Abstract
Proton transfer reactions in bacteriorhodopsin were investigated by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, using a mutant protein in which Asp-96 was replaced by Asn-96. By comparison of the BR - K, BR - L, and BR - M difference spectra (BR indicating bacteriorhodopsin ground state and K, L, and M indicating photo-intermediates) of the wild-type protein with the corresponding difference spectra of the mutant protein, detailed insight into the functional role of this residue in the proton pump mechanism is obtained. Asp-96 is protonated in BR, as well as another aspartic residue, which is tentatively assigned to be Asp-115. Asp-96 is not affected in the primary photoreaction. During formation of the L intermediate it is subjected to a change in the H-bonding character of its carboxylic group, but no deprotonation occurs at this reaction step. Also, in the mutant protein a light-induced structural change of the protein interior near the Asn-96 residue is probed. The BR - M difference spectrum of the mutant protein lacks the negative carbonyl band at 1742 cm-1 of Asp-96 and in addition a positive band at about 1378 cm-1, which is most likely to be caused by the carboxylate vibration of Asp-96. This argues for a deprotonation of Asp-96 in the time range of the M intermediate during its photostationary accumulation. On the basis of these results, it is suggested that the point mutation does not induce a gross change of the protein structure, but a proton-binding site in the proton pathway from the cytoplasmic side to the Schiff base is lost.
Full text
PDF
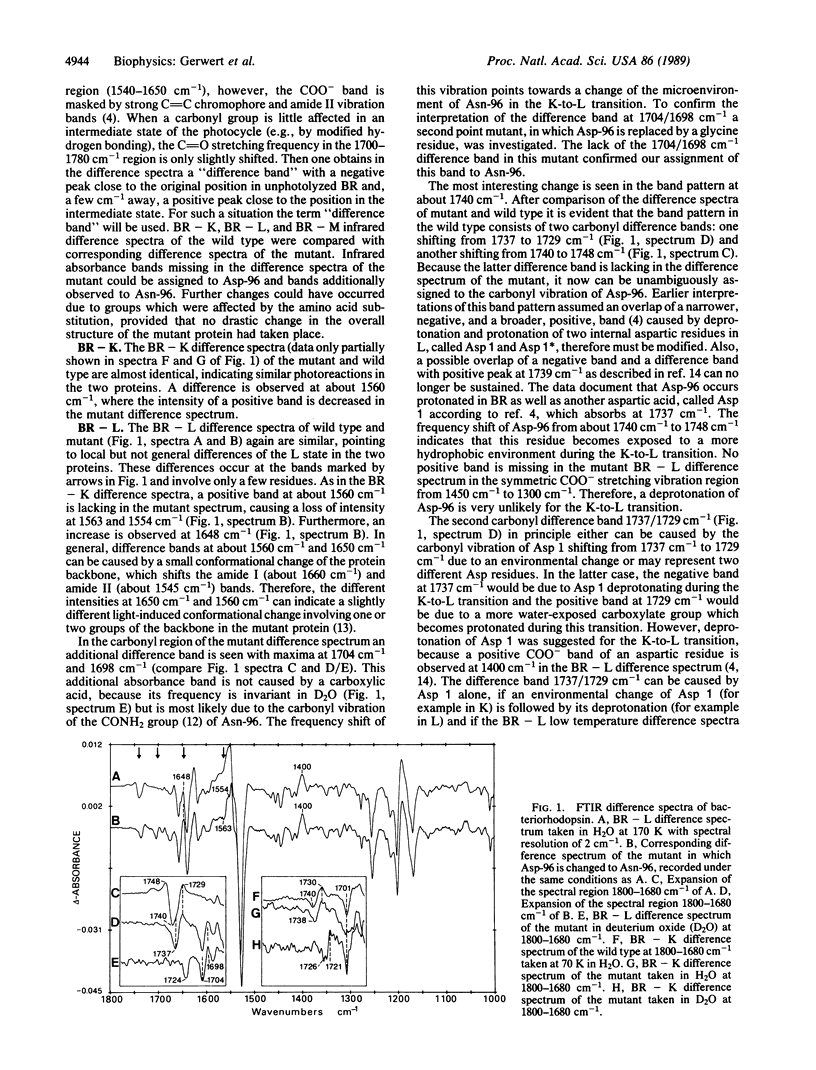
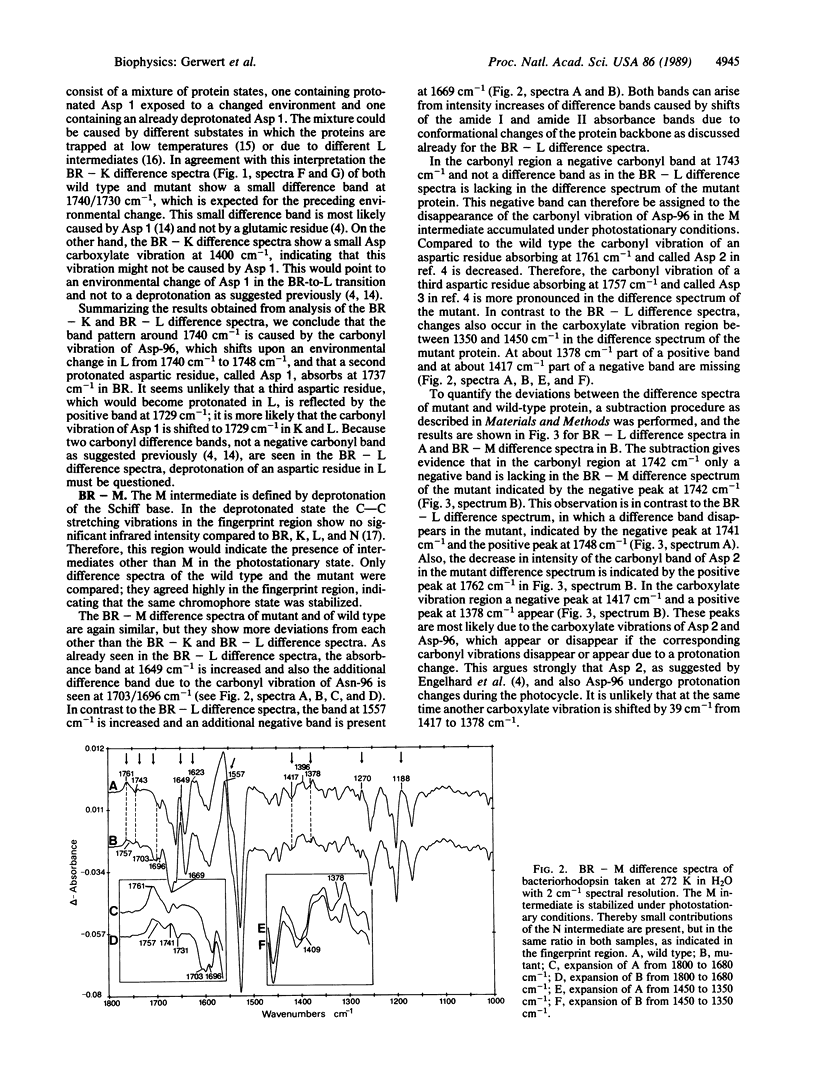


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Austin R. H., Beeson K. W., Eisenstein L., Frauenfelder H., Gunsalus I. C. Dynamics of ligand binding to myoglobin. Biochemistry. 1975 Dec 2;14(24):5355–5373. doi: 10.1021/bi00695a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braiman M. S., Ahl P. L., Rothschild K. J. Millisecond Fourier-transform infrared difference spectra of bacteriorhodopsin's M412 photoproduct. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5221–5225. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braiman M. S., Mogi T., Marti T., Stern L. J., Khorana H. G., Rothschild K. J. Vibrational spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin mutants: light-driven proton transport involves protonation changes of aspartic acid residues 85, 96, and 212. Biochemistry. 1988 Nov 15;27(23):8516–8520. doi: 10.1021/bi00423a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braiman M. S., Mogi T., Stern L. J., Hackett N. R., Chao B. H., Khorana H. G., Rothschild K. J. Vibrational spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin mutants: I. Tyrosine-185 protonates and deprotonates during the photocycle. Proteins. 1988;3(4):219–229. doi: 10.1002/prot.340030403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braiman M. S., Rothschild K. J. Fourier transform infrared techniques for probing membrane protein structure. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:541–570. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.002545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelhard M., Gerwert K., Hess B., Kreutz W., Siebert F. Light-driven protonation changes of internal aspartic acids of bacteriorhodopsin: an investigation by static and time-resolved infrared difference spectroscopy using [4-13C]aspartic acid labeled purple membrane. Biochemistry. 