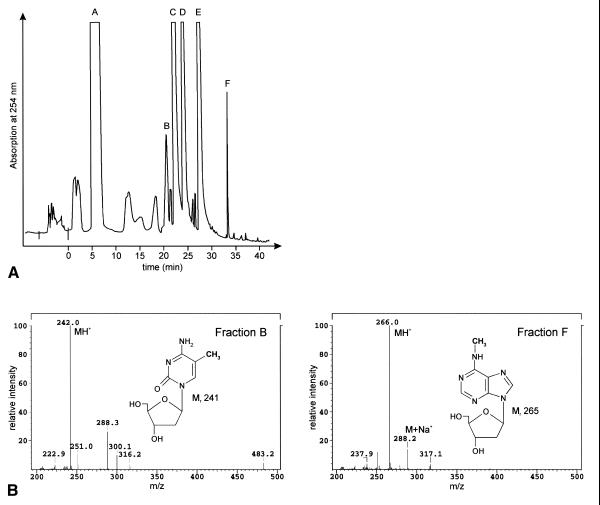
The combination of HPLC with ESI-MS based on an electrospray interface results in mass per charge (m/z) values that permit a structural assignment of the major and frequently the identification of unknown minor nucleosides. In pilot experiments with a Volvox hydrolysate separated by HPLC, no satisfactory resolution of dNs by MS was achieved when a coupled HPLC/MS device was used, possibly owing to interference by the ionic elution buffer (Materials and Methods). The HPLC peak fractions A–F (Fig. 1) were therefore separately lyophilised, redissolved in methanol/acetic acid and injected into the mass spectrometer. This resulted in well-resolved m/z signals for the protonated major compound from each HPLC fraction; secondary signals reflected protonated dimers and Na+ or K+ adducts of the monomeric nucleosides. The mass spectra of peak fractions B and F (Fig. 1A) that contain the modified species, 5mC and 6mA, are shown in Figure 1B together with their m/z values. HPLC fractions A, C, D and E (Fig. 1A) contained the four major 2′-dNs in the order C–G–T–A assigned on the basis of their m/z values (data not shown). The sequence of their elution from HPLC (Fig. 1A) was consistent with the elution order reported by Pomerantz and McCloskey (30). The complete HPLC and MS data with appropriate dNs assignments shown in Table 1 list the four major bases and the two methylated bases, 5mC and 6mA, as new constituents of V.carteri DNA.
Figure 1.
HPLC elution profile of dNs and mass spectra of fractions B and F. (A) dNs from 50 µg of hydrolysed and dephosphorylated V.carteri HK10 DNA were separated by HPLC and monitored by absorbance at 254 nm. Fractions A–F were collected and analysed by mass spectrometry. (B) Mass spectra of HPLC fractions B and F from (A). Signals assigned by their m/z values identify protonated molecules (MH+) of two methylated derivatives, 5mC and 6mA. The complete assignments of fractions A–F are compiled in Table 1.
Table 1. HPLC and MS data for dNs identified in V.carteri DNA (from Fig. 1).
| Nucleosidea | HPLC retention | Mass peaks (m/z)b | |||
| |
time (min) |
MH+c |
MMH+ c |
M+Na+c |
M+K+c |
| dC | 5 | 228 | 455 | – | – |
| 5mdC | 20 | 242 | – | – | – |
| dG | 22 | 268 | 535 | – | – |
| dT | 24 | 243 | – | 265 | 281 |
| dA | 27 | 252 | – | 274 | – |
| 6mdA | 33 | 266 | – | 288 | – |
aNucleosides are listed sequentially according to their retention time.
bm/z, mass per charge values.
cMH+, protonated molecule; MMH+, protonated dimer; M+Na+, sodium ion adduct; M+K+, potassium ion adduct.
Quantitative assessment of DNA methylation
The 5′-32P-labelled dNs derived from total DNA hydrolysates of V.carteri strains HK10 and Poona were separated by 2D-TLC on commercial PEI-impregnated cellulose sheets (31). Plasmid pSK– DNA propagated in the dC- and dA-modifying E.coli strain DH10B (dam+ dcm+) and in the non-modifying mutant strain JM110 (dam– dcm–) served as a reference for localising and quantifying 5mC and 6mA. TLC of DNA hydrolysates from strains HK10 and Poona both revealed distinct signals for 5mC and 6mA (data not shown), which were quantified by the Packard phosphoimaging system. Percentages of 5mC and 6mA present in these Volvox DNAs are listed in Table 2. With reference to the pSK– DNA standard, the standard and measured 5mC values were consistent, whereas the experimentally assessed 6mA values had to be down-corrected by a factor (F) of 0.74. Hence, V.carteri HK10 DNA contains 1.1% 5mC and 0.3% 6mA, and V.carteri Poona DNA contains 0.8% 5mC and 0.3% 6mA (Table 2). Taken together, DNA methylation at C and A demonstrated in V.carteri strains isolated in Japan (HK10) and India (Poona), is likely to be a general feature of Volvox nuclear DNA.
Table 2. Percentages of 5mC and 6mA in E.coli, V.carteri and C.reinhardtii DNAs.
| DNA source |
% 5mCa |
% 6mAexpa,b |
% 6mAcorr (6mAexp × F)b |
| pSK– (E.coli DH10B) | 0.69 ± 0.02 (3)c | 2.75 ± 0.06 (3)c | 2.04 |
| V.carteri HK10 | 1.1 ± 0.2 (4)c | 0.4 ± 0.1 (4)c | 0.3 ± 0.1 |
| V.carteri Poona | 0.8 ± 0.1 (2)c | 0.4 ± 0.1 (2)c | 0.3 ± 0.1 |
aThe 5mC and 6mA contents of DNA were calculated by comparing the radioactivities of methylated (pmdN) and unmethylated ‘parent’ (pdN) nucleosides on 2D-TLC according to:
% pmdN = [(pmdN)/(pmdN + pdN)] × 100
bCorrection factor, F = 0.74, equals the pSK– sequence-derived percentage of Dam-methylated 6mAcorr divided by the experimental value 6mAexp.
cValues represent the average of (n) experiments ± standard deviation.
Two transformant clones for an analysis of epigenetic silencing
Foreign genes (‘transgenes’) can be readily introduced into the reproductive cells (gonidia) of Volvox by co-transformation with a selectable marker (6), but often become silenced for reasons that are still poorly understood. To investigate a possible link between DNA methylation and epigenetic silencing of foreign genes in Volvox, we have compared the expression of transgenes in various nuclear transformants of V.carteri 153-81 (a derivative of the wild-type strain HK10). This search yielded two clones, Hill 181 and Hill 183, both generated by transformation with plasmid pIK2 bearing the genomic ars DNA of C.reinhardtii (C-ars) under the control of the strong P-Vβ2. One transformant (Hill 181) exhibited high-level Ars activity, the other (Hill 183) merely basal-level activity, like the negative control (Table 3). Both clones had been selected from the same transformation experiment in 1993 as high-expression clones, which have since been serially subcultured for an estimated 500–1000 generations. The loss of transgene function in Hill 183 (but not in Hill 181) may be caused (i) by damage or loss of the foreign gene(s) or (ii) by the modification of the foreign DNA. These alternative explanations for the observed gene inactivation have both been examined.
Table 3. Levels of Ars activity in V.carteri and two transformants.
| V.carteri strains | Ars activitya | |
| |
– o-dianisidine |
+ o-dianisidineb |
| 153-81 (no transgene) | 5 | 10 ± 3 |
| Hill 181 (active transgene) | 7 | 125 ± 14 |
| Hill 183 (inactive transgene) | 4 | 18 ± 7 |
aU/mg total protein.
bMean of three experiments.
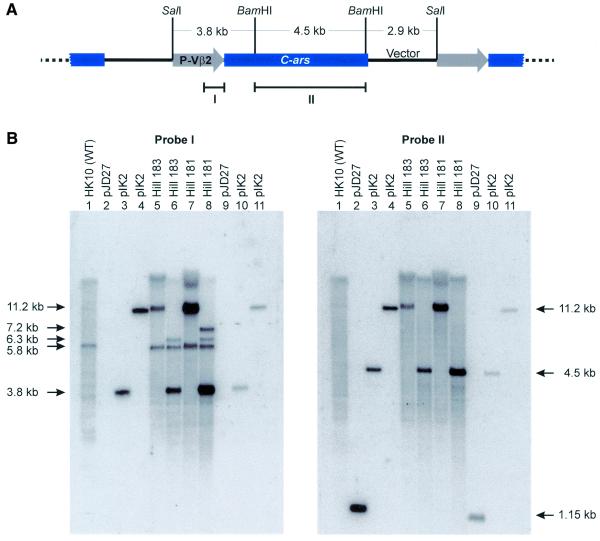
Transformants of V.carteri frequently contain multiple copies of the transforming plasmid DNA stably integrated into the nuclear genome (6). This pattern holds similarly for Hill 181 and Hill 183, as revealed by Southern blot analyses (Fig. 2). Blots containing the transformant DNAs (plus recipient and plasmid DNA controls) were digested by BamHI, SalI or BamHI–SalI and hybridised with two probes, one detecting the P-Vβ2 promoter (probe I) and the other the C-ars coding region (probe II) of the transgene. Free pIK2 DNA yields a 11.2 kb SalI plus a 3.8 kb BamHI–SalI band with probe I and 11.2 kb SalI and 4.5 kb BamHI–SalI bands with probe II, as delineated in Figure 2A and as is evident on the blots (Fig. 2B, lanes 3, 4, 10 and 11). Corresponding bands produced by the appropriately digested DNAs of Hill 183 (Fig. 2B, lanes 5 and 6) and Hill 181 (Fig. 2B, lanes 7 and 8) are most prominent, suggesting that both these transformants contain the complete transgene as multiple copies. Therefore, the missing Ars activity of Hill 183 (Table 3) cannot be the result of transgene loss or damage. The 3.8 kb BamHI–SalI fragment of a plasmid that underwent recombination in the P-Vβ2 promoter region (Fig. 2A) will be replaced by a new fragment containing genomic DNA flanking the integration site. A 6.3 kb band seen in BamHI–SalI digested Hill 181 and Hill 183 DNAs hybridised with probe I (Fig. 2B, lanes 6 and 8) is likely to reflect such an event. A separate recombination event of this sort involving another copy of pIK2 is represented by the 7.2 kb BamHI–SalI fragment seen in Figure 2B (probe I, lane 8).