1985 Jan 15;24(2):400–407. doi: 10.1021/bi00323a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelman D. M., Henderson R., McLachlan A. D., Wallace B. A. Path of the polypeptide in bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2023–2027. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fodor S. P., Ames J. B., Gebhard R., van den Berg E. M., Stoeckenius W., Lugtenburg J., Mathies R. A. Chromophore structure in bacteriorhodopsin's N intermediate: implications for the proton-pumping mechanism. Biochemistry. 1988 Sep 6;27(18):7097–7101. doi: 10.1021/bi00418a064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerwert K., Siebert F. Evidence for light-induced 13-cis, 14-s-cis isomerization in bacteriorhodopsin obtained by FTIR difference spectroscopy using isotopically labelled retinals. EMBO J. 1986 Apr;5(4):805–811. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04285.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A., Spoonhower J., Bogomolni R. A., Lozier R. H., Stoeckenius W. Tunable laser resonance raman spectroscopy of bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4462–4466. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogi T., Stern L. J., Marti T., Chao B. H., Khorana H. G. Aspartic acid substitutions affect proton translocation by bacteriorhodopsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4148–4152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagle J. F., Tristram-Nagle S. Hydrogen bonded chain mechanisms for proton conduction and proton pumping. J Membr Biol. 1983;74(1):1–14. doi: 10.1007/BF01870590. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Krippahl G. Phototrophic growth of halobacteria and its use for isolation of photosynthetically-deficient mutants. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1983 Jul-Aug;134B(1):137–150. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(83)80101-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Functions of a new photoreceptor membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2853–2857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Isolation of the cell membrane of Halobacterium halobium and its fractionation into red and purple membrane. Methods Enzymol. 1974;31:667–678. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)31072-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renthal R., Cothran M., Espinoza B., Wall K. A., Bernard M. Light activates the reaction of bacteriorhodopsin aspartic acid-115 with dicyclohexylcarbodiimide. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 30;24(16):4275–4279. doi: 10.1021/bi00337a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothschild K. J., Bousché O., Braiman M. S., Hasselbacher C. A., Spudich J. L. Fourier transform infrared study of the halorhodopsin chloride pump. Biochemistry. 1988 Apr 5;27(7):2420–2424. doi: 10.1021/bi00407a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebert F., Mäntele W., Gerwert K. Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy applied to rhodopsin. The problem of the protonation state of the retinylidene Schiff base re-investigated. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Oct 17;136(1):119–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07714.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