Figure 2.
Repeat structure of integrated C-ars copies and Southern analysis of transformants. (A) Proposed tandem arrangement of transgenic DNA (containing C-ars) in transformant clones Hill 181 and Hill 183, and extent of two restriction fragments (I and II) used for probing Southern blots. P-Vβ2, Volvox β2-tubulin promoter; C-ars, arylsulphatase gene from C.reinhardtii. (B) Southern blots of plasmids (pIK2, pJD27) and genomic DNAs (identified by clone numbers), probed as indicated. DNAs were restriction-digested as follows: lanes 2 and 9, BamHI; lanes 4, 5, 7 and 11, SalI; lanes 1, 3, 6, 8 and 10, BamHI–SalI. Genomic DNAs were applied at 2 µg per lane, plasmid DNAs were applied at 1950 (pIK2) or 950 pg (pJD27) per lane (corresponding to 10 copies per genome; lanes 2–4) and at 195 (pIK2) or 95 pg (pJD27) per lane (corresponding to one copy per genome; lanes 9–11). The resulting differences in signal intensities served as a reference for densitometric estimates of transgene copy numbers. Bands are identified by their sizes (indicated to the left or right of the gels).
The relative amounts of multiple copies of pIK2 were assessed densitometrically by reference to the single-copy genomic β2-tubulin gene hybridising to probe I as a 5.8 kb SalI band (Fig. 2B, lanes 1 and 5–8). In addition, pIK2 and pJD27 plasmid DNAs blotted at unit (Fig. 2B, lanes 9–11) and 10-fold (Fig. 2B, lanes 2–4) molar ratios relative to genomic DNA (Fig. 2B, lanes 1 and 5–8) served as references for the interpolation of signal intensities. As a result, Hill 183 and Hill 181 contain 7 (±2) and 24 (±7) copies, respectively, of the intact transgene. These values were confirmed by dot blot analyses (data not shown).
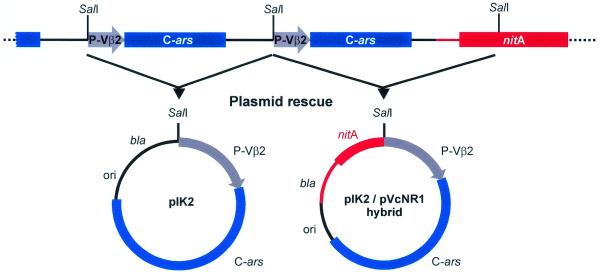
Can we deduce the configuration of these integrated multiple transgenes? It has been generally observed that upon biolistic transformation of Volvox, the bulk of integrated foreign DNA copies yield a dominant pattern of identical bands on Southern blots interpreted as ‘tandem integration of transgenes’ (6). We have further developed this concept by plasmid rescue experiments using SalI digests of Hill 181 and Hill 183 DNA, ligation, plasmid selection and propagation in an E.coli host, as illustrated in Figure 3. Physical mapping and sequence analyses of both transformant DNAs revealed reconstituted pIK2 and a new plasmid generated by recombination of pIK2 (C-ars marker) and pVcNR1 (nitA marker), fused within the identical pUC derivative vector portions (Fig. 3). This is a new twist to Volvox transformation implying that transforming plasmids frequently undergo homologous recombination (34) to form a circular concatemer of multiple copies, before being inserted into a random genome locus by a single crossover event. The transgene copy disrupted by this event then forms the termini of the linearly integrated concatemer adhering to genomic DNA. The disrupted transgene flanking the intact copies usually yields an extra band in Southern blots, like the 6.3 kb BamHI–SalI band seen in Figure 2B (lanes 6 and 8).
Figure 3.
Analysis of tandemly integrated transgenes by plasmid rescue. As illustrated, the transgenes (abbreviated as in Fig. 2; nitA, nitrate reductase gene) were recovered by SalI digestion of transformant DNA, ligation and plasmid replication (ori, origin of replication) and selection in an E.coli host on ampicillin (bla, β-lactamase gene). The plasmid structures were confirmed by restriction mapping and sequence analysis. The pIK2/pVcNR1 hybrid structure is suggestive of homologous recombination that joins transforming plasmids within the identical pUC-derived vector portions (black/red transitions) before they are integrated (as concatemers) into the genome.
In conclusion, both Hill 181 and Hill 183 contain multiple copies of tandemly integrated complete pIK2 DNA. The tandem repeats are thought to result from a circular concatemer of multiple transgenes formed before the integration event.
Transgene silencing correlates to DNA methylation
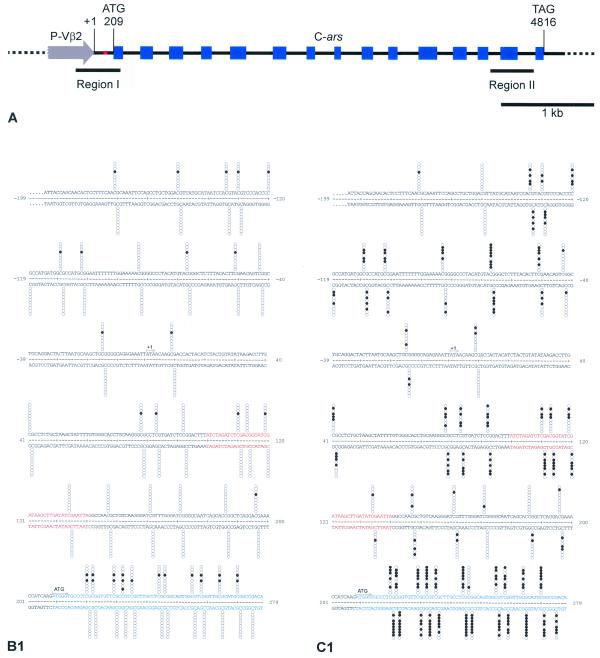
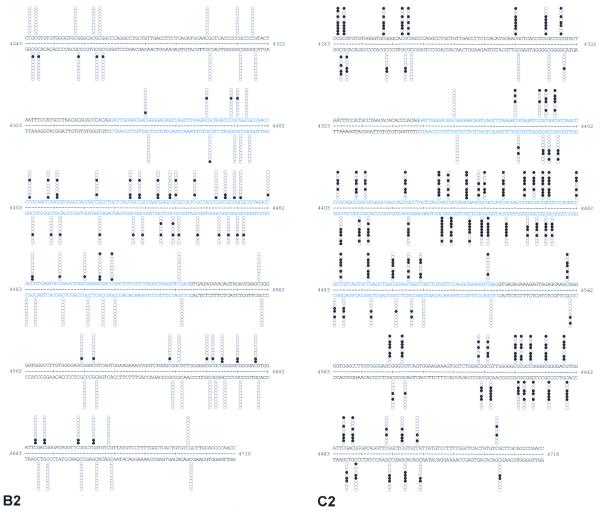
The above analysis of Hill 181 (active C-ars) and Hill 183 (inactive C-ars) provided the basis for a comparison of DNA methylation of the C-ars transgenes. In a pilot experiment, Hill 183 spheroids grown in the presence of 0.2 or 0.5 mM 5-azacytidine for 5–6 days regained part of the Ars activity (data not shown). This suggested a role of cytosine methylation in ars gene inactivation, since 5-azacytidine is known to promote undermethylation of cytosine nucleotides in DNA (35). This concept has been substantiated by applying the bisulphite protocol of genomic sequencing to the analysis of two typical regions of transgenic C-ars from Hill 181 and Hill 183 (Fig. 4B and C). Region I includes exon 1 of C-ars, the 5′ flanking linker and P-Vβ2; region II contains exon 14 and flanking intron sequences (Fig. 4A). Since the sequence-specific methylation of mammalian and plant promoters (9) is frequently associated with long-term transcription inactivation, it was of interest to study the precise patterns of DNA methylation in the promoter and exon 1 regions of the active and inactive C-ars transgenes in Hill 181 and Hill 183 DNAs, respectively. In addition, we have analysed the 3′-terminal exon and flanking introns to see whether C-methylation is restricted to a particular portion of an algal transgene shown to have been long-term inactivated. The results of bisulphite genomic sequencing of these transgene portions are shown by columns of 10 circles for each DNA strand representing 10 single cloned PCR products (and potentially independent transgenes) at each CpG position, which contain >99% of the methylated cytosines. Filled circles indicate methylated CpG dinucleotides, open circles unmethylated dinucleotides. The results summarised in Table 4 reveal interesting new aspects. (i) C-ars transgene inactivation in Hill 183 is distinctly associated with CpG methylation. In the relevant portions, the degree of methylation in Hill 183 DNA is between 3.5 and 14 times higher than in Hill 181 DNA. CpG methylation pertains to the promoter as well as coding and non-coding regions of the C-ars gene. (ii) Like in mammals (but unlike in plants), C-methylation is restricted to CpG dinucleotides. (iii) Exons contain the highest density of CpG dinucleotides, almost twice as many per unit length as intron and promoter sequences. Accordingly, exons exhibit the highest degree of methylation.
Figure 4.
(Opposite and above) Physical map of the P-Vβ2/C-ars transgene (A) and CpG methylation patterns in regions I and II compared between Hill 181 (B) and Hill 183 (C). (A) Sequence-derived map of the P-Vβ2/C-ars construct introduced into Hill 181 and Hill 183. The numbering of transcription initiation (+1), translation start (ATG) and stop (TAG) refers to the submitted Volvox β2tub (GenBank accession no. L24547) and Chlamydomonas ars (GenBank accession no. AF333184) genomic sequences. Exons (blue boxes), introns (black lines), promoter (grey arrow) and the P-Vβ2/C-ars junction (red) are delineated. Bars marked ‘Region I’ and ‘Region II’ delimit the portions analysed by bisulphite genomic sequencing (B and C). (B) Hill 181- and (C) Hill 183-derived transgene nucleotide sequences of region I (B1 and C1) and region II (B2 and C2), respectively. Numbering and colour codes as in (A). The methylatable CpG dinucleotide positions are marked by columns of 10 circles in each strand representing 10 clones isolated and sequenced for each set of primers. Each horizontal set of circles represents the methylation pattern of a single cloned PCR product. Filled circles indicate methylated cytosines, open circles unmethylated cytosines.
Table 4. CpG methylation of transgenic C-ars regions in Hill 181 and Hill 183.
| Position | Functional assignment | Frequency of CpG (%)a | CpG methylation (%)b | ||
| |
|
|
|
Hill 181 |
Hill 183 |
| Region Ic | –194/–135 | 5′ upstream | 3 | 5 | 3 |
| –134/–1 | β2-tubulin promoter | 7 | 4 | 35 | |
| +1/120 | 5′ UTR (β2-tubulin) | 7 | 3 | 40 | |
| 121/208 | 5′ UTR (C-ars) | 7 | 1 | 14 | |
| 209/279 | exon 1 (C-ars) | 17 | 8 | 60 | |
| Region IIc | 4243/4350 | intron 13 (C-ars) | 7 | 3 | 39 |
| 4351/4536 | exon 14 (C-ars) | 14 | 12 | 42 | |
| 4537/4710 | intron 14 (C-ars) | 9 | 6 | 39 | |
aNumber of CpG dinucleotides per 100 nt.
bPercent CpG-methylation in a given section.
cRegions I and II defined according to Figure 4A.
The results implicate an association between CpG methylation and epigenetic transgene inactivation in Volvox. It is probably the repetitive structure of the integrated transgenes that identifies them as targets for DNA methylation.
DISCUSSION
A problem frequently seen in nuclear transformation of Volvox is low levels or lack of expression of the foreign genes (6). This has been similarly observed in transformants of the related unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas (20,36). In an extensive study of this phenomenon, Cerutti et al. (8) arrived at the conclusion that in C.reinhardtii the local (hetero)chromatin structure rather than DNA methylation has a role in transgene inactivation. In analysing wild-type and transgenic V.carteri, we have again broached the question of DNA methylation and its possible role in gene silencing. By chemical analyses of DNA hydrolysates, we have detected 5mC (1.1%) and 6mA (0.3%) as constituents of HK10 nuclear DNA. Bisulphite genomic sequencing of DNAs from two Volvox transformants, one with transcriptionally active and the other with inactive copies of a heterologous C-ars gene, revealed a strong correlation between cytosine methylation of CpG dinucleotides and epigenetic silencing of the foreign DNA. Unlike 5mC, adenine methylation is rarely seen in multicellular eukaryotes (14), and its biological function in Volvox and other eukaryotes needs further scrutiny.
Two Volvox nuclear transformants, Hill 181 and Hill 183, generated by biolistic bombardment with the Chlamydomonas C-ars gene (22) under the control of the strong constitutive P-Vβ2 (24), were selected as Ars clones in 1993. The endogeneous Volvox V-ars gene (37) is transcriptionally silent, unless induced by sulphur deprivation, and thus did not interfere with the assay in sulphate-containing medium. After 6 years of serial subcultivations (equalling 500–1000 cell cycles), Hill 181 still exhibited high Ars activity, while Hill 183 was silent (Table 3). The loss of Ars activity was evidently not a result of a transgene deletion, since Southern blot analyses revealed approximately seven intact copies of the P-Vβ2/C-ars construct in Hill 183 DNA (and approximately 24 copies in Hill 181 DNA). Most of these foreign genes were inserted as tandem repeats into the Volvox nuclear genome. The repetitive pattern is most probably a consequence of homologous recombination between plasmids (introduced by biolistic bombardment) joined to form circular concatemers that are then integrated into random chromosomal sites. Homologous recombination events between plasmids introduced into V.carteri have been similarly observed by Hallmann et al. (34). Concatemeric intermediates deduced here from plasmid rescue experiments (Fig. 3) are an interesting feature with a potential for engineering transformation efficiency.
There is much evidence that sequence-specific methylation is part of the mechanism of gene silencing in mammals and plants (9). In analysing Hill 183, an initial cue came from treatment of single spheroids with 5-azacytidine known to alleviate DNA methylation at cytosines (35). Hill 183 responded to 0.5 mM 5-azacytidine by a partial reactivation of C-ars, a result that initiated a comparison of the Hill 181 and Hill 183 transgenes by bisulphite genomic sequencing. This study presents the first analysis of DNA methylation patterns of silenced transgenes in a green alga, notably V.carteri, by applying the bisulphite genomic sequencing technique. Before any interpretation of DNA methylation patterns, even in the relatively small 120 Mb Volvox genome (2), these patterns have to be determined in detail. It is no longer sufficient to base conclusions on restriction analyses, which may not pick up >20–30% of the methylatable CpG-containing sequences (11).
By applying the bisulphite genomic sequencing protocol to the analysis of two ‘diagnostic’ regions of C-ars, we found dramatic differences in methylated CpG dinucleotides between Hill 181 (average 7%) and Hill 183 (average 40%). The correlation between C-ars transgene inactivation and DNA methylation (Fig. 3) becomes even more evident when comparing the clonal patterns of CpG dinucleotide methylation. As listed in Table 5, all 10 Hill 183-derived clones are CpG-methylated, but only four out of 10 Hill 181-derived clones exhibit varying degrees of CpG methylation, whereas six (or more) non-methylated copies contribute to the Ars activity seen in Hill 181 (Table 3).
Table 5. Clonal analysis of CpG methylation (%) in each of 10 sense (SE) and antisense (AS) strand PCR clones from Hill 181 and Hill 183.
| Region Ia | Region IIa | |||||||
| Hill 181 | Hill 183 | Hill 181 | Hill 183 | |||||
| |
SE |
AS |
SE |
AS |
SE |
AS |
SE |
AS |
| 70 | 0 | 62 | 76 | 54 | 28 | 78 | 74 | |
| 21 | 0 | 54 | 76 | 42 | 10 | 74 | 64 | |
| 3 | 0 | 54 | 63 | 24 | 4 | 72 | 54 | |
| 0 | 0 | 51 | 47 | 4 | 2 | 70 | 42 | |
| 0 | 0 | 49 | 45 | 0 | 0 | 66 | 28 | |
| 0 | 0 | 46 | 42 | 0 | 0 | 52 | 18 | |
| 0 | 0 | 22 | 39 | 0 | 0 | 34 | 18 | |
| 0 | 0 | 14 | 24 | 0 | 0 | 18 | 14 | |
| 0 | 0 | 3 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 16 | 2 | |
| 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 8 | 2 | |
| Mean | 9 | 0 | 35 | 42 | 12 | 4 | 49 | 32 |
aRegions I and II of C-ars defined according to Figure 4A.
In vertebrate genomes, CpG islands are frequently located in the upstream regulatory regions, e.g. of the globin genes, as CpG methylation is directly related to their transcriptional regulation (38,39). By contrast, the volvocine C-ars gene contains the highest concentration of CpG dinucleotides in exons (14–17%), nearly twice the density seen in introns (8%) or in 5′ upstream promoter sequences (7%). The clustering of CpGs in exons may be a consequence of the high GC codon bias of volvocine algae favouring the CG combination (1). The distribution of CpG dinucleotides is also reflected by the methylation patterns that—unlike in mammalian, but like in many plant genes (9)—is not restricted to an upstream regulatory region, but spread across the entire gene, and is most eminent in the exon sequences. We conclude that transgenic silencing in Hill 183 clearly correlates with a high degree of methylation of the entire gene.
Repeat DNA structure may be one factor that identifies foreign DNA as a target for methylation, as silencing occurs more frequently when multiple copies of the transgene are inserted (40). The ‘genome defence model’ of Yoder et al. (17) proposes that the primary targets of cytosine methylation in plants and lower eukaryotes are invading DNA and endogenous mobile elements and the prevention of damaging transposition events. Thus, repetitious DNA elements are the preferred targets of cytosine methylation, just because of their reiteration or repetitive structure. Tandem repeats of a foreign gene may therefore be fitting targets for the methylating complex. It is not known why some transgenes can escape the silencing mechanism. As has been shown, DNA methylation is associated with altered chromatin structure (41,42). The different fates of transgenic C-ars in Hill 181 (active) and Hill 183 (inactive) may thus be a consequence of integration events that, in the former, placed a cluster of transgenes in a euchromatic domain (and another cluster evidently in a heterochromatic domain; see Table 5), whereas in the latter strain, transgenic C-ars were placed in a chromatin environment sufficiently close to a heterochromatic domain that facilitated the spreading of DNA methylation into neighbouring regions resulting in the ultimate methylation and inactivation of these transgenes.
Acknowledgments
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank Rainer Deutzmann and Eduard Hochmuth for the ESI-MS analyses and John P.Davies for providing plasmids pJD27 and pJD54. We are indebted to Ralph Remus for introducing us to bisulphite genomic sequencing and to Walter Doerfler for advice. This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB521/B1).
DDBJ/EMBL/GenBank accession no. AF333184
References
- 1.Schmitt R., Fabry,S. and Kirk,D.L. (1992) In search of molecular origins of cellular differentiation in Volvox and its relatives. Int. Rev. Cytol., 139, 189–265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Kirk D.L. (1998) Volvox: Molecular Genetic Origins of Multicellularity and Cellular Differentiation. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK.
- 3.Kirk M.M., Stark,K., Miller,S.M., Müller,W., Taillon,B.E., Gruber,H., Schmitt,R. and Kirk,D.L. (1999) regA, a Volvox gene that plays a central role in germ-soma differentiation, encodes a novel regulatory protein. Development, 126, 639–647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Miller S.M. and Kirk,D.L. (1999) glsA, a Volvox gene required for asymmetric division and germ cell specification, encodes a chaperone-like protein. Development, 126, 649–658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Meissner M., Stark,K., Cresnar,B., Kirk,D.L. and Schmitt,R. (1999) Volvox germline-specific genes that are putative targets of RegA repression encode chloroplast proteins. Curr. Genet., 36, 363–370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Schiedlmeier B., Schmitt,R., Müller,W., Kirk,M.M., Gruber,H., Mages,W. and Kirk,D.L. (1994) Nuclear transformation of Volvox carteri. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 91, 5080–5084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Ingelbrecht I., Van Houdt,H., Van Montagu,M. and Depicker,A. (1994) Posttranscriptional silencing of reporter transgenes in tobacco correlates with DNA methylation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 91, 10502–10506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Cerutti H., Johnson,A.M., Gillham,N.W. and Boynton,J.E. (1997) Epigenetic silencing of a foreign gene in nuclear transformants of Chlamydomonas. Plant Cell, 9, 925–945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Finnegan E.J., Genger,R.K., Peacock,W.J. and Dennis,E.S. (1998) DNA methylation in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol., 49, 223–247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Clark S.J., Harrison,J., Paul,C.L. and Frommer,M. (1994) High sensitivity mapping of methylated cytosines. Nucleic Acids Res., 22, 2990–2997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zeschnigk M., Schmitz,B., Dittrich,B., Buiting,K., Horsthemke,B. and Doerfler,W. (1997) Imprinted segments in the human genome: different DNA methylation patterns in the Prader–Willi/Angelman syndrome region as determined by the genomic sequencing method. Hum. Mol. Genet., 6, 387–395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chen R.Z., Pettersson,U., Beard,C., Jackson-Grusby,L. and Jaenisch,R. (1998) DNA hypomethylation leads to elevated mutation rates. Nature, 395, 89–93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Razin A. (1998) CpG methylation, chromatin structure and gene silencing—a three-way connection. EMBO J., 17, 4905–4908. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rogers S.D., Rogers,M.E., Saunders,G. and Holt,G. (1986) Isolation of mutants sensitive to 2-aminopurine and alkylating agents and evidence for the role of DNA methylation in Penicillium chrysogenum. Curr. Genet., 10, 557–560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Adams R.L. (1990) DNA methylation. The effect of minor bases on DNA–protein interactions. Biochem. J., 265, 309–320. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Adams R.L.P. and Burdon,R.H. (1985) Molecular Biology of DNA Methylation. Springer Verlag, New York, NY.
- 17.Yoder J.A., Walsh,C.P. and Bestor,T.H. (1997) Cytosine methylation and the ecology of intragenomic parasites. Trends Genet., 13, 335–340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Hattman S., Kenny,C., Berger,L. and Pratt,K. (1978) Comparative study of DNA methylation in three unicellular eucaryotes. J. Bacteriol ., 135, 1156–1157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sager R., Grabowy,C. and Sano,H. (1981) The mat-1 gene in Chlamydomonas regulates DNA methylation during gametogenesis. Cell, 24, 41–47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Blankenship J.E. and Kindle,K.L. (1992) Expression of chimeric genes by the light-regulated cabII-1 promoter in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: a cabII-1/nit1 gene functions as a dominant selectable marker in a nit1- nit2- strain. Mol. Cell. Biol., 12, 5268–5279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira,J. and Messing,J. (1985) Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene, 33, 103–119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Davies J.P., Weeks,D.P. and Grossman,A.R. (1992) Expression of the arylsulfatase gene from the beta 2-tubulin promoter in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Nucleic Acids Res., 20, 2959–2965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Ohresser M., Matagne,R.F. and Loppes,R. (1997) Expression of the arylsulphatase reporter gene under the control of the nit1 promoter in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Curr. Genet., 31, 264–271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Mages W., Cresnar,B., Harper,J.F., Brüderlein,M. and Schmitt,R. (1995) Volvox carteri α 2- and β 2-tubulin-encoding genes: regulatory signals and transcription. Gene, 160, 47–54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Gruber H., Goetinck,S.D., Kirk,D.L. and Schmitt,R. (1992) The nitrate reductase-encoding gene of Volvox carteri: map location, sequence and induction kinetics. Gene, 120, 75–83. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Gruber H., Kirzinger,S.H. and Schmitt,R. (1996) Expression of the Volvox gene encoding nitrate reductase: mutation-dependent activation of cryptic splice sites and intron-enhanced gene expression from a cDNA. Plant Mol. Biol., 31, 1–12. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Kirk D.L. and Kirk,M.M. (1983) Protein synthetic patterns during the asexual life cycle of Volvox carteri. Dev. Biol., 96, 493–506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Mages W., Salbaum,J.M., Harper,J.F. and Schmitt,R. (1988) Organization and structure of Volvox α-tubulin genes. Mol. Gen. Genet., 213, 449–458. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Crain P.F. (1990) Preparation and enzymatic hydrolysis of DNA and RNA for mass spectrometry. Methods Enzymol., 193, 782–790. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Pomerantz S.C. and McCloskey,J.A. (1990) Analysis of RNA hydrolyzates by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Methods Enzymol., 193, 796–824. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Gommers-Ampt J., Lutgerink,J. and Borst,P. (1991) A novel DNA nucleotide in Trypanosoma brucei only present in the mammalian phase of the life-cycle. Nucleic Acids Res., 19, 1745–1751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Leonard S.A., Wong,S.C. and Nyce,J.W. (1993) Quantitation of 5-methylcytosine by one-dimensional high-performance thin-layer chromatography. J. Chromatr., 645, 189–192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Sambrook J., Fritsch,E.F. and Maniatis,T. (1989) Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd Edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
- 34.Hallmann A., Rappel,A. and Sumper,M. (1997) Gene replacement by homologous recombination in the multicellular green alga Volvox carteri. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA, 94, 7469–7474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Klaas M., John,M.C., Crowell,D.N. and Amasino,R.M. (1989) Rapid induction of genomic demethylation and T-DNA gene expression in plant cells by 5-azacytosine derivatives. Plant Mol. Biol., 12, 413–423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Stevens D.R., Rochaix,J.D. and Purton,S. (1996) The bacterial phleomycin resistance gene ble as a dominant selectable marker in Chlamydomonas. Mol. Gen. Genet., 251, 23–30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Hallmann A. and Sumper,M. (1994) An inducible arylsulfatase of Volvox carteri with properties suitable for a reporter-gene system. Purification, characterization and molecular cloning. Eur. J. Biochem., 221, 143–150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Busslinger M., Hurst,J. and Flavell,R.A. (1983) DNA methylation and the regulation of globin gene expression. Cell, 34, 197–206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Gardiner-Garden M. and Frommer,M. (1987) CpG islands in vertebrate genomes. J. Mol. Biol., 196, 261–282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Linn F., Heidmann,I., Saedler,H. and Meyer,P. (1990) Epigenetic changes in the expression of the maize A1 gene in Petunia hybrida: role of numbers of integrated gene copies and state of methylation. Mol. Gen. Genet., 222, 329–336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lewis J. and Bird,A. (1991) DNA methylation and chromatin structure. FEBS Lett., 285, 155–159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kass S.U., Pruss,D. and Wolffe,A.P. (1997) How does DNA methylation repress transcription? Trends Genet., 13, 444–449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]